It is known that an example of the purpose of business trips can be easily found in specialized magazines for accountants. It would seem that it is not at all difficult to take advantage of ready-made experience. However, if the purpose of the trip is formulated incorrectly, the costs for it cannot be taken into account in expenses to reduce the taxable profit of the enterprise. Therefore, you need to justify your employee’s business “travel” thoughtfully and carefully.
Business trip concept
This concept has a clear definition, which is prescribed in labor legislation. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a business trip is the direction of an employee by management on a trip with a specific task. At the same time, the destination is quite remote from the main place of work, the trip has a clearly formulated purpose, stated in the documents, and the time frame for its completion is limited. Registration of accompanying documents, reporting at the end of the trip, guarantees for the employee are regulated by labor and tax legislation. Possible purposes of the business trip are also spelled out, examples of which are presented below.
Business trips of drivers
“Rudder workers” often have to travel to other cities in order to transport goods, documents, and deliver specialists to places of work.
A business trip for an employee in this category is usually associated with the following tasks:
- delivery of the commercial director of Standard LLC to the place of negotiations with Client LLC,
- receipt of materials at the supplier’s warehouse, delivery of cargo to the territory of Our Firm LLC,
- car repair, purchase of spare parts,
- technical diagnostics of the car in a certified car service center.
Why do you need business trips?
When an employee goes on a business trip, management determines for him a clear task that he must complete during the trip. The task may concern various areas of the organization’s economic activity. Examples of business trip purposes include the following:
- concluding contractual relations for supplies or sales with contractors;
- negotiations on cooperation;
- resolution of disputes, conflicts and other issues related to the legal side of activities;
- purchase of equipment, raw materials and materials;
- business conferences, participation in gatherings and exhibitions related to the company’s activities;
- promoting goods in new markets, expanding the customer base;
- participation in research projects related to the company’s activities;
- staff development;
- research of sales markets, competing organizations and other marketing issues;
- setting up equipment, software and working with other technical issues in subsidiaries or divisions;
- Conducting inspections of the operation of the branch network and divisions.
Business trips to purchase materials
Directors of enterprises, as well as employees of purchasing departments, often go on business trips to purchase goods for the needs of the enterprise.
In this case, the order can indicate any example of the purpose of business trips from the following:
- conducting negotiations with Possible Supplier 1 LLC and Possible Supplier 2 LLC, discussing the terms of cooperation;
- establishing business contacts with Zavod LLC, studying the production process and product samples;
- concluding contracts for the purchase of raw materials and components with LLC “Material” and JSC “Details”;
- agreeing on the terms of the contract with the supplier Manufacturer LLC.
What cannot be considered a business trip
Not every employee trip can be considered a business trip. Registration of a business trip is illegal in the following situations:
- lack of official registration of an employee in the organization, no concluded employment contract, no entry in the work book;
- the employee’s employment contract specifies the traveling nature of the work;
- the employee is a freelance worker who does not have a specific permanent place of work.
Chief Accountant
Sometimes the chief accountant is sent on trips.
It is worth noting that an accountant in any enterprise is a financially responsible person. After all, it is this person who keeps records of finances, money and property matters. Therefore, we can say that the employee is simply attached to his place of work. If he is sent on a business trip, then a part-time employment contract is drawn up. This is especially important to do if the employee leaves for more than one month. The goals for such a working trip of the chief accountant of an enterprise may be the following:
- Checking reporting and accounting in a branch of the enterprise;
- Creation of a new database at an enterprise that opened recently;
- Acceptance of cases. This happens if an accountant is transferred to a new position in another city. At first, he will need to travel to the enterprise to take over all the documents and get to grips with the business;
- Training. Training or a trip to a conference can significantly improve the professionalism of an accountant, which in the future will help him keep records correctly.
Types of trips and their timing
Corporate mission trips can be classified according to different characteristics. Thus, on a territorial basis, trips within the territory of the Russian Federation and to foreign countries are distinguished. According to the duration of business trips, short-term and long-term trips are distinguished. According to the composition of the travelers - group and single. There may also be planned and unscheduled business trips.
To date, there are no clear guidelines in the legislation regarding the timing of the trip. There are no minimum or maximum restrictions. The management of the organization independently determines the complexity of the task and the time required to complete it. Previously, there were restrictions. It was believed that the maximum duration of a business trip could not exceed forty days. In construction, the maximum threshold for a business trip reached a year.
Travel of production workers
Installation and assembly engineers, builders, and workers often have to “travel.” For these specialists, any example of a business trip task from the following is relevant:
- installation and initial testing of production equipment "Line-1" in workshops,
- installation, adjustment and commissioning of “Conveyor-100” equipment,
- warranty service of the machine “A-2”,
- routine maintenance on the production line of JSC “Customer”,
- unscheduled repairs, correction of machine breakdowns,
- equipment prevention.
Legal requirements and regulation
Travel issued as a business trip is subject to certain legal requirements. Business trips are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In the Labor Code, regulations regarding these work processes are described in Articles 166, 167, 168. They reveal a number of questions that may arise when completing this procedure: what can be considered a business trip, guarantees for the employee, as well as questions about reimbursement of expenses during the trip.
The Tax Code describes information on how to reflect travel expenses in accounting, what can be written off, and from what amounts payments are made to the social insurance funds of citizens. There are also separate resolutions containing the most complete information about amendments made to legislative acts, accounting innovations and meeting the requirements of regulatory authorities. You can find all this information in the following documents: Resolutions No. 749, 729, 812, 64.
Answers to common questions about how a business trip is arranged at the expense of the host party
Question No. 1: How to reflect in the accounting report the absence of an employee who was sent on a business trip?
Answer: The HR department employee must mark the days he is on a business trip as working days with the mark “K”.
Question No. 2: How to compensate for the expenses of an employee who was sent on a business trip abroad at the expense of the receiving party?
Answer: All employee expenses must be reimbursed in foreign currency, the same applies to advance payments.
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
What is guaranteed to the employee
Guarantees for an employee do not depend on the purpose of the business trip; there can be many examples. But with any of them, the employer bears some obligations to the employee. An employee who is sent on a business trip is provided with the following guarantees:
- preservation of position, workplace, average daily wage;
- payment for days off spent on a business trip at double the rate;
- reimbursement of expenses that may arise during a business trip in Russia and abroad, including obtaining a foreign passport, obtaining a visa, customs duties and other fees.
All these guarantees are prescribed in labor legislation and are subject to mandatory compliance by the employer.
Common mistakes
Error: An employee who was on a business trip abroad did not spend all the money given to him and returned part of the funds to the employer in rubles.
Comment: Reimbursement for travel expenses abroad for work is paid in the foreign currency of the country where the employee is sent. If there is money left, the employee returns it to the company’s cash desk, also in foreign currency.
Error: The employer sent the employee on a business trip at the expense of the host party, without offering to draw up an agreement to pay for the costs that the employee would incur during the trip.
Comment: As a guarantee, the employee must be provided with an agreement on payment for the trip by the host party for signature.
Who to send on a business trip
The choice of an employee to go on a trip depends on the purpose of the trip, examples of work assignments, its duration and the severity of the expected conditions. Different reasons for travel require specific knowledge and skills from the employee.
Thus, the execution of a supply agreement must be entrusted to a person savvy in business negotiations and diplomacy. This may be a specialist whose job responsibilities include procurement, planning and calculating the budget for business relations with suppliers, or a person who can competently explain his position and achieve optimal conditions in the concluded supply agreement.
If the purpose of the trip is to set up equipment or software, knowledge of office work and ordinary human charisma are not enough for the sent employee. An official with a technical background is sent on such a trip. The same situation occurs when conducting on-site inspections and audits. An accountant or economist should be sent on such a trip.
Examples of the purpose of a business trip for a director, driver, accountant and other employees
To better understand how to correctly draw up the purpose of a business trip, it is easiest to consider examples of drawing up goals for different categories of workers. They may look like this:
An example of setting the purpose of a director’s business trip:
take part in negotiations on concluding an agreement for the supply of products with a representative in Moscow on 10/01/2018.
The wrong goal setting is to conclude an agreement with a representative of the partners. In this case, the goal does not have specific indications of the date and place of negotiations. In addition, it presupposes the mandatory conclusion of an agreement, when in practice negotiations may end with a refusal to sign it.
Example of a driver's business trip purpose:
ensure from 10.00 to 20.00 the movement of citizen Ivanov within the city of St. Petersburg in the period from 01/11/19 to 01/25/19 in a VAZ-2114 company car, number E1913SN.
An incorrect example of setting the purpose of a business trip: to ensure the movement of the client. As in the previous situation, there is no specificity here either about the client’s identity, or about the employee’s terms of work and the specific car.
An example of the purpose of an accountant's business trip:
ensure the financial audit of branch No. 4 in the city of Saratov with the preparation of organization forms in form No. 14-85.
Wrong example: conduct a financial audit in the Saratov branch.
An example of the purpose of a lawyer’s business trip:
take part as a representative of the Vector organization in the court hearing in case No. 88-12-23 on May 1, 2019 in the Saratov Arbitration Court.
Wrong example: obtain a positive court decision in favor of the company at a court hearing in Saratov.
Practicing accountants easily give various examples of business trip purposes and point out the following:
- An employee's business trip must clearly be in the best interests of the company. The purpose of the business trip is formulated so that it is clear: the “travel” is beneficial for the company, directly or indirectly contributes to the enterprise earning profit, increasing the volume of activities, and improving the quality of goods and services. An employee of an organization cannot be sent on a business trip with the task of “resting,” “recuperating,” or “recovering.” For this purpose, leave is provided - annual or for health reasons.
- The purpose of the business trip should not contradict the employee’s job description. Thus, an accountant cannot be sent on a business trip to negotiate with clients. And the commercial director of a company cannot be sent to another city for the purpose of “transporting employees.”
- The reason for a business trip must correspond to the duration of the “travel” and its route. If the purpose of a business trip is, for example, participation in an exhibition, an employee of the organization is obliged to “move” in the opposite direction within 24 hours after the end of the event.
- You should be extremely careful when justifying business trips on weekends. If a company employee goes to another city, for example, for negotiations on Monday, and the travel time is one day, then he can leave no earlier than Saturday evening. Otherwise, the cost of tickets or fuel and lubricants cannot be classified as expenses.
- It is better to avoid general language. It is important to indicate why exactly an employee of the organization is sent to work outside his place of permanent duty. Otherwise, controllers may have doubts about the legality of attributing travel expenses to tax accounting.
- The purpose of the trip should be formulated in such a way that one can make an unambiguous conclusion about whether the assigned task was completed or not. After the trip, the employee will have to submit a report on the results and attach documents confirming the completion of the task. By the way, it is possible that the purpose of a business trip is not achieved. In this case, the employer requires an “explanatory statement” from the employee indicating the reasons why the official task could not be completed. If you have this document, travel expenses can be taken into account for tax purposes.
- If the purpose of the business trip is extensive and consists of several tasks, it is important to also write down the individual tasks of the trip, the completion of each of which will also need to be confirmed.
- If a specialist’s work is of a traveling nature and moving to another locality is associated with the performance of everyday affairs, then such a “travel,” according to the Labor Code, is not recognized as a business trip at all.
Who is prohibited from being sent on business trips?
In addition to the human factor, questions about the qualifications and personal abilities of candidates, there is another aspect in choosing an employee for a work trip. There are legal requirements regarding categories of citizens who cannot be sent on business under any circumstances. These include the following groups of people:
- minor employees, interns, interns;
- pregnant women;
- employees of the company working under an apprenticeship contract (except for business trips for the purpose of training);
- participants in election campaigns, candidates for political positions;
- people whose capabilities are limited by illness.
There are also groups of people who can be sent on a business trip only if their written consent is obtained:
- women with small children (up to three years of age);
- a single parent raising a child under five years of age;
- guardians of children under the age of majority;
- an employee whose family has a dependent in need of constant care.
Company lawyer
Very large enterprises always have their own lawyer, who, by the way, can also be sent on a business trip. The only reason for this is to resolve disputes that have arisen in other branches. Sometimes conflicts occur over land plots on which the construction of a branch is planned in the future. It is the head office lawyer who solves such problems.
Business trip arrangements
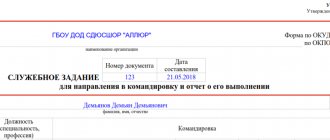
In order for a business trip to be taken into account in tax, accounting and management accounting, it is necessary to formalize it correctly. First of all, a business trip assignment is drawn up, dates and deadlines are set. The travel candidate must familiarize himself with the document drawn up and give his consent or refusal in writing.
If the answer is positive, the manager issues an order to send the specialist on a business trip. The employee is issued and issued a travel certificate and a work assignment. Upon completion of the trip, the traveler must provide a progress report and expense report with supporting receipts, receipts, and tickets.
Since 2021, a change has been made to the legislation, according to which the issuance of a certificate and official assignment is no longer mandatory. Instead, they use a memo. But many organizations continue to draw up these documents for internal accounting purposes.
When using personal or corporate vehicles, a memo and a waybill are required, as well as a power of attorney and other documents confirming the legality of using a particular vehicle.
Examples for various positions and specialties
Let us present the formulation of the purposes of business trips in administrative acts. For example, the director of an LLC goes on a business trip directly. In this case, not an order is formed, but an order, the wording is as follows:
“I’m leaving on a business trip with the goal of...”
What reasons might there be for a person in a leadership position to go on a business trip? For example, it is necessary to ensure participation in important negotiations necessary to develop new markets, find new customers, etc.
The goals can be formulated as follows:
- to participate in negotiations;
- for product presentation;
- to conclude an agreement for the supply of equipment, etc.
The tasks of a business trip are usually described to the sales manager in great detail. An order or instruction may set specific tasks (conclusion of contracts and agreements, contracts with customers), and determine quantitative indicators (volume of shipped products). These are the main tasks, which can also be divided into stages: developing a meeting plan and its implementation, visiting competitors’ retail facilities and compiling a comparative study of prices, assortment and other conditions, analysis.
Production engineers also go on business trips for very specific purposes: ensuring the operation of equipment, installations and devices, checking their efficiency and performance indicators. It is important to correctly and technically correctly identify the objectives of the trip, for example:
- installation of a device or product;
- setting up its operation;
- training the staff of an enterprise or branch in the rules of working on equipment;
- testing the operation of devices;
- service or warranty repairs;
- carrying out preventive work.
Common goals of lawyers: participation in a court hearing to consider a civil case. A lawyer can also be present at contract negotiations for a prompt analysis of the proposed conditions, in the process of concluding a transaction that requires notarization or state registration. The reason for the trip must also be clearly stated in the order.
Determining the need to register a business trip for employees with a traveling nature of work is the most difficult. It is necessary to be guided by the general norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the rules of local regulations, job descriptions. For example, a trip to repair a car is a business trip. The wording is similar: to ensure that the vehicle is repaired.
Other employees, for example, teachers, may be sent on business trips to participate in conferences, conduct a course of lectures by mutual agreement, organize practical classes, etc.
The main thing is to describe the tasks specifically so that the employee can professionally and at the proper level carry out management’s assignments and draw up reporting documents. This is necessary both for filing reports to the tax office and for organizing the efficient operation of the enterprise.
Business trip plan (form)
Information in documents
The memo is drawn up in free form, but there are a number of details that must be indicated: the dated period of the business trip, information about the transport used, the goals set for the employee and the results of their implementation.
All expenses incurred by the employee during the trip must be indicated in the advance report. This requirement applies to absolutely all types of expenses, including housing, transportation, fuel costs, food and others. In order to confirm the costs of paying for housing, it is necessary to provide to the accounting department at the end of the trip a check, receipt or receipt containing information about the lessor, the cost and rental period of the residential premises.
A management order must be issued accordingly. In office work, there is a unified form No. T-9, but the organization is not obliged to use it exclusively. The accounting policy of a particular organization may specify its own document form. You can also take advantage of the opportunity to create an order in free form. The main condition is that it contains the following data:
- the name and details of the organization that sent the employee on the trip;
- information about the employee;
- dates of the order;
- start and end dates of the travel period;
- tasks for the employee, purpose of the trip.
“Universal” wording for job assignments
Currently, experienced auditors recommend: if there is doubt that the purpose of the trip will be achieved, it is better to indicate it in the order in general phrases. When setting objectives, it is allowed to use free formulations. Here are examples of business trip purposes that do not oblige the employee to document the fact of completing the task:
“Ivanov I. And is sent to the city of Nsk for:
- solving production issues,
- negotiations on possible cooperation,
- establishing business contacts,
- market research for the possibility of purchasing goods.”
Example of a business trip assignment
The more important the task, the more levels it contains. The more a company invests in a business, the more results it aims to achieve. Not necessarily all the small details that the manager wants to know will be indicated in the order. Some of them can be discussed orally at meetings and when briefing the traveler. But, most likely, the employee will have to report on all points following the trip, even those that were not officially stated, but were announced orally. For clarity, we give an example of a job assignment below.
For example, let’s take the goal - “Concluding a supply agreement, advertising products.” For ease of reflection, we use the type of document generated by the 1C program. You can find it in personnel records, Form No. T-10a. This form contains 11 columns to fill out: structural unit, specialist position, country, city and organization to which the employee is sent, start and end date of the business trip, number of calendar days in total and excluding travel time, paying organization, basis, content tasks and a brief report on its completion. The document is signed by the head of the structural unit, the head of the organization and the employee himself.
The order contains travel information as follows:
- Last name, first name, patronymic of the employee and his personnel number: Sorokin Dmitry Evgenievich, 1 (personnel number in a separate window, according to personnel records).
- Structural unit: Marketing and Advertising Department.
- Position (specialty, profession): Leading marketer.
- Place of business trip (country, city, organization): Russia, Moscow, Realizator LLC.
- Basis (document, number and date): Service assignment No. 3 dated January 13, 2018
At the end of the order there are signatures of the manager and employee. The employee’s signature is placed opposite the inscription that he has read the order.
Can an accountant of a company be sent on a business trip?
Like any other employee, both ordinary and chief accountants can be sent to advanced training, various seminars on maintaining accounting records, and auditing activities.
In addition, to check the accuracy of the reports provided, the chief accountant can be sent to a branch located in another city, as well as when opening a new structural unit - transferring documents and introducing a new specialist to the basic working aspects.
Subtleties of design
If for some reason an employee does not provide supporting documents about expenses (checks, receipts), the organization does not reimburse him for these expenses. Therefore, during a business trip, it is so important not to forget about reporting. Even a trip in a taxi or bus must be confirmed by a travel ticket or a receipt from the driver.
An important point is also to indicate the structural unit of the organization and the purpose of the trip. Depending on the specified data, further costs will be written off in accounting and tax accounting. So, if the purpose of the business trip was to repair machine tools, when carrying out accounting calculations, the amount of expenses will be written off as depreciation of the repaired equipment. If the goal was to conclude an agreement, the write-off will take place as general business expenses.
And the last point is a business trip with an unfulfilled goal. In most cases, expenses for such a trip are not recognized by the tax service and do not reduce the tax base. You can try to defend your case in court, but in most cases the law remains on the side of the Federal Tax Service.
Head of the enterprise
The director of an organization, the first head of any enterprise, is primarily interested in developing the entire production and expanding the zone of influence to increase income and obtain greater profits.
Purpose of the director’s business trip, examples:
- When opening a new structural unit - hold meetings and negotiations with representatives of the organization that is the “Contractor” for the supply of goods and provision of services to conclude long-term contracts;
- When inspecting the control and control department of a branch located in an area remote from the main office - to resolve controversial issues that arose during the audit;
- In search of opportunities to expand business connections and develop production - holding meetings with potential partners to conduct a joint business.
Assignment of responsibilities
In cases where the manager is absent from the workplace, and in this case, went on a business trip, his powers are transferred to another employee in order to fulfill the duties of the director: signing contracts, orders, etc. The choice of such an employee may depend on the decision of the manager. But in most cases, such an employee becomes the one who is registered in the organization’s statutory documentation (Article 53 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
As a rule, these are the following employees:
- Deputy Director;
- head of HR department;
- head of any division or department;
- co-founder, if any;
- accountant.
What to consider when assigning the duties of the General Director to another employee:
- The employee begins to perform new duties that are additional to the main ones, so this fact must be agreed upon with the employee. New responsibilities and payment features must be specified in an additional agreement to the employment contract.
- To transfer the right to sign, it is necessary to issue a power of attorney (Article 185 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Its duration can be any, but, as a rule, it corresponds to the period of the business trip.
- The employee's written consent must be obtained.
- An order is issued to transfer the powers of the manager for a certain period.
Attention! If the employee was vested with the authority of a manager before the latter’s business trip was arranged, then he has the right to sign all documents related to the trip.
What are the goals?
The purposes of a work trip can be of different nature and conditionally divided into universal and special:
- Universal ones are aimed at developing the company’s business and may include finding clients or attracting investors.
- Special goals can be of a different nature and reflect the need of the enterprise at a particular point in time, for example, participation in a court case.
It is important to note that any goal must be specific and contain in its formulation complete information about the task, that is, be specific.
Purpose of the trip and examples:
- participation of a company representative in negotiations (the counterparty must be indicated) on issues (the subject of negotiations is stated);
- representation in a court hearing of the arbitration court (full name of the court) in the case (case number);
- conducting an inspection of the branch (branch address).
The purpose for a business traveler can also be specified in the work travel plan if this is required by the local regulations of the organization. The director or other authorized person draws up and signs this document. The employee signs the plan after reviewing it.
In addition to the task, the plan must contain information about the place or organization where the employee was sent, a list of issues to be resolved, and the duration of the business trip.
Sample travel plan
Based on Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2014 No. 1595, which entered into force on January 8, 2015, the preparation of a travel certificate is no longer mandatory and is required only if it is specified in the local regulations of the enterprise itself. In this case, the purpose of the trip in the travel certificate and examples can be seen above.