The Federal Tax Service (FTS) reminds you of the deadlines for filing an income tax return in Form 3-NDFL. In 2021, you must file a tax return on income received in 2021 by May 3, 2018.
A declaration of income received in 2021 must be submitted by May 3 (Thursday) inclusive. The Federal Tax Service of Russia reminds us of this on its official website. We are all accustomed to the fact that the declaration campaign ends no later than April 30. A special feature of this year is that the weekends from April 28 and January 7 have been moved to April 30 and May 2, respectively, so the deadline for filing declarations ends on May 3.
As a general rule, a tax return is submitted by taxpayers specified in Art. 227-228 of the Tax Code, no later than April 30 of the year following the expired tax period (clause 1 of Article 229 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But since in 2021 the weekends from April 28 and January 7 have been moved to April 30 and May 2, respectively (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 14, 2017 No. 1250), then taking into account clause 7 of Art. 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the deadline for filing a declaration has been postponed to the next working day - May 3, 2021.
It is important to remember that the deadline for filing a return of May 3, 2018 does not apply to receiving tax deductions - in this case, you can send a return at any time during the year
.
Is there a statute of limitations on deductions for an apartment?
When must an apartment be purchased in order to take advantage of the tax deduction for it in 2021? The law does not specify any statute of limitations in this regard, but there is a restriction that you can only receive a deduction for the last three years.
For example, if you bought an apartment 15 years ago, and found out about the existence of the deduction today, you will be refunded the 13% tax paid only for the last three years: from 2015 to 2021. If, of course, you received income on which tax was then paid.
However, you need to remember that the right to deduction appears only from the year in which you purchased the property. For example, if you bought a home in 2021, then in 2018 you can apply for a deduction starting in 2021, and not from 2015.
There is an exception to this rule - pensioners can receive a deduction for the three years that preceded the purchase of an apartment.
For example, if a pensioner purchased housing in 2021, then he can apply for a deduction starting in 2014. Provided that he had income on which personal income tax was paid. For example, when a person continues to work in retirement or retired and stopped working shortly before purchasing a home.
What is a single simplified tax return and why is it needed?
The unified tax return serves to simplify the reporting of taxpayers who, for whatever reason, do not have taxable items.
By law, all organizations and individual entrepreneurs are required to keep records of their income and submit tax returns to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration (Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Only those tax returns are not submitted to the Federal Tax Service for which taxes are not paid by payers due to the use of special tax regimes.
The mere absence of income and other objects of taxation is not a basis for exempting payers from submitting tax returns. In these cases, declarations with zero indicators must be submitted to the inspectorate. Otherwise, the payer may be held liable under Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for failure to submit a declaration.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility not to submit “zero” declarations separately for each tax, but to submit to the inspectorate a single “zero” declaration for all taxes at once. This is precisely why a single (simplified) tax return is used (clause 2 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is a statement by the taxpayer that he does not have an object of taxation for one or more taxes.
Submitting such a declaration to the Federal Tax Service relieves you from the need to submit “zero” tax returns, as well as from liability for failure to submit them.
Documents for a tax refund for a particular year can only be submitted next year.
Tax authorities must have an understanding of how much you paid in taxes on income to the treasury during the calendar year in order to return this amount to you. You cannot submit a declaration in advance in form 3-NDFL, even if you, for example, understand that by the end of the year you will not receive any income on which income tax is paid.
The only exception is if you do not collect the deduction yourself, but entrust it to your employer. You can write a deduction application to your accounting department or management in advance; they will take the necessary actions when it is possible.
Methods for filing a 3 personal income tax return
Today, the Federal Tax Service provides several options for filing 3 personal income taxes:
- sending a declaration by post with the obligatory attachment of an inventory of all documents;
- personal appeal of the taxpayer to the inspectorate;
- use of the Unified Portal for State and Municipal Services;
- use of the “Personal Account” application for individuals on the official website of the tax service.
By what date do you need to submit your tax return in 2018?
One of the key issues regarding receiving a deduction, about which there are many misconceptions.
A common myth is that documents must be submitted before April 30, then it will be too late.
Now, that's not true. Before April 30 of each year, you need to submit a 3-NDFL declaration to inform the state about the income received if you sold this or that property, rented out housing, etc. But this date has nothing to do with receiving tax deductions.
In fact, the question by what date you need to submit documents for deductions does not make any sense at all. This can be done on any day of the year. Only the period for which taxes will be returned to you is limited - the last three years. So even if you submit documents for a deduction every year, but don’t do this in 2021, nothing bad will happen; in 2021 you will apply for a deduction for two years at once.
Composition and structure of the updated tax report
The structure of the updated form of Form 3-NDFL, due to be submitted this year 2021 for the past 2021, is as follows:
- The title part contains basic information about the individual taxpayer. This reflects his TIN, full name, date/place of birth, country codes, category and status of the taxpayer, information about his identity card (passport), and telephone number. In addition, the reporting year, codes of the fiscal department and tax period, and the date of completion are indicated. The completeness and accuracy of the data provided (full name/signature of the individual) is confirmed.
- Section 1 (first) provides data on tax amounts paid (additional payment) to the budget or, alternatively, returned from the budget.
- In the second section, the tax base is determined and the amount of personal income tax is calculated.
- The first appendix records an individual’s income from sources located directly in the Russian Federation.
- The second appendix shows the income of an individual from sources located outside the territorial borders of the Russian Federation.
- The third appendix reflects the income of entrepreneurs, legal and private practice subjects. Professional personal income tax deductions are also calculated here.
- The fourth appendix calculates the amount of income of an individual that is officially exempt from taxation (the values for the relevant items are added up).
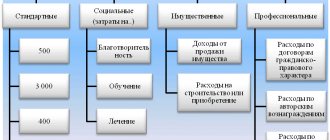
- The fifth appendix calculates the values of personal income tax deductions of a social, investment, and ordinary nature.
- The sixth appendix calculates the values of property and other personal income tax deductions. Deductions of a property nature are determined by an individual’s income from the sale of his assets and property rights.
- The seventh appendix calculates deductions of a property nature due to the actual costs of purchasing or constructing real estate.
- The eighth appendix calculates the values of real costs and deductions arising from transactions with financial instruments (securities) and transactions made by an individual in the context of the investment community.
- In the clarifying calculation to the first appendix, an individual’s income from the sale of his own real estate is calculated.
- In the clarifying calculation to the fifth appendix, the values of social tax deductions provided for by certain rules of tax legislation are calculated.
What sheets are prepared for the Federal Tax Service in various cases?
If the title (introductory) part of the declaration form is always filled out by the personal income tax payer, then specific applications and clarifying calculations for the corresponding applications are used only when there is a real need for this.
So, for example, sheets of the 3-NDFL form with 1 (first), 2 (second), 3 (third) appendices must be filled out if an individual has income or expenses within the Russian Federation, outside the territorial borders of the Russian Federation, income or expenses due to lawyer or entrepreneurial activity.
The declaration form sheet with the 4th (fourth) appendix is intended to record the income of an individual that is exempt from taxation.
Sheets with 5 (fifth), 6 (sixth), 7 (seventh), 8 (eighth) appendices are used only when an individual reasonably claims to receive personal income tax deductions of the corresponding types.
Section two, which determines the value of the tax base and the amount of personal income tax paid, is mandatory when drawing up 3-personal income tax. The first section contains summary information.
Who submits a single tax return
The ability to submit a single declaration does not depend on the status of the payer or on the tax regime applied by him. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using both OSNO and special tax regimes (USN, Unified Agricultural Tax) have the right to submit it.
The exception here is for payers who use UTII. The fact is that a simplified declaration is submitted only for those taxes for which there is no object of taxation. With UTII, the object of taxation is imputed income, which is a constant value, regardless of the fact of conducting/non-conducting business activity (clause 1 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Other organizations and individual entrepreneurs (not on UTII) are not deprived of the right to submit a single simplified declaration.
To be able to replace “zero” declarations with a single tax return, organizations and individual entrepreneurs must meet a number of mandatory conditions. These conditions are given in paragraph 2 of Art. 80 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, a simplified declaration is allowed to be submitted:
- in the absence of cash flow in the payer’s bank accounts and at the cash desk;
- in the absence of taxable objects.
For the purposes of submitting a single declaration, it is the totality of these conditions that is important.
If an organization, for example, conducts business and carries out expenditure transactions on its accounts or at the cash desk, it will not be able to submit a simplified income tax return. Moreover, even in the absence of taxable profit. In such situations, it is necessary to submit a “zero” income tax return.
Do you know what else will happen? Major legislative changes - 2019
Payment of taxes by foreign employees
Another category of additional profit tax payers are foreigners employed by Russian citizens. Two groups of foreign workers paying tax:
- who work for individuals and perform duties for personal, auxiliary and other needs, without carrying out entrepreneurial work;
- who work for legal entities, notaries, lawyers, other persons who conduct private practice or individual entrepreneurs under a GPC contract.
These citizens become tax residents after staying in Russia for more than 183 consecutive calendar days, but the fee is calculated from the moment the employment contract is signed. The date of payment of the fee depends on the mode of employment of the foreigner:
- “For yourself” or special modes (OSN, USN, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax) - until July 15 of the year following the reporting year. Advances: July 15, October 15, January 15.
- Foreigners on PSN. The date of payment of advance funds is before the start of the patent term or its renewal.
If a foreign citizen stops working in Russia and plans to leave, then the tax authorities must be notified about this one month before departure.
Tax transfer methods
A citizen has the right to transfer the fee in 4 ways:
- bank;
- cash desk of the local Federal Tax Service;
- Postal office;
- a non-bank credit enterprise with permission to conduct such operations, issued by the Central Bank.
It is recommended to pay taxes for other persons, including relatives, in cash. If the payer deposits tax funds through a bank card, without filling out a payment form, but using the details of the Federal Tax Service, the system will identify the card owner as the payer. In this situation, the person for whom the money was paid will face arrears and fines.
Deadlines for payment of personal income tax by tax agents
The timing of payment of personal income tax withheld by tax agents depends on the type of income (Article 223, paragraph 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In terms of non-cash income and excess daily allowance, the tax must be paid no later than the day following the day closest to the date of receipt of such income and payment of money. This type of income includes:
- material benefits from savings on interest on loans issued to employees and related parties;
- material benefit from the purchase of goods (work, services), securities by a related party at prices lower than the sales price of the same goods to non-related parties;
- income in kind;
- termination of obligations in any of the ways provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (offset of counterclaims, debt forgiveness, etc.);
- writing off a bad debt of a related party.
If it is impossible to withhold tax, you must inform the tax office about this before March 1 of the year following the tax period.
Tax withheld from cash payments must be paid no later than the next day after payment.
For which taxes is a simplified tax return provided?
It is allowed to submit a single simplified declaration for the following taxes:
- VAT;
- corporate income tax;
- single tax according to the simplified tax system;
- tax according to the Unified Agricultural Tax.
For property taxes, a single declaration is not submitted. This is due to the very essence of property taxes, for which “zero” declarations are not submitted.
For example, taxpayers of property tax are organizations that have property recognized as an object of taxation (clause 1 of Article 373 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If an organization does not have such property, it is not recognized as a property tax payer. Accordingly, she does not have to submit a return for this tax.
If there is no obligation to submit “zero” declarations, there is no obligation to submit a simplified declaration.
The same applies to all other property taxes (transport, land and water taxes).