Payout Basics
Objects covered:
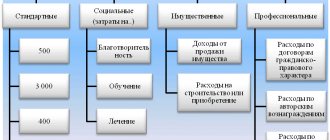
- Residential buildings, apartments, shares in an apartment.
- Land plots, their shares on which the object is located.
- Land intended for construction.
In addition, the tax deduction can include costs incurred for the purchase of building materials and renovation of the apartment (provided that it was rented out unfinished or rough). It is also allowed to compensate funds paid for the development of the project for work on connecting communications.
Important! All these costs can be included in the deduction only if there is documentary evidence that they had to be carried out. That is, if the purchased apartment has a fine finish, but you simply don’t like it, you shouldn’t count on reimbursement of the funds spent on repairs.
Providing a declaration form 3-NDFL for a refund when purchasing an apartment
When calculating a tax refund, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a tax deduction is based on an amount of no more than 2 million rubles, or more precisely thirteen percent of 2 million rubles. = 260,000 rub. The level of average wages in the Russian Federation at this time is low, so it often happens that the tax is returned to the applicant for more than one year. Thus, the tax return is submitted to the inspectorate annually - with the balance carried over from the previous year.
ATTENTION!
Due to recent changes in legislation, the information in this article may be out of date!
Our lawyer will advise you free of charge - write in the form below.
Who cannot count on a refund, regardless of the timing of the purchase of real estate
There are categories of persons who are not entitled to a deduction, among them:
- A child who is under 18 years of age.
- A student who does not have an official place of work.
- A pensioner who has no taxable income. But he can have any income, and this is not necessarily a salary. The key requirement is that income tax be paid from it.
- Individual entrepreneurs and legal entities.
- Any persons having income that is not subject to 13% tax.
- Those who bought property from a relative.
- A person who is not a resident of the Russian Federation, that is, stays in the country for less than 183 days a year.
- Those who do not have a certificate of title to housing.
- If the apartment was purchased with the assistance of a social service, with government funds or subsidies, including maternity capital. If assistance in the purchase was provided by the employer.
Yulia Dymova, director of the Est-a-Tet secondary real estate sales office, answers:
You can absolutely safely file a return for 2021 next year and receive a tax deduction. The only shame is that you receive a tax deduction in the amount that you were entitled to in 2007 - it will not be adjusted to take into account today's changes.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- Is it possible and how to deprivatize an apartment in 2021
- Alienation of an apartment - what is it?
- How can you double your maternity capital when buying an apartment in 2021?
- Cracks in the wall and foundation of an apartment building, where to go?
- Fire safety at home for parents and their children: you need to know - Review + Video
- Carlson to himself
- How to sell an apartment with a mortgage and buy another one with a mortgage, for example from Sberbank?
About statute of limitations
The laws of the Russian Federation do not establish a statute of limitations for obtaining a tax deduction. This means that no matter when the property was purchased, part of the money for it can be returned throughout your life.
- The period from which you can apply for a deduction begins from the moment you receive ownership.
- For the calculation, you can take the next 3 years; the period that preceded the acquisition cannot be included in the declaration.
- If housing was purchased under a sales contract, the right to a property deduction appears from the moment of registration of ownership rights.
- If purchased under a contract, the DU is the date of signing the transfer and acceptance certificate, that is, the period from which the house was put into operation.
There is one exception - it concerns the transfer of the right to deduction for pensioners. If a non-working pensioner bought real estate, then he has the right to use the income tax that he paid in the period 3 years before the date of purchase.
Maximum amounts that can be returned:
- When using your own funds - 260 thousand rubles.
- If you take out a loan - 390 thousand rubles, but only in payment of interest.
Examples
Citizen A purchased an apartment under a sales contract in August 2021, and a month later he issued a certificate of ownership for it. He wants to immediately receive the maximum possible deduction for the purchase. Therefore, he will have to wait until 2021, since it is at the beginning of it that he can receive a return for 2021, 2021, 2021. Citizen A could do differently and submit documents for a tax refund every year, in 2017, 2021 and 2021. Naturally, payments will be extended over such a period if the taxes he paid to the budget are not enough to pay the entire amount at once.
Citizen B registered a temporary residence permit in 2021, the facility will be commissioned at the beginning of 2021. As soon as he receives the acceptance certificate, he acquires the right to a tax deduction, but the first payment can only be received in 2021, since he will submit the declaration and the entire package of documents in 2021. A citizen can act differently, and in this same year, arrange personal income tax payment through the employer. In this case, after 1.5-2 months he can count on an increase in the form of 13% personal income tax, which will not be deducted from his salary.
This is important to know: When can you issue a deed of gift after purchasing an apartment?
For both examples there are important points:
- Both citizens must officially work for the entire period and pay 13% personal income tax.
- Both cannot get a refund using the previous year as the reporting period. For the first example, these are 2012, 2013, 2014. For the second, 2014, 2021, 2021, and it does not matter in what year the DDU was issued, because only the date of transfer of ownership of the object is taken into account.
Arbitrage practice
In practice, there are situations when the Federal Tax Service delays the time of payments, the authorities authorized to correct the situation after a citizen’s application and complaints did not react. Then the taxpayer goes to court to recover not only the due amount, but also a penalty for each day overdue.
For example:
Citizen Arapov sent documents, a declaration and an application for the return of the property deduction. The desk audit period has passed, Mr. Arapov received permission to receive payments. But after another two months, the funds still had not arrived in the account. An application to the head of the Federal Tax Service and a complaint to the supervisory inspection did not yield results. Then the citizen filed a claim in court, to which he attached all the necessary papers and indicated the reason for the appeal.
The court considered the claim and satisfied it in full: according to the law, a citizen has the right to timely payments for the purchase of an apartment or the construction of a new house, if all the necessary documents are available and filled out correctly.
There is no statute of limitations
Indeed, there is no statute of limitations for property tax deductions. You can claim the right to it any time after purchase, even after 20 years. Regardless of the year in which the refund application was submitted, only the previous 3 years can be taken into account. That is, if the apartment was purchased in 2000, and the application for refund followed only in 2021, then the years 2013, 2014, 2016 are taken into account.
It is also worth knowing these points:
- Real estate purchased before January 1, 2014 has a deduction base of 1 million, and not 2 as it is now. This means that you can return no more than 130 thousand rubles.
- As for apartments and other housing purchased after this date, the deduction amounts are 260 thousand for own funds and 390 thousand for credit.
Examples
Citizen B bought an apartment in 2002, but for 5 years, that is, from 2002 to 2007, she worked unofficially, that is, she did not make income tax deductions, then she was on maternity leave for 6 years. In 2021, she officially found a job, which means she began to transfer funds to the state budget. From 2021, she has the right to claim tax deductions. But she didn’t know about this right when she found out in 2021 and filed a declaration and the entire package of documents. As a result, she may receive a deduction for 2021, 2021, and next year 2021 she may claim the underutilized amount. Naturally, she can count on no more than 130 thousand rubles.
Citizen G bought an apartment in February 2014, but then quit his job. He did not know about the right to deduction. I only found out in 2016, but at that time I was not working officially. Starting in 2021, I got an official job. He will claim the deduction only in 2021, but he will be able to include 2021 in the calculation. The amount he expects is a maximum of 260 thousand.
The procedure for forced collection of personal income tax debt
Debt incurred as a result of failure to pay personal income tax on time (arrears) can be collected by the tax authority through the court. In the same way, penalties and fines that have not been paid on time can be recovered (clause 2 of Article 11, clauses 2, 8 of Article 45, clause 1 of Article 48, clause 2 of Article 57, clause 1 of Art. 75, paragraphs 1, 3, Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Before going to court, the tax authority must send the taxpayer a demand for payment of taxes (penalties, fines). Such a requirement is sent no later than three months from the date of discovery of the arrears, if the total amount of debt of an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur exceeds 500 rubles, or no later than a year from the date of discovery of the arrears, if the total amount payable does not exceed 500 rubles. (clauses 2, 4, 8 of article 69, clause 1 of article 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
If the taxpayer does not comply with the requirement within the established period (as a general rule, this is eight business days from the date of receipt of the requirement), the tax authority has the right to file an application with the court to collect taxes, penalties, and fines from the taxpayer’s property in administrative proceedings (clause 6 of Art. 6.1, paragraph 1, 3, article 48, paragraph 4, paragraph 4, paragraph 8, article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Such an application can be submitted within six months from the date of expiration of the deadline for fulfilling the requirement, if the debt on it exceeds 3,000 rubles. (paragraph 4, paragraph 1, paragraph 1, paragraph 2, article 48 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
If the total debt is determined by several demands for payment of taxes, penalties, fines, the tax inspectorate must submit an application for collection within the following deadlines (paragraph 2, 3, paragraph 2, article 48 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
):
• within six months from the date when the total debt exceeded 3,000 rubles;
• within six months after the expiration of a three-year period from the date of expiration of the earliest requirement for payment of taxes, penalties, fines, if the total debt does not exceed 3,000 rubles.
Based on this application, the magistrate at the taxpayer’s place of residence may issue a court order without a trial or court hearing. Within three days from the date of publication of the order, the taxpayer will be sent a copy of it. Before the court order is issued, as well as within 20 days after sending a copy of the order, he has the right to submit his objections.
If objections are submitted within the specified period, the application for a court order will be refused and the court order issued will be canceled. In this case, the tax authority may file an administrative claim with the district court no later than six months from the date the court issued a ruling to cancel the court order (Article 17.1, Part 3 of Article 123.5, Parts 1, 2 of Article 123.7, Art. Art. 286, 289 CAS RF
;
para. 2 p. 3 art. 48 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
;
paragraph 49 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2016 No. 36 “On some issues of application by courts of the Code of Administrative Procedure of the Russian Federation”
).
Upon an administrative claim from a tax authority for the collection of taxes (penalties, fines), the district court must consider the case before the expiration of three months from the date the application was received by the court (Article 19, Part 1 of Article 289 of the CAS RF
).
Within a month from the date of the court's decision, the taxpayer has the right to file an appeal. If it is filed, the court decision comes into force after the court considers this complaint, unless the appealed court decision is cancelled. If the decision of the court of first instance is canceled or changed by the ruling of the appellate court and a new decision is made, it enters into legal force immediately (Part 2 of Article 186, Part 1 of Article 298 of the CAS RF
).
Who is eligible to receive it?
- Russian citizens working and paying taxes;
- pensioners (see information above).
- minors;
- unemployed university students;
- Individual entrepreneur and legal entity;
- working unofficially;
- citizens who bought housing from relatives;
- persons who do not have Russian citizenship;
- persons who do not have a certificate of title to property.
Other limits include situations when an apartment or house was purchased at the expense of government subsidies, an employer, maternity capital or some other payments.
When can you apply for a property deduction?
Property deductions have no statute of limitations. This means that the owner has the right to declare his right to the tax office at any time after purchasing residential real estate. The period for applying for a deduction is not limited by law - it can be obtained even after a year, even after 20 or more years.
In this case, you can only return the income tax that was withheld during the last 3 years before the year in which the deduction was claimed. In addition, the citizen must have in the declared period (for which the 3-NDFL declaration is submitted) taxable income on which personal income tax was paid at a rate of 13%.
Validity period of personal income tax certificate 2 issued for tax deduction
- Number of the Federal Tax Service for which it was compiled.
- Full name of the employer, including its full details.
- Information about the employee, including passport information.
- Monthly deductions from salaries, with payment purpose codes.
- The amount of tax deductions.
- Total amounts for the reporting period.
Now such a document is generated automatically using computer programs. In this case, previously entered accounting data, which is maintained at each enterprise, is used. The document contains data by month from the beginning of the reporting period. The final part includes the total income received and retained. That is, exactly the one that interests the Federal Tax Service.
Results
The deadline for submitting Form 3-NDFL for declaring income is set for April 30, following the reporting year. If the deadline falls on a weekend or non-working date, it is shifted to the next closest working day. But for reporting for 2021, this rule does not apply and you must report no later than 04/30/2019, because it's a working day. For late submission of a tax return, the taxpayer will face a fine of at least 1,000 rubles.
When declaring tax for deduction, a specific deadline for filing 3-NDFL is not established by law. But the tax can be returned only for the last 3 years preceding the year of filing the declaration.
Buying your own home is a very pleasant event for every citizen, but the joy becomes more complete from the knowledge that you can reimburse part of the expenses incurred.
The essence of the phenomenon
In practice, receiving a property deduction is the return of income tax
.
What ordinary people usually get confused with are two types of INV:
- carried out upon sale;
- carried out upon purchase.
Note 1.
If, for example, we are talking about INV limits, you should clarify which of the two types of deductions is implied.