Almost all costing instructions indicate the need for a monthly inventory of work in progress. Checking the actual reserves confirms the reporting calculations and production costs of the closing period. However, the inventory of work in progress, unlike other assets, is not properly covered in the methods. This is understandable: in controlling “work in progress”, specialists are guided by the company’s accounting policy and technological specifics. The question is important, so we will consider issues related to the inventory of work in progress, using the example of a machine-building enterprise.
The essence of work in progress inventory
Inventory of work in progress involves determining the volume of such products at the enterprise and its actual cost, as well as the correspondence of this information to accounting data. At the same time, objects of work in progress are understood as goods that are only partially finished, that is, they have not gone through the entire manufacturing cycle, and therefore cannot be considered finished products and, accordingly, cannot be sold to consumers.
Work in progress items should include:
- products sent into the production process;
- defective items of goods;
- manufactured goods that have not passed tests (if this item is mandatory);
- incomplete products;
- work or services performed that were not accepted by the customer;
- semi-finished products of own production, not considered finished products.
Determining the actual cost of work in progress items can be carried out using several methods, namely:
| Method | Cost calculation |
| Simple (process-based) | Used for homogeneous products and involves the summation of all costs incurred divided by the number of units produced |
| Custom | Cost is determined in terms of costs incurred for each specific order |
| Lateral non-semi-finished | It is used in production, where products go through several stages of processing and are not sold until they are ready. Cost is calculated as the sum of all costs incurred at each stage of processing |
| Lateral semi-finished | It is used in production, where products undergo several stages of processing and can be sold at any of them. Cost is defined as the amount of costs incurred at past stages |
| Normative | The method is based on the use of standard cost, adjusted by indexes of changes in standards depending on deviations recorded at the final stage of production |
Cost increase factor
The cost structure during the production cycle rarely remains unchanged. To determine the characteristics of the increase in costs per unit of finished product, a special coefficient is used. This indicator is used in calculations when it is necessary to characterize the growth dynamics of a specific type of cost as part of the cost of production. For example, determine the dynamics of labor costs.
Cost increase coefficient in work in progress, formula:
K = Unit cost of work in progress / Total production costs.
This formula is generalized and reflects the key essence of the coefficient. Note that in practice, enterprises use more complex calculations that maximally reflect the specifics of their activities and cost structure.
The purpose and objectives of inventory of work in progress
The main purpose of the inventory of work in progress is considered to be to determine the actual presence of objects of work in progress, identifying unaccounted for defects, determining the completeness of products, determining the balances of canceled or suspended orders and calculating the cost of products that are in the stage of work in progress. In addition, the purpose of the inventory is to compare actual data with accounting indicators and identify factors influencing discrepancies in information.
In accordance with the goal, the following tasks should be solved during the inventory of work in progress:
- determination of the composition, structure and quantity of work in progress;
- drawing up inventory lists that will contain all the necessary information, including the name of the object or product, its quantity, degree of readiness and completeness, stage of production;
- identifying unaccounted for defects in production and determining its percentage of manufactured products;
- study and analysis of maps for the release of materials into production in order to identify the irrational use of the enterprise’s material resources;
- calculation of the cost of work in progress according to the method specified in the accounting policy and used in the organization.
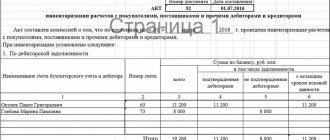
Rules for filling out the WIP verification report form
The act form is developed at the enterprise and approved by order of the manager, with subsequent consolidation in the accounting policy. It can be based on the forms given in appendices Nos. 6–15 to the guidelines, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49.
The act must indicate:
- Title of the document,
- link to administrative document,
- inventory start and end date.
It is recommended to summarize the results of the check in a table for the convenience of recording work in progress by quantity and cost. At the end of the act there must be signatures of all members of the inventory commission.
IMPORTANT! The absence of the signature of at least one member of the commission makes the act invalid.
The acts are filled out separately for each separate division of the enterprise.
WIP inventory report can be found here:
Preparatory activities
Before carrying out an inventory of work in progress, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparatory procedures in order for the process to produce effective results. Storekeepers need to sort work-in-process items according to their nomenclature, as well as separate defective items to make it more convenient to carry out direct counting.
Accounting employees should post all available documents on the movement of materials and work-in-progress items into synthetic and analytical accounting accounts. In addition, you need to prepare a scheme according to which the cost will be calculated, as well as identify orders that were canceled or suspended for some reason.
The director of the organization is obliged to issue an inventory order, which will specify the timing of the event and the composition of the working audit commission. In addition, the document indicates the reason for which the inventory is carried out and the list of property being inspected. As for the reasons, there may be several of them, for example, the dismissal of a storekeeper or other financially responsible person, the preparation of annual reports, suspicion of embezzlement or theft.
The main preparatory activities can be presented in the following table:
| Event | Description |
| Issuance of an order | The order is issued by the director of the organization. It indicates all the essential aspects of the inventory, including the period of conduct, objects of inspection, the reason for the audit and the composition of the working commission |
| Delivery and preparation of documentation | Materially responsible persons are obliged to submit to the accounting department all documentation on the movement of work in progress objects, and the accountant is obliged to enter documents into the program and process them in accordance with all established rules |
| Identifying groups of objects or individual units | The audit commission, together with accounting and economists, must develop a nomenclature according to which the inventory will be carried out. In addition, a scheme should be prepared according to which the cost of work in progress items will be assessed |
Inventory procedure
At the time of the inventory of work in progress, the audit commission receives documents that serve as the basis for the movement of material assets and checks that they are filled out correctly. Then a direct complete census of work-in-progress items is carried out into the inventory list. A separate inventory is drawn up for rejected products, since such items cannot be included in the general inventory list for work in progress. It is necessary to take into account that the absence of a financially responsible person or one of the commission members during the audit is considered unlawful, and therefore the results of the audit are considered invalid.
Upon completion of the inventory, all compiled documents are signed by members of the inspection commission and transferred to the accounting department for processing. In this case, the discrepancy between the actual and accounting indicators must be documented using a reconciliation sheet, and the results - surplus or shortage - are attributed to the appropriate accounts of synthetic and analytical accounting.
Reflection of shortages in excess of established standards
The accounting policy of an enterprise establishes certain standards, including a portion of property losses that are considered acceptable. In cases where the shortage occurs due to damage to the work in progress, there are two options for reflecting the results in accounting:
- If the culprits are identified, the shortage is restored at their expense. The accounting entries are as follows: Dt “Calculations for compensation of damage” Ct “Shortages”, Dt “Calculations for compensation of damage” Ct “Losses from damage to valuables”.
- If the court refuses to recover damages from the guilty parties, or they are not identified, then the shortfall is written off to the financial result: Dr. “Other expenses” Ch. “Shortages”.
- If property damage occurred due to an emergency or force majeure, then the procedure for reflecting losses is similar to clause 2.
Amounts of shortages in excess of the norm oblige the inventory commission to conduct an internal investigation in order to identify the perpetrators.
Work in progress in accounting occupies a special place in the assets of the enterprise. These are no longer raw materials and materials, but also not finished products. Controlling its quantity is as important as for any other property. In order to compare the data of primary documents with the actual availability of work in progress, inventories are carried out, as a result of which the indicators are adjusted, if necessary.
How is WIP inventory carried out in production?
At industrial enterprises, inventory of work in progress can be carried out both for individual objects and for their totality. The main points to pay attention to when taking inventory are the following:
- it is necessary to determine the actual quantity of all items in the nomenclature;
- it is necessary to establish the completeness of all work in progress items;
- you need to determine the balance of work in progress that relates to canceled or suspended orders.
The production process in a large enterprise involves a variety of operations, for which different areas of work can be organized. Accordingly, an inventory of work in progress should be carried out in the context of these areas, and for each of them a corresponding inventory list should be compiled, and then all the data obtained should be compiled into a general inventory sheet.
How is the inventory of work in progress carried out in construction?
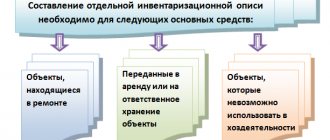
If the inventory is carried out on unfinished construction projects, then the inventory list indicates the buildings, the stage of their production, as well as the volume of certain work on them or individual structural elements. Objects that are currently under conservation are also subject to inventory, and the inventory list must indicate the reasons for their conservation.
It must be taken into account that buildings that are completely constructed, but not put into operation and do not have the appropriate documentation, are also considered work in progress, and therefore they must be recorded in a separate statement. This document reflects the reasons why the buildings were not put into operation and the delivery documents were not properly completed.
Peculiarities
If work in progress is a heterogeneous mass or mixture of raw materials (in the relevant industries), 2 quantitative indicators are given in inventories and comparison sheets:
- the amount of this mass or mixture;
- the amount of raw materials or materials (by individual items) included in its composition.
In this case, the quantity of raw materials or materials is determined by technical calculations in the manner established by industry rules for planning, accounting and calculating the cost of products (works, services).
Also see Inventory Matching Statements.
Typical entries for inventory of work in progress
When conducting an inventory, the commission can receive several results, and for each of them the corresponding entries are generated. The most common ones are:
- if a surplus of work in progress items is identified
Debit 20 Credit 91/1 market value of surplus accepted for accounting
- if a shortage is identified
Debit 94 Credit 20 reflects the cost of the shortage
- shortages according to the norm and in excess of it are allocated to different accounts
Debit 20 Credit 94 shortage within normal limits attributed to production
Debit 73 Credit 94 shortage in excess of the norm is attributed to the culprit, if he is identified
Debit 91/2 Credit 94 shortfall in excess of the norm is charged to other expenses if the culprit is not identified