Compliance with tax legislation is a mandatory condition for the functioning of any business entity. In order to carry out the control function assigned to it, the tax inspectorate has developed a reporting system, which includes a number of documents, each of which has its own rules for filling out and deadline for submission to the tax authority. Among such documents is personal income tax certificate 3 - what is it? You can find the answer to this question in this article, which discusses the main points that reflect the features of this reporting form.
Who is required to file a 3-NDFL declaration?
This should be done:
- individuals from among individual entrepreneurs (clause 1, clause 1, article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- practicing notaries and lawyers who have established law offices, as well as other persons engaged in private practice (clause 2, clause 1, article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons who received income from individuals or organizations (who are not tax agents) under a rental agreement, an employment contract and a civil law agreement, including a lease agreement for any property (clause 1, clause 1, article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- persons who received income from the sale of property owned for less than the minimum period of ownership, as well as from the sale of property rights (assignment of the right of claim) (clause 2, clause 1, article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons who are residents and received income from sources outside the Russian Federation (clause 3, clause 1, article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons who received other income that was not withheld by the tax agent (clause 4. clause 1 of article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- persons who have received winnings from the lottery or gambling in the amount of up to 15,000 rubles. (Clause 5, Clause 1, Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A complete list of persons required to submit a tax return is given in Articles 227 and 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Important points
The chapters of the Tax Code, as well as legislative acts, establish regulations for the submission of tax returns, with rules for calculation and mandatory deductions of payments.
The changes made to Article 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not force the payer to formulate statements about changes or additions that have occurred in the declaration with mandatory submission to the regulatory authority.
According to these changes, previously existing inaccuracies in the implementation of the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 81 were eliminated.
Deadlines for submitting the 3-NDFL declaration in 2020
The deadline for submitting the 3-NDFL declaration with the declared income is until April 30, the payment deadline is until July 15.
In 2021, by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 2, 2020 No. 409, the submission deadline was extended by three months - until July 30, 2021. The payment deadline for 2021 remains the same.
Please note that this year the payment deadline was earlier than the deadline for submitting the declaration. On this issue, the tax authority recommended that if you do not have time to submit the declaration on time, calculate the approximate amount of tax and pay it to the budget before submitting the declaration.
For individual entrepreneurs who are part of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the payment deadline has been postponed until October 15, 2020.
If the declaration claims deductions without income, the period for submitting the declaration is limited to only three years; the declaration can be submitted at any time during the year.
The 3-NDFL declaration is submitted to the tax authority in one of the following ways (clauses 3-4 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- on paper - directly to the inspectorate, by mail with a list of attachments or through the MFC;
- in electronic form - via TKS or through the taxpayer’s personal account.
Federal Tax Service information
On the main page of the service in section 3-NDFL, get information about previous declarations, if they were submitted.
Go to section 3-NDFL
Returns for past years will also be displayed here: social and property. That is, all tax deductions that were declared will be displayed in your personal account.
If such information was not submitted, then when asked about available declarations, the personal account page will look like this:
Lack of information on declarations
In what cases is it not necessary to submit a 3-NDFL declaration?
Citizens who have sold a property (apartment, house, room, land) that has been owned for more than a minimum period are completely exempt from income tax and the obligation to file a tax return.
From January 1, 2021, the conditions for exemption from personal income tax when selling real estate have changed. The minimum period of ownership of property was reduced from 5 to 3 years if the property (room, apartment, residential building or share in the specified property) is the only residential premises owned by the taxpayer (including joint property of spouses). This does not take into account housing that was purchased within 90 calendar days before the date of state registration of the transfer of ownership of the sold residential premises from the taxpayer to the buyer (Federal Law dated July 26, 2019 No. 210-FZ).
Until 2021, the minimum tenure of real estate was 3 years, but Federal Law No. 382-FZ dated November 29, 2014 introduced Art. 217.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which increased this period from 3 to 5 years for property that was acquired after January 1, 2021.
The three-year minimum time limit for ownership of a property has been retained only in cases where ownership of the property being sold has been obtained:
- by inheritance or under a gift agreement from an individual recognized as a family member or close relative;
- as a result of privatization;
- as a result of the transfer of property under a lifelong maintenance agreement with dependents.
From January 1, 2021, the sale of a single property (room, apartment, residential building) was added to these conditions. In all other cases, the minimum period of ownership of real estate will be 5 years.
After the sale of the property, next year the tax authorities will send you a notification about the need to submit a 3-NDFL declaration, regardless of the period of ownership of the apartment. The fact is that the tax authority sees only the date of alienation of the property without the detailed nuances of the transaction; it is obliged to warn you about the possible need to file a declaration.
If the period of ownership of the property exceeds the minimum period of ownership, there is no need to submit a declaration; in response to the notification to the tax authorities, it is necessary to send explanations and supporting documents (purchase agreement, gift agreement, certificate of registration of ownership, extract from the Unified State Register, certificate of payment share contribution, etc.).
This can be done through the taxpayer’s personal account on the tax website.
Obtaining an electronic key certificate
There are many more opportunities for using electronic signature, but obtaining it involves a personal visit to a certification center. In addition, this type of service is paid. And if the desire to purchase it is fulfilled, then registration in the LC takes place without problems. With this signature, you will have free access to your account on State Services.
Obtaining a certificate
On the new page, stop at “Generate a request for a certificate”, indicating the key password and confirming the data with sending a request to receive the necessary document (certificate).
Obtaining a certificate
How to determine the tenure of property
The period begins to apply from the moment the property is registered as ownership. But depending on the terms of the transaction, the beginning of the term is determined differently.
Let's look at the main examples.
Situation 1. Purchase of property under a sales contract
When purchasing an apartment, the tenure period begins from the date of state registration of ownership (Articles 131, 223 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Example
Krasnov entered into a purchase and sale agreement on December 25, 2021, and received the money within 5 days. I submitted documents for state registration on the day the contract was concluded. The registration period is set within 7 working days (depending on the method of submitting documents).
The certificate of state registration was registered on January 10, 2021 (including non-working days), received on January 11.
The ownership period begins on January 10, regardless of when the real estate purchase and sale agreement was concluded.
The tax-free sale of the apartment will be after January 10, 2021, if the apartment is the only one, otherwise - after January 10, 2022.
Situation 2. Purchase of property under an equity participation agreement
When purchasing an apartment under an agreement of shared participation, investment or assignment of the right of claim, the tenure period begins from the date of state registration of ownership of the apartment.
But a deduction for the purchase of an apartment can begin to be claimed from the moment the acceptance certificate for the apartment is signed (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 15, 2012 No. 03-04-05/9-1315; 02.14.2013 No. 03-04-05/9-103) .
Example
Inokov entered into a share participation agreement for the construction of an apartment in 2014. The apartment was built in 2015 and transferred under a transfer and acceptance certificate.
Ownership of the apartment was registered only in 2021. In 2018, the apartment was sold; the tenure in this case was two years.
Situation 3. Purchase of property under an agreement with a housing construction cooperative (HBC)
When purchasing an apartment from a housing cooperative, the tenure period begins with payment of the share contribution, receipt of a certificate of full payment and signing of the acceptance certificate, and not from the date of receipt of the certificate of state registration of ownership.
Registration of rights is of a declarative nature. Even if the apartment is not registered, copyright holders can take advantage of a property tax deduction based on a certificate of full payment.
Example
In 2009, Yakovlev entered into an agreement with the housing cooperative for the construction of an apartment. In 2011, the apartment was built, the share payment was paid in full.
In 2021, Yakovlev decided to sell this apartment, which required registering ownership.
In 2021, Yakovlev will receive a notification from the tax authority about the submission of a 3-NDFL declaration, in response to which he will only need to submit a certificate of full payment of the share contribution.
Situation 4. Acquisition of property as a result of privatization
If the apartment was privatized after January 1, 1998, the period of ownership begins from the moment of registration of ownership. And if privatization took place before January 1, 1998, the tenure period is calculated from the date of conclusion of the agreement on the transfer of property into ownership.
Example
Markelov privatized the apartment in 1991. In 2021, he decided to sell the apartment and issued a certificate of state registration of ownership.
In 2021, you do not need to submit a declaration and show income. In response to a notification from the tax authorities, you must attach a copy of the privatization agreement.
Situation 5. Property is inherited
If the apartment is inherited, then the period of ownership begins from the date of death of the previous owner.
Example 1
Loginova inherited an apartment from her grandmother in 2015. In 2019, she registered ownership and sold the apartment the following year. There is no need to submit a declaration, since the period of ownership is more than 3 years.
There are two exceptions to this case. If one of the spouses inherits an apartment acquired during marriage after the death of the other, the period of ownership is calculated from the date of state registration of ownership of the apartment.
Example 2
In 2014, the couple bought an apartment and registered it as joint shared ownership. In 2021, the husband died, in 2020 the wife decided to sell the apartment. In this case, there is no need to submit a declaration. The tenure period exceeds 3 years. Since the apartment was purchased during marriage, it is the common joint property of the spouses.
If the owner of one share in an apartment inherits another share as a result of the death of the owner, the period of ownership begins from the date of initial registration of ownership of the share in the apartment.
When the first share belongs to the new owner for more than 3 or 5 years, there is no need to pay tax when selling the entire property, even if the second share was received much later.
Example 3
In 2010, mother and son bought an apartment in shared ownership for ½ each. In 2021, the mother died, and the son received the inheritance.
In 2021, my son decided to sell the apartment. In this case, the period of ownership of the property is determined by the initial registration of ownership of the share in 2010.
Situation 6. The apartment was received free of charge
When receiving an apartment as a gift, the tenure period begins from the date of state registration of ownership.
Example
In 2014, Alferova received an apartment as a gift from her brother. In 2018, ownership was registered, and the apartment was sold in 2019.
In 2021, it will be necessary to submit a declaration, since the period of ownership was less than the minimum. In the declaration, you can declare a property deduction in the amount of 1 million rubles, since there are no documented expenses.
Situation 7. Built house
If the house is built independently, the period of ownership is calculated from the date of registration of ownership of this object.
Example
From 2010 to 2021, Sorokin built a house on a plot of land. Construction was completed in January 2021 and title was issued in March.
The house is the only real estate item. If sold after January 2021, it will not be taxed.
Situation 8. Property rights are recognized through the court
If the right to property is recognized in court, then the period of ownership begins from the day the court decision enters into legal force.
Example
In 2014, Novikov appealed the inheritance agreement in court. According to the inheritance agreement, all property went only to his brother.
In 2021, the court ruled that half of the property under the contract should become the property of Novikov. Registration of the right to property was completed in 2021, and implementation in 2020. The period of ownership of property begins in 2021, from the date the court decision enters into legal force.
How to reduce the payment in the declaration
When selling property before the expiration of the minimum period of ownership, the seller must fill out and submit a 3-NDFL declaration, and you can reduce the amount of tax by applying one of the deductions:
- the amount of actual expenses incurred related to the acquisition of this property, which must be documented: costs of acquisition, construction of real estate, mortgage interest (clause 2, clause 2, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- property deduction in the amount of 1 million rubles. when selling residential houses, apartments, rooms, garden houses, land plots (shares in listed real estate) or in the amount of 250,000 rubles. – when selling other real estate (for example, a car, a garage). This deduction is applied if expenses cannot be documented, for example, in a gift agreement (clause 1, clause 2, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, the sale of real estate worth up to 1 million rubles, as well as other property worth up to 250,000 rubles. is non-taxable.
An example of applying a deduction of 1 million rubles.
Modestov inherited an apartment in 2021 with a cadastral value of 3 million rubles. and decided to sell it that same year. The sale takes place before the minimum ownership period and there are no documented acquisition costs.
In this case, you can take advantage of a property deduction in the amount of 1 million rubles. The amount to be paid will be: RUB 260,000. = (3 million rubles – 1 million rubles)*13%
Example of using a deduction with confirmed expenses
Korablev bought an apartment in 2021 for 4.5 million rubles. and sold in 2020 for 4.2 million rubles, the cadastral value is 4.3 million rubles. Since the amount of expenses actually incurred is greater than the sum of the sale and the cadastral value, no tax will be payable in the declaration.
When selling property, an important indicator is its cadastral value. So, if the value of the property under the contract is less than 0.7 of the cadastral value, then the tax will have to be calculated based on the cadastral value.
Example calculation with cadastral value
Smirnov bought an apartment in 2021 for 3 million rubles. I sold an apartment in 2021 for 3 million rubles, the cadastral value of the apartment is 6 million rubles.
Although the amount of expenses actually incurred and the amount of income are the same and amount to 3 million rubles, tax will have to be paid, since the cadastral value is twice the actual value.
The amount to be paid will be: RUB 156,000. = (6 million rubles * 0.7 reduction factor - 3 million rubles (costs)) * 13%
How to prepare an XML file?
To generate a file document yourself, you need to understand where the XML format comes from. The formation of such a document is available in the Declaration program. To do this, it is necessary to fill in all the information about the taxpayer himself in the required forms, indicate his income and indicate tax deductions.
Having entered all the information necessary to generate the declaration, it is worth once again checking the correctness of all the indicators and, after making sure that the information entered is correct, select the next step, which is called the XML file.
File formation
Then, the program offers the opportunity to save the resulting file to any disk. Correct actions will result in a message that the file has been created and the XML extension is indicated at the end of this file after the dot.
Saving a file
Important point: the file name must not be changed under any circumstances. It is in this format and should be sent to the Federal Tax Service.
Main deductions claimed on the declaration
Residents of the Russian Federation who receive taxable income at a rate of 13% can claim tax deductions. That is, working citizens. The maximum amount that can be returned for a year is the amount of tax paid for the same year according to the 2-NDFL certificate. The deadline for submitting a declaration with the claimed deductions is not established and is limited to only three years.
Taxpayers have the opportunity not to wait until the end of the tax period, but to provide notice to their employer so that personal income tax is not withheld from their salary this year. To do this, you need to contact the tax office with the entire package of supporting documents, depending on the deduction.
After checking the documents in a month, the tax authority will prepare you a notice that must be submitted to the employer.
Sending a declaration
Now you need to click on the “Fill out/send the declaration online” button and click on the “Send the completed declaration” button.
Formation of a declaration for shipment
The window that appears will require you to indicate the year for which the declaration will be submitted and select a file document in XML format with the declaration. The operation is confirmed with the “OK” button.
Generating a file to send
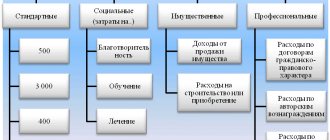
Types of tax deductions
Standard tax deductions
Available to certain categories of citizens and parents. In most cases, standard tax deductions are provided by the employer, who does not withhold personal income tax from wages. The deduction can be provided “for yourself” and for children.
Standard tax deduction for yourself
The following preferential categories of taxpayers may receive:
- disabled people;
- combatants, WWII veterans, military personnel;
- Chernobyl victims and other persons affected by radiation accidents or as a result of testing nuclear installations, nuclear weapons and space technology, as well as during exercises and other work at such facilities;
- other categories of persons listed in paragraphs. 1, 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Standard Child Tax Credit
Provided to parents, the spouse of a parent, adoptive parents, guardians, trustees, foster parents, the spouse of an adoptive parent who are providing for the child. That is, each parent receives such a deduction until the child reaches the age of 18 or until the age of 24 if the child is in full-time education. The single parent receives a double deduction.
To receive the deductions listed above, you must write an application at work and provide supporting documents (birth certificate, agreement with an educational institution, etc.).
To check whether you receive a deduction for children from your employer, you can take a 2-NDFL certificate for last year and look at the deduction codes in the certificate with numbers 126 (for one child), 127 (for the second child), 128 (for the third child) and etc. If they are, then you will be given a deduction. If you have the right to a deduction and did not receive it from your employer, then you can indicate them in the 3-NDFL declaration and return this amount to the tax office.
Social tax deductions
Provided if you have incurred the following costs:
- for the purchase of any medications for which there is a prescription from a doctor (since 2019, you can receive a deduction for the purchase of any medications, and not just from a special list, as before; to return, you will need a prescription from a doctor on an approved form and receipts from the pharmacy);
- for charitable purposes and donations (as a general rule, no more than 25% of your taxable income for the year);
- for your own education, as well as the education of your children, wards, brothers and sisters;
- for your own treatment, as well as the treatment of your spouse, parents, children and wards; Refunds for treatment of children are carried out until they reach 18 years of age;
- for non-state pension provision and voluntary pension insurance in one’s own favor or in favor of family members and close relatives, as well as for voluntary life insurance under contracts concluded for a period of at least five years in one’s own favor or in favor of a spouse, parents or children;
- to pay additional insurance contributions for a funded pension;
- to undergo an independent assessment of their qualifications.
The total amount of all social deductions declared according to the declaration cannot exceed 120,000 rubles. in year.
The deduction for expenses for educating children is limited to 50,000 rubles. per child for both parents. There are no restrictions on expensive types of treatment (code 2 is indicated on the certificate of payment for medical services). For conventional treatment, the limit is set at 120,000 rubles. (in the help the code is 1).
Investment tax deductions
The taxpayer who has carried out certain transactions has the right to investment tax deductions:
- With securities traded on the organized securities market, as a result of which income was received.
A deduction for the sale of securities is valid upon their sale if the documents were owned for at least 3 years in an amount of no more than 3 million rubles multiplied by the number of years of ownership. Provided that the securities were not placed in an individual investment account.
- He deposited personal funds into his individual investment account.
- Received income from transactions recorded on an individual investment account.
Property tax deductions
The taxpayer who has carried out certain transactions with property has the right to property tax deductions:
- sale of property (a deduction is applied in the amount of 1 million rubles);
- purchase of housing (house, apartment, room, etc.);
- construction of housing or acquisition of land for these purposes;
- redemption of property from a taxpayer for state or municipal needs;
- repayment of interest on targeted loans (credits) spent on the purchase of the specified real estate or received for the purpose of refinancing such loans.
Claim a tax deduction for the purchase of an apartment, house, room, etc. possible from next year after registration of ownership of the apartment. Pensioners can claim deductions for the three previous years that preceded the purchase of an apartment.
Housing must be purchased at your own expense, which can be documented. The maximum deduction for housing that can be received is 2 million rubles. That is, they will return 13% of this amount - 260,000 rubles.
The amount of the deduction for the year depends on the amount of personal income tax paid for the same year. Refunds can be made throughout your life until the entire amount is exhausted.
It will also be possible to receive a deduction when purchasing an apartment (house, etc.) for children (wards), regardless of age, if they are declared incompetent by the court.
Until 2014, it was possible to use the right to receive a property deduction for only one residential property. Since 2014, the right is limited only to the return amount of 260,000 rubles. That is, when purchasing a home after 2014 (provided that you have not previously exercised the right to deduct for housing), a refund can be made for several properties until the refund amount reaches the limit.
After the taxpayer uses the property deduction in full, that is, the entire maximum amount, re-providing this tax deduction is not allowed (clause 11 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When purchasing a plot of land for housing construction, you will be able to claim a deduction only after you have built a house and registered ownership (Clause 2, Clause 3, Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Part 1, Article 28 of Federal Law No. 218- dated July 13, 2015 Federal Law).
A deduction for repayment of interest on a loan spent on the purchase or construction of housing and land, or received for the purpose of refinancing a loan, is provided in the amount of interest expenses actually incurred, but cannot exceed 3 million rubles. and is limited to one dwelling. This restriction applies to loans received since 2014.
For loans received before 2014, the property deduction is provided without restrictions (clause 4 of article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clauses 1, 4 of article 2 of the Federal Law of July 23, 2013 No. 212-FZ).
Starting from 2021, it will be possible to receive a deduction when purchasing an apartment for mortgage interest when refinancing a loan, even if the refinancing was not done by a bank, but by another organization.
Professional tax deductions
As a general rule, professional tax deductions are provided in the amount of expenses actually incurred and documented. However, in exceptional cases, instead of taking into account actual expenses incurred, individual entrepreneurs can receive a deduction in the amount of 20% of the total amount of income they received.
List of income for which deductions can be obtained:
- income received by individual entrepreneurs;
- income received by notaries engaged in private practice, lawyers who have established law offices, and other persons engaged in private practice;
- income received from performing work (rendering services) under civil contracts;
- royalties or rewards for the creation, performance or other use of works of science, literature and art, rewards to the authors of discoveries, inventions and industrial designs received by taxpayers.
Tax deductions when carrying forward losses from transactions with securities and transactions with financial instruments of futures transactions traded on the organized market
Quite often, for persons carrying out transactions with securities and financial instruments of futures transactions (FISS), at the end of the year, the amount of expenses exceeds the amount of income from such activities.
The resulting negative financial result can be taken into account by the taxpayer either when calculating tax in the current period (if a profit is made from other transactions), or (if there is no taxable income from other transactions in the current year) the resulting loss can be carried forward to subsequent years (Article 220.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is necessary to remember the following restrictions:
- It is not allowed to carry over to future periods losses incurred on transactions with securities not traded on the organized securities market, and on transactions with financial instruments of futures transactions not traded on the organized market;
- the loss is taken into account when calculating tax on the relevant types of transactions;
- a loss received from transactions with securities traded on the organized securities market can reduce the tax base only for transactions with securities traded on the organized securities market;
- a loss received on transactions with financial instruments of futures transactions traded on the organized securities market can reduce the tax base only for transactions with financial instruments of futures transactions traded on the organized securities market.
After the declaration is received by the inspectorate, the tax authority will begin a desk audit - it is carried out within 3 months. If during this time the taxpayer submits an updated tax return, the countdown of the deadline will begin again.
After checking the declaration, the tax authority will make a decision on a refund, partial refund or refusal to provide a deduction.
A refund application with account details can be submitted simultaneously with a package of supporting documents or after a desk tax audit.
The refund is made within one month from the date the tax authority receives such an application. From 2021, the return application will be part of the 3-NDFL declaration.
How to reduce the fine
In case of untimely submission of the 3-NDFL declaration, taxpayers face a fine under paragraph 1 of Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The amount of the fine on a declaration with income without payment is 1,000 rubles. or 5% of the unpaid amount for each day of delay, but not more than 30% of this amount and not less than 1,000 rubles.
Until 2021, a taxpayer could not be fined if the return was not submitted to the tax office. From 2021, if a 3-NDFL declaration is not submitted, the tax office will simply conduct a desk audit without it and will add an additional fine based on the cadastral value of the housing. When selling, the income will be the transaction price or 0.7 of the cadastral value (whichever is greater in amount). When donating, the cadastral value of the property will be considered income.
The amount of the fine can be reduced by at least two times (or more) if there is at least one mitigating circumstance. The list of mitigating circumstances is not exhaustive: the more there are, the less the fine may be.
The minimum fine of 1,000 rubles can also be reduced. The list of mitigating circumstances is given in Art. 112 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- committing an offense due to a combination of difficult personal or family circumstances;
- committing an offense under the influence of threat or coercion or due to financial, official or other dependence;
- difficult financial situation of an individual held accountable for committing a tax offense;
- other circumstances that may be recognized by the court or tax authority considering the case as mitigating liability.
The last point may include the following:
- committing such an offense for the first time;
- the presence of minor children or children under 24 years of age who are in full-time education;
- advanced (retirement) age;
- minor period of non-submission of a declaration or non-payment of tax (from 1 to 10 days);
- repentance and admission of guilt;
- lack of intent to commit a violation.
The more mitigating circumstances are indicated in the petition, the greater the chance of reducing the amount of the fine by more than half.
Legislators will change the form starting in 2021
The Federal Tax Service published order No. ED-7-11/ [email protected] , which changed the rules and sample for filling out 3-NDFL based on the results of 2021. This means that the report for the current year will have to be filled out in a new way; the order comes into force on 01/01/2021.
IMPORTANT!
For reporting for 2021, use the new form!
Main changes in the 3-NDFL declaration:
- the field “Registered under No.” has been removed from the title page of the form;
- Section 1 “Information on the amounts of tax subject to payment (addition) to the budget / refund from the budget” is divided into two paragraphs: in the first, taxpayers indicate information on the amounts of tax subject to payment (addition) to the budget (except for amounts of tax paid in accordance with from clause 7 of Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or return from the budget; in the second - information about the advance payment paid in accordance with clause 7 of Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- an appendix to Section 1 “Application for offset (refund) of the amount of overpaid personal income tax” was introduced;
- a separate calculation sheet has been added to Appendix 3 “Calculation of advance payments paid in accordance with clause 7 of Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”.
IMPORTANT!
They will change the barcodes on all pages, which is why the old form will no longer be accepted. From 2021, the declaration will have to be filled out from scratch.
Last year, the rules for numbering adjustments changed. The new wording sounds like this: continuous numbering is provided, where the “adjustment number” for the primary declaration takes the value “0—”; for updated declarations, the number is indicated sequentially (“1—”, “2—”, “3—” and so on). It is not allowed to fill out an adjustment number for an updated declaration without a previously accepted primary declaration.