What are settlement documents
Payment documents are written requests or instructions from organizations to transfer funds by bank transfer for goods sold, work performed and services rendered.
The implementation of non-cash payments in the currency of the Russian Federation on the territory of the Russian Federation is regulated by the Regulations on the rules for the transfer of funds, approved by the Bank of Russia on June 19, 2012 No. 383-P (hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 383-P).
According to clause 1.12 of Regulation No. 383-P, settlement (payment) documents are:
- money orders;
- collection orders;
- payment requirements;
- payment orders;
- bank orders.
In this case, the transfer of funds using a bank order is carried out by the Bank of Russia, a credit organization (hereinafter referred to as the bank), taking into account the features provided for by the Bank of Russia Directive No. 2945-U dated December 24, 2012 “On the procedure for drawing up and applying a bank order” (clause 1.27 of Regulation No. 383-P).
- Payment order - the main document for non-cash payments, is an order from the payer to the bank to transfer (transfer) a certain amount from his account to the recipient's account. When funds are simultaneously transferred from one payer's account to the accounts of several recipients serviced by one bank, consolidated orders are drawn up.
- Payment request-order – a request from the recipient of funds to the payer to pay a certain amount through the bank. It is presented by the recipient of funds to the bank maintaining the payer’s account and is used by it after the payer’s acceptance as a payment order.
- Application for opening a letter of credit - an order from the payer in the letter of credit form of payment to deposit the amount of the letter of credit from his account to a separate account in the seller’s bank to pay for goods shipped against the letter of credit.
Unique payment identifier, Sberbank UIN, unique payment identifier code
To obtain a unique payment identifier in Sberbank, just use the capabilities of an ATM or telephone. In the first case, just go to the menu where Internet services are located. The ID and password for it can be obtained in printed form on the receipt. Before the operation, you need to insert your card into the ATM and enter your PIN code.
An alternative way is to call the bank's support service. There is a third option - use the capabilities of the Mobile Bank service. To do this, just send the code word “password” to the short number 900. The password will arrive in a few seconds, but you can use it only once.
Unique identifier of an accrual or payment
A unique accrual identifier has been used in payment orders for transferring amounts in favor of the Russian budget since 02/04/2014. The norm is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 107, which was issued on November 12, 2013. The UIN consists of 20 digits, with the symbols “///” at the end of the combination. The “Code” field is used for the identifier in the payment order. The rule applies to all payments in favor of the Russian budget. Unique payment identifier in the payment order.
A unique payment identifier is indicated in each payment order, which is generated when paying mandatory fees, taxes and other similar payments. State and municipal services are also paid for using the UIN. Almost all banks are required to indicate a payment ID for certain types of transfers. It is noteworthy that there are situations in which it is not necessary to indicate the UIN and in order to correctly transfer payments you should understand these subtleties.
Unique payment identifier code
The unique payment identifier code is issued by tax authorities at the place of registration. For this reason, you can only clarify the required combination of numbers at the territorial tax office of your locality. There are payers who do not have a UIN as such, and the state tax structure, for objective reasons, cannot generate and issue a number. In such cases, “0///” is indicated in the “Code” field. The issued UIN is necessarily separated from the identifying information by the symbols “///”.
Regulatory framework for primary documents
To reflect any business transaction in accounting, it is necessary to have a correctly executed primary document, as stated in paragraph 1 of Art. 9 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. Next we read in paragraph 4 of Art. 9 of this law, that the forms of primary documents must be developed and approved by the organization. Thus, the use of unified forms of primary documents is optional, with the exception of certain cases. The only obligatory condition is the presence of certain details in the document. On the other hand, there is no ban on the use of unified forms of documents, so the head of the organization must independently determine which forms of primary documents should be used
Regulatory regulation
Upon receipt of an advance payment from the buyer for upcoming shipments, the Organization must issue an advance invoice within 5 days (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), counted from the date of the bank statement or the date of the cash receipt order.
When selling goods for cash in the field of retail trade and public catering, as well as when performing work and providing services to the population, an invoice is not issued (Clause 7, Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An advance invoice is not issued if an advance payment is received against delivery:
- goods, the production of which takes more than 6 months (clause 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- taxable at a rate of 0% (clause 1 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- not subject to VAT or exempt from taxation (Articles 146, 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- An organization exempt from paying VAT (Articles 145, 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The rules for filling out an invoice are established in clause 5.1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Section II of Appendix 1 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137.
Important points to pay attention to:
- in page 5 “For payment and settlement document No.__from__” you must indicate the number and date of: payment and settlement document - for non-cash payments;
- cash receipt order—for cash payment. For a non-cash form of payment, a dash is placed in this line (clause 3 of clause 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137).
- in gr. 1 “Name of goods (description of work performed, services provided), property rights” indicates the name of the supplied goods, works, services provided for in the contract with the buyer.
Instead of specific names in gr. 1, you can indicate a general name (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 6, 2009 N 03-07-15/39).
- in gr. 7 “Tax rate” indicate the estimated VAT rate. For example, 18/118 (clause 4 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Is it possible not to issue advance invoices if less than 5 days have passed between the advance payment and shipment?
Strictly speaking, there are no rules in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation that would exempt the seller from drawing up an advance invoice. This means that in order to avoid claims from tax authorities, an advance document must be drawn up, even if the shipment occurred within 5 days (Letters of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 03/10/2011 N KE-4-3/3790, dated 02/15/2011 N KE- 3-3/354).
On the other hand, the completely opposite position of the Ministry of Finance is known: if payment and sales were made in the same quarter, an advance invoice may not be issued. The main condition is that no more than 5 days have passed between these two events (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 10/12/2011 N 03-07-14/99 and dated 03/06/2009 N 03-07-15/39). However, given that the letters from the Ministry of Finance are still advisory in nature, there is a risk of additional VAT charges if advance invoices are not drawn up.
Arbitration practice in favor of taxpayers:
- The Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District, in Resolution No. KA-A41/3467-08 dated May 5, 2008, concluded that an advance payment for goods is considered such until the actual sale occurs.
- The Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District, in Resolution dated February 13, 2006 N F04-233/2006 (19490-A03-31), established that a payment received from a buyer in the same tax period with shipment cannot be considered an advance payment.
- Resolution of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated March 10, 2009 N 10022/08 states that if prepayment and shipment are made in the same quarter, the payment cannot be considered an advance payment, and an invoice does not need to be issued.
Considering that the legislation, controllers and judges do not have a single position regulating this issue, we believe that the risk of additional VAT assessment cannot be excluded. In addition, failure to issue invoices can be regarded as a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income, expenses and taxable items (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Liability - fine 10,000-30,000 rubles. depending on whether a violation was committed in one or more tax periods. And these violations are identified, taking into account the electronic procedure for submitting reports and VAT registers, very simply.
In the 1C program you can choose different options for issuing advance invoices
Is a prefix (such as the letter "A") required on the advance invoice number?
The rules and procedure for filling out documents for calculating VAT are enshrined in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137. They do not provide for any special designations for advance invoice numbers. This is also confirmed by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (Letter dated October 16, 2012 N 03-07-11/427), in which it draws attention to the fact that all invoices must be numbered in a single chronological order.
At the same time, we believe that tax authorities will not be able to deny you a deduction due to the addition of a letter prefix to the invoice number, since this does not interfere with the identification of the data necessary for the correct calculation of VAT.
In the 1C program you can select different options for numbering advance invoices
Is it acceptable to indicate in gr. 1 invoice wording Advance payment ?
According to clause 2 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. By Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137, in gr. 1 of this document, upon receipt of partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights, the name of the goods supplied (description of work, services), property rights for which the advance payment is transferred is indicated.
At the same time, the law does not prohibit indicating in gr. 1 invoice additional information in addition to what is required. This means that if in gr. 1 write Advance payment for... and then provide the name of the product, description of the work or service (or their general name), then this cannot become a basis for refusing to accept a VAT deduction. The main thing is that the invoice does not prevent tax authorities from identifying the information necessary for calculating VAT (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 10, 2011 N 03-07-09/10).
A completely different situation is the indication in gr. 1 wording Advance payment without specifying the names of goods (or their general name), which is not provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. The risk that tax authorities will not accept VAT deductions on such invoices is very high.
What documents does the individual entrepreneur work with?
There are many primary accounting documents. But at first, in order to correctly formalize the purchase and sale of goods, the provision of services or the performance of work, you can get by with only a few of them. In some cases, invoices will also be needed.
- Agreement. Any transaction begins with the conclusion of an agreement. It defines the basic terms of cooperation: what the entrepreneur and the client do, for what price and in what time frame. If the client is a regular one, then you can draw up one agreement for several transactions.
- An invoice for payment. In this document, the entrepreneur indicates the amount to be paid, a list of goods sold or services provided, as well as his bank details.
- Payment documents: cash receipt or sales receipt . These documents confirm payment. Give them to the client who pays in cash or by card. If payment is made via bank transfer, it is confirmed by a payment order.
- Bill of lading is a document that the supplier issues to the buyer when shipping goods.
- An act of provision of services or work performed. This document is signed by the customer and the contractor based on the results of the provision of services or performance of work.
- Invoice. Usually it is made up of organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the general taxation system, because they pay VAT. In rare cases, invoices are issued by entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax or patent.
Exchange with client bank, numbering
IGood afternoon, I have a question about numbering in the client bank. The organization works with several banks, so each bank has its own numbering in the client bank. Perhaps I’m taking a workaround and there is a simpler solution. The first decision was made by an external client bank, which in 1C uploads numbers with its own prefix for each bank. But the problem remains, the task is to be able to create payments in both KLB and 1C, while the possibility arises that two different payments with the same numbers can be created, one in 1C and the other in the client bank. The numbering must be respected.
Get your work in order using the 1C configuration “IT Department Management 8”
ATTENTION!
Agreement
The contract describes the rights and obligations of the parties to the transaction. Typically it contains the following sections:
- Subject of the contract: what will happen as a result of the transaction (for example, sale of goods, provision of services, performance of work);
- Contract amount and payment procedure: when and how much to pay.
- Rights and obligations of the parties: what actions the parties to the contract can (or should) take.
- Responsibility of the parties: what will happen if the individual entrepreneur or the client violates the terms or other terms of the contract.
- The procedure for changing and terminating a contract: how to terminate a contract or accept additional agreements to it.
- Details of the parties: current accounts, INN, OGRN and addresses of the entrepreneur and his counterparty are indicated.
The agreement is usually drawn up in two copies and signed by each party.
If you use a standard contract form to work with clients, replacing the necessary details in Word or Excel, use the templates from Kontur.Elbe. Upload your agreement template, and the program will automatically fill in the details of the counterparty from the directory.
For some transactions, a written contract is not necessary at all. For example, a retail sales contract is considered concluded from the moment the buyer is issued a cash receipt, sales receipt or other document that confirms the fact of payment.
Payment order
When filling out a payment order, it is important to correctly indicate the order of payment. If it is entered incorrectly, the bank will refuse to carry out the transaction.
- Payments that occur under executive acts on compensation for harm caused to health or life and payment of alimony.
- Transfers in accordance with writs of execution for the payment of severance pay upon dismissal or salary arrears and payment of royalties.
- Payment of debts on taxes, fees and contributions and payment of salaries to employees.
- Cash payments for other executive acts.
- All other payment documents in the calendar order of their receipt.
The Constitutional Court of Russia invalidated the distribution of the 3rd and 4th stages, however, changes have not yet been made to the Civil Code. All acts or their individual provisions recognized as unconstitutional shall lose force. The court classified all payments to the budget and state extra-budgetary funds as the third priority. It turns out that the fourth stage includes only payments to non-state extra-budgetary funds. Debiting funds from the account for claims that relate to one queue occurs in the order in which documents are received.
An invoice for payment
In fact, an invoice for payment is not a strictly mandatory document, but it is often used for convenience in work. The invoice indicates the quantity and cost of the goods, as well as details for transferring payment. You can develop your own invoice form for payment. But it’s easier to use a ready-made template in “Kontur.Elbe” - select the counterparty, indicate the goods or services, their quantity, price and the document is ready.
What applies to payment documents
Payment documents confirm payment for goods, work or services. In particular, such documents are cash and sales receipts, payment orders, strict reporting form (SRF).
If the buyer paid with cash, a bank card or electronic means of payment, you must give him a cash receipt, sales receipt or strict reporting form. Which of these documents should you choose? It depends on what type of activity you have and what tax system you use.
If you receive payment through a bank by bank transfer, you do not need to issue a payment document. The client retains the payment order. With this document he will be able to confirm that he transferred the funds using your details.
A sales receipt is issued at the buyer's request. The form of the sales receipt has not been established, so you can develop your own form. It must contain the following mandatory details: name, number and date of the document, full name and TIN of the entrepreneur, designation of goods or services, payment amount, signature with transcript.
Entrepreneurs who provide services to individuals have the right to issue strict reporting forms. BSO can replace a cash receipt, but only until July 1, 2021, and if an individual entrepreneur on UTII or PSN works in the catering industry and has hired employees - until July 1, 2018. Forms must be printed at a printing house or through a special service. It is not possible to print the BSO on a regular printer.
Unique payment number SUIP Sberbank: what is it
It is difficult for an uninitiated client of Sberbank to understand the concept of SUIP. What is this in a payment order? What is this additional number for? In simple terms, this is the identifier of each specific payment document in electronic form. The letter "U" stands for unique. When performing any payment action, you receive a receipt in which a set of numbers and letters is added to other data, which is the identifier of your payment.
Why did SUIP appear?
In March 2014, any payment order began to receive its own identifier.
UIN is used when it comes to payments to the budget of the Russian Federation. UIP is an identifier for other payments. Both UIN and UIP consist of 20 digits.
Unique payment identifier (field 22)
Based on the above, you can understand what SUIP is in a Sberbank check. The letter "C" stands for the name of the bank. This way, Sberbank will be able to identify any payment made in its electronic system.
The Sberbank identifier consists of 16 characters. Of these, the first 12 are a combination of digital characters, the next 4 are capital letters of the English alphabet.
It is important to know how to check the unique payment number of Sberbank SUIP. It is indicated on each electronic receipt. Approximately in the middle of the receipt, along with the amount and information about the payer’s wallet. SUIP Sberbank is a number related to the electronic payment system.
Why do you need a unique number?
Every day, millions of people make electronic payments through Sberbank. What to do if the system fails and the payment does not go through? The money could have gone to the wrong place and due to an error in the details, perhaps the account to which it was sent no longer exists.
It is important to get not only an answer to the question “Unique payment number SUIP Sberbank - what is it?”, but also to understand that by saving the receipt or rewriting this number, you can find your money wherever it goes or make sure it goes as intended.
The need for a unique electronic number arose due to the large flow of funds and the need to track them. By saving the receipt, you will be able to find your payment if you contact any Sberbank office or the company where you made the transfer. This may apply to utilities, social networks, online stores, and any other payment. SUIP makes it possible to systematize cash flow and select what you need from it.
Packing list
This document formalizes the sale of goods to another entrepreneur or organization. This document is not used to work with individuals. The invoice is issued in two copies: the first remains with the supplier and records the shipment of goods, and the second is transferred to the buyer and is needed by him to accept the goods.
Usually the invoice is drawn up according to the standard form No. TORG-12. You can use the invoice template.
In Kontur.Elbe you can create an invoice based on an invoice.
Create an invoice for free in Kontur.Elbe
Results
The payment order number is not only mandatory, but also useful information. Information about it is reflected in many important documents (invoices for advance payments and shipments, books of purchases and sales, acts of reconciliation of mutual settlements).
To ensure that the payment document number does not cause much trouble for the payer and the recipient of the money, it is necessary to follow the basic rules for its formation, which include the presence of no more than 6 characters in its composition and the inadmissibility of indicating the combination 000 in the last 3 digits.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus . Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Certificate of provision of services or work performed
This document confirms that the services have been provided or the work has been completed, and the customer has no complaints about their quality. The act is signed by both the contractor and the customer.
In “Kontur.Elbe” the act is drawn up very simply. It is enough to select a counterparty, indicate the service and price. Then you need to send the counterparty a completed document containing your signature and seal.
Invoice
This document is required to be issued by value added tax payers. That is, mainly those who work on the general taxation system. An invoice is the basis for deducting VAT. Entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax and patent usually do not pay VAT, and therefore are generally not required to issue invoices.
The invoice is issued in two copies and signed by the supplier of the product or service. One copy is given to the buyer, the other remains with the seller. The invoice must be issued no later than 5 days after the goods are shipped or the service is provided.
Types of payment orders
The payment order can be urgent or early. Urgent payment orders can be used in cases where:
- prepayment (advance payment) is made;
- payment is made after the goods have been shipped;
- Partial payments are made for large transactions.
Early payments are deferred payments and are used only by agreement of the parties involved in the contract, for example, during a sale and purchase, and if it does not incur monetary losses to the parties to the transaction.
Key document details
Despite the differences between the types of settlement documents, depending on the specifics of the form and procedure for making payments, such documents must contain the following details:
- name of the settlement document and form code;
- number of the payment document, day, month and year of its issue;
- payment type;
- name of the payer, his account number, taxpayer identification number (TIN);
- name and location of the payer's bank, its bank identification code, correspondent account or sub-account number;
- name of the recipient of funds, his account number, TIN;
- name and location of the recipient's bank, its code, correspondent account or sub-account number;
- purpose of payment. The tax to be paid is highlighted in the payment document as a separate line (otherwise there must be an indication that the tax is not paid);
- payment amount indicated in words and numbers;
- order of payment;
- type of transaction in accordance with accounting rules;
- signatures of authorized persons and seal impression (in certain cases).
A payment order (electronically or on paper) is drawn up by the bank for the purpose of partial execution of orders for the transfer of funds in cases provided for by law or agreement (clause 4.4 of Regulations N 383-P).
Payment orders, collection orders, payment requests are drawn up by payers, collectors, recipients of funds in electronic form or on paper, as follows from paragraphs 5.4, 7.3, 9.5 of Regulation N 383-P. Let us remind you that payers and recipients of funds are legal entities, individual entrepreneurs, individuals engaged in private practice in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, individuals, and banks. Collectors of funds may be recipients of funds. According to the orders of the recoverers of funds, including enforcement authorities, tax authorities, the recipient of funds may also be the body to which, in accordance with federal law, the collected funds are transferred. The recoverer of funds, in the order sent with the enforcement document on collection, indicates as the recipient of the funds himself or the body to which, in accordance with federal law, the collected funds are transferred. This is indicated by paragraph 1.2 of Regulations N 383-P.
The list and description of the details of orders: payment order, collection order, payment request, payment order are given in Appendices 1 and 8 to Regulation N 383-P. The forms of payment order, collection order, payment request, payment order on paper are given in Appendices 2, 4, 6 and 9 to Regulation N 383-P. The details of the payment order, collection order, payment request, payment order are given in Appendices 3, 5, 7 and 10 to Regulation N 383-P.
The maximum number of characters in the details of a payment order, collection order, payment request, payment order drawn up electronically is established by Appendix 11 to Regulation N 383-P. Please note that the forms of payment order, collection order, payment request, payment order on paper must not exceed an A4 sheet, as established by clause 1.13 of Regulation N 383-P. The number of copies of these orders on paper is established by the bank. You should also pay attention to the fact that the payment order is valid for submission to the bank within 10 calendar days from the day following the day of its preparation (clause 5.5 of Regulation N 383-P). A collection order or payment request submitted through the recipient's bank is valid for submission to the recipient's bank within 10 calendar days from the day following the day of their preparation. This is stated in paragraphs 7.7, 9.6 of Regulations N 383-P.
When accepting orders for execution, the bank, in accordance with clause 2.1 of Regulation N 383-P, must carry out a number of procedures (hereinafter referred to as the procedures for accepting orders for execution), which include:
- certification of the right to dispose of funds.
Let us note that the certification of the right to dispose of funds when accepting an order in electronic form for execution is carried out by the bank by checking an electronic signature, an analogue of a handwritten signature and (or) codes, passwords, and other means to confirm that the order is electronically signed and (or) certified in accordance with clause 1.24 of Regulations N 383-P (clause 2.3 of Regulations N 383-P).
Certification of the right to dispose of funds when accepting an order on paper for execution (with the exception of an order from an individual to transfer funds without opening a bank account on paper) is carried out by the bank by checking the presence and compliance of a handwritten signature (signatures) and a seal imprint (if availability) samples declared to the bank in the card with samples of signatures and seal impressions (hereinafter referred to as the card).
When accepting for execution an order from an individual to transfer funds without opening a bank account on paper, the credit institution checks for the presence of a handwritten signature. Certification of the right to use an electronic means of payment is carried out by a credit institution by checking the number, code and (or) other identifier of the electronic means of payment;
- control of the integrity of orders.
By virtue of clause 2.4 of Regulation N 383-P, control of the integrity of the order in electronic form is carried out by the bank by checking the immutability of the order details. Control of the integrity of the order on paper is carried out by the bank by checking the absence of changes (corrections) made to the order;
- structural control of orders.
Structural control of orders in electronic form in accordance with clause 2.6 of Regulation N 383-P is carried out by the bank by checking the established details and the maximum number of characters in the order details. Structural control of orders on paper is carried out by the bank by checking the compliance of the order with the established form.
When accepting an order on paper for execution using coding technologies (digital, bar), the location of the codes is checked in a place free from specifying details;
- control of order details values.
Based on clause 2.7 of Regulation N 383-P, control of the values of order details is carried out through verification in the manner established by the bank, taking into account the requirements of the law, the values of order details, their admissibility and compliance;
- control of cash sufficiency.
Control of the sufficiency of funds in the payer’s bank account is carried out by the payer’s bank when accepting for execution each order multiple times or once in the manner established by the bank (clause 2.10 of Regulation No. 383-P).
The sufficiency of funds in the payer’s bank account is determined based on the balance of funds in the payer’s bank account at the beginning of the day, and taking into account:
- amounts of funds debited from the payer’s bank account and credited to the payer’s bank account before determining the sufficiency of funds in the payer’s bank account;
- amounts of cash issued from the payer's bank account and credited to the payer's bank account before determining the sufficiency of funds in the payer's bank account.
In cases provided for by law or agreement, the sufficiency of funds in the payer’s bank account is determined taking into account:
- amounts of funds subject to debiting from the payer’s bank account and (or) crediting to the payer’s bank account on the basis of orders accepted for execution and not executed until the sufficiency of funds in the payer’s bank account is determined;
- amounts of credit provided by the payer's bank in accordance with the agreement in the event of insufficient funds in the payer's bank account (overdraft);
- other amounts of money in accordance with federal law or agreement.
If there are sufficient funds in the payer's bank account, orders are subject to execution in the sequence in which orders are received by the bank, unless legislation or an agreement provides for a change in this sequence. When operations on the payer's bank account are suspended in accordance with federal law, the specified orders are placed in a queue of orders awaiting permission to carry out operations.
If there are insufficient funds in the bank account of the payer - a legal entity, an individual entrepreneur, an individual engaged in private practice in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, a credit organization, after monitoring the sufficiency of funds in the bank account (repeatedly or once), the orders are not accepted by the bank for execution and are returned (cancelled) to the senders of orders no later than the business day following the day the order was received or the day the payer’s acceptance was received, with the exception of:
- orders of the fourth and previous priority for debiting funds from a bank account established by federal law;
- orders of collectors of funds of the fifth priority to write off funds from a bank account established by federal law;
- orders accepted by the bank for execution or presented by the bank in accordance with the law or agreement.
For reference. The order of debiting funds from bank accounts is established by Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, according to which, if there is insufficient money in a bank client’s account, funds are debited in the following order:
- first of all, according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds from the account to satisfy claims for compensation for harm caused to life or health, as well as claims for the collection of alimony;
- secondly, according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements for the payment of severance pay and wages with persons working or who worked under an employment agreement (contract), for the payment of remuneration to the authors of the results of intellectual activity;
- thirdly, according to payment documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements of wages with persons working under an employment agreement (contract), instructions from tax authorities to write off and transfer debts for the payment of taxes and fees to the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation, and also instructions from the bodies monitoring the payment of insurance premiums to write off and transfer the amounts of insurance contributions to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds;
- fourthly, according to executive documents providing for the satisfaction of other monetary claims;
- fifthly according to other payment documents in calendar order.
The specified orders accepted for execution are placed by the bank in the queue of orders not executed on time for further monitoring of the sufficiency of funds in the payer’s bank account and execution of orders on time and in the order of priority for debiting funds from the bank account, which are established by federal law.
When placing an order in the queue of orders not executed on time, the bank sends a notification to the sender of the order in electronic form or on paper in the form established by the bank, or returns a copy of the order on paper no later than the business day following the day the order was placed in the queue not orders executed on time. In an order placed in the queue of orders not executed on time, the bank indicates the date the order was placed in the queue. When placing the order of the recipient of funds, presented to the payer's bank through the recipient's bank, in the queue of orders not executed on time, the specified notification is sent by the payer's bank to the recipient's bank for transfer to the recipient of the funds.
When operations on the payer's bank account are suspended in accordance with federal law, orders that are in the queue of unfulfilled orders subject to suspension are placed in the queue of orders awaiting permission to carry out transactions. When the suspension of transactions on the payer's bank account is canceled, the specified orders are subject to execution if there are sufficient funds in the payer's bank account or are placed in the queue of orders not executed on time if there are insufficient funds in the payer's bank account in the sequence of placing orders in the queue before the suspension of transactions on the payer's bank account .
If there are insufficient funds in the bank account of the payer - an individual, the orders, unless otherwise provided by law or the agreement, are not accepted by the bank for execution and are returned (cancelled) no later than the business day following the day the order was received. The queue of orders not executed on time for the bank accounts of payers - individuals is not maintained. The sufficiency of funds for orders accepted for execution for the purpose of transferring funds without opening a bank account is determined by the credit institution based on the amount of funds provided by the client.
In addition to the above actions, the payer's bank, upon receipt of an order from the recipient of funds requiring the payer's acceptance, must monitor the presence of a pre-given payer's acceptance in accordance with subclause 2.9.1 of clause 2.9 of Regulation N 383-P or, in the absence of a pre-given payer's acceptance, obtain the payer's acceptance in in accordance with subclause 2.9.2 of clause 2.9 of Regulations N 383-P.
Based on clause 2.13 of Regulation N 383-P, in the order received, the payer’s bank must indicate the date of receipt of this order. In the order received from the recipient of funds, the recipient's bank must indicate the date of receipt of the order by the recipient's bank.
If the results of the procedures for accepting an order for execution in electronic form are positive, the bank must accept the order for execution and send the sender an electronic notification about acceptance of the order for execution, indicating information that allows the sender to identify the order and the date of its acceptance for execution. If an order is placed in the queue of orders not executed on time, the bank must indicate the date the order was placed in the queue in the order and in the notification in electronic form. Please note that the notification in electronic form must be sent in the manner established by the bank no later than the business day following the day the order was received by the bank.
If the results of the procedures for accepting an order for execution in electronic form are negative, the bank must send the sender of the order a notice in electronic form about the cancellation of the order, indicating information that allows the sender to identify the order being cancelled, the date of its cancellation, as well as the reason for cancellation, which can be indicated in the form of a code, established by the bank and brought to the attention of the sender of the order. In this case, the specified notification must be sent in the manner established by the bank no later than the business day following the day the order was received by the bank.
If the results of the procedures for accepting for execution a paper order submitted for the purpose of transferring funds to a bank account are positive, the bank must:
- accept the order for execution;
- confirm its acceptance by affixing the date of acceptance of the order for execution, the date of placing the order in the queue of orders not executed on time (if placed in the queue), the stamp and signature of the bank’s authorized person;
- return a copy of the order to the sender in the manner established by the bank no later than the business day following the day the order was received by the bank.
If the results of the procedures for accepting for execution a paper order submitted for the purpose of transferring funds through a bank account are negative, the bank must return it to the sender in the manner established by it no later than the business day following the day the order was received by the bank. In this case, in the returned order, the bank must include the date of return, a note about the reason for the return, a stamp and the signature of an authorized person of the bank. Please note that a note about the reason for the return, a stamp and the signature of an authorized person of the bank can be placed both on the front side of the order in a place free from indicating the values of the details, and on the back side of the order, as indicated by the Bank of Russia in the Information “Answers to questions on application of Bank of Russia Regulation No. 383-P dated June 19, 2012 “On the rules for transferring funds.”
If the results of the procedures for accepting for execution an order on paper, submitted for the purpose of transferring funds without opening a bank account, are positive, the credit institution must accept the order for execution and immediately after completing the procedures for accepting the order for execution, provide the sender of the order with a copy of the order on paper or a document credit institution on paper, confirming acceptance of the order for execution, with the date of acceptance and marks of the bank, including the signature of the bank’s authorized person.
If the results of the procedures for accepting for execution an order on paper, submitted for the purpose of transferring funds without opening a bank account, are negative, the credit institution must immediately, after completing the procedures for accepting the order for execution, return it to the sender of the order. Please note that the bank can once confirm the positive result of completing all or several procedures for accepting orders for execution.
An order is considered accepted by the bank for execution if there is a positive result of completing the procedures for acceptance for execution provided for the corresponding type of order, including when placing the order in the queue of orders not executed on time.
It should be said that payers, as well as recoverers of funds, have the right to withdraw submitted orders. According to clause 2.14 of Regulation No. 383-P, the withdrawal of an order is carried out before the irrevocability of the funds transfer occurs. Revocation of an order submitted for the purpose of transferring funds to a bank account is carried out on the basis of a revocation application in electronic form or on paper submitted by the sender of the order to the bank. Drawing up an application for revocation and the procedure for accepting it for execution are carried out by the bank in a manner similar to the procedure provided for the application for acceptance (refusal of acceptance) of the payer in subclause 2.9.2 of clause 2.9 of Regulation N 383-P. The bank, no later than the business day following the day of receipt of the application for revocation, must send to the sender of the order a notice in electronic form or on paper about the revocation, indicating the date, possibility (impossibility due to the irrevocability of the funds transfer) of revocation of the order and marking on the order on paper with the stamp of the bank and the signature of an authorized person of the bank.
The application for revocation serves as the basis for the bank to return (cancel) the order.
Revocation of the order of the recipient of funds presented to the payer's bank through the bank of the recipient of funds is carried out through the bank of the recipient of funds. The recipient's bank revokes the recipient's order by sending to the payer's bank an application for revocation, drawn up on the basis of an application for revocation of the recipient of funds in electronic form or an application from the recipient of funds on paper, indicating the date of receipt of the application of the recipient of funds, the stamp of the recipient's bank and signature authorized person of the recipient's bank.
Revocation of an order transmitted using an electronic means of payment is carried out by the client by canceling the operation using an electronic means of payment.
The return (cancellation) of unexecuted orders is carried out by the bank no later than the business day following the day on which the basis for the return (cancellation) of the order arose, including the receipt of an application for revocation (clause 2.15 of Regulation No. 383-P).
When returning (cancelling) orders, the bank carries out the procedures provided for in paragraph 2.13 of Regulations N 383-P if the results of the procedures for accepting the order for execution are negative. The return (cancellation) of an order can be carried out upon the first negative result of the procedures for accepting the order for execution. The procedure for performing the procedures for recall and return (cancellation) of orders is established by the bank taking into account the requirements of clauses 2.14 and 2.15 of Regulation N 383-P.
ConsultantPlus:Forums
Field 105 – OKTMO code
(territorial municipality code) at the place of registration of your company - information is filled in from a document issued to your company by the Statregister of Rosstat, Moscow.
Field 106 – basis of payment
– TP – payments of the current year
Field 107 – tax period
–– the period is indicated - quarter (then written CV) or month (then indicated MS), then the number of the period (number of the quarter or month) for which the tax payment is made and the year. All fields are separated by dots. For example:
- When paying for the 4th quarter of 2014, you should indicate KV.04.2014
- And when paying for the month of February 2015, you should write MS.02.2015
Field 108 - No. of the payment basis document
— 0 or the date of the document – for example, a requirement (if such a requirement was received by your company).
Field 109 – Document date
– date of declaration or date of demand (if such a demand was received by your company).
Field 110 – Payment type
– from 01/01/2015 it is not filled in or takes the value 0
Field 22 – UIN code – 0
The payment order always contains the field “Purpose of payment”, which must be filled in with the following text: “Payment of insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance for (indicate the month and year for which contributions are paid) Registration number (indicate the registration number of your company in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, assigned when registration in format) 000-000-000000
Documentation of transactions on the current account
The issuance and transfer of funds from the current account is carried out by the bank, as a rule, on the basis of an order from the account owner (organization) or with his consent (acceptance).
Current account transactions are documented with the following documents:
— An announcement for a cash contribution is issued when money is deposited from the cash register to the organization’s current account;
— A cash check serves as an order from the organization to the bank to issue the amount of cash specified in the check from the current account;
— A settlement check is used to transfer funds from the payer’s current account to the recipient’s current account;
- Payment order. A payment order is a settlement document containing an order from the account owner (payer) to the bank serving him to transfer a certain amount of money to the recipient’s account opened in this or another bank.
Payment orders can be used to: transfer funds for goods supplied, work performed, services rendered; transfers of funds to budgets of all levels; transfer of funds for the purpose of returning/placing credits (loans)/deposits and paying interest on them; transfers on the orders of individuals or in favor of individuals (including without opening an account); transfers of funds for other purposes provided for by law or agreement.
Payment orders are used to make payments: for contributions to the budget, with insurance and social security authorities, when transferring wages to employees' bank accounts, when paying off debts, for preliminary and subsequent payment of bills for inventory, work performed and services.
— The payment request, in contrast to the settlement check and payment order, is issued by the recipient of the funds (supplier). It is intended for payments for products, works and services.
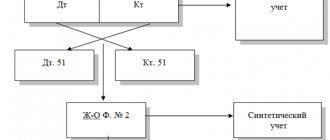
The organization also periodically receives from the bank an extract from the current account containing the transactions made, turnover and balance.
The statement is accompanied by monetary settlement documents on the basis of which transactions were made on the current account.
Based on the statements, records are kept for current accounts.
IT'S EASIER TO MAKE CORRECTIONS THAN ARGUE
Of course, the commented document will further strengthen the position of arbitration courts. However, it is not a direct indication for tax authorities. This means that the risks of additional charges cannot be excluded. If litigation arises, with a high degree of probability it can be argued that victory will be on the side of the payer. But it’s still easier not to bring the matter to court, but to ask the seller to indicate the payment order number in the invoice.
If the supplier is geographically located far from your organization, by agreement with him, you can supplement the invoice yourself by entering the number by hand. The tax authorities should not have any complaints, since invoices filled out partly using a computer and partly by hand are allowed to be registered in the purchase book (clause 14 of the Rules).
The following situation is also possible: money is credited to the seller’s account as payment for goods and they are shipped to the buyer on the same day. Is it necessary to fill out line 5 of the invoice in this case?
Here you need to consider the following. For non-cash payments, payment received on the day of shipment of goods is not considered an advance payment. At the time of shipment, the seller may not know whether money from the buyer has been transferred to his bank account (he usually receives the relevant information from a bank statement only the next day). Therefore, if the money arrived in the bank account on the day of shipment, the seller has every right to put a dash in line 5 of the invoice.