Basics of carrying out SOUT
SOUT is a special assessment of work activity criteria, which has the goal of classifying the level of danger and harm in the workplace. Based on the results, the manager has the right to improve the working conditions of employees.
This process refers to a set of special measures, the purpose of which is to identify dangerous and harmful factors in the implementation of professional and labor activities. The audit may reveal that working conditions at the production site do not meet the standards set by the government. In this case, representatives of the audited organization will be required to implement recommendations to eliminate the negative impact.
Important! SOUT is a process that creates the environment for organizing work activities and the conditions necessary to protect the worker.
According to Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, all companies and individual entrepreneurs are required to carry out special safety assessments in relation to the workplaces of hired workers participating in production and technological processes.
This rule applies to all workplaces except:
- vacant;
- home-based;
- remote;
- for places created by an individual without individual entrepreneur status (clause 3 of article 3 of Federal Law No. 426 of December 28, 2013).
The analysis of working conditions is based on the working environment and the impact of a number of factors on it. The employee comes into contact with these factors while performing work. They can be both beneficial and threaten his health or even life.
The SAL should be carried out with the participation of people properly prepared for this process. These should be people familiar with the provisions of labor protection rules relating to a specific type of work activity, related to ensuring proper working conditions, and issues of working conditions, for example, health and safety services, technologists.
When organizing SOUT, the employer must pay attention to:
- organization of workplaces, including placement of equipment, ensuring compliance with safety requirements in the workplace;
- condition of equipment components: is operation safety ensured, including protection against electric shock;
- load on the musculoskeletal system;
- burdening employees with physical factors: insufficient lighting;
- psychological stress on workers resulting from the organization of work.
Important! If it is determined that working conditions in certain workplaces may pose a threat to the health, safety or undue nuisance of employees, immediate action should be taken to improve those conditions by informing employees of the hazards and their nature.
The most important regulatory act that should be highlighted here is 426-FZ. The presented federal law defines the organizational basis for the rights, duties and responsibilities of assessment participants.
It should be noted that Federal Law No. 426 is far from the only regulatory act that defines the conditions and principles for the functioning of assessment work at a particular enterprise. There is also the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as certain regulations at the local level.
It is necessary to highlight an important norm provided for in Article No. 2 of Federal Law No. 426. This indicates the principle of the priority of international law over national law. Therefore, this regulation must also comply with international standards.
List of compensations
Compensation is provided for workers for work under special conditions:
- For exceeding harmful factors . After taking measurements of gas pollution, noise or dust levels, it turned out that the employee was working in excess. It is calculated how many times excesses are allowed. Based on what is received, the payout percentage is set. Typically from 4 to 12%. Accruals are made depending on the minimum tariff rate for the time actually worked.
- Depending on the type of work or profession, the time for additional days of vacation is established. For this purpose, there is a document regulating this circumstance.
- A shortened working day is also established for work in hazardous conditions based on standards.
- Preferential retirement experience is provided to the employee based on the norms.
All information is recorded in a card for a special assessment of working conditions and is taken as a basis when calculating compensation or providing additional rest time. That is, the concept of “additional payment for harmfulness” can be different.
SOUT schedule: main characteristics
Basic documents for conducting SOUT:
- order on the formation of a commission on SOUT;
- schedule of activities for SOUT.
The schedule is a table indicating the number, name and date for each event.
In accordance with Part 6 of Art. 27 of Law No. 426-FZ, the schedule for carrying out special assessments should be a step-by-step process. Its completion date is no later than December 31.
Thus, according to the schedule, the timing of the SOUT is compressed.
Features of step-by-step scheduling:
- carrying out preparatory activities;
- the schedule is drawn up as a separate order, or can be included in the text of the order on SOUT. Another option: annex to the order;
- the schedule is developed taking into account the time reserve in order to be able to eliminate the identified violations.
Rules for drawing up a schedule
Basic rules to follow when drawing up a schedule:
- it is necessary to systematize the sequence of stages;
- it is important to indicate exact deadlines for the start and end dates of each stage;
- provide space for signatures in the schedule;
- special assessment is carried out once every five years;
- exceptions are situations in which an examination is required;
- compiled in free form;
- the content must comply with statutory guidelines;
- You can have graphics on the Internet;
- you can add information from the company’s local regulations;
- The schedule should be discussed with company employees.
Example No. 1. Below is an example of stages from the graph:
- preparation of information and documentation: 7 days;
- factor identification procedure: 15 days;
- formation of a list of factors: 3 days;
- filling out a declaration of conformity with working conditions: 2 days;
- creating a list of factors to be analyzed: 3 days;
- research, analysis of factors from the list: 17 days;
- decision on the impossibility of assessing a number of factors: 10 days;
- report: 12 days;
- employee familiarization: 20 days.
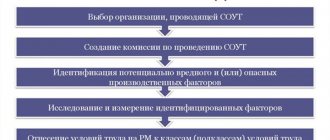
Important! When forming a commission on SOUT, its composition includes the following employees:
- certified workers with specialization in the field of labor protection from the company’s staff;
- if there is no separate unit in the staffing table, then the person who is entrusted with security functions in the company;
- from the trade union.
Information about equipment and raw materials
The next step in the experts’ work will be to establish information about the equipment and materials used in the production process.
To do this, information is requested about:
- Models of machine tools, personal computers, lifting equipment and other equipment on which work is performed.
- Information about the materials: name, what operations are performed, what are the emissions of harmful substances to one degree or another, are there any excesses in terms of harmful factors.
- The expert organization requests data from the management of the facility, studies literature in these areas, and takes measurements.
Basic operations included in the schedule
The table below provides a list and characteristics of the main operations that can be included in the schedule.
| Operation, stage | Characteristic | Who is responsible? |
| Pre-preparation stage | Formation of the commission. Schedule, cost - all these and many other points are fixed in the contract. The commission is headed by the employer (representative). A list of tasks for checking and evaluation is generated. Once such a list is ready, you can get to work. | Employer |
| Preparatory stage | · . · preparing initial information; · information on working conditions is collected; · source documents are generated | Commission |
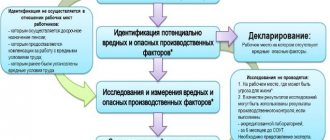
| Carrying out identification | Harmful and dangerous factors in the workplace are identified | OP SOUT |
| Formation of a list of factors | A list of negative harmful and dangerous factors is compiled that are subject to analysis, but have no basis for identification | OP SOUT |
| Declaration | A document is being prepared on the compliance of the criteria for labor activity of the workplace with state regulations and safety standards | Commission |
| List of factors in the workplace | After identification, a list of hazardous and harmful factors to be investigated at places of work is compiled | Commission |
| Research stage | Measurements, tests and studies of actual harmful production factors are carried out | OP SOUT |
| Research Based Solution | Preparation of a final decision on the possibility of using the results of monitoring working conditions | OP SOUT |
| Decision-making | A decision is made on the impossibility of conducting research and testing on certain harmful factors in a situation where such a measurement could pose a threat to the lives of experts and employees participating in the special assessment system. | Commission |
| Drawing up a report on SOUT | · information about the company conducting SOUT; · list of jobs according to SOUT; · SOUT cards; · certificates of testing and research; · acts when assessing the effectiveness of PPE used; · an act on the impossibility of assessing a number of factors due to a threat to the life of the inspectors; · summary statement of SOUT; · a list of measures that are recommended to improve working conditions in certain workplaces; · final conclusion of the SOUT expert | Commission |
| Evaluation results | Results include the following areas: · carry out control functions; · informing employees about possible risks; · planning and high-quality implementation of measures to eliminate identified deviations; · analysis and resolution of disagreements related to safe working conditions, etc. | |
| Familiarization with the results of the SOUT | Employees are familiarized with the results of the SOUTH and work safety assessment against signature at their workplaces. The employee must be given thirty days (calendar) for the familiarization process. The countdown begins from the moment of approval (signing by all members of the commission) of the report on the results of the SOUT. This period does not include the period of employment of the employee, vacation or illness, or business trip. The fact of acquaintance must be confirmed by the signature of the employee. | Employer |
| Data is posted officially | Data on SOUT should be posted: · on the Internet regarding the establishment of classes of working conditions in the workplace Basic conditions of accommodation: · term – 3 days; · the labor inspectorate is notified within 30 days; · posting data on the website in the form of scans of results. | Employer |
What legislative changes came into force on January 1, 2020
- The customer has the right to demand from the organization that conducted the special assessment confirmation that information about the conducted special assessment is posted in the Federal Information System (FSIS).
- The assessment report is signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature. It may also be sent by mail with a notification.
- The results of the special assessment can be used by the customer only after they are entered into the FSIS SOUT database. The results, which contain information containing state secrets, can be used immediately after the approval of the examination report.
- From January 1, 2020, the validity period of the SOUT declaration is counted from the moment of registration of the report in the FSIS SOUT.
- The report on the special assessment is approved within 30 days after receiving an expert opinion from the state executive body of the subject of the Federation.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
Question No. 1. What harmful factors are not included for assessment in the EAS schedule?
Answer: The following factors are not taken into account in the SOUT schedule:
- microclimate in open areas;
- daylight;
- light pulsation coefficient, brightness;
- lighting of the working surface in production premises;
- electromagnetic fields created by a PC;
- most labor intensity indicators;
- workplace injury;
- psychological and emotional stress.
Question No. 2. What are the requirements for drawing up the SOUT schedule?
Answer: They are indicated in Part 1 of Article 9 of Federal Law No. 426 of December 28, 2013. Among them:
- There is no legally approved form. You can develop it yourself in the company;
- the schedule must indicate deadlines and stages;
- the schedule can be either a separate order or an appendix to the order to carry out the Special Operations Operations;
- All members of the commission must be familiar with the schedule upon signature.
Question No. 3. What is the employer’s responsibility for violating the terms of the schedule?
Answer: In accordance with Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- warning or imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 5 to 10 tr., on individual entrepreneurs: from 5 to 10 tr., on legal entities: from 60 to 80 tr.;
- in case of repeated violation - disqualification for a period of 1 to 3 years.
Most common mistakes
Error No. 1. Often, when changing the name of an employee’s position, the corresponding amendments are not reflected in the SOUT schedule, which is an error. It is necessary to issue an order to change the name of the position, but with reference to the unchanged working conditions at this workplace. The order is agreed upon with the trade union.
Thus, every employer must remember that conducting a special assessment of working conditions in the workplace is his responsibility, enshrined at the legislative level in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This implementation is based on the main document - the SOUT schedule. For non-performance or improper performance, the employer may be held liable. Analyzing the norms of the Federal Law, we can conclude that the following actions on the part of employers are recognized as a violation of the procedure for conducting a special assessment: failure to comply with the established deadline for drawing up a schedule, an incorrectly drawn up schedule, the absence of a specially created commission, etc.