IMPORTANT!
In connection with the situation with COVID-19 and the publication of Presidential Decree No. 206 of March 25, 2020 “On declaring non-working days in the Russian Federation,” the employer is obliged to provide employees with paid days off. If it is possible to switch to remote work and the employee does not mind, then an agreement must be concluded. If there is no opportunity to work remotely, and the employer forces you to write an application for leave at his own expense, he is breaking the law, the employee has the right to complain to the State Labor Inspectorate.
Some businesses or services, such as lifeguards, operate 24 hours a day, seven days a week. This approach is objectively necessary and socially significant. For commercial enterprises, this option of using the working time of their employees is also sometimes justified. For example, the property of an enterprise requires 24-hour security.
What is a shift schedule
IMPORTANT!
If your organization is operating during the quarantine period and employees are actually present at their places, then there is no need to make changes to the schedule. If the organization is not a continuous cycle enterprise or serving the population, then employees must stay at home in accordance with the presidential decree. The period of non-working days is subject to payment. In this case, the shift schedule does not need to be changed, the work is simply not performed, and the working time sheet will have to be filled out after the fact. Until now, HR specialists have not reached a consensus on what code to put on the report card. Some put code B (day off), some put code I (appearance). According to the editors, enterprises should develop and approve a separate code for this case, for example OND, so that there is no confusion in the future.
A standard daily work schedule for the entire team is not always beneficial for both the employer and the employees themselves. To ensure continuity of the production process, optimize the use of equipment and obtain maximum production volume, shift work is required in some cases. Typically, two-, three-, or four-shift schedules are established. For each shift, strict time frames are determined.
How to calculate an employee's salary
An employee's salary can be calculated based on an hourly rate or salary. In the first case, the number of hours worked is multiplied by the rate. In the latter case, everything is somewhat more complicated:
- if the employee has worked the number of hours established by the standard, he is paid a salary;
- if you have worked more, overtime is added to your salary;
- if less hours are worked, the salary will consist of the number of hours worked multiplied by the tariff rate.
How can you find out the size of the tariff rate if the salary amount is known? There are several ways:
- The salary is divided by the average number of hours per year according to the standard. In this case, the rate will remain unchanged for 1 year.
- The salary is divided by the average number of hours in the reporting period (month, quarter). In this case, the rate will be the same for the selected period.
- The salary is divided by the average number of hours per month. With this calculation, the rate remains unchanged for a month.
The employer has the right to choose any of these methods; it is only important to enshrine this in local regulations.
When to use
Most often, shift work mode is used when equipment downtime causes serious damage to the enterprise. If the work requires attentiveness, regular rotation of groups of workers is essential. This allows us to maintain quality at a high level, reduces the risk of industrial injuries and increases production volumes.
Shift work is also common in institutions providing emergency assistance: doctors, emergency workers, gas and fire services, police officers. At the same time, it is quite common, for example, for guards to have a shift work schedule.
How does a removable one differ from a regular one?
Ordinary
The employee works within strictly designated hours: from Monday to Friday, from nine in the morning until six in the evening, with a lunch break from 13.00 to 14.00. There are no options here - every day, every month and all year the employee comes and leaves at the same time. For this category of employees, enterprises have ready-made tables for filling out work schedules within the established time frame. But such a schedule is suitable only for those employers who do not have a technological and production need to complete tasks outside the normal time frame. As a result, the organization does not need to keep total records of staff time, since the normal working week for employees will not exceed 40 hours, which complies with legal requirements.
Removable
To understand how to make a work schedule for a month in Excel (or any other program), remember our example about a metallurgical plant. The employer, due to its production and technological characteristics (continuous production or provision of services to the population), has a need to perform professional activities either around the clock or for a period of time that significantly exceeds the normal duration (a person can work 40 hours in a couple of days, not in a week) , in connection with which a shift of workers is established.
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to draw up a work schedule with summarized work time tracking. Use these instructions for free.
Number of shifts and workers in them
If we talk about the time period of one shift, then the range of options ranges from 3 to 12 hours in one day. The number of shifts is set by the management of the enterprise and is determined by the specifics of the production process and the degree of workload. The shift schedule (can be found online, for example, in our article “Working time schedule”) is applied year-round or seasonally - during periods of increased demand for certain products. Social services operate in this mode all year round.
The number of workers on each shift is not limited. When drawing up the next shift schedule for 2021, the employer is obliged to take into account the opinion of the trade union and formalize the document as an annex to the collective agreement.
The updated work schedule (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) is brought to the attention of each employee at least a month before implementation. The Labor Code categorically prohibits scheduling two or more shifts in a row for the same group of workers.
Answer:
Russian labor legislation gives the employer the right to organize shift work if necessary. The procedure for shift work is determined by Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which states that work in two, three or four shifts is introduced in cases where the duration of the production process exceeds the permissible duration of daily work, as well as for the purpose of more efficient use of equipment. In this case, a shift schedule must be established, which is brought to the attention of employees no later than a month before implementation, and working for two shifts in a row is strictly prohibited.
The duration of a shift is not regulated by the Labor Code, with the exception of certain categories of workers specified in Art. 94 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, the duration of daily work (shift) cannot exceed: for workers aged 15 to 16 years - 5 hours, for workers aged 16 to 18 years - 7 hours; for students of general education institutions, educational institutions of primary and secondary vocational education, combining study with work during the school year, from 14 to 16 years old - 2.5 hours, from 16 to 18 years old - 3.5 hours; for disabled people - in accordance with a medical report. In accordance with Art. 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the features of the working time and rest time for transport, communications and other workers with a special nature of work are determined in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation. The Government of the Russian Federation in Resolution No. 877 dated December 10, 2002 (as amended on September 4, 2012) “On the peculiarities of the working time and rest time regime for certain categories of workers with a special nature of work” established that the peculiarities of the working time and rest time regime for certain categories of workers, having a special nature of work are determined by the relevant federal executive authorities in agreement with the Ministry of Health and Social Development. RF. The regulations of the relevant executive authorities do not currently establish working hours for the category of workers specified in the question.
Thus, if the organization’s employees do not belong to categories for which the duration of daily working hours is limited by Art. 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we believe that an organization can independently determine the duration of daily work (shift), based on factors of the production and labor process, as well as labor protection requirements. In this case, the following conditions must be taken into account:
- the maximum working week cannot exceed 40 hours per week, and for workers under the age of sixteen - no more than 24 hours per week; for workers aged sixteen to eighteen years - no more than 35 hours per week; for workers who are disabled people of group I or II - no more than 35 hours a week (Articles 91, 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- impossibility of working more than one shift in a row (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- The duration of weekly continuous rest cannot be less than 42 hours (Article 110 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Examples of shift modes of operation may be as follows:
- Double shift work
There are two shifts, usually “day” and “evening”, 12 hours each.
- Three-shift work (four-team schedule)
The workers are divided into four teams, and every day three teams work, each on its own shift, and one rests. The typical shift distribution for a 4-team, 3-shift operation is as follows:
- four days on the night shift from 23:00 to 07:00, then two days off;
- four days on a day shift from 07:00 to 15:00, then one day off;
- four days on the evening shift from 15:00 to 23:00, then one day off.
In such a schedule per month, with a norm of 167 hours, the teams will actually work different times - 128, 178, 152, 184 hours, so the schedule is drawn up for an accounting period lasting several months, which makes it possible to compensate for overtime in one month with shortfalls in others and, on average, ensure compliance weekly working hours.
- Three-shift work (five-team schedule)
The workers are divided into five teams. The typical shift distribution for a 5-team, 3-shift operation is as follows:
- two days on a day shift from 08:00 to 16:00, then two days off (48 hours);
- two days in the evening shift from 16:00 to 24:00, then one day off (the so-called “transition” = 24 hours);
- two days on the night shift from 00:00 to 08:00, then three days off (one “sleep” + two days off = 72 hours).
One cycle is 10 days. Each month, the teams will work from 136 to 152 hours.
Please note that if it is impossible to maintain normal daily or weekly working hours, in accordance with Art. 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must keep a summary record of working time and ensure that its duration for the accounting period (month, quarter, etc.) does not exceed the normal number of working hours. In this case, the accounting period cannot exceed one year. The procedure for introducing summarized recording of working time is established by the internal labor regulations of the organization.
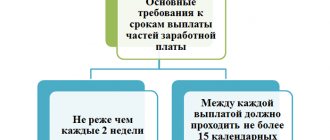
If an organization uses a shift work schedule, it should be borne in mind that if part of the employee’s time is spent at night, it must be paid additionally. Night time is considered to be from 10 pm to 6 am (Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). According to Art. 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, each hour of work at night is paid at an increased rate compared to work in normal conditions, but not lower than the amounts established by laws and other regulatory legal acts.
The specific amounts of the increase are established by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees, in accordance with the collective and/or labor agreement.
In accordance with Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, work on a non-working holiday is paid at least double the amount. This article does not establish any exceptions for employees working on a schedule.
In our opinion, the working hours, in which work can be performed by one group of workers during the day (working mode “every two days”, “three days”), is not prohibited by current legislation, but it is not a shift mode. We can talk about shift work in cases where work is performed during the day alternately by different groups of workers replacing each other, with at least two shifts per day. The specified operating mode can be classified as an operating mode with the provision of days off on a sliding schedule. At the same time, all of the above regarding the shift mode of operation can be fully attributed to this mode.
Article 97 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for cases when the employer has the right to involve an employee in work beyond the working hours established for this employee in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation and local regulations, an employment contract: for overtime work and if the employee works on irregular conditions working day.
In view of the fact that the question does not clarify what documents were used to document the overtime of the organization’s employees, it is not possible to unambiguously attribute it to one or another type of work outside of working hours.
Work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work (shift), and in the case of cumulative accounting of working hours - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period, is overtime (Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). An employer’s involvement of an employee in overtime work without his consent is permitted in the following cases:
1) when carrying out work necessary to prevent a catastrophe, industrial accident or eliminate the consequences of a catastrophe, industrial accident or natural disaster;
2) when carrying out socially necessary work to eliminate unforeseen circumstances that disrupt the normal functioning of centralized hot water supply, cold water supply and (or) sewerage systems, gas supply systems, heat supply, lighting, transport, communications;
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 7, 2011 N 417-FZ)
3) when performing work the need for which is due to the introduction of a state of emergency or martial law, as well as urgent work in emergency circumstances, that is, in the event of a disaster or threat of disaster (fires, floods, famine, earthquakes, epidemics or epizootics) and in other cases, threatening the life or normal living conditions of the entire population or part of it.
In all other cases, in order for an employer to involve an employee in overtime work, his written consent is required.
The duration of overtime work should not exceed 4 hours for each employee for two consecutive days and 120 hours per year. Overtime work in excess of the specified norm is a violation of the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
Overtime work is paid for the first two hours of work at least one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - at least twice the rate. Specific amounts of payment for overtime work may be determined by a collective agreement, local regulations or an employment contract. At the request of the employee, overtime work, instead of increased pay, can be compensated by providing additional rest time, but not less than the time worked overtime (Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an irregular working day is understood as a special work schedule, according to which individual employees may, by order of the employer, if necessary, be occasionally involved in the performance of their labor functions outside the working hours established for them. The list of positions of employees with irregular working hours is established by a collective agreement, agreements or local regulations adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
Overtime during irregular working hours is not paid. Articles 116 and 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation oblige employers to provide additional leave of at least three days in this working regime. Please note that employees working irregular hours must be paid for work on weekends and holidays according to the general rules using Articles 113 and 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, that is, either at least double the daily rate, or at single daily rate with the provision of an additional day recreation. This position is confirmed in the Letter of Rostrud of the Russian Federation dated 06/07/08 No. 1316-6-1.
Schedule generation process
The number of shifts, employees in them and the transition of employees from one shift to another are regulated by the shift schedule. When working at night, the shift is reduced by one hour. Some employees are allowed to work on night shifts only with their written consent. These categories include:
- young mothers whose children have not reached the age of three;
- disabled people or their parents (until they reach the age of majority);
- caregivers;
- single mothers or fathers and guardians of children under five years of age.
Watchmen's shift schedule, sample for 3 people
Using this sample, it is easy to draw up a shift schedule for guards (sample) for 4 people. The employer is obliged to develop work schedules for guards in such a way that the number of working hours per year does not exceed the established norm (1981 hours).
Issues that require resolution by the employer when establishing summarized recording of working time
When introducing summarized accounting, the employer must decide on the following points:
- Length of the accounting period (month, quarter, year). The employer has the right to choose any accounting period within the year. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that if there are positions where work is associated with harmful or dangerous conditions, the accounting period is selected within a quarter (3 months).
- Standard working hours (can be viewed in the production calendar).
- Development of a work schedule. When approving the document, you should pay attention to the standard working hours: if it is exceeded, then the employee is paid for these hours as overtime work. In addition, the number of workers in a shift should allow the load to be distributed evenly between them.
- The procedure for calculating wages (hourly rate or salary). If an hourly rate is selected, then its size for 1 hour is multiplied by the total number of hours of work. It should be noted that Art. 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for an additional payment of 20% for work from 22 to 6 o’clock.
Two-by-two schedule with a 12-hour workday
When drawing up such a document, it is important to ensure that in the case of a summarized accounting of the working period there are no violations and it fully satisfies the requirements of the shift schedule (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Let's give an example.
When working 12 hours a day, an employee works 30 / 2 × 12 = 180 hours in a month. Consequently, there is an overtime of 20 hours and it is necessary to comply with the number of days off during the week and month. The total number of working hours per month should not exceed 167. Another feature of the 2-by-2 work mode with a 12-hour shift is that the employee also works on official days off, i.e., on public holidays. At the same time, his work is paid according to the rules of Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Results
The working time schedule contains information about the standard working hours, the number of days off and working days, the boundaries and duration of the working day, as well as the combination of working periods with rest periods.
The work schedule in 2021 is largely similar to similar schedules in previous years. As in 2021, the current year is characterized by a standard set of weekends/holidays (118 days), but there are 1 more working and calendar days (248 and 366, respectively).
Sources: Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Basic rules for daily work according to the Labor Code
Most often, the daily work mode is used, which means that work shifts are scheduled at intervals of two or three days. Then there is a violation of the provisions enshrined in legal acts on the length of the working week.
This period should not exceed forty hours per week. For this reason, when a company uses 24-hour work, a requirement is established to use a summarized procedure for recording hours worked. These provisions are spelled out in the provisions of Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
This rule provides that if it is impossible to comply with the reflected working time standards for a specific period, the company management is charged with monitoring the hours worked by a specific person. As a result, the resulting value cannot be greater than the value enshrined in legislative acts.
Sleeping at work
In Russian labor legislation there is no such thing as “sleep time”, and there are no clear requirements for rest rooms.
The duration of the work break and the possibility of sleeping at the workplace are determined only by internal regulations.
The employer equips rest areas based on the capabilities of the enterprise. Some employees prefer to doze right “at the machine,” and there are no prohibitions in this regard in the Labor Code. However, if the employer considers this unacceptable, he must introduce the corresponding clause into the labor regulations, a list of which everyone should be familiar with at the hiring stage.
Payment for night hours
When a person’s work schedule is established every other day, this indicates that part of such a shift falls at night. It may also be that a citizen works at night on holidays or non-working days. Then you need to understand how payment for such days is made.
It is established by law that when performing work duties at night, payment is made in an increased amount. This rule is spelled out in the provisions of Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The minimum amount of increase in this situation has been established. It is 1/5 of what you earn on a normal day.
In an individual case, provisions for increased pay at night should be reflected in the collective agreement. Also, this information can be included in local standards, which are adopted taking into account the opinion of the organization’s trade union.
To understand the amount of payment, you need to give a specific example. Citizen Petrov works on a 24/7 basis. At the same time, his salary is 35 thousand rubles. There are 2 rest periods during the work shift, each equal to an hour. The surcharge is 25%.
The standards for hours worked are based on the fact that the work week is 40 hours. It is necessary to calculate the level of earnings for September, provided that this month Petrov worked all the shifts noted in the schedule. It turns out that in September the citizen worked 7 shifts of 22 hours and another 14 hours, for a total of 168. Of these, 58 were night hours. The calculation is based on the following indicators:
- hourly rate is 208.3 rubles
- surcharge for night work: 208.3 *25%*58= 3020.8 rubles
Based on the total for September, Petrov will receive 35,000 + 3020.8 = 38020.8 rubles.
Work during non-working hours or holidays is paid using a double tariff.
If a citizen has overtime work during the month worked, then payment is made at an increased rate. At the same time, the legislator sets the minimum amount of payment. The first couple of hours you need to pay 1.5 times the amount. The rest of the time is paid at double rates.
Kinds
There are three types of work schedules: shift, rotating, weekly. All schedules have both advantages and disadvantages, but their type is necessary to meet the specifics of the work of a particular institution.
The shift schedule is used mainly by organizations with a 24-hour work system. In addition, in those organizations (the majority of them), the schedule assumes that employees work in succession. Sometimes charts calculate the period of joint work of two or more specialties at one workplace; this is mainly found in education, culture and healthcare. Shift work allows for non-stop production. The definition of the shift work schedule is given in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 103.
The law identifies 2 cases of using a shift schedule:
- Non-stop (continuity) of the production process. The working hours exceed the daily production norm - 7.2 hours (women), 8 hours - men.
- Efficiency of the equipment used (stopping the operation of units, or constant switching on/off leads to production losses).
Shift work schedules are compiled according to the forms offered by the electronic version of the program. Shifts, their number, time period are determined, and then the data is entered into the program. Most often, the shift schedule is made for a month in order to change employees in shifts within a month (1,2, night). If shifts are arranged correctly, there will be no overtime for one employee and shortcomings for another.
Shift work schedules can be changed or left unchanged. It all depends on the capabilities and characteristics of production.
A sliding work schedule is used in institutions where the traveling nature of work (business trips) is used: employees of railway institutions. In their schedules, the start time of the working day (train crews) and the end of the work shift (freight transportation), for road transport (long-distance trips) and other similar services are unknown. The personnel officer records upon receipt of information that the employee has begun his duties and their completion. From the fact of finishing work, the calculation of time for rest begins, then the start time of work (trip, departure on a flight) is determined again, i.e. Truly, the schedule slides according to the calendar and is individual for each individual employee. The electronic version of the sliding schedule allows you to track the hours worked by each member of the work unit. The weekends here are also sliding, only approximate dates are set, and the fact is revealed during the labor process.
The weekly schedule is used when employees work out the standard hours without being directly at their workplace every day, but only in the sum of the numerical values of the time worked for the week. The departure to work is selected by a specialist and agreed with the head of the department, workshop, etc. individually. This mode is also called flexible working mode. It is considered the most common abroad. There are many benefits to the weekly regimen: increased work efficiency, a decrease in the level of disciplinary violations, and improved psychological health of employees.
Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also defines the weekly operating hours. The weekly schedule is used in the following cases:
- Working outside the office (working place at home, coming to the organization to receive a task or to coordinate assignments, handing over completed work), so-called homeworkers.
- Real estate companies where employees are forced to work according to a schedule that is set not by the employer, but by the client. These are, for example, real estate specialists: agents, managers, couriers.
- Accountant. Nowadays it is becoming fashionable to hire one accountant. Small companies, private entrepreneurs, and individual entrepreneurs prefer not to maintain an accounting staff, but to carry out accounting through a separately hired specialist. In this case, the accountant processes documents at home, or in some room, but outside of production. It makes no sense to set him any kind of work schedule other than a weekly one, since he can complete the entire amount of work at a time convenient for him.
The wages of these employees do not depend on the time worked, so the employees themselves control its implementation. The norm for them corresponds to the norm of ordinary workers, but the regime is different. It is difficult to record the work time of a given employee in a specific schedule, so the form is filled out, indicating the approximate standard of hours, rather than tracking the actual value.
The schedule must include time to restore physical strength. Rest time usually divides the working day into two parts of approximately equal time. Most often, this is one lunch break. The actual length of time used for rest and food is not included in working time. According to Art. 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, breaks provided to an employee during a working day (shift) can be no more than 2 hours and less than 30 minutes. There are organizations where they choose short technological breaks, they last no more than 15 minutes. If you have been tasked with drawing up a work schedule, then you must first decide on the type of schedule that is most appropriate for your organization (enterprise).
Tabular work schedule
If you need to change your schedule
There are different situations in which it becomes necessary to change the work schedule or shift conditions.
For example, in case of employee illness, unplanned leave, and so on. Changes are made in the same order as the work schedule itself. Such changes must be personally familiarized to each employee against signature.
Example of a shift schedule.
Then the employer will have written proof of several facts:
- That employees received notification of changes to the routine.
- Employees' agreement with the new regime.
- No unauthorized changes on the part of employees.
How to do accounting if you are an individual entrepreneur? The answer is contained here.
If this procedure is not properly executed, many serious problems arise:
- Employees begin to change shifts.
- The time sheet is compiled only on the basis of actual data, which is why errors occur.
- Management does not understand who is actually on site during a work shift.