The main task of the tax authorities in 2021 was to whiten the income of citizens. But the pandemic disrupted the plans of tax officials; mass audits were postponed until better times. However, by the end of the year, some citizens had already begun to receive information letters from the Federal Tax Service demanding that they provide justification for the reasons for the discrepancy between their income and expenses.
And in the near future we will have total control of income and expenses. It should be noted that the state has not carried out such a large-scale fiscal attack on the population since the early 1990s.
How this will happen, what the tax authorities have already begun to check and what awaits us in the near future, I will tell you in today’s publication.
On-site inspection of the “simplified”
The basis for conducting an on-site tax audit, as a rule, is the need to make sure that the taxpayer has the right to use the simplified tax system, that is, complies with all the requirements established for “simplified tax”, and also that he correctly calculates the simplified tax.
Potential auditees are those “simplified” who have been declaring unprofitable activities for many years, or those who are often transferred from one Federal Tax Service Inspectorate to another. Find out who can apply the simplified tax system from the publication.
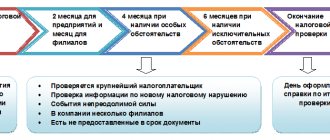
On-site inspection on the basis of clause 8 of Art. 89 of the Tax Code begins from the day when the tax authority made a corresponding decision to conduct an audit. The inspection lasts up to 2 months, although in some cases this period can be extended to 4–6 months (Clause 6 of Article 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). All grounds for extending the inspection are mentioned in clause 4 of Appendix 2 to the Federal Tax Service order dated December 25, 2006 No. SAE3-06/ [email protected]
Read about the procedure for extending an audit in our article “How and when an on-site tax audit can be extended .
The audit may cover all activities of the taxpayer over the last 3 years. All documents available to him are checked, including accounting ones, because since 2013, “simplified” legal entities have an obligation to keep accounting records. If necessary, during the audit, an inventory, inspection, seizure of documents and other special tax control activities may be carried out.
Based on the results of the inspection, a certificate is issued, and after 2 months - a report (Clause 1 of Article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ATTENTION! In connection with the coronavirus pandemic, Prime Minister M. Mishustin instructed to suspend all on-site tax audits until May 1, 2020 (instruction of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 18, 2020).
What documents should an entrepreneur have?
Tax and individual entrepreneurs - how to register with the Federal Tax Service and what is needed for this
A full check of an individual entrepreneur involves the consideration of a number of documents that are directly related to the activity. What documents should an individual entrepreneur have in case of an audit? The following papers are of greatest importance:
- certificate of registration of a person as an individual entrepreneur. It will help you find out at what point the individual entrepreneur began to conduct its activities and function;
- documents confirming registration with the Pension Fund and the Health Insurance Fund;
- tax returns for periods of activity;
Entrepreneur's documents
- financial statements;
- bank statement confirming the existence of a current account;
- cash reporting (for retail trade and similar activities).
These are the basic documents that every entrepreneur needs to successfully pass the audit. In some cases, documentation may be required to demonstrate eligibility for a benefit.
Important! If the activities of an individual entrepreneur require a license, then this license must also be provided to tax office employees.
Desk check on the simplified tax system
Conducting a desk audit is regulated by Art. 88 Tax Code. The audit is carried out by tax inspectors without visiting the taxpayer. Sometimes the taxpayer may not even know about such an audit until the inspectors require explanations or documents explaining the unclear points identified in the declaration.
Find out what reports a simplified student must submit in 2021 here.
If, as a result of an audit, violations of tax legislation are revealed, the inspectors draw up a report within 10 days after its completion. This procedure is specified in paragraph 1 of Art. 100 Tax Code.
Desk and on-site audits can be combined in terms of time: during a desk audit, the reports submitted by the taxpayer for the current year are examined, and during an on-site audit, for a longer period, and there may be broader grounds for its appointment. The possibility of carrying out 2 types of inspection simultaneously is indicated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated March 13, 2014 No. ED-4-2/4529.
The criteria by which tax authorities check a declaration under the simplified tax system are discussed in detail in the expert opinion of ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system and start learning the material for free.
Disputing the results
The results of a tax audit can be very disappointing for an entrepreneur. And this is predictable if the entrepreneur actually committed gross violations. If the entrepreneur does not agree with the results, he can file a complaint with a higher tax authority. This can be done during tax actions if they involve gross violations of current legislation. In this case, the entrepreneur draws up a special complaint and sends it to higher authorities and the prosecutor's office.
Disputing the results
Disagreement with the results can be expressed in a special act, which will be provided within a certain time from the moment of inspection. There, violations in the procedure are indicated and protests are expressed about the results. This act is sent to higher tax authorities.
Note! If the entrepreneur’s claim is found to be legal, a re-inspection will be carried out to change the decision. Otherwise, the complaint will be rejected and the results will remain the same. But even in this case, there is a chance to change the decision of the tax authorities by applying to an arbitration court.
Features of checking the simplified tax system 6%
Those who apply the simplified tax system at a rate of 15% must be prepared to document both their income and their expenses. As for conducting an on-site audit of taxpayers who have chosen a simplified taxation system with the object “income,” the inspectors may also request expense documents from them. First of all, you will need documents confirming the payment of insurance premiums, because they have a direct impact on the calculation of tax.
Which insurance premiums reduce the simplified tax, see the material “Single Tax under the Simplified Taxation System (STS)”.
If a “simplified person” (6%) pays a trade fee for one of several types of activity, he can take the paid fee into account when calculating the simplified tax system if he organizes separate accounting of income and the simplified tax system for the type of activity for which the trade fee is paid. The presence of such accounting is also under the close attention of tax authorities when checking the “simplified tax”.
The article “How to calculate the trading fee for individual entrepreneurs?” will help you calculate the amount of the trading fee..
Also, documents on expenses may be needed in case of checking the correctness of the accrual and withholding of personal income tax, if the simplifier acts as a tax agent.
For more information about what you need to know about accounting in the simplified tax system with the taxable object “income”, read our article “USN “income” in 2019-2020 (6 percent): what do you need to know?” .
How does the tax office find out about Internet income?
It would seem that the Internet is a completely uncontrolled system by the state. But here, in fact, it all depends on what amounts we are talking about. If you have several thousand in your e-wallets, naturally, no one will check you because of such a trifle. But if large enough amounts are transferred between accounts, these transactions fall under the law on the national payment system. Payment systems between which the transfer took place must transmit information to the state. It is very easy to understand whether the transfer data will be transferred to government agencies. When you try to transfer a large amount, the system will ask you to enter your personal data and confirm your identity. In addition to entering data, you may be asked to send scans of the necessary documents.
If funds are withdrawn from electronic wallets to a bank card, the bank takes control of the finances there. And the same system works here as with regular bank accounts.
You can avoid electronic payments by using the cash on delivery system. However, Russian Post is also a state organization. The Federal Tax Service can request from it data in your name and receive information about all payments made.
Tax audits of simplified people and new art. 54.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation: what to pay attention to
Art. 54.1 appeared in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation quite recently (introduced by law dated July 18, 2017 No. 163-FZ) and is devoted to issues of unjustified tax benefits.
You will become familiar with the concept of “unjustified tax benefit” in the material “Presumption of good faith of the taxpayer - a new article in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” .
When conducting desk and field audits, controllers will collect evidence of the reality of transactions, and will also look with particular scrupulousness for evidence of deliberate tax evasion.
For example, a “simplifier” may be suspected of deliberate tax evasion if he fragmented his business solely for one purpose - to reduce the tax burden through the use of special tax regimes. The controllers themselves directly indicate this in their letter No. ED-4-2/13650 dated July 13, 2017 (clause 13.2 of the Methodological Recommendations for establishing, during tax and procedural audits, circumstances indicating intent in the actions of taxpayer officials aimed at non-payment of taxes ).
Get free trial access to ConsultantPlus and find out 17 criteria for assessing business fragmentation, which tax authorities focus on when conducting an audit.
Thus, a “simplifier” needs to be ready to prove a reasonable business purpose for his actions (for example, the purpose of splitting up a business), as well as take care of documentary support for the reality of his transactions, confirm due diligence when choosing counterparties, etc.
Question
Our organization uses the simplified tax system (income minus expenses). 03/29/2017 a declaration under the simplified tax system for 2021 was sent electronically and accepted by the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate. Upon a call from the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate, we personally received it on 07/04/2017. The request for clarification, dated June 28, 2016 (exactly 2021), hereinafter reads: “IFTS. in accordance with Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it reports that during a desk tax audit based on a declaration under the simplified tax system for 2021, which revealed errors and (or) contradictions between the information contained in the documents, or inconsistencies in the information provided by the taxpayer, information available to the tax authorities and received during tax control, there is a discrepancy between the amount of income (expenses) reflected in the tax return and the amount of receipts (write-offs) to the r/account (from the r/account). Reflection in the tax return of a loss based on the results of the organization’s financial and economic activities for 2021. Provide an explanation of the discrepancy and reflection of the loss. Explanations must be confirmed with documents: D&R book for 2021, loan agreements, cashier-operator’s journal for 2021.” We provided an explanatory note on July 11, 2017. At the moment, today is July 26, 2017, there are no verification documents from the tax office. We twice called the inspector of the Federal Tax Service checking us, who insists that we submit an updated declaration under the simplified tax system for 2021. We have for 2021. It’s really not a big loss, and there are no errors in the declaration. There is also another point: on April 24, 2017, we submitted an application to the Federal Tax Service to begin the procedure for reorganizing a closed joint-stock company into an LLC. The 3-month period has expired, after which we must submit form P12001 “Application for state registration of a legal entity created through reorganization.” Questions: 1) Does the Federal Tax Service behave lawfully in terms of the timing of the desk audit? 2) Can the Federal Tax Service refuse to reorganize based on this inspection?
Results
Checks of simplified tax authorities are not much different from checks of taxpayers working under the general taxation system. The exception is that there are fewer reasons for conducting a tax audit of the activities of businessmen using the simplified tax system.
All information about tax audits is contained in our “Tax Audits” .
Usually, if tax inspectors do not have any questions regarding the declaration, then an audit should not be expected. Nevertheless, you should carefully maintain accounting and tax records and store all documentation, because the decision to conduct a desk audit is executed by inspectors immediately, without prior notification to the taxpayer, and the audit period during an on-site audit covers 3 years.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 18, 2020
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Inquiries to banks
It doesn’t matter what type of activity you are engaged in, you are an individual entrepreneur or an LLC, or you earn money through freelancing, in any case you must have a bank account where the money goes. Even if you are not a legal entity and have not officially registered any business at all, you probably have a bank card that receives funds. If these funds come in regularly and they are quite large in size, the tax service may have questions for you. The bank is obliged to transmit data on such charges to the Federal Tax Service if it requests information.
Moreover, the bank must notify the state of various suspicious transactions. The amount of these suspicious transactions must exceed 600 thousand rubles. Only then can it arouse the bank's suspicion. For example, if a payment was transferred for this amount or higher, the bank is obliged to report this to the relevant authorities. It is considered suspicious if the account receives several transfers in a row. If the tax office discovers that this income was hidden by the company or a smaller amount is indicated in the declaration, this can lead to serious problems.
Also, based on Article 86 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (which was amended in 2014), the bank is obliged to notify the Federal Tax Service about the opening of a bank account by an individual. This does not threaten conscientious citizens; the tax office, most likely, will not even be interested in how much money you have in this account. But if your company comes under suspicion, all accounts will be checked, especially new ones.
However, the bank does not notify tax authorities about all banking transactions of the company. It’s better to say that it doesn’t notify you of practically anything. And the tax office has other things to do than check the receipts in the bank accounts of all small companies. Therefore, there is no total control here. The Federal Tax Service may be interested in you if, for example, the company with which you cooperate was suspected of tax evasion.
There are other cases like this. The company pays employees a “gray” salary, and the employees put this money on a bank card. The regularity of deposits and their amount may seem suspicious to the bank, and this will be reported to the Federal Tax Service. Then the tax authorities will check the employees, and with them the entire company.