Tax deductions for individual entrepreneurs in 2021 are amounts by which the tax base can be reduced. This is one of the ways to reduce the tax burden for an entrepreneur.
A deduction is a way, an opportunity to reduce the financial burden on an entrepreneur, which means that the topic of tax deductions for individual entrepreneurs is always relevant. In letter No. 03-04-03/66945 dated November 19, 2015, the Ministry of Finance even clarified whether an individual entrepreneur can receive a tax deduction. According to the ministry's response, individual entrepreneurs, like all individuals, have the right to tax benefits, including deductions, if they receive income subject to a 13% rate. And the right to deduction has nothing to do with the taxation system chosen by the individual entrepreneur. This thesis needs clarification.
Right to deduct personal income tax
Most of the deductions are provided for by the personal income tax. It is paid by all citizens working under labor and civil contracts. In addition, personal income tax is subject to certain other types of income, for example, received from renting or selling property, from investing, under insurance contracts, and others.
Free tax consultation
Individual entrepreneurs in the main tax regime (OSNO) also pay personal income tax. Can an individual entrepreneur receive a tax deduction if he uses this tax system? Of course, it can, since all the rights of a taxpayer apply to it. But those individual entrepreneurs who have chosen preferential regimes (USN, UTII, PSN, Unified Agricultural Tax) do not have the right to deductions for personal income tax. They are not payers of this tax, they have no tax base, which means they have nothing to reduce.
At the same time, it cannot be said that entrepreneurs in special regimes are completely deprived of the right to tax deductions for personal income tax. After all, at the same time as their business, they can receive other income that is subject to this tax. For example, if an individual entrepreneur on a simplified system simultaneously works for hire or rents out real estate, then he retains the right to deduction. But it can only be applied to income subject to personal income tax.
Thus, the rule is very simple: if an individual entrepreneur pays personal income tax at a rate of 13%, then he can receive the deductions provided for in its calculation.
Example 1
Citizen Smirnov worked in a company and received a salary of 40 thousand rubles, from which his employer withheld monthly and transferred personal income tax to the budget. When calculating the tax, a standard deduction per child was used in the amount of 1,400 rubles. The tax was calculated as follows: (40,000 - 1,400) * 13% = 5,018 rubles.
Smirnov decided to try his hand at business, for this he registered an individual entrepreneur and immediately switched to a simplified tax regime. However, he had not yet quit his job, meaning he still received wages. The employer still continued to calculate personal income tax from her and apply the child tax deduction. The entrepreneur must calculate the tax on business income under the simplified tax system himself; deductions are not applied in this case.
A few months later, Smirnov decided to devote his time entirely to a new business and left his job. He no longer had income that was subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%. Accordingly, Smirnov no longer has the right to apply a personal income tax deduction.
Starting from the next calendar year, the businessman decided to change the tax regime from simplified to basic - it was more profitable for the business. He began to pay personal income tax, since it is provided for by the basic taxation regime, which means that the right to apply tax deductions has arisen again.
There are several types of personal income tax deductions. Articles 218-221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are devoted to them. Let's look at the most common ones in more detail.
general characteristics
Tax deductions under Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are provided only to individuals whose income is taxed at a rate of 13%. Registration as an individual entrepreneur does not prevent the implementation of the right. If a businessman pays income tax, he can file a 3-NDFL declaration and insist on recalculating liabilities.
The easiest way to get a property deduction for entrepreneurs is through the general system. The law recognizes businessmen as personal income tax payers. They are required to submit an annual declaration indicating their actual income. Advance payments are collected regularly, and therefore impressive amounts can be claimed for refund. To use the right of OSNO payers, it is enough to indicate the relevant data in the declaration.
It is more difficult to return money to “special regime officers”. They can claim a deduction only if they have third-party income, taxed at a rate of 13%. If there is no income outside of the business, it is worth transferring the right to compensation to a spouse or other adult co-owner. This is allowed when registering real estate as joint or shared ownership.
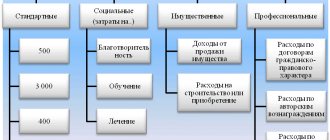
Professional deductions
Let's start with them, since this is the only type of deduction intended specifically for entrepreneurs. These deductions are also used by individuals who are engaged in private practice, receive royalties or income under civil contracts. When calculating the personal income tax base, they can deduct documented expenses. But only those that are directly related to generating income.
It happens that there is no documentary evidence. In this case, can an individual entrepreneur receive a professional tax deduction without them? Yes, but only in the amount of 20% of the income. For example, his revenue was 100 thousand, and his expenses were 80 thousand rubles. If the individual entrepreneur has supporting documents, then the tax will be calculated as follows0) * 13% = 2,600 rubles. If there are no documents, only 20 thousand rubles can be deducted. The tax will be 0) * 13% = 10,400 rubles.
Nuances of filling out 3-NDFL when buying an apartment
The correct preparation of the declaration is recognized as a mandatory condition for tax refund. Features of working with form 3-NDFL follow from the content. Each page of the report is dedicated to a specific deduction. In the case of purchasing housing, you need to fill out the title page, sections 1–2, pages A, B and D1.
Detailed instructions are given in order No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] On the first sheet of the form, indicate the applicant’s personal data, tax period, adjustment number, and put a personal signature.
Sections 1 and 2 are general in nature. This reflects the total amount of income, the amount of property deduction and tax to be refunded.
Sheet A indicates the source of earnings, subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%, as well as the total amount of income in favor of the declarant.
Entrepreneurs on OSNO will also need to fill out page B. Here you should reflect income from commercial activities, business maintenance costs and advance payments.
Experts recommend paying the most attention to sheet D1. It is important not to make a mistake with the type of property, to accurately enter the address of the purchased apartment and the amount of costs. The guidelines will be the appendices to the instructions of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
Note! Special programs will help you avoid mistakes when drawing up a declaration. A service for automatically generating a 3-NDFL report has been launched on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. You can use the tool for free.
Standard deductions
The peculiarity of these deductions is that they are in no way related to the expenses incurred by the citizen, and therefore resemble benefits. Another distinctive feature is that in most cases they are of symbolic size.
The most common option is the children’s deduction mentioned in the example about IP Smirnov. For the first and second children, 1,400 rubles must be deducted from the tax base, for the third and each subsequent child - another 3,000 rubles, for a disabled child - 12,000 rubles. A deduction in this amount can be claimed for each month of the year until the taxable income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 350,000 rubles.
There are other deductions in this group - for veterans, heroes of the USSR or the Russian Federation (500 rubles), liquidators of the Chernobyl disaster (3,000 rubles) and other persons.
Base
There are several types of situations that lead to the state owing to the taxpayer, and not vice versa:
- if the tax budget received a larger amount than necessary (Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the decision on the previously collected tax is canceled in court (Article 79 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if a citizen is entitled to a tax deduction (Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the court decided to return the previously paid state duty (Article 333.40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if you have the right to other tax refunds, for example, excise taxes (Article 203 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or VAT refund (Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Each of these cases has its own article of the Tax Code, therefore the refund procedure has its own characteristics. In general, this right is the basis of tax legislation on taxpayer rights: Art. 21 clause 5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which also contains an indication of the timeliness of execution of such a procedure.
Attention! Not only the taxpayer may be charged penalties for late payment of taxes, but also the tax authority itself. This can happen if there is a delay in returning overpaid amounts. The amount of the penalty is calculated as standard at the Central Bank refinancing rate.
You can dispose of overpaid tax not only by way of a refund, but also by making an offset against upcoming payments. But this also has its own peculiarities, since all taxes are divided into several levels:
- federal (personal income tax, VAT, mineral extraction tax, water tax, simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax, PSN);
- regional (for transport);
- local (for property and land).
There is a rule according to which offsets are made only between taxes of the same level. For example, if a businessman has an overpayment of the simplified tax system, then he can direct it towards the upcoming payment of other taxes at the same federal level, the same simplified tax system in the future, but he cannot pay with it for his personal property or transport.
Social deductions
This group includes 5 types of deductions:
- for education – your own, your children’s, your brother’s or sister’s;
- for medical services, medicines and voluntary health insurance for yourself, a child, parents or wife/husband;
- for voluntary insurance or non-state pension provision for oneself, a spouse, parents or a disabled child;
- on the funded part of your labor pension;
- for charity (up to 25% of income).
The maximum amount of social deductions in total is 120,000 rubles. The payer decides for himself how to distribute them. Amounts transferred to charity are not included in this limit, as are expensive treatment and education of children. For each child's full-time education, up to 50,000 rubles can be deducted per year. You can apply for a social deduction no later than 3 years after the date in which the right to it arose. This follows from Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Does a citizen have the right to such a deduction if he studied, for example, in a foreign language course? The law does not stipulate any restrictions on the direction of study. These can be any required courses. The main rule is that the educational institution must have the appropriate license.
Social deductions
To receive such a tax deduction, you will need to confirm that the individual entrepreneur incurred the following expenses:
- for charity; here it is necessary to pay attention that the amount spent on good purposes cannot exceed a quarter of the annual income;
- for the education of the citizen himself or his children;
- for treatment of a citizen, his children, parents or spouse;
- contributions to pension funds outside the state system;
- contributions to the funded part of the pension made at the initiative of a citizen.
The basic rule continues to apply in this case. The amounts of tax deductions are established by law, taking into account the conditions important for their determination.
Property deductions
Property deduction is due to those personal income tax payers who:
- incurred costs for the purchase of housing or land for building a house;
- received income from the sale of real estate or other property;
- sold the shared construction project, that is, assigned the right to claim it;
- sold a share in the organization.
Most often, those who have purchased housing apply for a property deduction. The following expenses can be deducted:
- in the amount of the cost of the object, but not more than 2 million rubles;
- in the amount of interest paid on targeted loans for the purchase of real estate or for refinancing such loans, but not more than 3 million rubles.
Example 2
Individual entrepreneur Pavlov bought an apartment for 3 million rubles and another 1 million was interest on the mortgage. He can claim a deduction for the cost of the apartment, but not more than 2 million, and return 2,000,000 * 13% = 260,000 rubles from the budget. From interest you can return the amount of 1,000,000 * 13% = 130,000 rubles. Total 390 thousand. Let’s assume that personal income tax for the past year amounted to 130 thousand. This means that this exact amount will be returned, and the rest will be transferred to the next 2 years.
The property deduction is granted once in a lifetime and can be claimed at any time after such a right arises. The question arises: does a citizen have the right to keep the remainder of the deduction if the apartment cost less than 2 million? There is a nuance here related to the acquisition period:
- If this happened in 2014 or later, the deduction can be divided between the objects. Let's say the apartment cost 1.5 million rubles. This amount will be declared as a deduction, and the remaining 500 thousand will remain. They may come in handy when purchasing another property.
- If the apartment was purchased before 2014, then the deduction cannot be divided. In this case, it can only be declared within the limit. That is, if the apartment costs 1.5 million, the deduction of 500 thousand will simply disappear.
Free accounting services from 1C
Opportunity for individual entrepreneurs in a special mode
The greatest interest usually arises among special regime officers regarding property deductions. Does an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system or UTII have the right to a tax deduction when buying an apartment? We explained above that an entrepreneur cannot use it on his own, because he does not pay personal income tax. However, there is a nuance - his spouse can claim a deduction if he has the right to do so.
For example, an entrepreneur Petrov bought an apartment using the simplified tax system. He does not have the right to a property deduction, since he does not pay personal income tax. But the businessman’s wife, who works in the company, has it. The apartment was acquired during marriage and is considered the joint property of the husband and wife. Therefore, citizen Petrova has the same right to deductions as he himself.
When you can't get a tax refund
Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation describes in what cases the territorial inspection is supposed to reject an application. Taxes paid to the budget cannot be returned if:
- residential premises or land were purchased from close relatives;
- the purchase was made using maternity capital or other subsidies;
- the transaction was financed by a third party other than the spouse.
The Russian Ministry of Finance explains the purchase of real estate from relatives No. 03-04-05/85621. The Agency recognizes the parties to such agreements as interdependent persons.
You cannot receive the same property deduction several times. You are allowed to use the preference once, but in full. If the declarant has received an exemption for an amount less than the approved limit, the balance can be declared again.
Example. An entrepreneur bought a house on OSNO for 1,800,000 rubles. He has the right to insist on a tax refund from the budget:
1,800,000×13% = 234,000 rubles.
Since the costs of the transaction did not exceed 2 million, the merchant will subsequently be able to once again refer to Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the limit will only be:
2,000,000–1,800,000 = 200,000 rubles.
Important! The rule on transferring unused property deductions does not apply to expenses on targeted loans. The mechanism can be implemented only under one agreement. The borrower will not be able to re-claim the right, even if the balance “burns out.”
The procedure for obtaining an individual entrepreneur deduction
Unlike ordinary personal income tax payers, individual entrepreneurs calculate their taxes, pay them and submit reports independently. If deductions are required, they are declared in the 3-NDFL declaration, which must be submitted by April 30 of the following year. The current form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 3, 2018 No. MMB-7-11/ [email protected] Otherwise, tax deductions for individual entrepreneurs are provided according to general rules, since there are no special rules in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For each deduction you will need an individual set of documents. If we talk about property deductions for the purchase of an apartment, you will need:
- Passport.
- Certificate of ownership of the apartment or extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate.
- An apartment purchase and sale agreement or other document on the basis of which the property was purchased.
- Transfer acceptance certificate.
- If at the same time a deduction is claimed for interest on a loan - a mortgage, loan or other agreement.
- Payment documents.
- Marriage certificate, if the owner is a member of it.
- Certificate 2-NDFL, if the individual entrepreneur works in parallel.
These documents are provided in the form of originals and copies. They are attached to the 3-NDFL declaration.
What if the purchased apartment is sold again?
A situation may arise when an individual entrepreneur purchases real estate, submits documents for a tax deduction, and then sells the apartment. It's not illegal. Moreover, even if this action was taken before the deduction amount was exhausted, it is legal. Everything that its owner does with real estate after purchase no longer concerns tax payments. The deduction will be provided until the amount is completely exhausted.
Based on the information above, we can summarize that an individual entrepreneur, in principle, can receive a tax deduction. However, for this it is necessary that it meet certain parameters, the main one of which is the businessman’s payment of personal income tax (13%). To do this, you can use two options: either apply the general taxation system in your activities, or find a part-time job that will generate additional income subject to personal income tax.
Deductions for certain other taxes
Personal income tax deductions are the largest and most common, but not the only ones. Entrepreneurs are given other opportunities to save a little on taxes.
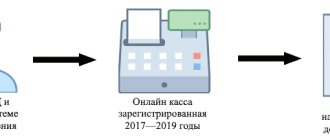
- Individual entrepreneurs on UTII and PSN in 2021 can deduct the amount of costs for an online cash register. The deduction is applied not to the tax base, but to the amount of tax already calculated. Its size is 18,000 rubles per device. The cost of the cash register and fiscal drive, installation costs, personnel training and other related expenses are taken into account. Those individual entrepreneurs who registered their cash register before July 1, 2021 have the right to deduction. But they have very little time. The deduction is temporary, and the last period in which it can be claimed is the 4th quarter of 2021.
- Individual entrepreneurs on UTII and simplified tax system with the object “Income” have the right to deduct the amount of insurance premiums when calculating tax. If you have employees, you need to add up the contributions for them and for yourself, and subtract the resulting amount from tax. Tax reduction is allowed by 50%. If there are no employees, then your contributions can be fully deducted from tax. It is impossible to go into negative territory, that is, nothing will be returned from the budget. This way you can save on tax every year. For example, in 2021, an individual entrepreneur without employees will be able to reduce tax by more than 36,000 rubles through contributions.
- Individual entrepreneurs on the “profitable” simplified tax system from Moscow who are engaged in any type of trade can save on paying the trade tax. After reducing the tax on insurance premiums, they deduct the amount of this payment from it. An important condition is that in order to be able to apply the deduction, the entrepreneur must independently register as a payer of the trade tax. If he doesn't do this, he won't be able to save money.
So, we have considered the question of whether an individual entrepreneur can receive a tax deduction for personal income tax. The right to a deduction arises for any citizen, including an entrepreneur, if he receives any income on which he pays personal income tax at a rate of 13%. If he does not have such income, then he will not be able to make a deduction when calculating his taxes.
Changes in legislation on tax deductions: important points
In 2021, no significant amendments were made to the regulations. The adjustments concerned the taxation of transactions with assets legalized under the capital amnesty. The innovations were of a clarifying nature.
Major changes in legislation occurred about 4 years ago. In 2014, parliamentarians separated the deduction for repayment of targeted loans into a separate category. It can be used separately. Thus, individuals have the opportunity to use two methods of tax refund. They can be applied to different objects and contracts. The norm applies to objects that came into possession after 01/01/2014.
A positive change was the exclusion from Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation of references to the distribution of deductions among co-owners. Now the limit is calculated per person. Each of the owners has the right to make a claim for the return of personal income tax within the limits of the approved standard and the actual costs incurred.
Features of purchasing commercial real estate
Real estate purchased by an individual entrepreneur may have a commercial purpose. An apartment, house, or part of the property can be used in the future for renting out, using it as office housing, or converting it into non-residential premises. The purpose of purchasing an apartment does not affect the deduction in the case of purchasing residential real estate.
When purchasing non-residential real estate for commercial purposes, no deduction is provided. The right does not arise when purchasing a house built on a garden plot. In houses of this type it is not allowed to register citizens, which does not allow them to be classified as residential real estate.