During or after completion of an on-site or desk-type tax audit, inspectors may need additional information about the activities of the tax entity being examined related to its partners or other structures. In such situations, it may be necessary to conduct a counter-check.
The concept of “counter inspection” was removed from the content of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (01/01/2007), but in practice a similar name was retained for the procedure for requesting information and documents from enterprises related to specific transactions to confirm the accuracy of the information provided by the inspected legal entity (Article 93 of the Tax Code RF).
What is meant by the term “counter check”
The concept of “counter tax audit” actually existed, but until 01/01/2007, when from para.
2 tbsp. 87 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation excluded such additional tax control measures carried out during desk or field tax audits. Its essence was simple: the tax inspectorate requested documents from the counterparties of the taxpayer being inspected, and then compared the information received with that reflected in the organization’s documents.
However, instead of the term “counter check”, excluded from the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a new article 93.1 was introduced into the code. It involves requesting information and documents about the taxpayer and specific transactions. At the same time, within the framework of such requests, the tax authorities have significantly increased powers.
However, in business practice, such events are still called a counter tax audit, since their essence has not changed: requesting documents and information from third parties to verify the accuracy of the information provided by the taxpayer being audited.
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, check whether you have correctly prepared the documents for verification. If you don't have access, get a free trial of online legal access.
Why documents must be submitted as part of the counter, read the material “The counterparty is obliged to submit the documents required by the tax authorities .
How to quickly send a large number of documents to the Federal Tax Service
Often the number of documents specified in the requirement amounts to tens, hundreds and even thousands. It takes a lot of time and effort to prepare and send such an impressive package to the inspection. And even if the Federal Tax Service extends the deadline for submitting documents, it can be difficult to meet it.
In this regard, many companies and entrepreneurs use modern services that make it easier and faster to send documents to the inspectorate. Such services, in particular, include “Connector Kontur.Extern”. It makes it possible to send tens of thousands of electronic documents to tax authorities at a time, while approximately 9 thousand documents are processed per hour.
Through the “Connector” you can transfer to the Federal Tax Service any electronic documents created in approved formats (for example, invoices, TORG-12 invoices, etc.). Such documents are sent in the form of XML files. Also, “Connector” sends scanned images of any documents created on paper: acts, contracts, bills, etc. Scanned images are transmitted in the following formats: pdf, jpg, png, tiff. An inventory of sent documents is generated automatically.
Taxpayers who have to submit a lot of “primary information” to the Federal Tax Service proceed as follows. They install the “Kontur.Extern Connector” on different computers and start parallel sending. Thus, the risk of missing the deadlines for submitting documents is reduced to zero.
Connect to the Kontur.Extern system
Counter audit of the tax inspectorate: its essence and purpose
Despite the name, counter check, according to Art. 87 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is not included in the list of tax audits. The fact is that based on its results, decisions are not made that are binding on the taxpayer. This is just one of the activities carried out as part of tax control. As a result of its implementation, the tax inspectorate receives information about the taxpayer from his counterparties and partners. This essence of the counter-check can be judged by paragraph 1 of Art. 82, paragraph 1, art. 93.1, para. 3 paragraph 6 art. 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 16, 2007 No. ШТ-13-06/ [email protected]
The objectives of the counter audit of the tax inspectorate are as follows:
- checking the reality of the existence of a counterparty cooperating with the taxpayer on transactions of interest to the Federal Tax Service;
- the reality of transactions performed by the taxpayer;
- reconciliation of information on financial and economic transactions that is available to the audited taxpayer and its counterparty.
If discrepancies are detected between the data of the counterparty and the taxpayer, tax inspectors examine this data to determine whether these discrepancies affected the tax base or not. If the tax base has decreased, the data obtained is reflected in the audit report, the documents are attached to the report and are subsequently used as evidence of the taxpayer’s guilt in committing an offense.
It may happen that the taxpayer under audit remains above suspicion, but questions arise regarding the counterparty. In such circumstances, the counterparty should first wait for a desk audit, and then an on-site audit (if a preliminary analysis has confirmed its unreliability).
Basic Concepts
- A tax audit is an action that is procedural in nature. This check must be carried out by the tax office. The main purpose of the inspection is to identify possible violations. During this audit, tax control data is reconciled with the data reflected in reporting declarations.
- Declaration - A legal act that formulates the basic principles, as well as the goals of the two parties.
- A counter inspection is an inspection conducted by the Federal Tax Service. The goal is to study the financial and economic activities of the organization’s counterparties.
- A document is a different kind of information carrier that has details. The document records all the basic information that reflects the activity.
- Counterparty is the party with whom the contract was concluded. The counterparty can be either an individual or a legal entity who is entrusted with fulfilling various types of obligations.
In what cases is a counter tax audit carried out?
pp. 1 and 2 tbsp. 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that a counter tax audit is carried out in the following cases:
1. If an on-site or desk inspection is carried out (paragraph 1, clause 1, article 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the on-site inspection may even be suspended while counter requests are sent. This norm is regulated by sub. 1 clause 9 art. 89 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; in addition, it is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 28, 2008 No. 03-02-07/1-433.
2. After the counter or desk audit has already been completed (paragraph 2, clause 1, article 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, a counter-check is carried out during the period of consideration of the materials and appears here, in accordance with paragraph. 3 paragraph 6 art. 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as an additional tax control measure.
In addition, the tax authority has a little more time to conduct a counter audit. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not clearly define when tax control measures end during an audit. Therefore, courts may accept documents received in response to requests made after the completion of the on-site inspection, but before drawing up the final act. There is an instruction in this regard by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, contained in the ruling dated February 11, 2010 No. VAS-24/10.
Apparently, the Supreme Court takes into account the norm of paragraph 2 of Art. 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which determines that the tax authority may require information from third parties outside the framework of official inspections. However, inspectors have the right to make such requests only for specific transactions.
In what other cases a counter-inspection may be ordered, read the article “The inspection may request documents from you as part of an inspection of your counterparty’s counterparty .
Why are they checking?
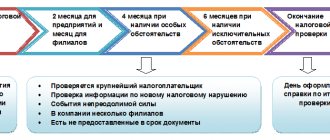
The basis for a desk audit is the very fact of filing a tax return; the audit is carried out automatically; an order from management is not required for this.
For an on-site visit, on the contrary, the sanction of the manager is needed - the corresponding inspection plan is approved. The most common reason for inclusion in the plan is deviation from industry averages (tax burden, wages, profitability). In addition, the reason will be losses (especially several quarters in a row) and a change in tax “registration”. You can assess the risks and likelihood of an audit yourself - the criteria are publicly available. You can also independently calculate the tax burden and compare it with industry average indicators - there is a calculator on the tax office website.
What documents are the tax authorities entitled to request?
When conducting inspections, tax authorities have the right to demand any documents relating to the activities of a particular taxpayer. This is defined in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 9, 2012 No. 03-02-07/1-246 and dated October 8, 2012 No. 03-02-07/2-136.
According to the internal regulations of the Federal Tax Service, such documents are contracts, invoices, acceptance and delivery certificates, invoices - everything that may contain information about the interaction of the taxpayer being audited with counterparties.
Whether it is necessary to submit documents if their exact details are not indicated in the request, find out here.
The tax authorities may request from the counterparty information about the taxpayer who is being audited.
It should be borne in mind that if documents or information do not relate to the subject of the audit, then the tax authority does not have the right to demand their presentation.
Example
When conducting a desk audit, the tax inspectorate requested the staffing table from its counterparty, Gerkon LLC. Such a requirement is unlawful, since the staffing table of Gerkon LLC cannot be used to judge the activities of the company being inspected, even indirectly.
Arbitration courts share a similar opinion, which is reflected, in particular, in decisions of the FAS of the East Siberian District dated 02/25/2013 No. A10-2227/2012, FAS of the North-Western District dated 07/30/2010 No. A56-59024/2009 and the FAS of the Far Eastern District dated November 16, 2012 No. F03-5399/2012.
It may happen that the document is not directly related to the activities of the taxpayer being audited, but there is a mention of his business transactions. Such documents are likely to be requested. For example, when a counterparty's sales book contains a record of one transaction with a taxpayer. The tax authority has every right to request it in accordance with Art. 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 19, 2012 No. VAS-17466/11).
However, it is possible to find out the validity of the request only in court, where qualified lawyers will check whether the requested document is really related to the activities of the taxpayer.
But the period to which such documents relate is not limited. For this reason, inspectors quite often request materials not only for the period for which the inspection is being carried out, but also for a wider time frame. The Ministry of Finance, in letter No. 03-02-07/1-519 dated November 23, 2009, confirmed that the tax authorities have such powers.
What to do if you have already submitted documents to the inspection, and it again asks you to submit them as part of a counter inspection, read the material “Can the inspection request for a “counter meeting” documents that have already been submitted in connection with a desk or field inspection? .
Price issue
Tax statistics for last year: 3.5 million desk audits revealed violations. Fines, penalties and additional taxes in total exceeded 55 billion rubles. The average bill is 16 thousand (higher for Moscow). In total, there were almost 68 million such checks, that is, sanctions followed in every twentieth case. In other words, when you file a return, there is a 5% chance that you will have to pay another 16 thousand. Or more.
During the same time, there were 14,152 on-site inspections. Violations were found in 13,838 cases, this is almost 98% - the same guarantee of success that we talked about above. Fines, penalties and additional charges amounted to 307 billion. The average bill in the country is 22.2 million. And that is not all.
Request procedure
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation during tax audits, the tax authority that conducts it has the right to request documents. It is he who can send an order to the tax office, where the person who has information about the activities of the taxpayer being inspected is registered.
These and other rules are established by Art. 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the Procedure for interaction of tax authorities on the implementation of orders for the requisition of documents (information), approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 7, 2018 No. ММВ-7-2/ [email protected]
The counter-verification procedure according to these standards is as follows:
- First, the inspection inspection sends an order to the tax authority at the place of registration of the person who has information about the taxpayer being inspected. The order is drawn up in writing and contains a request to obtain documents or information (possibly both) from this person.
- The local inspection is given 5 working days to formalize and send the request to the counterparty. This request, containing a list of documents and information, must be accompanied by a copy of the original order.
- The counterparty, in turn, is also given 5 working days to respond to the local tax authority. Within this period, he must either provide all the requested documents or report the absence of any. If difficulties arise in preparing the materials needed by inspectors, you can contact the tax authority with a request to extend the deadline. By decision of the inspectorate, the time frame for submitting a response may be extended.
When preparing the materials necessary for inspectors, you can contact the tax authority with a request to extend the deadline. By decision of the inspectorate, the time frame for submitting a response may be extended.
In what form to submit a notification about the impossibility of providing documents (information) on time, we tell you here.
Is it possible to refuse tax authorities if they did not send a complete package of documents in a request for a counter ticket? Find out in ConsultantPlus. Learn the material by getting trial access to the system for free.
What to do if documents are requested again
The Federal Tax Service has the right to request documents again, and the taxpayer, in turn, has the right not to submit papers that were previously submitted. In this case, the taxpayer needs to notify the inspectorate that these documents have already been submitted. The notification should indicate the details of the document with which the requested contracts, invoices and invoices were submitted or to which they were attached, and the name of the inspection that received it. This must be done within the deadlines designated for submitting the requested documents.
This rule does not apply to original documents submitted by the taxpayer and received back by him, as well as to documents lost by tax authorities “due to force majeure circumstances.” Such papers must be submitted a second time.
Results
Tax authorities have the right to request from you documents or information about your counterparty as part of the so-called counter audit - a special tax control event. The number of documents requested and the period for which they are requested are not regulated in tax legislation.
It is necessary to submit documents (information) about the counterparty or report their absence within 5 working days from the date of receipt of the request from your tax office.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 7, 2018 No. ММВ-7-2/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Deadlines and forms of submission
Having received a request to provide documents (information), the company must comply with it within five days or, within the same period, report that it does not have such documents (information).
At the request of the organization, the period may be extended. But if the company does not submit the documents and ignores the requirement, this will be a tax offense, liability for which is provided for, as mentioned earlier, by Article 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, for failure to provide information necessary for tax control, paragraph 1 of Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation establishes a fine for officials in the amount of 300 to 500 rubles.
The requirement can be submitted to the head (representative) of the organization personally against signature or electronically via telecommunication channels (TCS). If it is impossible to transmit the demand using the indicated methods, it is sent by registered mail and is considered received after six days from the date of sending.