The trade tax (TS) is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Chapter 33. It can be introduced in cities of federal significance and in municipalities. Today, this type of tax has been in effect in the capital of the Russian Federation since July 1, 2015, on the basis of Moscow Law No. 62 of December 17, 2014, and has not yet been introduced in St. Petersburg and Sevastopol. Municipalities will be able to introduce a fee after the publication of an additional Federal Law. The region where the CU was introduced sets its own rates and benefits. In this article we will look at how to calculate the trading fee for a month or an incomplete quarter in Moscow.
Trade tax - what kind of tax is it?
The provisions of legislative acts establish that a trade tax is a mandatory payment from trade, which is calculated every quarter by business entities for payment to the budget in certain regions.
It applies to local taxes. It is expected that it will be collected by municipalities in three cities of federal significance - Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Sevastopol. However, local legislators must prepare a special legislative framework for this fee.
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for the purposes of calculating the trade tax, trade means the activity of selling goods through stationary facilities with and without retail space, non-stationary trade facilities, as well as the sale of goods from a warehouse. The obligation to calculate the trading fee also arises for the organizers of market trade.
Trade tax is levied on trade objects, which means the real and movable property of companies and entrepreneurs used by them to carry out sales.
Attention! Thus, the basis for the trade tax is not the income received from the sale of goods, but the physical indicators of the object of trade.
Where applicable in 2021
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that a trade tax should be introduced in three regions of Russia, which are cities of federal significance. These are Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol.
In order for local authorities to levy a trade tax on the territory of these subjects, they must prepare and approve a number of regulatory documents.
Currently, the corresponding law has been adopted only by the Moscow authorities. Therefore, today the trade tax is paid by business entities operating in the field of trade in the capital. The rest of the federal cities are still engaged in preparatory work.
Important! In this case, the business entity may not be registered in Moscow. It is enough that he uses a trade facility located on the territory of a given city. Before starting activities, he needs to submit a notification to the Federal Tax Service at the location of this facility.
Who pays it
Determining the need to pay a trade tax depends on two indicators.
Tax system
The law establishes a trade fee for individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system and OSNO, as well as companies using the same regimes. If a business entity applies an agricultural tax or a patent system, then they are exempt from paying the fee.
A special situation has been established for those who apply UTII. The law determines that it is impossible to pay imputation and trade fees at the same time. Therefore, it is necessary to withdraw from UTII, switch to a different system, and depending on this, determine the need to use the trade tax.
Activities
By law, all business entities that trade in retail, small wholesale or wholesale are required to make payments when using the following facilities:
- Stationary facilities with a sales area;
- Stationary facilities without a sales area;
- Non-stationary objects;
- Warehouses.
However, this type of activity must additionally be specified in local law. Thus, on the territory of Moscow, trade from warehouses is not subject to trade tax, since this type of activity is not prescribed in the adopted legal act.
Attention! The activities of retail markets are also subject to the trading tax. However, in this case, payment is made not from each trading place, but from the area of the entire market.
Results
To calculate the amount of the trading fee you need to know:
- category of the retail facility (that is, whether it is stationary, non-stationary, a retail or delivery facility, or part of a retail market);
- physical characteristics of the retail facility, which is used in calculating the vehicle value (determined based on the category of the corresponding facility);
- the rate established by the law on vehicles for the corresponding object.
In addition, do not forget to check if there are any benefits in the Customs Union legislation for the trading infrastructure used in your business.
You can find out more about the trading fee in the following articles:
What is subject to trading tax in 2020
To calculate the trade fee, it is not the income indicator (real or conditional) that is used, but the very fact of the existence of a retail facility. The latter refers not only to real estate in the form of kiosks or shops, but also delivery trade.
Thus, payment of the trade fee does not depend on the following indicators:
- Availability of ownership rights to the retail outlet. Business entities that use real estate for trading activities are required to pay the fee, regardless of whether they are owners or tenants;
- Amount of income. This indicator is not involved in determining the fee. In fact, the amount of tax determines the type and location of the object;
- Place of registration of the business entity. If the activity is carried out in a territory that is subject to a trade tax, it must be paid regardless of the actual registration of the businessman;
- Regularity of trade. The fee must be calculated and paid once a quarter, regardless of whether trading activity was carried out during this period or not.
Attention! The sales fee is determined based on two physical characteristics - the actual presence of the object and the area of the trading floor.
If in the first case a ready-made rate indicator is used, then in the second case it is necessary to allocate the area of the hall from the total area of the store. To avoid problems with regulatory authorities, the last figure must be taken from official documents.
Nuances of determining the area of the hall at a retail facility
So, the trade fee can be calculated based on 2 types of physical characteristics of retail facilities - the area of the trading area (or hall) and the actual presence of the facility. In the second case, the corresponding object acts as a very simple component of the formula - in the form of a coefficient equal to 1. However, if we are talking about determining the retail space, there are already possible nuances associated with its correct allocation from the total area of the store.
In accordance with sub. 5 clause 3. art. 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the area of the trading floor should include:
- areas of the facility used to place equipment used for displaying goods and making payments to customers;
- areas where cash registers are located;
- areas where retail facility personnel work;
- passages for visitors.
Ancillary, household premises, as well as premises used for receiving, preparing and storing goods, administrative offices - those areas of the territory of a retail facility where customer service is not provided are not included in the area of the trading floor.
Specific figures reflecting its area can be determined based on information from inventory documents, certificates of ownership, registration certificates, extracts from Rosreestr, rental contracts, etc.
What types of activities are not subject to trade tax?
Local authorities have the right to determine a list of activities for which it is not necessary to calculate and transfer the trade tax. The following activities are established for Moscow:
- Retail trade using automatic machines;
- Sales at weekend fairs, special and regional fairs;
- Trade in theaters, museums, cinemas, provided that at the end of the quarter the income from ticket sales is at least 50%;
- Trade at vegetable warehouses;
- Trade through facilities located on the territory of markets;
- Autonomous budgetary and government institutions;
- Post offices;
- Non-stationary retail outlets that sell printed products;
- Religious organizations when selling in their places of worship.
You might be interested in:
Limit value of the base for calculating insurance premiums in 2019: table of values
In addition, the following types of household services are exempt:
- Hairdressers and beauty salons;
- Laundries, dry cleaners;
- Repair of shoes, clothes, watches, jewelry;
- Manufacturing of haberdashery and keys.
However, for all these objects additional conditions are established:
- Providing services is the main source of income for them;
- The size of the object is no more than 100 sq. m., while the display and demonstration of goods is carried out on no more than 10% of the area.
Attention! Online stores do not need to pay a fee, provided that they do not provide courier delivery of goods with payment on the spot.
All business entities that fall under the trade tax benefit must still register with the Federal Tax Service, indicating the type of benefit in the notification.
Table: fee rates 2021
Different areas of Moscow have their own sales tax rates. Here are the current sales tax rates in 2021 in Moscow.
The amount of the fee does not depend on how many days you traded and how much revenue you received (clause 1 of Article 412 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 03.03.2016 No. 03-11-13/12306, Federal Tax Service dated 07.07.2017 No. SD-4- 3/13187). It doesn't matter whether you opened your store in January or March, your sales fee for the first quarter will be the same. There is no need to pay the fee only if you did not work for the entire quarter.
The remaining rates for medium and large stationary trade can be viewed in Moscow law dated December 26, 2018 here.
Trade tax rates in Moscow in 2021: table
Let's consider the rates for trade fees in Moscow in 2021, which are set depending on the location of the trade facility.
| Type of trade | Central administrative district (CAO) | Zelenogradsky, Trinity and Novomoskovsky JSC | Southern administrative district (Southern Administrative District) |
| Trade through a stationary network that does not have halls (without gas stations) | 81000 rub. for each object | 28350 rub. for each object | 40500 rub. for each object |
| Trade through a non-stationary network (except for delivery and distribution) | 60,000 rub. for each object | 21000 rub. for each object | 30,000 rub. for each object |
| Trade through facilities with halls up to 50 sq. m. | 1200 rub. for every sq. m. area up to 50 sq. m. | 420 rub. for every sq. m. area up to 50 sq. m. | 600 rub. for every sq. m. area up to 50 sq. m. |
| Trade through facilities with halls over 50 sq. m. m. | 50 rub. for every sq. m. area over 50 sq. m. | 50 rub. for every sq. m. area over 50 sq. m. | 50 rub. for every sq. m. area over 50 sq. m. |
| Delivery and distribution trade | 40500 rub. for each object | ||
| Retail markets | 50 rub. for every sq. m. market | ||
Continuation:
| Type of trade | Molzhaninovsky district of Northern Administrative Okrug Northern district of NEAD Vostochny, Novokosino and Kosino-Ukhtomsky districts of the Eastern Administrative District Nekrasovka SEAD Northern Butovo and Southern Butovo South-Western Administrative District Solntsevo, Novo-Peredelkino and Vnukovo CJSC Mitino and Kurkino North-West Administrative District | All areas of the Northern Administrative District (except Molzhaninovsky) All districts of NEAD (except Northern) All districts of the Eastern Administrative District (except for the districts of Vostochny, Novokosino and Kosino-Ukhtomsky) All districts of the South-Eastern Administrative District (except for the Nekrasovka district) All districts of the South-Western Administrative District (except for the Northern Butovo and Southern Butovo districts) All districts of the closed joint-stock company (except for the districts of Solntsevo, Novo-Peredelkino and Vnukovo) All districts of the Northwestern Administrative District (except for the Mitino and Kurkino districts) |
| Trade through a stationary network that does not have halls (without gas stations) | 28350 rub. for each object | 40500 rub. for each object |
| Trade through a non-stationary network (except for delivery and distribution) | 21000 rub. for each object | 30,000 rub. for each object |
| Trade through facilities with halls up to 50 sq. m. | 420 rub. for every sq. m. area up to 50 sq. m. | 600 rub. for every sq. m. area up to 50 sq. m. |
| Trade through facilities with halls over 50 sq. m. m. | 50 rub. for every sq. m. area over 50 sq. m. | 50 rub. for every sq. m. area over 50 sq. m. |
| Delivery and distribution trade | 40500 rub. for each object | |
| Retail markets | 50 rub. for every sq. m. market | |
Where to get the data to calculate the trading fee (rates and physical characteristics)
Let us recall that Moscow is the only city in Russia in which, as of the beginning of 2021, a trade tax has been introduced. Therefore, in practice, its calculations are so far carried out only by entrepreneurs in the capital. The main regulatory source for them is the Moscow City Law “On Trade Fees” dated July 17, 2014 No. 62.
Physical characteristics and vehicle rates for Moscow are defined in the provisions of Art. 2 of Law No. 62. These and other indicators are determined, first of all, based on the geography of the location of retail facilities. The city authorities have identified 3 main tariff zones for trading:
- zone 1 - central areas (located in the Central Administrative District of Moscow);
- zone 2 - areas located primarily outside the Moscow Ring Road (including New Moscow);
- zone 3 - areas located primarily within the Moscow Ring Road, but not included in the Central Administrative District.
Tax calculation example
Stolitsa LLC owns three kiosks in the Central Administrative District of Moscow, as well as a store with an area of 76 square meters. m. on the territory of the Southern Administrative District.
The rate for a kiosk on the territory of the Central Administrative District is 81,000 rubles per object. The rate for a store in the Southern Administrative District is 600 rubles for the first 50 square meters. m, and 50 rubles for all subsequent ones.
Collection amount for the store: 600 x 50 + 26 x 50 = 31,300 rubles.
Collection amount for kiosks: 81,000 x 3 = 243,000 rubles.
Total fee per quarter: 31,300 + 243,000 = 274,300 rubles.
How much will you have to pay
Specific collection rates, the exact composition of payers and the territory of coverage are determined by local authorities. The law allows setting a trade tax rate no more than the cost of a patent for 3 months for the relevant type of activity in a specific region. In Moscow there is a law on trade tax, here are the rates from it for 2020-2021:
- kiosks and tents in central areas will pay 81,000 rubles per quarter, in other areas of the city - from 28,350 rubles to 40,500 rubles per quarter;
- trays, auto benches and carts - 40,500 rubles per quarter;
- shops and pavilions with a retail area of up to 50 sq.m in central areas - 54,000 per quarter, within the Moscow Ring Road - 27,000 per quarter; outside the Moscow Ring Road - 18,900 rubles;
- shops and pavilions with a retail area from 50 sq.m to 150 sq.m - 54,000 rubles per quarter for the first 50 meters and plus 60 rubles for each meter above; within the Moscow Ring Road - 27,000 rubles per quarter and plus 55 rubles for each meter above; outside the Moscow Ring Road - 18,900 rubles and plus 50 rubles for each meter over.
Submit reports in three clicks
Elba will calculate taxes and prepare business reports based on the simplified tax system, UTII and patent. It will also help you create invoices, acts and invoices.
Try 30 days free Gift for new entrepreneurs A year on “Premium” for individual entrepreneurs under 3 months
Procedure for registering as a tax payer
The payer of the trade tax is an entrepreneur or company that has sold goods at least once during the quarter in the territory of the municipality where the trade tax has been introduced. In this case, you must independently register with the tax authority as a payer.
For this operation, a special notification has been developed in the TS-1 form. It can be submitted in one of the following ways:
- In person in paper format;
- By mail with the described attachment;
- When using Internet services, the document must be signed with an electronic signature.
The business entity is given five days to complete this operation. The application must indicate the type of activity, as well as the details of the outlet. After processing the notification, the Federal Tax Service provides the taxpayer with a certificate of registration.
Important! Even those business entities that fall under the established benefits are required to submit a notification and do not have to pay customs duties.
If trading activities are terminated, the entity must draw up a special TS-2 notification. It specifies a specific end date for the activity and the fee must be calculated for that date. It is mandatory to submit this form; if the activity is actually completed, but the notification has not been sent, then the business entity will still be required to calculate and transfer the trade fee.
Registration and deregistration with the tax authorities
Registration/deregistration as a trade tax payer is carried out:
- To the tax office at the location of the immovable object of trade.
- In other cases - to the tax office at the location of the organization or place of residence of the individual entrepreneur.
If there are several retail outlets, one notification (indicating all the “points”) is submitted to the tax office to which the retail outlet listed first in the notification belongs.
List of necessary actions:
- Submit a notification using the recommended form TS-1. This is done within five days from the start of trading in written or electronic form (naturally, using an electronic signature in electronic reporting systems). The notification must reflect all objects carrying out taxable activities. If the objects are located in different territories, information about them is still submitted in one notification, and the tax authority is selected the one to which the object at the top of the list belongs.
- Wait for registration as a trade tax payer, which is done within five days after the tax authority receives the documents. Within five days from the date of registration, the trade tax payer is sent a certificate of registration with the tax authority of an organization or individual entrepreneur as a trade tax payer.
Important! If a notification from an organization or individual entrepreneur was not received, but the tax office received information from the Moscow Department of Economic Policy and Development that the person carried out taxable activities, then it has the right to register it based on the information received.
- Set off or return the amounts of overpaid fees according to the rules provided for in Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This opportunity remains for three years from the date of payment.
- Submit a notification of changes to the object (its area, actual availability, address, etc.) within five days from the moment such changes occur.
- Submit cancellation information if it turns out that the activity is not subject to the trade tax. Frightening fines for the majority of entrepreneurs who failed to clearly determine whether they had an obligation to register, in practice caused a stream of erroneous notifications. After this, the Federal Tax Service of Russia issued a special letter dated August 20, 2015 No. GD-4-3/ [email protected] , explaining that in order to reset the excessively submitted information, it is enough to submit an application in free form to the same tax authority indicating the reasons and a copy of the erroneous information. notifications.
- Make sure that the erroneous registration is cleared. Upon receipt of a cancellation application, the tax office must deregister the person on the same date on which the registration was made, and if the system has already accrued tax amounts for payment, then reverse them.
- Submit a notification in the recommended form TS-2 at the moment when the taxable activity is no longer carried out, and make sure that the tax authorities have deregistered the payer.
Where is the notification sent?
I defined the nuances of registering as trade tax payers in my letter.
It says that the registration and deregistration procedure must be carried out:
- If the activity for which it is necessary to pay a trade fee is carried out using a property - at the location of the property;
- In all other situations - at the location of the company or the place of residence of the entrepreneur.
For example, if an entrepreneur is registered in the Moscow region, or another region of the country, but in Moscow carries out activities in the form of trade in real estate, then he is obliged to send a notice of the trade fee to the inspectorate for the location of this property.
Attention! However, the same entrepreneur who sells in Moscow from a car shop or trade tent must register at his place of residence.
If an entrepreneur has several points in the territory of the municipality from which he is obliged to pay the trade tax, but they belong to different inspections, then the notification must be sent to the Federal Tax Service authority, whose outlet will be indicated first on the form.
General rules
Trade tax is not a tax, but all organizations and entrepreneurs who engage in trade in Moscow are required to pay it.
Individual entrepreneurs and organizations that engage in trade are required to calculate the trade fee quarterly and transfer the payment to the inspectorate at the place of registration (Article 417 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The basis for paying the trade fee is the notification of registration in the TS-1 form, submitted to the Federal Tax Service (approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 22, 2015 No. ММВ-7-14/249).
Penalty for late submission of notice
If a business entity carries out trade that is subject to the trade tax, but has not issued a TS-1 notification within the established time frame, this will be equated to illegal entrepreneurship, i.e., conducting activities without tax registration.
For this violation, a fine is provided in the amount of 10% of the income received from this activity, but not less than 40,000 rubles. This punishment is established by the Tax Code.
In addition, according to the Code of Administrative Offenses, a fine may be imposed on officials. It will be 2-3 thousand rubles.
Is there reporting on vehicles?
No additional reporting has been introduced for the trading fee. Therefore, there is also no obligation to provide a declaration at the same time as paying the fee. However, there are several mandatory forms that every fee payer must fill out.
When registering, each payer sends a notification TS-1. In the event that a business entity changes information about the taxable object, its location, etc., then you also need to fill out and submit the TS-1 form.
Since payers of the fee have the right to reduce calculated income taxes or similar ones by these amounts, the amount of the fee is indicated in the corresponding declaration:
- In the income tax return, which is prepared by those located on OSNO, data on the trading fee is entered on Sheet 02, in lines 265-281.
- Entrepreneurs who report income by filing a 3-NDFL declaration indicate the amount of the fee paid in Section 2 of this form;
- Individual entrepreneurs and companies that use the simplified tax system for income submit a declaration under the simplified tax system. It contains a separate Section 2.1.2 for the purposes of the trade fee. Business entities that do not pay the fee simply do not fill out this sheet of the form;
- Individual entrepreneurs and companies that use the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” reflect the amount of the fee paid in the Book of Income and Expenses in the column “Expenses”. There are no separate fields in the declaration for this case.
We reduce taxes
The explanations of the Federal Tax Service in the letter concerning the specifics of the application of the legislation on trade tax pay special attention to the fact that in order to have the right to take into account the trade tax when calculating other taxes, it is necessary:
- Have a tax payer certificate (i.e. be registered with the tax authority);
- Actually pay to the budget, and not just accrue, the amount of the trade fee.
For different categories of payers, the right is provided to reduce the amount of trade duty paid by:
- Personal income tax (NDFL) – for individual entrepreneurs.
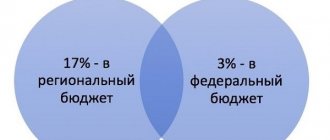
- Income tax – for organizations subject to the general taxation system. Moreover, the fee can only be deducted from the amount to be transferred to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation (i.e., to the budget of the city of Moscow), since the trade fee itself was also sent to the regional budget.
- Tax paid by organizations and individual entrepreneurs under the simplified taxation system:
- according to the “Revenue” system - subtracting the paid fee from the amount of tax payable under the simplified tax system;
- according to the “Income – Expenses” system - taking into account the amount of the trade fee in the list of expenses when calculating the amount of tax to be paid according to the simplified tax system.
The trade tax is a mandatory payment so far only in the territory of Moscow, mandatory for payment from the second half of 2015. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that the trading fee is paid in full for the quarter in fixed amounts stipulated by law.
This means that if the fact of taxable activity was carried out at least once during the quarter, the amount of the fee must be paid in full and it will not depend on anything other than the presence of the object of trade or its footage.
Where do you need to pay for the vehicle?
The Tax Code establishes that the trade fee is a local level tax. Local authorities are directly involved in determining the procedure for its calculation, as well as benefits. It follows from this that the payment of this payment should be made to the local budget.
According to the Tax Code, the tax period is set to a quarter. The amount of the fee must be calculated starting from the quarter in which the notification was sent to the tax authority.
The transfer of the fee is made before the 25th day of the month that follows the billing quarter.
If the authorized body reports to the tax office about identified objects of taxation for which the business entity itself has not sent a notification, then the trade tax must be transferred within 30 days from the date of receipt of the information.
The payment order is issued as for ordinary taxes. The KBK trading fees are set as follows:
- for tax - 182 1 0500 110;
- for penalties - 182 1 0500 110;
- for a fine - 182 1 0500 110.
Payment
The trade fee must be transferred to the budget quarterly no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. Thus, the deadlines for transfers will be January 25, April 25, July 25 and October 25. If the due date falls on a weekend, then transfer of payment on the next business day will not be considered late.
How to transfer the trading fee? – Registration of payment order
On the official website of the Federal Tax Service there is an answer to the question of whether it is possible to send to the budget the amount of the trade tax calculated for all existing objects in one payment. The tax authorities inform you that the fee must be paid for each object in a separate amount, making as many payment orders as necessary.
KBK (budget classification code) , according to Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 20, 2015 N ММВ-7-1/ [email protected] :
- for payment of the principal amount - 182 1 0500 110;
- for payment of penalties – 182 1 0500 110;
- to pay a fine - 182 1 0500 110.
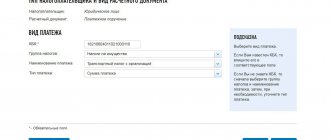
A payment order for the transfer of trade fees is drawn up according to a standard form. Here are the main points that you need to pay attention to when filling out the payment:
- the order of payment when paying the fee is indicated with the value 5;
- payer status for organizations – 01, for individual entrepreneurs – 09;
- code according to the All-Russian Classifier of Municipal Territories (OKTMO), indicated in statistical documents. Tax officials explained that the payment for the trade tax must include the OKTMO code related to the territory in which the trade object is located, regardless of where the organization is registered. In fact, this coincides with the territory of the tax authority in which the payer registered for the trade tax.
- basis of payment – TP (current payment);
- tax period – KV.XX.YYYY, where KV is the letter code of the quarterly period, XX is the number of the quarter for which the payment is made, YYYY is the year the fee is charged;
- purpose of payment – “Trading fee for the XX quarter of YYYY”
It is very important to fill out the order for payment of the fee correctly, without making a mistake in the BCC, otherwise the transferred amount may get lost among the unknown budget revenues and will be difficult to find later.
The procedure for reducing taxes by the size of the vehicle
According to the law, taxpayers in some cases may indicate the listed amounts of trade tax as expenses in the applicable tax systems, and in others they have the right to reduce the calculated income tax (or a payment replacing it) by the amount paid.
BASIC
With this system, the trade tax cannot be expensed, but the amount of the calculated income tax (or advance payment) can be reduced. It is necessary to take into account that only that part of the tax that is transferred to the local budget is subject to reduction.
Entrepreneurs paying personal income tax
They can reduce the amount of personal income tax, which was determined at the end of the year at a rate of 13%. There is a nuance when reducing taxes. This operation can only be done if the entrepreneur trades at the place of registration and pays personal income tax in the same area.
Important! However, in the case when an individual entrepreneur pays tax at his place of registration, but carries out trading activities and pays trade taxes in another city, then it is impossible to reduce the tax.
simplified tax system income minus expenses
In this system, it is allowed to include the amounts of the listed trade fee among the expenses that reduce income when determining the single tax.
simplified tax system income
Entrepreneurs and companies on this system have the right to reduce the single tax by the amounts of trade tax that were paid in the same period. But there is also a nuance here - such a reduction is only possible if the single tax and the vehicle are transferred to the same local budget.
If several types of activities are carried out on the simplified tax system, then a trade tax deduction can only be obtained from the tax on receipts from retail trade. In this case, the individual entrepreneur or company will need to organize separate accounting of income from trade and other activities.
Why a fee and not a tax?
Art. 8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, defining tax and fee, confirms that one of the main differences between these concepts is the meaning of payment: if the tax is charged free of charge, then the fee provides for a legally significant response from the authorities for its payment. In particular, a trade fee is paid for the right to conduct certain types of commercial activities in urban areas.
Another feature of the trade tax is that its introduction, according to experts, will not increase the tax burden on bona fide entrepreneurs. The fact is that the law provides for the taxpayer’s right to deduct the amount of accrued trade tax:
- For organizations - depending on the taxation system - from the amount of income tax (in its regional part) or a single tax according to the simplified tax system;
- For individual entrepreneurs - from the amount of the single tax according to the simplified tax system or personal income tax.
The specifics of applying such deductions directly are not spelled out in the Moscow Law “On Trade Fees”; however, during the second half of 2015, the Federal Tax Service issued a large number of letters in which it explains many controversial aspects of the specifics of calculating the fee.