Special assessment of working conditions is a relatively new process in labor protection.
Therefore, many occupational safety specialists, both experienced and young, consider OSH an extremely difficult task, and do not fully understand why this event is carried out at all. In this article we will tell you how to carry out a special assessment without difficulty, and in which case you can save the employer’s money without conducting a special assessment again. Article navigation
- Purpose of SOUT
- Requirements for an expert organization
- Frequency of SOUT
Useful templates prepared by our experts:
Sample order approving an action plan to improve the working conditions and safety of workers
A sample action plan for an action plan based on the results of the SOUT for publication on the website
What is a special assessment card for working conditions?
A special assessment card for working conditions is a document containing information about the employee’s place of work. To do this, you do not need to additionally use other documents.
It contains information:
- About the company where the certification is carried out.
- About an enterprise that provides services of a similar nature.
- Description of the work process.
- Parameters for measuring gas and dust levels in the air of the working area.
- Measurement parameters for noise, illumination and temperature and humidity conditions.
- What benefits are provided: shortened working hours, additional payments, additional leave, etc.
- How often are medical examinations carried out?
- What measures need to be taken to eliminate cases of injuries and occupational diseases.
A special assessment card for working conditions is a workplace passport, which contains all the comprehensive information about the employee’s working conditions in the organization. The employee must be familiar with the documents.
An example of entering data into a special assessment card for working conditions
When filling out the card, use the instructions in the appendix. No. 4 to Order of the Ministry of Labor dated January 24, 2014 No. 33n.
Documents for SOUT, sample filling:
If this document is missing
The employer must have a special assessment card for working conditions, and in its absence, the consequences may be different. Based on the requirements of labor legislation and Federal Law, this work is required. Every five years a special assessment of working conditions must be carried out.
Failure to comply with these requirements will result in administrative penalties for the employer. It turns out that the employee is working in a workplace where it may not be possible to work. The reasons may be non-compliance with sanitary standards and unfulfilled compensation assessments, and in the event of an accident, an assessment of hazardous factors was not carried out.
Requirements for an expert organization
Despite the fact that there are hundreds of expert organizations in the state register, it must be remembered that in remote areas of our country there is a shortage of experts. Therefore, SOUT can be carried out by organizations whose legal addresses are located in other regions, for example, in Moscow or St. Petersburg. This is allowed because it does not contradict the requirements of Law No. 426-FZ. At the same time, it is not allowed for the expert not to come to the enterprise, but to conduct the SOUT remotely.
Another violation is the provision of services without accreditation in the registry. In this case, the employer is at risk, since the requirements for the expert organization are prescribed in Law No. 426-FZ.
Therefore, you need to carefully choose such an organization.
You need to look at accredited organizations in the register posted on the Ministry of Labor website at the link https://akot.rosmintrud.ru/ot/organizations. If it is revealed that the employer made a mistake in choosing an expert organization, the SOUT will have to be carried out again, and there may be fines for late completion and additional monetary costs.
It is imperative to involve a legal service in this process, since it is necessary to check the expert organization for financial solvency and insure possible risks.
It is necessary to weed out expert organizations that have a negative reputation. This can be done by checking whether the expert organization has any tax debts, debts from lawsuits, as well as the presence of lawsuits in this organization, including in the arbitration court. Therefore, check the TIN on the FSSP website, as well as on the counterparty verification website.
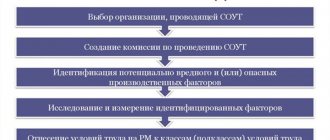
How to conduct a special assessment step by step: from the commission to the transfer of the declaration to the State Tax Inspectorate
Step 1. Creation of a commission to conduct SOUT
When an employer decides to conduct a special assessment, an order must be created to create a commission.
- the commission must consist of an odd number of participants
- The commission must include representatives of the employer. They are the leading employees of the organization. One of them must be appointed chairman of the commission
- The commission also includes labor protection service workers and chief specialists. For example, you can include lawyers, technologists, and economists in the commission. This will be useful in the future when it is necessary to implement measures based on the results of the SOUT
- The commission must include representatives from employees. Such persons are labor protection commissioners, if the enterprise has created a labor protection commission, or representatives from a trade union organization
Note! It happens that an organization does not have a representative body of employees. In this case, there will be no representative from the employees on the commission, and this may lead to the fact that the employees will object to the SOUT carried out by them. This is very risky from the point of view of a possible state examination of working conditions and recognition of special labor conditions carried out in violation of the interests of workers.
If it becomes necessary to make changes to the composition of the commission, an order must be issued. The expert organization must also be familiarized with this order so that it can make timely changes to the text of the report.
Step 2. Compiling a list of jobs, identifying similar jobs
As soon as the members of the commission and its chairman are elected, work can begin on organizing the SOUT. At the same stage, an expert organization is selected and an agreement is concluded.
Experts and laboratory workers must be given an introductory briefing on the first day of their work at the enterprise and, if necessary, be issued with duty PPE. After this, specialists from the expert organization can begin their work.
The experts need to submit a list of jobs approved by the employer, indicating similar ones. This list includes jobs according to the staffing table and qualification directories. In this case, it is necessary to evaluate the signs of similarity.
Example: if four milling operators work in one workshop and operate the same machines in the same mode, then SOUT will need to be carried out not at four, but only at two workplaces.
This saves the employer money and reduces time. But if the organization has drivers of different brands of cars or forklifts, then a special assessment will have to be carried out at each workplace, since the principle of similarity is violated - different equipment, different tools, different brands and even the year of manufacture of the car or machine are important for assessing the level of exposure to harmful factors.
At one enterprise, several jobs of forklift drivers were assessed as similar, but later it turned out that one half of these forklifts are powered by electricity, and the second has a gasoline engine. The employer was forced to conduct an additional special assessment and pay a fine for incorrect calculation of similar places.
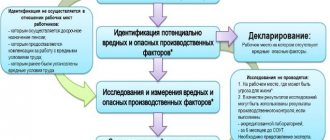
Step 3 Identification
After the commission for carrying out the special assessment process transfers the approved list of workplaces to the expert, the process of identifying harmful and hazardous production factors (HAPF) begins.
This process consists of identifying job responsibilities and data from qualification reference books and professional standards; the equipment, tools, and personal protective equipment maintained by the employee are considered.
During identification, the expert can interview workers. At the same time, the employer is prohibited from putting pressure on both the expert and the employees, or narrowing the expert’s range of interests.
Step 4. Declaration
The expert must assess whether it is necessary to conduct laboratory and instrumental studies. If he comes to the conclusion that working conditions in the workplace are optimal or acceptable , and the profession is not on the list for preferential leave or early retirement , he will write a conclusion that the VOPF have not been identified.
In this case, it is not cards that are drawn up for such jobs, but a SOUT declaration . The SOUT declaration includes all workplaces, including similar ones, for which VOPFs have not been identified. SOUT maps are not drawn up. The declaration includes information about the expert’s conclusion.
Declaration of workplaces allows the employer not to re-conduct the SAW, if during the 5 years of validity of this document no accidents have occurred, or there have been no requests or demands for carrying out the SAS from the representative body or the State Labor Inspectorate inspector. This is a good saving for the organization . Thus, the desire to create jobs with optimal and acceptable working conditions is encouraged by the state.
Step 5. Laboratory and instrumental research
In relation to those workplaces where the expert has identified VOPF, laboratory and instrumental studies must be carried out. They are carried out by a laboratory belonging to an expert organization. Such an organization can also involve a third-party laboratory in research.
The scope of measurements is determined by the SOUT expert. Laboratory research protocols remain in the expert laboratory. The SOUT card indicates the number and date of the measurement protocol . The expert is obliged to explain, at the request of the employer, the mechanism for taking measurements, as well as provide other advice within the framework of the procedures he carries out.
Step 6. Signing the report
The SOUT expert prepares a report and, after all sections are completed, passes it to the employer’s commission for signing.
After the commission members sign the report, the commission chairman must approve it. Then the commission must notify the expert within three days that the report has been approved. After receiving such confirmation, the expert organization transmits the report to the federal information system.
The employer remains:
- draw up an order establishing guarantees and compensation
- within 30 calendar days, familiarize employees with the results of the SOUT
- within the same period of thirty days, you need to post a summary statement and an action plan to improve working conditions and safety
The summary statement does not contain personal data. The action plan must be approved before publication. Both of these documents must be stored on the employer’s official website. As a rule, they are placed in the “About the company” tab.
How to prepare a special assessment card
Map preparation is carried out in several stages:
- The number of jobs to be assessed is determined. As a rule, this work is entrusted to the HR department.
- A list of jobs is compiled, signed by experts and approved by the organization’s management.
- An administrative document on the work is being prepared. Enterprise specialists are appointed members of the commission, and the head of the facility is appointed chairman.
- Next, the work of the expert commission begins together with the management team.
- Based on the results of the work, a map is drawn up. And so on for each place.
- The list of facilities at which a special assessment of working conditions was carried out is also agreed upon with specialists and approved by management.
How to submit a special assessment declaration
The completed form is submitted to the territorial body of Rostrud - in person or by mail. If you select the second option, you must select a postal item with a notification of receipt and a description of the attachment. It is possible to submit a declaration to eclaration.rostrud.ru in electronic form - the form is filled out directly on the Rostrud website. At the same time, the method of document certification is selected:
- qualified electronic digital signature;
- signature using crypto-pro.
There, on the Rostrud website, step-by-step instructions are given for filling out the electronic form and a sample is posted in electronic form.
Filling algorithm
The special assessment card for the labor process is filled out sequentially. For this, the following information is taken into account:
- All information about the company conducting the certification. Name, address, location, license number and certificate of right to engage in this type of work.
- Data about the workplace and similar places.
- Indicate the SNILS number of employees.
- What negative environmental factors exist, how do they affect the body.
- What compensation are due to employees for harmful production conditions: a shortened day, how many days the vacation is increased, what amount of additional payment is due.
- List of measures according to which working conditions are improved.
- This information is provided from the company's certificate of incorporation, state schedule. The bulk of information is entered into the cards by experts, as well as by the management of the enterprise where the special assessment was carried out.
- Information from the administration data
Information about the organization, employees and their insurance certificates
The first step is to fill out the information by the enterprise administration, that is:
- Information about the manual.
- Full name of the organization.
- Where is the enterprise located?
- Information from the passports of managers and superiors.
- Contacts of the facility management.
- Other information based on the table requirements.
- Card number, information about employees, positions
It is required to enter information about the number of employees in workplaces that require a special assessment. It indicates what positions and job functions the employees perform. The staffing table is taken as a basis, and the numbers are indicated in order.
Based on the data from ETKS, the details are filled in. The table below fills in the actual information.
Filling out is carried out by personnel service employees, health and safety specialists.
Afterwards, the information from the employees’ insurance certificates is filled in. But the table provides for filling in other lines that are left empty before a new employee is accepted into the organization.
Filling out is carried out by the HR department.
Where is the SOUT card stored?
The law does not provide for a special place for storing this kind of documentation. The production manager is free to decide for himself where to store the special assessment cards. There are several options:
- department in production, which is responsible for labor protection;
- an employee of an enterprise who is a labor protection specialist;
- Human Resources Department;
- accounting
Important! If the company has several branches, it is more advisable to leave the cards for storage in the branch where the inspection was carried out. This will eliminate the need to request a document from the main office if necessary.
Information about equipment and raw materials
The next step in the experts’ work will be to establish information about the equipment and materials used in the production process.
To do this, information is requested about:
- Models of machine tools, personal computers, lifting equipment and other equipment on which work is performed.
- Information about the materials: name, what operations are performed, what are the emissions of harmful substances to one degree or another, are there any excesses in terms of harmful factors.
- The expert organization requests data from the management of the facility, studies literature in these areas, and takes measurements.
Structure of the regulation on SOUT
As a rule, the regulations are developed by the company's legal department. The structure of the provision includes the following sections:
| Sections of the provision | What do they include |
| First section | Contains general provisions. It specifies the concept of SOUT, the rights and obligations of employees and the employer when carrying out this procedure. In addition, this section also states that the assessment is carried out jointly by the company itself and a specialized organization. |
| Second section | This section describes the preparation process in SOUT. The procedure for creating a commission to conduct an assessment assessment is provided, the number of participants in the assessment is established, the person heading the commission is identified, and other issues. |
| Third section | The third section describes the assessment process itself. The assessment is carried out by a third party company, and this section describes all stages of its work. |
| Fourth section | Describes the procedure for interpreting the results of an assessment carried out by a company commission. This section outlines the actions that the commission has the right to take based on the assessment results. |
Harmful and dangerous production factors
Harmful and dangerous factors are two different things that should be clearly distinguished from each other.
A harmful factor has a detrimental effect on the human body through the respiratory, hearing or vision organs. This includes noise, insufficient lighting, and excessive levels of gas or dust as a result of the release of harmful substances.
For example, in the workplace, toluene is used in paint production. This chemical element has a harmful effect on the body, since its excess in the air of the work area is 1.1 times higher than the norm. Exceeding the noise level also plays a negative role in its impact on the body. Ultimately, there is a risk for an employee to become ill under the influence of factors of this kind, including an occupational disease.
Hazard is a factor that poses a threat to life or health to a person. For example, explosive substances are used at the work site. It turns out that it is dangerous to be near them, since they can detonate and a person will be injured as a result.
List of compensations
Compensation is provided for workers for work under special conditions:
- For exceeding harmful factors . After taking measurements of gas pollution, noise or dust levels, it turned out that the employee was working in excess. It is calculated how many times excesses are allowed. Based on what is received, the payout percentage is set. Typically from 4 to 12%. Accruals are made depending on the minimum tariff rate for the time actually worked.
- Depending on the type of work or profession, the time for additional days of vacation is established. For this purpose, there is a document regulating this circumstance.
- A shortened working day is also established for work in hazardous conditions based on standards.
- Preferential retirement experience is provided to the employee based on the norms.
All information is recorded in a card for a special assessment of working conditions and is taken as a basis when calculating compensation or providing additional rest time. That is, the concept of “additional payment for harmfulness” can be different.
Recommendations on how to improve conditions
Based on the results of the work, experts provide information on improving working conditions. How it's done:
- An assessment is made of the risk of injury at the workplace. For example, where an employee may fall or an excess of a harmful factor is established. Then additional measures are prescribed: repair the floor covering or wear a respirator.
- Measures to reduce the level of danger are set out in a special plan, which is agreed upon with the management of the facility and must be completed in accordance with the deadlines.
- Activities that do not require costs are usually carried out in the near future. Those activities for which funds need to be spent are carried out at the time agreed with the employer.
- After signing the measures, the injury hazard class to which the workplace belongs is indicated.
Commission members
When preparing an organization to conduct a special assessment of workplaces, an administrative document is initially issued, which indicates the members of the commission in the organization. The commission includes:
| Commission members | A comment |
| Head of the facility | This is the chairman of the commission. He organizes control over the certification process and approves documents. In case of disagreement, organizes meetings at which all controversial issues are resolved. |
| HR Representative | Prepares a list of employees and a list of workplaces where certification is planned to be carried out. After approval of the list, work begins. |
| Health and Safety Specialist | Controls the certification process and helps commission members correctly assess the employee’s position, provides the commission with available documents on occupational safety upon their request, including administrative acts, instructions, personal cards for issuing personal protective equipment and training. |
| Chief power engineer and chief mechanic | Specialists are needed to show work sites and equipment on their farm. |
| Other specialists and managers of sites and facilities taking part in the certification. |
Members of the commission and the chairman must be familiar with the order to carry out work against signature. It is important that the date is placed next to the signature.
Purpose of SOUT
Goals and objectives of the special assessment
Carrying out SOUT is the responsibility of the employer, established in Article 212 of the Labor Code. SOUT has been carried out since January 1, 2014, replacing workplace certification. The main purpose of the special assessment is to determine the class of working conditions. To do this, identification of harmful and hazardous production factors (HOPF) and laboratory studies of the levels of exposure to harmful substances are carried out in comparison with hygienic standards. Based on the results of the SOUT, the tariff for contributions to pension and social insurance is established.
Important! All guarantees and compensation established in the Labor Code and other by-laws can be established exclusively during a special assessment.
The results of the conducted special assessment system are used to assess occupational risks , and they can also replace laboratory tests for industrial sanitary control. Therefore, this important event is separately highlighted in the code of administrative offenses, as well as in the rules for the reimbursement of funds for labor protection from contributions to compulsory social insurance.
Responsibility for violations in the conduct of SOUT
Violations during the SOUT procedure may entail punishment for both the employer and the expert and expert organization.
In the Code of Administrative Offenses, the employer's responsibility is specified in Part 2 of Article 5.27.1.
If the SOUT is not carried out on time, a mistake is made when creating the commission, or the employees are not familiarized with the results of the special assessment, the legal entity will be fined in the amount of 60 to 80 thousand rubles . If an individual entrepreneur commits the same violations, the fine may range from 5 to 10 thousand rubles. But that's not all.
Officials may also bear personal liability from 5 to 10 thousand rubles. Such officials include members of the commission, a labor protection specialist, as well as other authorized persons who are brought to administrative responsibility by decision of the State Labor Inspectorate or the court. But not only the employer is responsible for the quality of the SOUT.
The Code of Administrative Offenses has article 14.54. It states that if an expert organization violates Law No. 426-FZ, the SOUT expert will be fined in the amount of 25 to 30 thousand rubles. In this case, the expert organization itself may be fined from 70 to 100 thousand rubles.
If this is not the first time that an SOUT expert has been “caught”, and has previously been fined under the same article, he can be fined 40-50 thousand rubles, but the worst thing is that the expert can be disqualified for 1 to 3 years, by a court decision. In this case, the expert organization will be fined up to two hundred thousand rubles, or its activities will be suspended for three months. This is a long period of time during which an accredited organization can lose clients, and the disqualification of an expert means that he will not be able to work in his specialty.
About getting acquainted
It is necessary to familiarize yourself with the employee’s certification card; there are several compelling circumstances for this action:
- This is a requirement of regulatory and legislative documents.
- The employee must know what compensation and benefits he is entitled to and for what reasons they are not determined.
- It is important to know whether you need to undergo medical examinations and how often.
- What harmful factors are present in the workplace and measures to combat them.
- List of personal protective equipment used in the workplace.
- Safety measures that the employee must know, including training.
- Regulations on work, duration of lunches and work breaks.
- Length of working day and vacation.
How to prescribe working conditions in the workplace without SOUTH
Until the letter from the Ministry of Labor came out, which, by the way, also did not add clarity, but at least lifted the veil of uncertainty, many personnel specialists indicated in their employment contracts working conditions, who is good at what (working conditions are normal, working conditions will be determined after a special assessment (before such dates), etc.).
How can one prescribe working conditions at an employee’s new workplace when a period of one year is given for this? But Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation requires this, without any exceptions.
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, in its letter No. 5-1/OOG-2516 dated July 14, 2016, advises that if an employee is accepted into a newly organized workplace where an assessment of working conditions has not previously been carried out, then before conducting a special assessment of working conditions in the workplace A contract with an employee hired for such a workplace may indicate the general characteristics of the workplace (description of the workplace, equipment used and features of working with it).
The Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation did not provide any, at least approximate, formulation. And what will you write? Use your imagination again?
The Labor Inspectorate, in its online responses after the release of this letter, began to refer specifically to it, also without providing any wording. Although, you can still come across answers that until a special assessment of working conditions is carried out, nothing needs to be specified in the employment contract.
Question: A mandatory condition of an employment contract is working conditions in accordance with the results of a special assessment (optimal, acceptable, harmful, dangerous). What should be indicated in the contract if an employee is hired for a position that has just been added to the staffing table, for which a special assessment has not yet been carried out and must be carried out within 12 months?
Answer: If a special assessment of working conditions (SAL) was not carried out in relation to the newly introduced workplace, then nothing needs to be specified in the employment contract with the employee regarding working conditions at his workplace. In such a situation, it is necessary to immediately conduct a special assessment and, based on its results, conclude an additional agreement to the employment contract indicating information about the working conditions at the employee’s workplace.
Information portal of Rostrud “Online inspection of the Russian Federation”, April 2017
It is also worth mentioning the letter of Rostrud dated November 20, 2015 No. 2628-6-1, which also asked a question about working conditions when there is no special assessment. In the said letter, the department noted that Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for any temporary deferrals in the fulfillment of this obligation of the employer, therefore, in order to avoid violations of labor legislation, in the absence of valid results of certification of workplaces for working conditions, a special assessment of working conditions must be carried out as soon as possible.
In fact, working conditions need to be spelled out in an employee’s employment contract. Indicate in the contract everything that the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation advises, namely, describe the employee’s workplace, the equipment he uses and the features of working with it (at the end of the article I provided an approximate example). Because the judicial system has not yet come to a common denominator on this issue .
The employer lost
The employer indicated in the employees’ employment contracts that “working conditions in the workplace will be determined after carrying out the special labor assessment,” which he was obliged to carry out within 12 months, because these were newly organized workplaces. There were no violations on his part; he still had time.
The Samara Regional Court, in its decision of October 2021, did not agree .
The court referred to Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as to the above-mentioned letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated July 14, 2016 No. 5-1 / OOG-2516, based on which, the employment contracts of employees must indicate the general characteristics of the workplace (description of the worker places, equipment used and features of working with it).
In addition, the court noted that failure to inform workers about the working conditions at their workplaces violates the labor rights of workers and creates a threat of harm to their life and health, since those dangerous and (or) harmful production factors that may affect workers in the process of their work.
Thus, the employer received the minimum possible administrative fine in the amount of 50,000 rubles under Part 4 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (maximum 100,000 rubles), but there was still no indication of the working hours in the part-time worker’s employment contract, which is also mandatory for inclusion in the contract.
But a judge in the Arkhangelsk region decided that the absence of working conditions in an employee’s employment contract (without conducting a special labor assessment) is not a violation of the law.
The employer won
The employment contract of the new HR director stated that working conditions in the workplace were normal. The employer had another whole year to conduct a special assessment of working conditions.
The labor inspectorate inspected the organization in May 2021 and brought the employer under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (fine from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles), although it should have been under Part 4, as for improper execution of an employment contract, well, that’s not the point.
The court did not agree with the position of the State Labor Inspectorate, noting that this was a newly organized workplace, so the employer still had time to conduct a special assessment.
The court also referred to the fact that the position of “HR Director” does not belong to the category of workplaces containing potentially harmful and (or) hazardous production factors (Part 6 of Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ) , namely:
- workers' workplaces, professions, positions, specialties of which are included in the lists of relevant works, industries, professions, positions, specialties and institutions (organizations), taking into account which the early assignment of an old-age insurance pension is carried out;
- workplaces in connection with work in which employees, in accordance with legislative and other regulatory legal acts, are provided with guarantees and compensation for work under harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions;
- workplaces in which, based on the results of previously conducted certification of workplaces for working conditions or a special assessment of working conditions, harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions were established.
Consequently, the absence of working conditions at the workplace in the employment contract concluded with the employee is not a violation of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Working conditions in the workplace without SOUTH (sample)
The stated wording of working conditions is approximate! The main thing is to remember that what you write down in the employment contract can only be changed by agreement of the parties . Therefore, if your furniture and office equipment are constantly changing, then try to write general phrases, do not write about types of monitor screens (liquid crystal, based on a cathode ray tube), do not list all types of peripheral devices that an employee can use (such as an external hard drive , flash drive, uninterruptible power supply, projector, etc.). Prescribe only those things that you are 100% sure will be consistent. Also, you cannot write that working conditions are safe (optimal, acceptable), because... you don’t know about it yet (there are no special assessment results). The fact that working conditions comply with labor protection requirements. So this is the responsibility of the employer (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)...
Regarding the timing of the special assessment. I wrote a general phrase, although many indicate a specific date by which a special assessment will be carried out (in the case of a newly organized workplace, this is 12 months). As I wrote above, Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not make any exceptions, therefore, in order to comply with the law, a special assessment of working conditions must be carried out as soon as possible .
By the way, you can take some phrases from the sanitary rules (just don’t overdo it), at the same time you will emphasize a lot:
— SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization”; — SanPiN 2.2.2.1332-03 “Hygienic requirements for organizing work on copying equipment”; — SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 “Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises”; — SanPiN 2.2.4.3359-16 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for physical factors in the workplace”; — SanPiN 2.2.0.555-96 “Hygienic requirements for working conditions for women”; - Set of rules. Administrative and domestic buildings. Updated version of SNiP 2.09.04-87.
Sample card
How to fill out the special assessment card correctly:
- The name of the expert organization that carried out the certification is indicated: details, legal address, index.
- Information about the employer: insurance certificate TIN, organizational structure codes, address, zip code, registration certificate number.
- The number of places for which conditions are assessed is indicated. This information is provided by a specialist from the HR department, as well as information about the structural unit.
- How many employees work in the workplace, including women, the number of persons under the age of majority, SNILS number of employees.
- What equipment and materials are used in the technological cycle.
- What payments and benefits are due?
- A class for assessing working conditions is established in accordance with legal requirements.
Updated declaration on special assessment of working conditions
As mentioned above, changes have occurred in matters of filing a declaration: it is allowed to include those areas of activity in the organization that correspond to the first and second safety classes. If, based on the results of the special assessment, the employer has such specialties, he needs to clarify the previously submitted information and include additional information in the declaration. For this, legislators provided only 30 working days from the date of entry into force of the new requirements.
All other employers submitting a report to the labor inspectorate on a special assessment of working conditions later than this date must include optimal or acceptable conditions in the document immediately, as required by the new edition of Article 11 of Federal Law No. 426-FZ of December 28, 2013. This means that in 2021, no one needs to submit updated information.
Storage and modifications
The special assessment card for working conditions is kept by the employer, usually in the personnel department. Storage is carried out for five years, that is, until the next certification. The document is presented at the request of management and supervisory authorities.
Changes and additions are not made to the SOUT map, since periodic assessment work is required in the following cases:
- After five years, the next certification is carried out.
- If changes have been made to the technical process or new equipment has been purchased, then experts must be involved in the assessment again within 6 months.
- When organizing a workplace, certification is carried out again after a year.
No changes are made to the special assessment card for the conditions of the labor process; the document is drawn up again. This is a requirement of regulations and regulatory documents.