Kontur.Accounting is a web service for small businesses!
Quick establishment of primary accounts, automatic tax calculation, online reporting, electronic document management, free updates and technical support.
Try it
Kazakhstan and Russia are members of the EAEU customs union, so they have a single customs territory. This makes importing easier: there is no need to go through customs clearance, declaration, or pay duties. At the same time, the import of goods from the countries of the customs union differs from imports from third countries in the procedure for paying VAT and the rules for preparing documents. Read the article on how to register the import of goods from Kazakhstan and pay taxes.
Rules for importing goods into the Russian Federation
The rules that apply when calculating VAT on goods transported to the territory of the Russian Federation are determined by the presence of customs at the state border. Tax is calculated at the time of import of goods.
The procedure for calculating and paying royalties is subject to customs legislation. The tax is paid to the customs service.
Between a number of states that were previously part of the Soviet Union, customs was abolished.
These states were united into the EAEU - the Eurasian Economic Union. Now the import and export of goods across the borders of the countries participating in this treaty follow the same rules of interaction.
These rules were set out in the agreement on the EAEU, which was concluded in Astana in 2014.
You can read the text of the agreement on our website.
When importing from Kazakhstan, as well as when importing goods into Kazakhstan from Russia, the following customs rules are now relevant in relation to VAT:
- taking into account the absence of customs, the importer undertakes to independently calculate VAT and pay it;
- the tax base is calculated taking into account the cost of exported products;
- the price indicated in foreign currency is recalculated at the exchange rate on the date the goods were accepted for accounting;
- the optimal period is the 20th day of the month, which follows the month in which the export products were imported. If the end of the period coincides with a weekend or holiday, then for the Russian Federation it is possible to shift to another date that corresponds to the nearest weekday.
More detailed rules can be found by following the link.
It is also recommended that you read Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Watch the video: registration of goods when importing from EAEU countries.
Read on our website: list of prohibited goods for import into Russia.
Composition of reports generated upon import from the EAEU
The reporting created when importing from the EAEU countries is distinguished (clause 20 of section III of Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the EAEU):
- the emergence of a unique report form for this situation - an application for the import of goods (approved by the protocol “On the exchange of information in electronic form between the tax authorities of the EAEU member states...” dated December 11, 2009);
- application of a tax return of a special form KND 1151088 (approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 27, 2017 No. SA-7-3 / [email protected] );
- the emergence of an obligation, together with the application and declaration, to submit documents confirming the payment of tax and information included in the application both in terms of data about the supplier and in relation to the calculation of VAT.
The specific set of supporting documents depends on the conditions under which the delivery is made. As a rule, these include a contract (supply or intermediary) and shipping documents. There may be an invoice and an information message containing information about the third party to the agreement, if there is such a party.
All documents forming EAEU-VAT reporting may be submitted to the tax authority both in paper form (confirming documents in certified copies) and electronically. The application, prepared on paper, must be executed in four copies, two of which, after the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate mark appears on them, should be sent to the foreign supplier.
Recommendations from ConsultantPlus experts will help you fill out a declaration on indirect taxes when importing from the EAEU. Get trial access to the system for free and go to the Ready-made solution.
Procedure for payment of VAT
When goods are imported into Russia, VAT is paid by the importer. This applies to everyone who makes purchases in Russia.
The difference is that when transporting products from countries that do not belong to the member countries of the customs union, the tax is paid when passing customs control.
When importing from the EAEU, money is transferred by the entrepreneur to the budget through the Federal Tax Service.
This applies to goods that were produced on the territory of states that are members of the EAEU and are put into free circulation on the territory of the Eurasian Economic Union.
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1 : Is it necessary to calculate VAT on imported goods from Kazakhstan if the Organization is on a simplified basis?
Answer : Organizations, regardless of the taxation regime, pay VAT when importing goods from the EAEU and submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service. But only companies on OSNO can deduct VAT. But there is a list of imports that are exempt from VAT when imported into the Russian Federation (Article 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Question No. 2 : Is it necessary to submit a VAT return if there have been no transactions on imported goods?
Answer : The special declaration must be submitted monthly. There is no need to submit such a VAT return if within a month:
- imports were not accepted for accounting
- the lease payment was not due in accordance with the agreement
How is tax calculated?
The price of products that are imported into Russia can be determined under a sales contract. The transaction price reflected in the contract and the one paid to the seller by the buyer are taken into account. The tax base for VAT does not increase due to the presence of expenses for the transportation of goods.
The final tax amount that is paid to the budget can be calculated using the following formula:
price of imported products + excise taxes (relevant for excisable products) x tax rate (10–18%).
Probability of error
The tax amount is billed by the seller according to the documentation, in accordance with current legislation.
Against this background, the person purchasing the goods determines the VAT independently and then makes payments to the Federal Tax Service.
The tax base is necessarily calculated on the date when the goods were accepted for accounting.
It is necessary to proceed from the final price of the product. If it was purchased for foreign currency, then the amount in rubles can be determined by converting it into foreign currency at the Central Bank exchange rate. In this case, the date when the imported products were accepted for accounting is taken into account.
This base is multiplied by the tax rate. Then the amount to be deposited is determined.
VAT rate and date of determination of the tax base
The VAT rate on imported goods is determined in accordance with the procedure in force in the Russian Federation, that is, 10% or 18%, depending on the type of imported product
The tax base is determined on the date of acceptance of imported goods for registration, i.e. date of reflection of received goods in accounting accounts: 10, 41, 07, 08. with the exception of imported goods under a leasing agreement, reflecting the transfer of ownership of goods to the lessee. In this case, the tax base is determined for each of the payment dates under the leasing agreement, and the dates and amounts of payment transfers do not matter.
VAT on imported goods is not charged or paid provided that the supplier has shipped the goods, but the goods have not reached the importer of the Russian Federation, because it was not accepted for accounting; accordingly, there is no tax base.
Accounting for imported goods from the Republic of Kazakhstan
The order is presented in the table:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Price of goods imported from the Republic of Kazakhstan | 42 | 61 |
| Paid imported products | 61 | 52 |
| Tax accrued for payment | 20 | 69 |
| Return of sales proceeds | 63 | 90-2 |
Example.
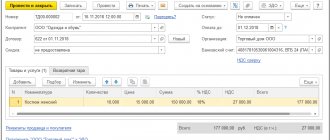
In July, Slon LLC imported products from Kazakhstan to Russia for further resale. The cost under the supply agreement is 500.0 thousand rubles.
The amount of VAT that was paid by the company to the budget of the Russian Federation amounted to 90.0 thousand rubles. (at a tax rate of 18%).
Foreign trade contract with Kazakhstan
Although Russia and Kazakhstan have a single customs territory, the legislation of the countries is not uniform. When concluding a supply agreement, the parties must determine the law applicable to the concluded agreement; they can be guided by Incoterms.
Foreign economic activity begins with the preparation of a foreign trade contract. It takes into account the legislation of both parties to the transaction and includes:
- names of companies of the parties to the contract;
- purpose of the agreement;
- terms of payment: payment currency, contract amount, payment terms, fines, liability for delay;
- delivery conditions;
- procedure for action in case of force majeure;
- details of organizations;
- settlement of disputes.
If any conditions were missed, they can be included in an additional agreement to the contract.
According to the rules, all clauses of the contract must be interpreted unambiguously and the contract must be drawn up in two languages - Kazakh and Russian. Each contract has a number, place and date of signing, these are indicated in the specifications.
Payment under the contract can be made in rubles or tenge; in any case, you will need a foreign currency account for settlements. Submit to the bank a payment order, a certificate of currency transactions and other documents that the bank requests.
There are no more transaction passports, but contracts must be registered with the bank. Moreover, only those that exceed the limit - 3 million rubles for imports to Russia and 6 million rubles for exports.
VAT reporting
The company submits a declaration.
The following documents are attached to it:
- application (4 copies, paper and electronic versions);
- Bank statement;
- shipping documentation;
- invoice;
- agreement for the purchase of products;
- intermediary agreement (upon its conclusion).
All documentation is provided in the form of photocopies, which are notarized. The exception is the application - it is submitted in the original.
The same requirements are relevant when exporting to Kazakhstan.
A desk audit is required. If during the process no discrepancies are identified, then the inspection undertakes to put a VAT payment stamp on all copies of the application. Duration – 10 days.
The tax office returns three copies of the application with a mark to the applicant. The applicant gives two copies to the exporter, one remains with him.
Is it necessary to prescribe an ESF?
When selling imported goods, the seller is required to issue an ESF. This obligation arose for sellers from 01/01/2019. The deadline for issuing ESF for importers is until the 20th of the following month.
At the same time, you can sell goods even before tax reporting is provided and VAT on imports is paid.
And here it is necessary to take into account the following nuance: the deadline for issuing ESF for importers is until the 20th, but for all other sellers in the chain (who bought the goods from the importer) - 15 calendar days. At the same time, if the importer delays the deadline for submitting reports and paying VAT on imports, the buyer, when further selling the goods, will face difficulties in issuing his own ESF - he will not have the correct data:
- line numbers;
- HS code;
- registration number of the application.
Therefore, it is advisable for the importer to either promptly submit reports after the sale of the goods, or refrain from selling until the reports are submitted.
Changes in EAEU legislation
TCEAES came into force on 01/01/2018. The new document calls for ensuring unified customs regulation on the territory of the EAEU, creating acceptable conditions for participants in foreign economic activity, as well as simplifying customs formalities.
Main changes:
- providing participants with the opportunity to take advantage of a deferred payment of import customs duties (period - no more than 30 days);
- presentation of a product declaration without documentation that confirms the declared information;
- improvement of the institution of authorized economic operator;
- providing the opportunity to make additions to the product declaration.
More details about the changes can be found at the link.
When to submit a declaration
The declaration must be submitted no later than the 20th day of the month following the month in which the organization accepted for accounting goods imported from the territory of the Republic of Belarus or the Republic of Kazakhstan. But, let’s say, a company imports leased items into Russia (under an agreement that provides for the transfer of ownership of them to the lessee). Then the declaration must be submitted no later than the 20th day of the month following the month in which the payment due date stipulated by the leasing agreement occurs.
The provisions of Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that the tax period for VAT is a quarter, do not apply in this case. This is explained by the fact that international treaties on taxation issues take precedence over Russian tax legislation (Article 7 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The agreement dated January 25, 2008 refers to such agreements. An integral part of this Agreement is the Protocol, ratified by Law No. 98-FZ of May 19, 2010 (Article 4 of the Agreement of January 25, 2008). The requirements provided for by this Protocol are mandatory for all Russian organizations.
Simultaneously with the declaration, submit to the inspection a package of documents, which is provided for in paragraph 8 of Article 2 of the Protocol, ratified by Federal Law No. 98-FZ of May 19, 2010 (clause 6 of the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 22, 2010 No. 03-07-15/ 101). If the deadline for submitting a declaration and a package of documents falls on the weekend, send them to the inspectorate on the first next working day (clause 5 of the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 7, 2010 No. 69n).
Documents for customs clearance
List of documents for customs clearance:
- passports of the director and chief accountant;
- constituent documentation, as well as documents on the organization;
- balance sheet of the foreign trade entity for the last reporting period;
- company charter;
- order on the appointment of a chief accountant;
- memorandum of association + amendments;
- decision of the meeting on the appointment of a director;
- tax registration certificate;
- certificates from banks.
For a list of additional documents, see the link.
We recommend watching the video: the procedure for registering customs duties on goods imported from the EAEU countries.
VAT for the provision of services between residents of Russia and Kazakhstan
For VAT purposes, it is important who you are under the contract with a resident of Kazakhstan - the contractor or the customer and which country will be the place of sale of services - Kazakhstan or Russia.
For example, if you are a contractor and the place of sale is Russia, then you pay VAT as usual, as with Russian customers. And if the place of sale is Kazakhstan, then you pay tax in Kazakhstan according to the law of this country.
The place of sale is determined according to special rules and depends on the specific type of service. For example, for educational services, the place of sale is considered to be the country in which these services are provided, and for advertising services, the place of sale is the country of the customer of the service.
How to determine the place of sale of services between residents of Russia and Kazakhstan
To determine the place of sale of services, follow clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU.
So, in particular, the place of sale of services will be:
- if services are related to real estate (including rental) - the country where the real estate is located. For example, if a Russian company rents real estate in Kazakhstan, it means that the service is sold in Kazakhstan (clause 1, clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU);
- if services are related to movable property (except for rent and leasing) - the country where this movable property is located (clause 2, clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU);
- When renting and leasing, the place of sale of services depends on the property that is the subject of rent (leasing).
If this is transport, then the place of sale is the country of the lessor. For example, if a Russian company leases transport to a Kazakh company, it means that the service is sold in Russia (clause 5, clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
If this is other movable property, then the place of sale is the country of the lessee. For example, if a Russian company leases equipment to a Kazakh company, it means that the service is provided in Kazakhstan (clause 4, clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU);
- for services in the field of culture, art, education, sports, tourism - the country in which they are provided (clause 3, clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU);
- for consulting, legal, accounting, advertising, design, marketing services - the country of the customer of these services. For example, if a Russian company conducts marketing research for a Kazakh company, the place of sale of services will be Kazakhstan (clause 4, clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
If any type of service is not named in clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU, then the place of their sale will be the country of the performer (clause 5 of clause 29 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
VAT when ordering services from a resident of Kazakhstan
If services are provided to you by a resident of Kazakhstan, then the procedure for assessing VAT depends on which country is the place of sale of services.
If the place of sale is Russia , then you are a tax agent for VAT and when transferring payment to a Kazakh counterparty you must (clause 28 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU):
- charge and withhold VAT on the income of the Kazakh performer (clauses 1, 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- transfer the tax to the budget simultaneously with payment to the Kazakh contractor (clause 4 of article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- issue an invoice (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The VAT paid is reflected in section. 2 VAT returns for the quarter in which you transferred payment for services (clauses 3, 35, 37.6 of the Procedure for filling out a VAT return).
You can deduct the listed tax (clause 3 of Article 171, clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the place of sale of services is Kazakhstan , then you do not have any VAT obligations. The tax will be paid by the contractor in Kazakhstan in accordance with its legislation (clause 28 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
You will not be able to deduct “input” VAT, since it was paid to the budget of Kazakhstan, not Russia.
VAT when providing services to a resident of Kazakhstan
If you provide services to a customer from Kazakhstan, the procedure for paying VAT will depend on which country is the place of sale of the service.
If the place of sale is Russia , accrue and pay VAT as for the normal sale of services in the Russian Federation (clause 28 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
On the day you receive the advance, charge VAT at the rate of 18/118. Issue an advance invoice within five calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment (clauses 3, 4 of Article 164, clause 2, clause 1 of Article 167, clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Some services are subject to VAT at a rate of 0%. There is no need to charge VAT on the advance payment (clause 1 of Article 154, clause 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
On the day of signing the act of services rendered, charge VAT on the full cost of services at a rate of 18% (clause 3 of Article 164, clause 1 of clause 1, clause 14 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Some services are subject to VAT at a rate of 0%.
Issue an invoice within five calendar days from the date of signing the act of provision of services (clause 3 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If you calculated VAT on an advance payment, you can deduct it in the quarter when the act of provision of services was signed (clause 8 of Article 171, clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the place of sale of services is Kazakhstan , then you do not pay VAT in Russia. The tax is paid in Kazakhstan in accordance with the legislation of this state (clause 28 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU). Most likely, the Kazakh customer will withhold tax from you when paying for services and will transfer it to the budget.
You will not be able to deduct “input” VAT on goods (work, services) that you used when providing services to a resident of Kazakhstan, since Russia is not the place of sale of services. Take VAT into account in the cost of these goods (works, services) (clause 2, clause 2, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT for the provision of services in Kazakhstan
If the place of sale of services is recognized as the territory of Kazakhstan, then the procedure for imposing VAT on them depends on who you are under the contract with a resident of Kazakhstan - the customer or the contractor.
If you are a performer , then in Russia you do not pay VAT. The tax is paid in Kazakhstan in accordance with the legislation of this state (clause 28 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU). Most likely, the Kazakh customer will withhold tax from you when paying for services and will transfer it to the budget.
You will not be able to deduct “input” VAT on goods (work, services) that you used when providing services to a resident of Kazakhstan, since Russia is not the place of sale of services. Take VAT into account in the cost of these goods (works, services) (clause 2, clause 2, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If you are a customer of services , then you do not have any VAT obligations. The tax will be paid by the contractor in Kazakhstan in accordance with its legislation (clause 28 of the Protocol on the collection of indirect taxes within the EAEU).
You will not be able to deduct “input” VAT, since it was paid to the budget of Kazakhstan, not Russia.
Source: https://urist7.ru/nalog/nds/nds-pri-okazanii-uslug-mezhdu-rezidentami-rossii-i-kazaxstana.html
How to fill out a declaration
When importing goods from outside the EAEU countries, fill out the declaration report in the general manner. Use the KND form 1151001. Please note that the import operation itself is not reflected in the declaration. That is, customs VAT is not highlighted as a separate line in the VAT return. Detailed instructions for preparation are reflected in the article “VAT Declaration for the 3rd quarter of 2021: instructions for filling out”.
To report on import value added tax on EAEU goods, use the special declaration form - KND 1151088, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 27, 2017 No. SA-7-3 / [email protected] Structure of the form:
| Title page | To be filled in anyway. |
| Section No. 1 | To be completed if during the reporting period the taxpayer:
|
| Section No. 2 | Issued if excisable goods are imported, with the exception of ethyl alcohol from all types of raw materials. |
| Section No. 3 | Formed by taxpayers who import ethyl alcohol from all types of raw materials, including denatured ethyl alcohol, raw alcohol, wine, grape, fruit, cognac, Calvados, and whiskey distillates. |
Instructions for filling out are as follows.
Title page
The title page of the report is filled out according to standard rules. In the header of the page we indicate the TIN and KPP of the reporting organization. Individual entrepreneurs enter only the Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) (the checkpoint is not filled out).
The adjustment number in the primary report is 0. If you are submitting a corrective report, please indicate the serial number of the adjustment.
Fill out the tax period in accordance with Appendix No. 1 to the Procedure approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 27, 2017 No. SA-7-3 / [email protected] For example, when filling out a declaration for January, indicate 01, February - 02, and so on. If the organization is in the process of reorganization, then enter 71 - code for January, 72 - February, 73 - March, and so on until code 82 - December.
Enter the reporting year in standard mode. For example, for reporting for 2021, reflect “2020” in the field.
The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate code to which the declaration is submitted is specified in the registration documents issued when registering the taxpayer.
Enter the location code in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to the Filling Out Procedure.
Please indicate the full name of the taxpayer. Individual entrepreneurs indicate their full name. Middle name is entered if available.
Section 1
In the first section of the declaration calculation we reflect the amounts of value added tax calculated on goods imported to Russia. Fill in the lines:
| Line number | What to indicate |
| 010 | OKTMO - enter the code according to the all-Russian classifier. |
| 020 | KBK - 182 1 0400 110. |
| 030 | Amount of taxes to be paid. Calculated by summing the values of the lower lines of section No. 1 (031-035). |
| 031 | The amount of tax not indicated in lines 032-035. Fill in after lines 032-035. |
| 032 | VAT on processed products. |
| 033 | Tax on goods resulting from work. |
| 034 | Collection from goods received under a trade credit agreement, under a goods exchange contract. |
| 035 | VAT on leasing payment. |
| 040 | Cost of goods exempt from taxation. |
Section 2 and 3
The second section is filled out by importers of excisable products, except for ethyl alcohol and its derivatives. Several sections No. 2 are drawn up in the declaration at once, if the BCC and OKTMO for which fees are credited differ. The first part of the section reflects OKTMO, KBK and the amount of excise tax payable to the budget. In the second part of the section, the amount of tax is distributed for each type of excisable goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation.
The third section must be completed if ethyl alcohol and its derivatives are imported into Russia. The filling rules are similar to section No. 2. In the first block we reflect OKTMO, KBK and the amount of excise tax. If there are several OKTMO or KBK, we create a separate section No. 3 for each code. In the second block of the section we detail the excise tax amounts for each type of imported alcohol.
What documents to submit to customs
The statistical form for recording the movement of goods must be submitted to the customs of the region in which the company is registered for tax purposes. The deadline is no later than the 10th day of the month following the month in which the company imported the goods. The document must be drawn up according to the form given in Appendix No. 1 to the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 29, 2011 No. 40.
You can fill out the statistical form on paper. The easiest way to fill it out is on the website edata.customs.ru. Certify the completed document with your signature and seal, then submit it to customs or send it by registered mail. If you choose to submit the form electronically, it will need to be electronically signed.
In addition, the statistical form must be submitted to the bank along with a certificate of supporting documents. If a company submits a certificate of supporting documents to the bank, but has not yet submitted the statistical form to customs, then this document can be submitted to the bank later (clause 6 of the Bank of Russia information letter dated January 21, 2014 No. 43). The main thing is that at the time of closing the transaction passport, the bank has all the statistical accounting forms that contain information about the goods received under the contract.
How to calculate VAT on import of services
When purchasing services from a foreign supplier, calculations are made in a special manner. For example, sometimes the buyer acts as a tax agent. Responsibilities arise if foreign services are sold on Russian territory. The Russian buyer transfers payment to the supplier immediately minus VAT. And the tax itself is transferred to the state budget.
The tax amount from payment to the supplier is transferred to the Federal Tax Service simultaneously with the calculation of the importer. Please take into account the specifics of filling out a payment order. BCC for enrollment in field 104, enter 182 1 03 01000 01 1000 110. Payer status (field 101) - enter 02.
Don’t forget to report to the Federal Tax Service, that is, reflect the VAT on imports in your VAT return. File a regular return for the quarter in which the agency tax was withheld. The due date is the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter.
When is it safest to deduct VAT on goods imported from the Customs Union?
A company can deduct VAT paid when importing goods if the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- imported goods are registered;
- import VAT is transferred to the budget;
- On the application for the import of goods, tax officials put a mark on the payment of VAT.
For example, a company imported goods and paid tax in December. Inspectors marked the application for indirect taxes in January. Then VAT can be deducted in the first quarter (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 17, 2011 No. 03-07-13/01–36).
Note! To deduct import VAT in the purchase book, be sure to register an application for the import of goods with marks from inspectors regarding the payment of tax, and also provide the payment details for the transfer of tax.
It can be proven in court that the company has the right to claim a deduction in the period in which the tax is transferred to the budget. That is, without waiting for the Federal Tax Service's mark on the application for the import of goods (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated July 25, 2011 No. KA-A41/7408–11). But if the company wants to avoid a dispute, it is safer to wait for the mark. And after that, register the application in the purchase book. The date and number of the application are given in column 3 of the purchase book. And the payment details for transferring VAT to the budget are in column 7.
At the same time, the import application, unlike ordinary incoming invoices, does not need to be registered in the invoice journal (clause 15 of the Rules for maintaining the invoice journal, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137).
Please note: payment of import tax is reflected in a special declaration, but the deduction can only be declared in a regular one. To do this, fill out line 190 of section 3 (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 20, 2010 No. ШС-37-3/ [email protected] ).
What documents and within what time frame need to be submitted to the tax authorities at the bank and customs?
Package of necessary documentation
In order to display import data in the declaration and submit it to the tax office at the place of registration, you will need a package of documents:
- statements (four copies);
- Bank statements;
- extracts of transport documents;
- issuing invoices;
- extracts of contracts;
- extracts of information messages;
- other documents that were involved in the import of goods.
What documents should I prepare for the bank?
The import of goods from the countries of the Customs Union, like any other import, is subject to exchange control. Therefore, a company importing goods into Russia from Belarus or Kazakhstan needs to prepare a number of documents for the bank. Alternatively, you can entrust the bank with filling out these documents. To do this, you need to conclude a separate agreement with him or draw up an addition to the current bank account agreement. For these services, the bank will charge a commission, the amount of which depends on the tariff plan in force in a particular bank.
If the company does not submit documents or prepares them later than the established deadlines (they can be seen in the diagram below), a fine of 5,000 to 50,000 rubles is possible. (Article 15.25 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Transaction passport
A transaction passport is a document that contains general information about the transaction. The company is required to issue a transaction passport from the bank if the value of the contract is equal to or exceeds $50,000. This limit is determined as of the date of conclusion of the contract or amendments and additions to it (clauses 5.1, 5.2 of Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012).
Note! The transaction passport must be issued before payment for the goods and no later than 15 working days after the end of the month in which the delivery documents were issued. Fine for delay - up to 50,000 rubles.
A company that imports goods from the Republic of Belarus or Kazakhstan must submit to the bank one copy of the transaction passport in the form given in Appendix No. 4 to Instruction No. 138-I. As well as the contract or an extract from it. Other documents may be required if they contain information that the company provided in the transaction passport. The deadline for submitting documents is before payment for goods and no later than 15 working days after the end of the month in which invoices and transport documents for goods were issued (clause 6.5 of Instruction No. 138-I).
The transaction passport is considered completed after bank specialists assign it a number, date it and sign it. Then the bank must send this document to the company within two working days (clause 6.8 of Instruction No. 138-I). After the supplier transfers the goods and the buyer pays for it, the bank, based on the importer’s application, closes the transaction passport (clause 7.1 of Instruction No. 138-I). This will mean that this foreign economic transaction has been completed and all obligations under it have been fulfilled.
If a company submits documents with a delay, bankers do not have the right to refuse to issue a transaction passport. But they will transmit information about the violation to the Bank of Russia, which will report to Rosfinnadzor. As a result, inspectors can fine the company up to 50,000 rubles. At the same time, this will not affect the company’s VAT obligations, including the right to deduction.
In practice, it happens that a long-term contract is concluded with a supplier, the final amount of which is unknown in advance. If a company sees that the amount of obligations under such an agreement will soon reach $50,000, then a transaction passport can be issued at the bank at any time, but no later than the date when this amount exceeds the limit (clause 1 of the Bank of Russia information letter dated May 7 2014 No. 44).
Certificate of foreign exchange transactions
A certificate of foreign exchange transactions is a document in which a company provides data on payments under an import contract. And if the company transfers an advance to the seller, the certificate must reflect the date when the supplier must ship the goods under the contract.
When making payments in foreign currency, the company importing the goods issues a certificate of foreign exchange transactions in any case. When making payments in Russian rubles, a certificate is submitted to the bank only by companies that have issued a transaction passport. It must be filled out according to the form given in Appendix No. 1 to Instruction No. 138-I. And hand over to the bank simultaneously with the payment slip for transfer to the supplier of money for the goods (clause 2.1 of Instruction No. 138-I).
Certificate of supporting documents
Companies that have issued a transaction passport must submit a certificate of supporting documents to the bank. It provides data on the delivery of goods. The document must be submitted to the bank within 15 working days after the end of the month in which the delivery documents were drawn up (clause 9.2.2 of Instruction No. 138-I). The form for a certificate of supporting documents is contained in Appendix No. 5 to Instruction No. 138-I. Along with the certificate, it is necessary to submit transport (shipping) and commercial documents. As a rule, these are waybills, CMR, specifications, invoices, various certificates and certificates.