TAX CONSULTING
In case of disagreement with the results of a tax audit, the taxpayer has the right to appeal them.
The right to appeal the results of a tax audit is established in sub-clause. 12 clause 1 art. 21, art. 137 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The appeal procedure includes a number of successive stages. Based on the results of an on-site and desk tax audit, tax authority officials draw up a tax audit report.
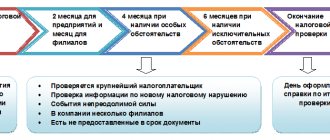
Procedure for appealing the results of a tax audit
Expert opinion
The procedure for appealing acts of tax authorities consists of four successive stages, but it is not always necessary to use each of them. If a solution is acceptable to the company at any stage, the rest are not required.
Objection to the tax audit report
So, the fiscal authorities conducted an audit, a report was drawn up, but the company does not agree with the results of the audit, what to do? Draw up written objections to the tax audit report and send the document to the head of the service that carried out the procedure. According to paragraph 6 of Art. 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the ANP can be appealed either as a whole or as a separate part.
The legislation establishes a deadline for filing an objection - no more than one month after receiving the inspection report and documents confirming the violations stated in the report. Within a month, the tax service must make a decision on the filed objection; in some cases, when there are objective reasons, the deadline for making a decision may be extended, but not more than a month.
In accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the head of the fiscal service reviews the act and objections to it and makes a decision:
- on bringing to responsibility;
- on refusal to be held liable for violation of tax laws.
This is important to know: Limitation period between legal entities
The company receives a corresponding decision, which comes into force after a month from the date of its receipt. An enterprise has the right not to wait until the decision comes into force and to begin implementing it in whole or in part, or, if it disagrees with the decision of the tax authority, to proceed to the next stage of appealing the decision based on the results of the audit to a higher tax authority.
Challenging a tax decision
If the company is not satisfied with the tax decision made based on the results of consideration of objections, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation gives the taxpayer the opportunity to challenge it (paragraph 3, clause 1, article 138 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is important to remember that the decision of the territorial tax authority comes into force after one month has passed from the date of delivery of the decision. That is, a company can file a complaint and challenge a decision that has not yet entered into legal force; such a complaint, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is called an appeal. To do this, the company draws up an appeal addressed to a higher authority, but it should be submitted to the inspectorate that made the controversial decision. Employees of the territorial tax authority themselves, within three days after receiving the appeal, are obliged to transfer it to a higher tax authority.
The complaint is considered without the participation of representatives of the appellant company. An exception to this rule is those situations when, when examining the audit materials, a higher authority discovered that the audit data does not correspond to the documents submitted by the organization when challenging the tax audit report.
It happens that a company does not have time to file an appeal before the expiration of the period specified by the Tax Code and the decision of the fiscal authorities comes into force. In this case, the enterprise has another opportunity to challenge the decision of the tax authorities - drawing up a complaint and sending it to a higher authority in the same way as an appeal.
The decision on the complaint (appeal) must be made by a higher tax authority no later than one month from the date of receipt of the complaint by the Federal Tax Service. The decision of the higher tax authority, in accordance with clause 6 of Art. 140 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, comes into force from the moment of its adoption.
Based on the results of consideration of a complaint against the decision of the Federal Tax Service on a tax audit, a higher tax authority may (clause 3 of Article 140 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- leave the complaint (appeal) unsatisfied;
- cancel the decision of the tax authority in whole or in part;
- cancel the decision of the tax authority completely and make a new decision on the case;
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 101.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a new decision on an objection to a tax audit report comes into force immediately after its adoption. In cases where a higher fiscal authority refuses to satisfy an appeal, the initial decision also immediately enters into force.
Complaint to the Federal Tax Service
If the company received a response to the appeal from the Federal Tax Service for an entity that did not satisfy it, it, according to paragraph. 3 p. 2 art. 139 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, can file a complaint directly with the Federal Tax Service. Moreover, even if the organization missed the deadline for filing a complaint, but for a good reason, it, in accordance with paragraph 4 of the same article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, can apply to the tax authority with a petition for its restoration.
Going to court
The fourth stage of appealing the ANP is going to court. This is only possible if the mandatory pre-trial procedure for appealing to a higher tax authority is followed. The statement of claim is filed with the court within three months from the moment the response to the complaint (appeal) was received.
The organization also has the right to go to court if the fiscal services have not made any decision in response to an appeal against the decision of the Federal Tax Service within the time limits established by law.
Some features of filing complaints on the Federal Tax Service website: what to pay attention to
The possibility of remote filing of complaints is provided on the website of the Federal Tax Service (www.nalog.ru). You can create a request using the “Contact the Federal Tax Service of Russia” service. It can be found in the “Electronic Services” section.
Rice. 1. Appeal to the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
The Federal Tax Service offers two options for appeals. The first concerns the incorrect content of a notice, demand or receipt regarding tax payments. A second form is provided for requests and inquiries. It is filled out in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 59 dated May 2, 2006 and is of particular interest.
In particular, applicants can be: legal entity, individual, individual entrepreneur. Key points: the text of the appeal must contain the applicant’s full name, address for response (postal or electronic), and the essence of the question. The content of the appeal should not exceed 4000 characters. You can attach files up to 5.5 MB and only those formats that are indicated there. Consideration of such an appeal under Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 59 usually lasts up to 30 days.
On the Federal Tax Service website you can track the status of a filed complaint (other appeals). The “Find out about a complaint” service is intended for this purpose. The actual result of its consideration can be found out through the “Resolutions on Complaints” service.
Appealing the desk inspection report
A desk audit, unlike an on-site audit, is carried out without notifying the organization being audited. In cases where violations of tax legislation are detected, based on the results of the audit, a tax audit report is drawn up, which is transferred to the taxpayer company no later than 10 days after the completion of the desk audit.
There are cases when an organization does not receive an inspection report. In this case, if the company’s management can prove that the reason for not receiving the document is valid, for example, the fiscal authority did not notify that after an inspection of the enterprise an act was drawn up, and the postal item was lost, they have the opportunity to restore the deadline for challenging the act. If the taxpayer was deprived of the opportunity to submit objections to the audit report due to the fault of the tax authority, this may become a basis for canceling the tax authority’s decision on such an audit.
There are often cases when taxpayer organizations avoid receiving the report in every possible way. That is, they know that such an act has been drawn up, but they do not pick it up themselves and avoid receiving the mail. In this case, the date of receipt of the act will be considered the sixth day after sending it by registered mail. As a result, the tax audit report is considered delivered and comes into force within the time limits established by law.
This is important to know: The deadline for appealing a decision in a simplified manner under the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation
But even in this case, the company can challenge the decision that has entered into force by appealing to a higher organization with an appeal within a month from the date of receipt of the decision or with a regular complaint - within a year after the inspection decision is made.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1: If the deadline for appealing a desk audit has been missed, can anything be done?
Missed deadlines for appeal can be restored if the reason for the absence is valid and this can be confirmed. To do this, you need to draw up a petition for reinstatement of the deadline, explaining the reasons for the missed deadline. Supporting documents must be attached to it. The deadline is restored by the higher tax authority.
Question No. 2: Is a desk audit of the updated declaration carried out?
Yes, it is carried out in a general manner. As expected, after submitting it for three months. In this case, the desk audit of the primary declaration is terminated. During the verification, “clarifications” can use the data obtained from the previous verification.
Non-standard situations
When appealing an inspection decision, a company does not always get the result it was striving for, especially in cases where the dispute has reached the court. There are often situations when fiscal services, as an interim measure, petition the court to prohibit the use of property and monetary assets of an enterprise until a court decision is made. In other words, all the company’s accounts are frozen until the court’s decision on the company’s claim to appeal the tax audit acts comes into force.
Our company's lawyers have positive experience in these types of cases. But, it is easier to prevent any trouble than to correct its consequences later. Practical experience shows that a company, when appealing a tax audit decision, without involving specialists, may miss important nuances and make mistakes when forming an evidence base, which will be difficult to correct in the future.
How we can help your business
We can help any company even before the tax authorities begin an audit. Our company offers comprehensive assistance and support for your business with:
- checking the reliability of your counterparties;
- legal support of all ongoing and already concluded transactions;
- consulting all employees of the organization before the start of the fiscal audit;
- support of on-site tax audit;
- support of desk tax audit;
- appealing the results of an inspection already carried out if they do not suit the enterprise.
In each specific case, we develop a separate strategy to help the business, depending on the current situation at the time of contacting us and the client’s wishes.
Under what conditions is it possible to challenge a tax act?
To appeal a tax audit report, certain grounds are required. If you file a complaint without such grounds, it will be rejected, in most cases - without even consideration. Therefore, it is very important to know under what conditions it is possible to file a complaint. Here are the most common grounds for challenge:
- tax inspectors committed certain violations during the audit - quite often you can encounter situations where inspectors violate the law during business inspections. Violations can be either very serious or minor, however, even the most insignificant violation (for example, they forgot to indicate the date of the inspection, did not put a signature or seal, etc.), if it is recorded on time and correctly, makes it possible to challenge the final inspection report or parts of it. Therefore, it is very important that during the inspection there is a lawyer present who can monitor compliance with the law by inspectors;
- the deadlines for conducting audits have been violated - both desk and field tax audits have legally limited periods of implementation. However, in practice, deadlines are often violated, which makes it possible to challenge the tax audit report. It does not matter of fundamental importance whose fault the delay occurred: if the deadlines are violated, you can file a complaint, because the law has already been violated;
- unlawful or groundless application of sanctions - almost any inspection, especially an on-site inspection, ends with the imposition of penalties or additional tax payments. However, there are not always sufficient reasons for this. If you find out that additional tax assessments, fines or other restrictive actions on the part of the Federal Tax Service (for example, blocking of accounts) were applied without proper grounds, this may serve as grounds for challenging such a tax audit act. But in order to discover the groundlessness of the sanctions, one cannot do without consulting a professional tax lawyer ;
- other violations that could in one way or another affect the result of the audit - this includes more rare situations, for example, when third-party organizations are involved in the audit that do not have the appropriate certification, if documents and equipment were seized that are not related to the current audit, if they were used information that does not correspond to reality, etc. All this information, with proper preparation, can be used as arguments to challenge the results of a tax audit.
This is important to know: Deadline for appealing a disciplinary sanction of the Ministry of Internal Affairs
When preparing to challenge, pay enough attention to preparing the justification, because often it is the insufficient motivational part that serves as the reason for refusing to satisfy the complaint. support of tax audits is also very important - this increases the likelihood that all violations will be recorded.
REQUEST FOR ADDITIONAL DOCUMENTS
During an inspection of an enterprise, the inspector has the right to request the necessary documents relating to the financial activities of the enterprise. The basis is clause 1 of Article 93 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (No. 146-FZ of July 31, 1998).
During an on-site inspection, the company may be asked for absolutely any papers related to the time periods or issues indicated in the notice of the upcoming inspection.
During a desk audit, the list of reasons giving the inspection body the right to request papers in excess of those provided or to demand any clarification is clearly stated. Reasons for requesting additional data may be:
- Errors in the income statement, inconsistencies, differences between the information indicated in it and the data contained in other documents provided. According to paragraph 3 of Article 88 of the Tax Code, the tax service may require that the declaration be corrected or request clarification on this issue.
- When declaring the amount of tax refund. If the company has not provided a justification for the correctness of VAT deductions, the tax office may request the relevant documents.
- Providing an amended declaration with a reduced amount of tax payable in comparison with that previously declared. The tax office has the right to demand that the company being inspected explain the reasons for changes in these amounts.
- Submitting an updated declaration that differs from the previous version in terms of increasing the amount of losses or reducing the tax accrued for payment. In this case, the tax office can either demand an explanation of the reasons for the changes, or request documents to confirm the correctness of the calculations and the legality of increasing losses or reducing taxes. This can be any paper, including primary documents or tax registers.
In other cases, the tax authority does not have the right to request additional documents from the subject being inspected.
How to sue the tax authorities based on the results of an audit?
Going to court is the final stage of challenging a tax audit report. The statement of claim is submitted to the arbitration court at the place of registration of the company. The defendant is the Federal Tax Service department, whose decision is being challenged. The text of the claim must indicate the specific inspection report, the date of the audit, and all identified violations. In addition, it must be indicated that the complaint procedure for resolving the dispute was followed - complaints were filed against the actions of the tax authorities. The claim is accompanied by documents that can confirm the plaintiff’s position.
The documents are then submitted to the court for review. A copy must be sent to the Federal Tax Service in order to notify them of the filing of a lawsuit. During the hearings, the main goal is to convince the court that violations actually occurred and could affect the decisions made based on the results of the audit. In this case, the judge may satisfy the applicant's demands and cancel the act or its individual provisions. An experienced tax lawyer can help you prepare and file your claim and can represent your company during the claim.
Conclusion
If a tax audit act violates the rights of your company, imposes unreasonable penalties, or violations were committed during the tax audit, you can file a complaint and have the Federal Tax Service’s decision reversed. There are pre-trial and judicial options for resolving the dispute, and going to court without the pre-trial stage is impossible. A competent, specialized lawyer will help with the appeal and ensure that the dispute is resolved in your favor.