What kind of donation can you get a deduction for? Rules for calculating the deduction. Non-monetary charity. Documents for a tax deduction. When and for what period can you get a deduction?
A social tax deduction is a benefit that the state provides when the taxpayer performs any socially significant actions. Such actions also include charity.
If you donated money to a children's hospital, charity, or animal welfare fund, you can officially repay some of those expenses. Base: pp. 1 clause 1 art. 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The conditions for receiving a deduction for charity are the same as for property, social and other deductions. First of all, you must be a personal income tax payer at a rate of 13%.
To do this, it is enough to have an official salary, from which your employer transfers 13% of income tax to the state budget. Or have other income subject to personal income tax. This could be income from renting an apartment, car, garage, etc. In addition, you must be a tax resident of the Russian Federation, that is, stay in Russia for more than 183 days within 12 consecutive months.
By carrying out charitable activities, you can return up to 13% of the donation amount to your account. Despite the fact that the deduction for charity is a social deduction, the rules for its calculation have their own characteristics, and the maximum amount is not limited to 120 thousand rubles, such as, for example, a deduction for treatment and education.
Today we will look at the rules for receiving a deduction, tell you about the restrictions, procedure and size.
Receive a tax deduction within a week with the Quick Deduction service!
Get a service
The concept of charity and legal aspects
According to Federal Law No. 135 of August 11, 1995 (as amended on December 18, 2018), charity is considered free and voluntary assistance to those in need. It can be in the form of donations, provision of services, transfer of property, and so on. The law determines the legal regulation of charitable activities, forms of its support and stimulation by the state. Such measures include tax optimization. For enterprises helping charitable organizations, VAT benefits are provided. Since 2016, such activities have been exempt from taxation if carried out for purposes specified by law.
Benefits from the state are also provided for individual philanthropists. According to Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a citizen has the right to return part of the donations made.
ATTENTION! A mandatory requirement for assigning a refund is the presence of deductions from the citizen’s income to the state budget.
By paying personal income tax and making donations, a person has the right to receive a refund of up to 13% of the amount of assistance provided. The deduction for charity is considered a social deduction and is aimed at reducing the taxable portion of income.
Video - What is a charitable deduction?
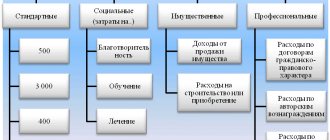
Who is entitled to a tax deduction for charity?
A reduction in personal income tax for a benefactor is permitted when providing selfless support to socially oriented structures.
Table. List of organizations to which donations entitle you to benefits
| Organizations | Peculiarities |
| Charitable | Must be officially registered as legal entities. For charitable support of representative offices and divisions of Russian organizations and funds created by them, no deduction is assigned. |
| Non-profit socially oriented structures | Donations are made for the type of activity established by Federal Law No. 7 of 01/12/1996 (with innovations that entered into force on 01/01/2019) |
| Non-profit organizations working in the educational, scientific, cultural, health and environmental spheres, the field of physical education and sports, protection and support of civil rights | The list does not include enterprises operating in the field of professional sports |
| Religious organizations | Charitable support is taken into account in the statutory functions, which must be indicated in the payment documentation |
| Non-profit structures | Assistance is allowed for the formation and increase of their target funds (the procedure is prescribed in Chapter 2 of Federal Law No. 275 of December 30, 2006) |
ATTENTION! It should be understood that the deduction will be denied when providing charitable support to citizens (individuals) or organizations that are not officially registered legal entities or not included in the presented list.
Amount and calculation of compensation
The citizen is reimbursed 13% of charity expenses if the conditions established by the legislation of the Russian Federation are met.
Tax deductions are calculated according to schemes similar to other types of deductions.
To determine the amount of possible compensation, you need to know the person’s income and the amount of deductions made from it to the state and for gratuitous support to those in need. When calculating, data for the calendar year is taken into account.
Conditions for calculating benefits:
- the refund must not exceed the amount of the transferred tax;
- The amount to be reimbursed is not calculated in excess of 25% of income for the year.
It should be noted that the 25% limit is assumed not for each type of charitable support, but for their totality.
Example 1
In 2021, a citizen transferred 20 thousand rubles for charitable purposes. His income for the year is 250 thousand rubles. Since the amount of transfers is not higher than 25% of this amount (250 thousand * 25% = 62,500 rubles), the tax deduction for charity issued by a citizen in 2021 is 2,600 rubles (20 thousand * 13%).
Example 2
In 2021, a person donated 100 thousand rubles to a charitable organization. His income for the year is 300 thousand rubles. Since the amount of support is higher than 25% of the specified amount (300 thousand * 25% = 75 thousand rubles), a citizen cannot apply for full coverage. The maximum possible amount is 75 thousand rubles. In 2021, the citizen will receive compensation: 75 thousand * 13% = 9750 rubles.
Example 3
In 2021, a person donated 40 thousand rubles to charitable purposes to protect nature and 70 thousand rubles to protect health. His annual income is 320 thousand rubles. Since the total amount of assistance (110 thousand rubles) is higher than 25% of income (80 thousand rubles), a citizen cannot apply for full coverage. In 2021, he will receive a deduction of 80 thousand rubles, hence the compensation will be 10,400 rubles (80 thousand * 13%).
ATTENTION! If funds for charitable purposes for which a refund was made are returned to the benefactor, the amount of the deduction must be entered in the 3-NDFL declaration for the year in which the return was recorded.
Example 4
In 2021, a citizen donated 50 thousand rubles to charity. In 2021, he received a full tax refund (50 thousand * 13% = 6500 rubles). But this same year the funds were returned. Now, in 2021, a citizen must add the amount of compensation to his income (50 thousand) and return personal income tax (6,500 rubles).
According to Article 219 of the Tax Code, at the level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation it is possible to increase the maximum deduction amount to 30% of taxable income. Donations are aimed at supporting cultural institutions and non-profit structures. The list of such organizations is established by the law of the subject of the Russian Federation.
Charity from legal entities to foundations
Among Russian businessmen, it is more common to provide assistance indirectly to those in need, through specially created structures - charitable foundations, one of which is the St. Petersburg charitable foundation AdVita (For Life). In most cases, this approach is driven by the desire to independently determine the circle of recipients of donations, as well as confidence in controlling costs. After all, a fund that collects and distributes funds, for example, for the treatment of cancer patients, is registered in Russia as an NPO, its activities are regulated by law, and the donor can be sure that his funds will be spent in the targeted manner. Such funds have a staff of employees responsible for searching for projects, and also submit reports to the tax authorities.
Although all charitable organizations, including foundations, are exempt from income taxation within the framework of their statutory activities, they are required to annually submit reports to the tax authorities on the expenditure of funds received as part of charitable contributions. If the Federal Tax Service considers such expenses to be inconsistent with the statutory goals, then all funds received will be recognized as income of the fund, subject to taxation. For example, a charitable foundation does not have the right to buy real estate or make other investments with donors’ money.
As for the charitable organizations themselves, as mentioned above, you can transfer money to a charitable foundation or transfer property only at the expense of your profits, if the taxpayer applies the general taxation system. Taxpayers under the simplified taxation system also cannot reduce their income by amounts of charitable assistance. A closed list of expenses by which organizations using the simplified tax system can reduce the income received is given in Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and charity expenses are not included in it.
Is it possible to deduct a donation in kind (non-cash)?
Until 2012, it was possible to exercise the right to a personal income tax refund only with monetary assistance, that is, taking a refund when providing charitable support in kind before 2012 is unacceptable. This is indicated by the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 2, 2010 No. 03-04-05/8-78. However, currently the legislation does not impose restrictions on forms of support. In 2021, it can be both money and property (equipment, car, securities, premises). The Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines a donation as the transfer of a thing or right as a gift, without specifying a specific form.
The possibility of a deduction in 2021 for non-monetary charitable support is also indicated by Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation does not consider donations in kind to be an obstacle to granting benefits, which is confirmed by letter No. 03-04-08/58234 dated December 30, 2013.
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 03-04-08/58234
ATTENTION! If a citizen paid for the property and donated it next year, the right to the benefit is acquired in the year the property is transferred. This is reflected in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated May 21, 2015 No. BS-4-11/8662. For example, a person purchased property in 2021, and transferred it for a charitable purpose in 2021. Compensation can be received for 2021.
Example . In 2021, a citizen bought and donated 3 laptops to a charity organization. The market value of each is 10 thousand, respectively, the full assistance is valued at 30 thousand rubles. A citizen’s annual income is 400 thousand rubles. Since 25% of this indicator (400 thousand * 25% = 100 thousand) is higher than the cost of equipment (30 thousand), compensation is calculated: 30 thousand * 13% = 3900 rubles. A person has the right to submit documents for it in 2021.
Accounting for charitable donations
Organizations that engage in charitable activities are required to reflect this in their accounting records. The general procedure for recognizing expenses in accounting has been established (hereinafter referred to as PBU 10/99).
Paragraph 17 of PBU 10/99 states that the expenses of a business entity are subject to recognition in accounting, regardless of its intention to receive revenue or other income, as well as the form of such expenses (monetary, in-kind and other). All expenses, according to paragraph 4 of PBU 10/99, are divided into:
- expenses for ordinary activities;
- other expenses.
According to clause 11 of PBU 10/99, other expenses include the transfer of funds (contributions, payments, etc.) related to charitable activities, as well as expenses for sporting events, recreation, entertainment, cultural events educational activities and other similar events. Thus, taking into account the provisions of the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations and the Instructions for its application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n, in the accounting records of the organization, the transfer of donations will be reflected using account 91 “Other income and expenses” .
In accordance with clauses 4 and 7, the organization must exclude from the calculation of the tax base for income tax for both the reporting and subsequent periods the costs incurred in connection with the provision of gratuitous charitable assistance. According to this indicator, a permanent tax liability is formed in accounting. The wiring is as follows:
Debit 76 - Credit 51 - funds were transferred in the form of donations; Debit 76 - Credit 41 - goods transferred as part of charitable assistance; Debit 91 - Credit 76 - donation expenses are included in other expenses; Debit 91 - Credit 76 - the cost of goods donated is included in other expenses; Debit 91 - Credit 68 - VAT is charged on the cost of goods transferred free of charge; Debit 99 - Credit 68 - reflects the permanent tax liability on the cost of transferred funds, transferred goods and the amount of VAT.
Procedure for filing a deduction
Reimbursement for expenses for charitable purposes is made only for the period during which support for organizations was provided. The declaration is completed in the year following the year in which the assistance was provided: for example, for donations made in 2021, the benefit is assigned in 2021. Later registration is possible, but no more than for the previous 3 years. For example, gratuitous payments were made in 2014-2018, but the benefit was announced only in 2019 - tax refunds are possible for 2016-2018. There is no deduction for 2014 and 2015. If the donation was made in 2012, 2014, 2018, and the intention to use the benefit was reported only in 2019, it is available to take only for 2021. For other years, no deduction is issued, since more than 3 years have passed.
ATTENTION! If the amount of compensation for charitable expenses in the current year is not fully spent, the balance is not carried forward to a future period.
For example, a citizen transferred 30 thousand rubles to charity. His income for the year is 100 thousand rubles. Since the amount of assistance is more than 25% of income for the year (100 thousand * 25% = 25 thousand), the deduction will be 25 thousand * 13% = 3250 rubles. The balance of 30 thousand - 25 thousand = 5 thousand cannot be transferred to a future period.
The registration procedure usually takes about 4 months, most of which is spent checking the data provided by the citizen. If approved, the funds are transferred to the account specified by the recipient.
Where to contact?
The deduction is issued through the tax office at the place of registration of the citizen. Reimbursement is not assigned through the employer (clause 2 of Article 219 of the Tax Code).
Correctly completed documentation, including a tax return, must be sent to the Federal Tax Service. It is allowed to do this by mail (registered letter with an inventory), in person or via the Internet (through the taxpayer’s account on the Federal Tax Service resource). No application required.
List of documents
To assign a deduction to the Federal Tax Service, you need to send a package of documentation, which includes:
- declaration 3-NDFL;
- passport (copy). It is possible to provide another identification document;
- data on income and contributions to the state budget. Information is provided by the employer using a special form. If during a period a citizen worked in several places, data is provided from all enterprises.
Certificate of income 2-NDFL
- copies of confirmations of donations made. These are bills, receipts, bank statements, and so on.
- copies of the contract, agreement for the provision of charitable support.
ATTENTION! If a citizen provided assistance in non-monetary form, it is important to reflect this in the documentation with a note on the value (according to the market) of the transferred property or services provided by a third party. In this case, an act of acceptance and transfer of assistance must be attached to the agreement.
- copies of documentation indicating the status of the recipient and the purpose of the assistance provided (founding papers, estimates, license to operate). There are no official mandatory requirements for providing such information to the Federal Tax Service, but in practice this allows you to speed up the procedure for assigning benefits and avoid questions from inspectors.
All papers are issued in the name of the applicant, their purpose is to show that it was he who incurred the costs of the charity. Tax authorities have the right to request additional documentation for control purposes.
If a third party made donations on behalf of the applicant, it is important to prove that they acted on behalf of the applicant. To do this, provide a notarized power of attorney, which is executed before sending a payment or providing other charitable assistance (Article 185 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Spouses have the right to receive benefits for each other, regardless of who made the donation and for whom the papers confirming the expenses were issued. In this case, no additional evidence or powers of attorney are required (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 1, 2015 No. BS-4-11/17171).
Letter No. BS-4-11/17171
Sample of filling out the 3-NDFL declaration on charity expenses
Proper execution of documents helps speed up the process of assigning benefits. You can fill out the declaration yourself or use the services of professionals (accountants, lawyers). The form can be obtained from the Federal Tax Service, but it is more convenient to download it from their official website. When visiting the Federal Tax Service in person to submit documents for deduction, it is recommended that the declaration is already filled out; this will significantly reduce the time of the registration procedure. To fill out the document yourself, it is advisable to use the provided sample.
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 1
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 2
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 3
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 4
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 5
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 6
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 7
Sample of filling out 3-NDFL for charity. Page 8
more about filling out a tax return in a special article on our website.
The state encourages and stimulates charitable activities in order to support organizations working in various fields: cultural, scientific, health, nature, animals, and so on. People who selflessly perform good deeds are offered a reward in the form of a partial refund of the funds they spent helping those in need.
Deadline for submitting documents
The deadline for submitting documents to receive a deduction is determined by the deadline for filing a declaration in Form 3-NDFL.
If the declaration states only deductions (standard, social, property), then it can be submitted along with other documents at any time after the end of the year in which the donations were made. There is no deadline for submitting such reports (clause 2 of Article 229 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the declaration states not only deductions, but also income that a person must declare himself (for example, from the sale of personal property), then the entire package of documents must be submitted no later than April 30 of the next year (clause 1 of article 229, clause 1 Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The declaration and all other documents for receiving a social deduction can be submitted to the tax office in person (through a representative), sent by mail with a list of investments, or transmitted electronically via telecommunication channels (clause 4 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).