Labor legislation in the Russian Federation is structured in such a way that it provides opportunities for mobility of citizens in the performance of their labor duties.
One of these options for labor mobility should be considered the temporary transfer of an employee to another position, that is, providing him with temporary work. In what cases is such a transfer possible and how should it be implemented? Dear readers! To solve your specific problem, call the hotline or visit the website. It's free.
8 (800) 350-31-84
Differences between temporary transfer and other types of labor functions
The main legislative provisions of a temporary transfer, regardless of its reasons, are defined in Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: these provisions apply only if the employee has an employment agreement with the employer and within the same organization with the same employer. If there is a production need to transfer an employee to another employer, then in such a situation completely different rules apply (with the exception of athletes, but more on that below). Temporary transfer, excluding some cases described by federal labor legislation, is made only with the written consent of the employee with the conclusion of an additional agreement.
Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, regulating temporary transfer to another job
Temporary transfer and business trip. Firstly, business trips include trips by an employee at the order of the employer for any period of time to carry out business assignments outside his permanent place of permanent work (Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Such trips are mandatory, and unreasonable refusal from them can be considered a violation of labor discipline, while temporary transfer, as a rule, is possible only with the consent of the employee (by agreement of the parties).
Article 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Business trip concept
Secondly, unlike a business trip, it can be carried out in the same area and place of work.
Thirdly, a business trip involves the fulfillment of a specific official assignment, and not the assignment of any other duties to the employee, that is, it does not entail a change in the essential terms of the employment contract, and a transfer to another location or place of work assumes that the employee regularly performs work duties. functions during the entire period of transfer during working hours.
And fourth: the provisions of local regulations of the company where he carries out instructions from management are not applied to a posted worker, unless otherwise provided by the local regulations of his direct employer. When an employee is transferred temporarily, the effect of local regulations applies to him in the general manner.
Business trips are related to the performance of basic duties, and not a change in job functions
Temporary transfer and part-time work. Do not confuse the temporary transfer of an employee to another job with part-time or part-time work. The definition of part-time work is specified in Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It means that an employee carries out other paid work activities in his free time from his main job, while the law does not limit the number of such part-time jobs, most importantly, not to the detriment of his main job responsibilities.
Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. General provisions on part-time work
For part-time work, a separate employment contract is concluded indicating that this activity is not the main one. Part-time work happens:
- Internal, when they work for the same employer, in the same organization.
- External, if the citizen works in other organizations and with other employers.
Temporary transfer and combination. Let us note that a temporary transfer to another job must be distinguished not only from relocation, but also from the performance by an employee, on behalf of the employer, of the duties of a temporarily absent employee simultaneously with the duties stipulated by the employment contract, that is, combining duties. The concept of “combination” is contained in Art. 60.2 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Here, the law does not limit the period for fulfilling duties: it is determined by agreement of the parties. In this case, the employee is not released from his main job and performs the duties of another employee during the main time, that is, a large burden falls on the employee. When combined, an employee can perform additional work in different professions. With this type of employment, the law does not require the conclusion of a new employment agreement, which distinguishes part-time work from part-time work. In this case, an employee who temporarily replaces an absent employee is subject to, in accordance with Art. 60.2 and 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an additional payment, the amount of which is also established by agreement between the employee and the employer.
Article 60.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Combination of professions (positions)
Article 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Remuneration for combining professions
Translation and relocation. The content of the concepts “temporary transfer” and “relocation” is associated with the concept of labor function. Its definition is described in Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The labor function is understood as
1) work in a particular position determined by the staffing table, by profession and specialty with the obligatory indication of the employee’s qualification level,
2) the specific type of work activity assigned to the employee.
Definition of labor function specified in Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
That is, both permanent and temporary transfer to another job entails a change in the clauses of the employment agreement, since this changes
1) the employee’s labor functions and (or) the department in the company structure where he works (if the department was specified in the employment contract),
2) the place of work itself, if the employee is sent to work in another area together with the employer, while the employee continues to work for the same employer.
The labor function and place of work are essential terms of the employment contract, and their changes almost always require the consent of the employee, therefore the transfer is formalized by an additional agreement to the employment contract.
Temporary or permanent relocation, for example, transfer of an employee within the same organization to another workplace, assignment of work on another mechanism does not require the consent of the employee, because these actions do not entail a change in labor functions or essential terms of the employment contract (Part 3 of Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). These circumstances are also indicated by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its ruling dated June 19, 2007 No. 475-О-О. The judges' conclusions were made in relation to the norm of Article 72.1 of the previous edition of the Labor Code, which was in force before the Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006 came into force, but they can be taken into account in relation to the current code. This is explained by the fact that the legal understanding and content of the relationship between the parties to the employment contract during the transfer has not changed significantly.
Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Transfer to another job, relocation
Important! If the employment contract does NOT specify a structural unit, the transfer of an employee from the same employer to another workplace, to another structural unit located in the same area is considered a relocation.
Table 1. Differences between translation and relocation
| What's changing | Translation | Moving |
| Essential terms of the employment contract | Yes, since translation often requires special skills or certain qualifications from a specialist | No |
| Labor function (profession, specialty, qualification, position) | Yes | No |
| Terrain | And no, and yes (if we are talking about a case of transfer to another location) | No |
| Employee consent | Required | No |
| Entry into the work book | Mainly introduced | Not included |
| Additional agreement | Is concluded | Not included |
Important! When moving and transferring, it is prohibited to move an employee to a job that is not suitable for him due to health reasons.
Types of temporary transfer
Lawyers distinguish the following types of translation:
- permanent - to another job/relocation (Article 72, 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), we have already written about its features in one of the articles;
- temporary - by agreement of the parties (part 1 of article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- to replace an absent employee (part 1 of article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- temporarily at the initiative of the employer (part 2, 3 of article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- translation in accordance with a medical report;
- to another location together with the employer (Part 1 of Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), both temporary and permanent;
- temporary transfer to another job due to suspension of special rights (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Suspension from work
Important! As soon as the circumstances of the temporary transfer cease to apply, the employee is returned to his previous place. If the employee’s previous job is not provided, and he does not require it and continues to work at the place of transfer, then the agreement on the temporary nature of the work loses force, and the previously completed transfer becomes permanent. All rules for registering a permanent transfer apply to it - from drawing up an additional agreement to making an entry in the work book, and the date of transfer is considered the first day of the temporary transfer.
Let us note that such behavior of the employer is erroneous when the employee was dismissed after the end of the transfer period, since another employee was hired in his previous place. It is worth remembering that during a temporary transfer, the employee retains his job and he has the right to return to it after the expiration of the transfer period. This case was considered by the Russian Constitutional Court. The conclusion made by the judges is contained in the Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2013 No. 1912-O, where the court explains that in Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for cases of temporary transfer to another job, while by written agreement of the parties, an employee can replace a temporarily absent employee, and in accordance with regulatory legal acts, his place of work is retained until this employee returns to work. At the end of the transfer period, the employee is guaranteed the return of his previous position; if the employee did not occupy it and did not demand its provision and continues to work at a temporary place of work, then the condition of the agreement on the urgent nature of the transfer loses force and the transfer is considered permanent.
Table 2. Documentation of temporary transfer
| Type of transfer | Employee consent to transfer | Additional agreement to the employment contract | Order in form T No. 5 | Entry in the work book | Entry in personal card | Changes in timesheets |
| Permanent transfer to another job (and in accordance with a medical report) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Temporary transfer by agreement of the parties | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Temporary transfer to replace an absent employee | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Temporary transfer at the initiative of the employer | No, but required if the transfer is to a position of lower qualifications | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Temporary transfer in accordance with a medical report and | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Temporary transfer due to suspension of special rights for up to two months | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Transfer to another location together with the employer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Video - Temporary and permanent transfers to another job
Let's take a closer look at some of the features of temporary transfer of employees to another job.
Comment on the rating
Thank you, your rating has been taken into account. You can also leave a comment on your rating.
Is the sample document useful?
If the document “Sample.
An example of an order for temporary transfer in case of production necessity" was useful for you, we ask you to leave a review about it. Remember just 2 words:
Contract-Lawyer
And add Contract-Yurist.Ru to your bookmarks (Ctrl+D).
You will still need it!
Temporary transfer with the consent of the employee
Temporary transfer to another job can be carried out by written agreement of the parties. The employer first offers the employee a vacant position or a position where an absent employee needs to be replaced. Then, if agreed, an additional agreement is concluded on a temporary transfer to another job, position or to another structural unit. The period is up to one year, and if the transfer occurs to the position of a temporarily absent employee - until he appears in the service. This temporary approach is now being used to temporarily fill a vacant position until a permanent employee takes it.
With a temporary transfer, it is also possible to change the salary amount. This is an essential condition of the employment contract, and the law imposes restrictions on its changes. Limits allowed by part 4 of Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are defined as follows: wages must be no lower than the average earnings for the previous job. In addition, the same clause stipulates the prohibition of transferring an employee to a job that is contraindicated for him for health reasons. But, if the employee has the consent, then he can be transferred to work with harmful or dangerous working conditions.
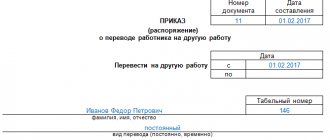
As for documenting a temporary transfer to another job, the employer issues an appropriate order (instruction) containing information about the reasons for the temporary transfer, labor functions, payment terms and the duration of this transfer.
Unified form T-5 (order to transfer to another job)
Download the unified form T-5 in .rtf format: Order on transfer to another job (form T-5).
If a temporary transfer is carried out to a vacant position, it is better to determine the expiration date of the transfer, and if to replace a temporarily absent employee, it is worth determining the condition upon the occurrence of which the employee will return to his previous job, since the absent employee may return from vacation or sick leave later.
Important! If an employee is transferred to another job or position, he must be familiarized with the job description and other local regulations that are relevant to the performance of this work. In addition, it may be necessary to conduct training in TY or conclude an agreement on financial liability.
What is the basis for the order?
Orders issued by company management must always have a basis. In this case, it may be a statement written on behalf of the employee himself (with justification for this desire) or a memorandum from the head of the structural unit, which must indicate compelling arguments for carrying out this procedure. If the transfer occurs at the initiative of the employer, then the employee must first be notified of the upcoming changes in his career.
Temporary transfer of an employee without the employee’s consent
Let us note that the written consent of the parties is almost always required, with the exception of situations provided for in parts 2 and 3 of Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (their list is exhaustive). Such extraordinary circumstances include natural or man-made disasters, accidents and industrial accidents, cataclysms, widespread livestock diseases, epidemics and other exceptional cases that threaten people’s lives or the normal conditions of their existence - in these cases, the employer can transfer the employee to a job not provided for by work contract for work for a period of up to 1 month to prevent these cases or eliminate their consequences.
The second group of circumstances under which it is possible to transfer an employee without consent is dictated by production necessity. At the initiative of the employer, a temporary transfer is carried out during downtime, and also, if it is necessary to prevent destruction or damage to property, to replace any employee who is temporarily absent, if these cases are caused by emergency circumstances. If new job functions require lower qualifications, such a transfer is permitted only with the written consent of the employee.
Forced transfer of an employee is possible to eliminate an accident or man-made disaster
Important! The employer’s initiative in such cases is limited only by a very vague wording, which is not specified in labor legislation - in this case we are talking about exceptional situations that threaten “the life or normal living conditions of the entire population or part of it.” In this part, some employers may abuse their right.
If the transfer period exceeds the limit established for temporary transfers, then even in situations of urgent need, the transfer is carried out only with the written consent of the employee. Labor legislation does not indicate anywhere the number of temporary transfers of an employee per year, since in such exceptional cases work is carried out that cannot be foreseen or postponed.
The Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation commented on the application of parts 2 and 3 of Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which allow the urgent transfer of an employee to another job without his consent: the court once again clarified that the obligation to prove the existence of reasons on the basis of which the transfer can be made is assigned to the employer.
An example from judicial practice . Thus, S. has worked as a cardiovascular surgeon at the Pskov Regional Hospital since 1999. By order of the head physician, he was temporarily transferred without his consent to the clinic of the regional hospital to the position of cardiovascular surgeon. The reason for the transfer was the need to fill a vacant position and in order to prevent a threat to the life and health of the population. Considering such a transfer illegal, S. refused to perform his duties at the clinic. For this they were subjected to disciplinary action in the form of a reprimand. The court declared both the reprimand order and the temporary transfer order illegal, since the management of the institution did not provide evidence of the existence of extraordinary circumstances that explained the need for a temporary transfer without the employee’s consent (appeal ruling of the Pskov Regional Court dated October 2, 2012 in case No. 33-1580).
In terms of remuneration in a situation of forced temporary transfer, the state guarantees the following:
- If the wages for the new work performed exceed the average for his usual job, then he is paid the wages for the work performed (in fact, an additional payment is added to his previous salary).
- If the wages for work performed as a temporary transfer are lower than the employee’s average earnings for his previous job, then he is paid his previous average earnings, determined in the prescribed manner).
Let us note that the employer has the right (but this is not an obligation) to provide additional financial incentives to employees who are temporarily transferred to another job without their consent.
Important! If an employee refuses to perform work during a legitimate transfer, then in this case he violates labor discipline; in case of absenteeism, such behavior is recognized as absenteeism.
Leave a comment on the document
Do you think the document is incorrect? Leave a comment and we will correct the shortcomings. Without a comment, the rating will not be taken into account!
Thank you, your rating has been taken into account. The quality of documents will increase from your activity.
| Here you can leave a comment on the document “Sample. An example of an order for temporary transfer in case of production necessity”, as well as ask questions associated with it. If you would like to leave a comment with a rating , then you need to rate the document at the top of the page Reply for |
Right to refuse forced transfer
On the basis of Part 1 of Article 219, Part 7 of Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a disciplinary sanction cannot be imposed on an employee for refusal to perform duties if there is a danger to his life and health due to violation of labor protection requirements, until such danger is eliminated and except in cases provided for federal legislation. An employee also has the right to refuse, without consequences, to perform work of a difficult nature, with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, if they are not provided for in the employment contract. Let us note that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain articles that prohibit employees from using the above right even in the situation of an employee’s refusal to temporarily transfer to another job.
Article 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part 1. Employee rights in the field of labor protection
Article 220 part 7 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, guaranteeing the impossibility of bringing an employee to disciplinary liability for refusing to perform duties in unfavorable working conditions
Temporary transfer of an employee due to health reasons
In accordance with Art. 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to transfer the employee to another job (position) if he needs it in accordance with a medical report. Moreover, other work should not be contraindicated for the employee due to health reasons. A medical report is issued in accordance with the procedure established by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 2, 2012 No. 441. A sick leave certificate is not considered a medical report. Such a transfer is also carried out with the written consent of the employee. When receiving a medical report from an employee, you must pay attention to the transfer period indicated in the certificate, since the employer’s further actions depend on this.
Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Transfer to another job in accordance with a medical report
If an employee is indicated for a temporary transfer to another job for a period of up to 4 months, the employer must offer him another job that is suitable for health reasons. If there is no one or the employee rejects the vacancy, the employer removes him from work, retaining his place of work (position) for the entire time specified in the medical certificate. To do this, the employer issues an order in any form. The order specifies the period for which the employee is suspended. If the period is not specified, upon admission to work, the personnel service issues an appropriate order.
Job offer for an employee requiring transfer due to health reasons
When an employee is transferred to another job in accordance with a medical certificate to a lower-paid job, the employer retains his previous average earnings for a month from the date of transfer, and when transferred due to work injuries or the presence of an occupational disease - until the employee returns to work or permanently loses ability to work (Article 182 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 182 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Guarantees when transferring an employee to another lower-paid job
If an employee who, in accordance with a medical report, needs a temporary transfer to another job for a period of up to 4 months, refuses the transfer or the employer does not have the corresponding job, then the employer is obliged to suspend the employee from work for the entire period specified in the medical report while maintaining his job. (positions). During the period of inadmissibility to work, the employee’s salary is not accrued, except in cases provided for by labor legislation, collective or individual agreements. Please note that if the employer refuses a vacancy or has no vacancies, the employment contract is not terminated, the employee is simply suspended from work, as a rule, without saving his salary.
If, in accordance with a medical report, an employee needs a temporary transfer to another job for a period of more than 4 months or a permanent transfer, then if he refuses the transfer or the employer does not have the appropriate work, the employment contract is terminated under clause 8 of part 1 of Art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - the employee’s refusal to transfer to another job, which he needs in accordance with a medical report, or the employer does not have the appropriate job. Upon dismissal in this case, the employee is paid compensation - two weeks' average earnings (Part 3 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Article 77. General grounds for termination of an employment contract
Article 178, part 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Payment of severance pay in the amount of two weeks' average earnings
Organization of translation for pregnant women
Transfer for medical reasons is regulated by Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but the special provisions of Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation take precedence, since they regulate the specifics of transfers of pregnant women and employees who have children under 1.5 years of age.
Article 254 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Transfer to another job of pregnant women and women with children under the age of one and a half years
If a woman expecting a child has a medical certificate, then she is temporarily transferred to another job that excludes the influence of unfavorable production factors, while she retains her earnings from her previous job. Until another position is provided, the pregnant woman is released from work while maintaining the average earnings for all working days missed due to waiting for a vacancy at the expense of the employer. A similar guarantee is provided for women with children under the age of one and a half years. The latter, if it is impossible to perform the previous job, are also subject to temporary transfer upon their application to another job with wages for the work performed, but not lower than the average earnings for the previous job until the child reaches the age of one and a half years. The employer has no right to refuse to make such transfers.
Transfer proposal for a pregnant woman
If the term of the employment agreement with a pregnant woman expires during her pregnancy and it was concluded during the performance of the duties of the absent employee, then in this case the employer is obliged to offer the employee a new position (Part 3 of Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) for transfer. The law allows the dismissal of a woman at the end of the employment contract during her pregnancy and the impossibility, with her written approval, of transferring before the end of pregnancy to another job that is available to the employer (a free position at the level of the woman’s work experience, lower-level or less paid), Moreover, her state of health allows her to perform the proposed duties. The employer is obliged to offer the pregnant woman all of his vacancies that meet legal requirements in the given area. Company management is obliged to offer vacant positions in other localities if such an option is provided for in a collective or individual agreement.
Art. 261. Guarantees for a pregnant woman and persons with family responsibilities upon termination of an employment contract
If the employee agrees to the transfer, then the parties sign an additional agreement to the old contract with the inclusion of amended clauses (about labor function, place of work, term of the employment contract).
Temporary transfer of an athlete
Unlike other types of temporary transfer, which are carried out only within one organization and employer, this is a special type of temporary transfer - it can be carried out to another employer. So, on the basis of Art. 348.4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in cases where the employer is not able to ensure the participation of an athlete in sports competitions, a temporary transfer of the athlete with his written consent is allowed to another employer for a period not exceeding one year, and an agreement has been reached between the employers. In this case, the employer at the place of temporary work enters into a fixed-term employment contract with the athlete in accordance with the requirements of Art. 348.2 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. During the transfer, the original employment contract is suspended, but the duration is not interrupted.
Article 348.4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Temporary transfer of an athlete to another employer
If an athlete wants to work part-time in such a situation, then permission must be obtained from both the main and temporary employers.
If a temporary employment contract is terminated early for any of the reasons provided by law, the contract, the originally concluded contract, is valid in full from the next initially working day after the calendar date with which the termination of the temporary employment contract is associated.
When the period of temporary transfer to another employer expires and the athlete continues to work there, and none of the parties to the agreement demands termination of the temporary labor contract and renewal of the original one, then the latter is terminated, and the validity of the employment contract concluded for the period of temporary transfer is extended for a period determined by agreement of the parties, and in the absence of such agreement - for an indefinite period.
If the deputy is a new employee
Sometimes an employer decides to hire another person to replace a temporarily absent employee. In this case, registration is carried out in the same way as with a regular hire, but with one caveat - the employment contract is fixed-term, i.e. it is concluded for a certain period of time. The features of its preparation are indicated in Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When selecting an applicant, it is better for the manager to immediately indicate that the employment will be temporary. After all, not everyone agrees to come to a new organization for a month. In general, this format of labor relations is more logical to use in case of temporary absence of the main employee due to maternity leave.
Temporary transfer due to suspension of special rights
Temporary transfer of an employee whose labor functions are related to the presence of a special right, license, or permit is the responsibility of the employer if this right is suspended for a period of up to two months. These are categories of workers such as drivers, hunters, security guards, ship crew members, etc. The employer must offer employees all vacancies, including lower positions, that the employee can occupy taking into account his state of health. Free places are offered both in the area where the company is located and in another, if this is provided for by the collective and labor agreement. All these proposals are carried out in any form. In this case, an order on suspension from work is not issued, since the employee is transferred to another position. If the employee refuses the offered vacancies, the employer by order removes him from work.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that if the employment contract defines duties that an employee can perform without special rights, then he is suspended from work only in relation to the performance of specific tasks and functions, and not from work in general.
An employer has the right to terminate an employment contract with an employee who is deprived of a special right for a period of more than two months, but only when he cannot be transferred to other positions (Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Information about available places in the institution is presented to the employee in the form of an offer in any form. He must write on the document whether he agrees or refuses the vacancy. The legislation does not establish the time for the employee to make a decision, but according to the usual interpretation of Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to dismiss the employee immediately after receiving information about the suspension of the special right and the impossibility of transferring him to another job. It follows from this that the employee must agree to a vacant position or refuse it at the time of familiarization with the list of vacant positions. If the transfer is agreed to, no dismissal order is issued; the parties sign an additional agreement to the employment contract, and then a transfer order is issued; in case of refusal, the employee is fired.
Important! The employer is obliged to offer vacancies that are available at the time of suspension (deprivation) of rights, and not those where, for example, the employee is temporarily absent (he is on maternity leave or vacation).
The legal nuances of temporary transfer to another job are not limited to the material described above. Each specific case, if it has become the subject of a legal dispute, may have its own characteristics, therefore, if a particular translation raises more questions, it is better to seek advice from either a professional lawyer specializing in labor relations or the local branch of the State Labor Inspectorate .
When is the replacement processed?
It is not always possible to predict the replacement of an employee. If the time of going on vacation or maternity leave is at least approximately known in advance, then it is impossible to guess when a person will go on sick leave or recover. Most often, a replacement is issued if the main employee:
- got sick;
- went on vacation (including maternity leave);
- cannot temporarily work due to other circumstances (in the event of the death of a loved one, for example).
How much time the employer has to find a person who will be assigned the responsibilities of a temporarily absent employee depends on the prevailing circumstances. There are only two options here: arrange for a combination/replacement of one of the existing employees, or hire a new one under a fixed-term contract. When time is short, they usually choose the first option, and for long-term replacement (during maternity leave) they can hire a new employee.