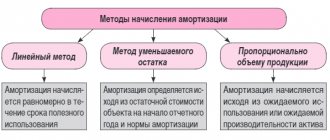
In accounting, fixed assets worth no more than 40,000 rubles can be taken into account as part of inventories. From January 1, 2021, the limit on the value of fixed assets in tax accounting increased from 40,000 to 100,000 rubles. Fixed assets put into operation from January 1, 2021 are taken into account taking into account the new limit of 100,000 rubles (Federal Law of June 8, 2015 No. 150-FZ).
The unit of accounting for fixed assets is an inventory object:
- a separate item (for example, a safe);
- a single complex of several items that are mounted on a single foundation and have common control (for example, a computer, which includes a system unit, monitor, keyboard, mouse).
You must charge depreciation on fixed assets. How to proceed, see account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets”.
How to define a fixed asset object
In the case of buildings, structures, structures and premises, it can be difficult to correctly determine the inventory item. And here it is important to focus on several rules:
- an inventory unit is a separate building or a whole complex of buildings erected on a single foundation that perform one or more common functions;
- adjacent buildings with different functions are different objects;
- if auxiliary buildings support the operation of the main building, they are considered part of it;
- all kinds of outbuildings, fences and other structures that support the operation of several buildings or have an independent purpose (garage, summer kitchen) are counted as separate objects.
For example, a free-standing bathhouse is a building with an independent purpose, a separate accounting object. But the room for the household equipment of the institution’s employees is auxiliary, it ensures the operation of a specific building, therefore accounting does not single it out as an independent room.
The accountant assigns an individual inventory number to each newly received object. It is maintained throughout the entire life of the building/premises by the institution. The institution has the right to come up with the structure of numbers and the logic for assigning them to objects independently.
Groups of real estate objects according to their purpose are determined by the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets (OKOF). Buildings/premises of various types intended for human habitation are considered residential. Non-residential buildings are administrative, industrial, service buildings, including garages and warehouses. In this regard, budget accounting is no different from accounting in commercial enterprises.
Which OKOF to use
Based on OKOF, the accountant determines the useful life of the object and calculates monthly depreciation. In 2017, the Russian Ministry of Finance seriously changed the structure of the classifier (letter dated December 27, 2016 No. 02-07-08/78243); the department removed some positions altogether or replaced them with generalizing concepts. The type of coding of fixed assets has also changed. The previous code consisted of 9 digits of the form XX ХХХХХХХ, for example:
11 0000000 Buildings (except residential):
- 11 0001000 Buildings, except residential, not included in other groups
- 11 4521000 Buildings of fuel and energy, metallurgical, chemical and petrochemical enterprises
The new codes have a different structure - ХХХ.ХХ.ХХ.ХХ.ХХХ. For comparison, here is the classification of some buildings according to the new OKOF:
Fifth group (property with a useful life from 7 to 10 years inclusive)
| Building | ||
| Buildings (except residential) | Prefabricated and movable buildings | |
| Dwellings | ||
| General purpose residential buildings | Frame-reed and other lightweight dwellings | |
The new OKOF applies only to buildings, structures and premises that were put into operation and registered after January 1, 2021. There is no need to revise the groups of previously received property; the previous classification remains for them.
List of useful documents
Documents for download:
| No. | Links | Description |
| 1 | Sample technical specifications for construction, reconstruction | |
| 2 | Sample application for a permit to construct a new building | |
| 3 | Sample technical plan for registering a building | |
| 4 | Sample application for cadastral registration | |
| 5 | Sample USRN extract | |
| 6 | Sample application for a commissioning permit | |
| 7 | Sample application for project examination | |
| 8 | Recommendations for preparing design documentation for examination |
Key accounting principles
The instruction approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n specifies how to generate account numbers for fixed assets. For synthetic accounting, account 010100000 “Fixed Assets” and two subaccounts are allocated in the Chart of Accounts for Budget Accounting:
- 010111000 “Residential premises”;
- 010112000 “Non-residential premises”.
Any movement of fixed assets: receipt, internal movement, restructuring, write-off, etc. - the institution draws up standard primary forms (see below for details), including special ones intended only for buildings and structures (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52H). The documents are drawn up in two copies, one of which is kept by the MOL, and the second is taken by the accounting department.
Our services and prices
Do you need to quickly register non-residential premises in Rosreestr? Then Smart Way will help you. We provide legal services. persons and citizens:
- design, development of all types of real estate documentation;
- preparation of technical plans in the shortest possible time;
- support of all procedures in Rosreestr and MFC with receipt of ready documents;
- assistance in preparing documents for real estate transactions.
All work is performed only by experienced and qualified specialists. This will ensure that you will not have any problems when contacting government agencies. The preliminary cost of work, services and documents can be found in the table below.
| No. | Service, document | Price |
| 1 | Design of construction of a new facility | from 30,000 rub. (depending on the area and features of the building) |
| 2 | Support of approval procedures | from 25,000 rub. (depending on the area and features of the object |
| 3 | Preparation of a technical plan | from 8000 rub. |
| 4 | Support of the cadastral registration procedure in Rosreestr or MFC | from 12,000 rub. |
| 5 | Representation in court to obtain a decision and cadastral registration | from 30,000 rub. |
How to register a building
Institutions, as a rule, are not the owners of property, but only manage it with operational management rights in accordance with the purpose of the property, the goals of their activities and the tasks of the owner, that is, the founder.
Instruction No. 157n dictates a strict rule: real estate objects can be accepted and deregistered only on the basis of primary forms with the mandatory attachment of registration documents (certificate of registration of ownership or operational management rights (extract from the Unified State Register). This means that when accepting a building or premises for registration , the head of the institution and the accountant first of all clarify the conditions for the transfer of property (rent, storage, etc.) These conditions must be recorded somewhere: in a separate letter or in the transfer and acceptance certificate, the owner indicates that before registering the right of operational management, the property is transferred to gratuitous use by the institution.When the status of the object has already been clarified, the accounting department can apply the corresponding norm of Instruction No. 157n.
If an institution plans to use the property before registering its right to operational management, it draws up an agreement for gratuitous use and registers the object in off-balance sheet account 01 (clause 333 of Instruction No. 157n).
Public sector organizations accepting real estate must remember that no property can appear on the balance sheet of two institutions.
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Before state registration of the property | ||
| The acceptance certificate was signed on the basis of the administrative act of the owner | 01 | |
| Utility costs reflected | 0 401 20 223 | 0 302 23 730 |
| After state registration of the property | ||
| An object is written off off-balance sheet on the basis of state registration of rights to real estate | 01 | |
| The fixed asset is accepted for accounting upon state registration of rights to real estate: | ||
| by the amount of book value | 0 101 1x 310 | 0 210 06 660 0 401 10 180 |
| by the amount of accrued depreciation | 0 210 06 560 0 401 10 180 | 0 104 1x 410 |
When real estate objects are received, the manager or an employee authorized by him signs form 0306030 “Act of acceptance and transfer of a building (structure)”, to which documents on state registration of rights are attached. If we are talking about moving an object from one materially responsible person to another within the same institution - form 0306032 “Invoice for internal movement of fixed assets”.
For accounting, the acceptance certificate together with the technical documentation for the object is the basis for drawing up an inventory card or making a record of changes to an existing one. The accountant draws up inventory cards for each of the inventory numbers and registers them in a special inventory.
Maintain budget accounting and generate reports in the Kontur-Accounting Budget program
Assessment for putting on the balance sheet of the enterprise within a period of 3 days
In turn, reliable data on market value is required when placing on the balance sheet objects received by an organization under gratuitous transfer agreements, as well as those created on its own and not having documents confirming their value. Quite regularly, the determination of the value for putting on the balance sheet is carried out in relation to the intangible assets of the organization. In addition, an assessment is required when writing off an object from the organization’s balance sheet and its future sale, which may require confirmation of its market price.
How to reflect modernization in accounting
The book value of fixed assets consists of their initial cost and the costs of changes made, which is especially important for buildings, structures and premises that are often reconstructed, completed, etc. These changes increase the initial cost of the object if, as a result of the operations performed, the main regulatory indicators are improved: efficiency of use, service life, etc. The book value will also change in the case of revaluation of objects (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 29, 2014 No. 89n).
The difference in book value, change in the initial cost and technical characteristics of the fixed assets should be reflected by the accountant in the same form 0306002 “Act on acceptance and delivery of repaired, reconstructed, modernized fixed assets.”
How to write off a building
The most common reasons for writing off buildings and premises include:
- moral and physical deterioration of the object, inappropriateness of further operation and/or ineffectiveness of its restoration;
- transfer of real estate to another institution, state authority or local government;
- liquidation of an object as a result of an accident, during natural disasters and other emergency situations.
All cases of disposal/write-off of objects are listed in clause 51 of Instruction No. 157n.
Along with the value of the property, the amount of accrued depreciation is also written off from the balance sheet. This can be done only on the basis of a decision of the owner of the object and an act certified by the head of the institution. Until all measures to liquidate/write off the property are completed, the accounting department cannot carry out any operations.
How to reflect the disposal of such fixed assets in accounting depends on the basis for the write-off and the type of institution. State institutions rely on Instruction No. 162n, budget institutions - on Instruction No. 174n, autonomous institutions - on Instruction No. 183n.
| State institution | State-financed organization | Autonomous institution | |||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit |
| Sale, shortage, theft, physical and moral wear and tear | |||||
| 1 104 1х 410 1 401 10 172 | 1 101 1x 410 | 0 104 1х 410 0 401 10 172 | 0 101 1x 410 | 0 104 1x 000 0 401 10 172 | 0 101 1x 000 |
| Destruction, destruction, rendering unusable due to natural disasters | |||||
| 1 104 1х 410 1 401 20 273 | 1 101 1x 410 | 0 104 1х 410 0 401 20 273 | 0 101 1x 410 | 0 104 1х 000 0 401 20 273 | 0 101 1x 000 |
Example. The flood destroyed a section of the Petrovskaya Library MKU building; the founder decided to write off the building, which had fallen into disrepair. The book value of the fixed assets is 3,200,000 rubles, the amount of depreciation at the time of destruction is 1,300,000 rubles.
Business transactions for writing off an object:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| Write-off of accrued depreciation of a building | 1 104 12 410 | 1 101 12 410 | 1 300 000 |
| Write-off of the residual value of the building | 1 401 20 273 | 1 101 12 410 | 1 900 000 |
When disposing of fixed assets, the accountant fills out one of the documents:
- form 0306003 “Act on write-off of fixed assets (except for vehicles)”;
- Form 0306033 “Act on the write-off of groups of fixed assets (except for vehicles).”
Timing and cost
Real estate accounting is a free public service. Since objects are usually registered simultaneously with the registration of rights, a fee must be paid for the combined procedure. Its size is 22 thousand rubles. (for enterprises) and 2 thousand rubles. (for individuals). The amount of the fee does not depend on how the documents are submitted.
The duration of the procedures, on the contrary, depends on the method of filing the application:
- if the applicant only needs accounting of the premises, an extract from the Unified State Register is issued after 7 days (Rosreestr) or 9 days (MFC);
- with simultaneous registration and accounting, the procedures will take 10 days (Rosreestr) or 12 days (MFC).
It is impossible to speed up the procedures, since all deadlines are specified in the law. But you can avoid suspensions by Rosreestr, which can last up to 3 months. To do this, carefully consider the choice of a cadastral engineer in order to receive a technical plan without errors.
The production time of technical plans depends on the size, area and type of premises. The Smart Way company offers document processing in just 1-3 days. We guarantee that the technical plan will fully comply with Order No. 953.
What does the inventory commission check?
One of the important components of accounting for buildings and premises is timely inventory. The procedure is set out in detail in the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, guidelines for inventory of property and financial obligations (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 13, 1995 No. 49) and other regulations.
A commission specially created by the head of the institution inspects the objects and enters the obtained data on their presence and condition into the inventory list. The commission also checks the extent of technical documentation for the facility, whether inventory cards, inventories and books are maintained correctly, and whether the institution is using the property legally.
The head of the institution and the accountant should take the inventory of buildings, structures and premises carefully. However, this advice also applies to other stages of working with real estate, because it makes up a significant share of the assets of institutions. Errors in accounting and incorrect calculation of depreciation can lead to irregularities in financial statements and lead to serious fines from regulatory authorities.