For an individual entrepreneur, OSN is the most unfavorable tax regime, since when applying it you have to pay all taxes, submit all reports and keep accounting records. It is worth doing business on the OSN only if the majority of counterparties are VAT payers or the company’s activities are related to the import of goods. You can switch from the OSN to one of the special tax regimes (USN, ENDV, Unified Agricultural Tax, PSN) only by submitting an application to the tax office before December 31 of the current year. The new tax regime can be applied from the beginning of the next one.
Individual entrepreneurs on OSN must pay the following taxes: personal income tax, VAT, personal property tax and other local taxes.
Concept and advantage of OSNO
If, upon registration, an individual entrepreneur did not indicate which taxation system he would use, then he will automatically switch to the general taxation system. If he wants to switch to another taxation system within a year, then he will not be able to do so, since the switch can only be made from the beginning of the calendar year. Individual entrepreneurs very rarely choose this taxation system, since accounting and reporting is very complicated compared to the simplified system.
OSNO is considered the most complex scheme for calculating taxes; accounting is also labor-intensive work. An entrepreneur needs to organize control in such a way as to avoid misunderstandings with tax authorities and penalties. But some entrepreneurs still choose this taxation system.
OSNO's big advantage is VAT. Many large companies are VAT payers and work only with such counterparties. And here the entrepreneur is faced with the choice of either losing a major supplier or buyer, or switching to OSNO. Also, when choosing to pay taxes, the type of activity, the number of employees, and the amount of revenue are taken into account.
Enterprises that choose OSNO:
- Enterprises that work with VAT payers;
- Organizations with large volumes of expenses;
- Unprofitable enterprises, or have a “zero” balance;
The main advantage of OSNO is the payment of personal income tax, so the amount of this tax is determined as a percentage of the difference between the expenses and income of the enterprise. And then the personal income tax turns out to be less than the income tax.
OSN for individual entrepreneurs: tax burden for VAT
So, the first tax that an individual entrepreneur pays on the OSN is VAT. It must be transferred by the entrepreneur to the federal budget at the rates determined by Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation from each transaction reflecting payment by the counterparty for the delivered goods or services.
Find out about the current VAT rates in 2020-2021 here.
VAT, which must be paid to the budget by the individual entrepreneur on his own behalf, is called outgoing, since it is accrued on goods and services supplied by the individual entrepreneur to other persons.
There is also input VAT, which can be included in the cost of goods and services purchased by individual entrepreneurs or can be deducted. This VAT is paid on its own behalf not by the individual entrepreneur, but by his supplier, but only if he is also a legal VAT payer and can confirm this by issuing an invoice.
Russian tax legislation allows individual entrepreneurs to apply deductions for amounts paid as input VAT (if its supplier is itself a VAT payer and issues an invoice).
Example:
Jupiter LLC, which assembles televisions, purchased components for TV assembly from IP Stepanov A.V. in the amount of 120,000 rubles. including VAT 20%, which will be included in Jupiter LLC. Subsequently, the company, having assembled the televisions, sold them for the amount of 360,000 rubles, also taking into account VAT of 20%, which will be outgoing for Jupiter LLC and incoming for buyers of televisions.
As a result, Jupiter LLC received the right to accept input VAT amounting to 20,000 rubles for deduction in the presence of output VAT amounting to 60,000 rubles.
Features of OSNO
An individual entrepreneur on OSNO must pay the following taxes:
- Personal income tax 13% – if the individual entrepreneur is a resident and 30% if a non-resident;
- VAT at the rate of 0%, 10%, 18%;
- property tax for individuals at a rate of up to 2%.
- From the moment of registration, the individual entrepreneur does not meet the basic requirements and restrictions on the requirements of the preferential treatment, or over time has ceased to meet them;
- An entrepreneur must be a VAT payer;
- An entrepreneur, by the type of his activity, falls into a preferential category for income tax;
- Due to the lack of knowledge that there are other taxation systems for individual entrepreneurs.
Types of individual entrepreneur reporting on OSN
Entrepreneurs operating under the OSN are required to submit the following types of reporting documents to the Federal Tax Service:
- VAT returns (quarterly);
- declarations in form 3-NDFL (annually);
- reports on other taxes if there is an object of taxation (within the time limits established by legal regulations).
Individual entrepreneurs and employees, in addition to the specified documents, hand over:
- information on the average number of staff (from the 2020 report submitted as part of the ERSV);
- personal income tax reporting for employees;
- reporting to funds.
Expenses that reduce personal income tax from business activities
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, individual entrepreneurs keep records of expenses in the manner determined by the Ministry of Finance of Russia.
Expenses for an entrepreneur include:
- Material costs;
- Expenses are related to labor costs;
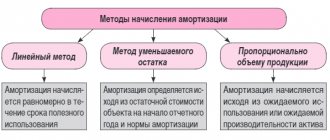
- Depreciation of fixed assets that belong to the entrepreneur and are used in business activities.
- Other expenses related to business activities;
- Amounts paid for pension and social insurance;
- Paid taxes, except personal income tax and VAT.
Professional deductions also include contributions to compulsory pension insurance (OPI) and compulsory health insurance (CHI).
Property tax for individuals is included in deductions only when it is used in business activities.
PSN: who can buy a patent in 2021
The patent tax system was introduced in 2013 to support individual entrepreneurship. Working with such a tax burden is provided only for individual entrepreneurs. PSN implies taxation of an individual on the basis of a patent - a special permit for the right to engage in certain activities.
Payment for a patent replaces personal income tax, VAT, property tax, and also allows you to reduce insurance payments for hired employees (fees are transferred to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, but contributions are not paid to the Social Insurance Fund).
The cost of a patent is fixed for each type of business at 6% of the base profitability for the current year.
The basic income is established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation depending on the region and industry specifics of management.
You can switch to PSN if the number of employees is no more than 15 people, the annual turnover is no more than 60 million rubles, and the area of the rented premises is up to 50 sq. m. An application for transfer to a patent is submitted no later than 10 banking days before the planned transfer. The patent is paid until its expiration date, regardless of whether the company made a profit or suffered losses. If the patent validity period is more than 6 months, payment is possible in two payments.
The following aspects are of interest in PSN:
- independence of the tax paid from the amount of profit received;
- the opportunity to purchase a patent for a period of 1 month to 1 year;
- the only regime in which filing a tax return is not required;
- simplified accounting and tax accounting;
- you can purchase several patents for different types of work and services;
- You don't need a cash register to operate.
For an individual entrepreneur who falls under the list of types of activities permitted for PSN, whose bulk of clients are individuals or small business organizations that are not VAT payers, such taxation is very profitable and promising. And also in this mode it is convenient to try out new commercial directions. All the nuances of the patent system are described in detail on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
The French writer, jurist and philosopher Charles Louis de Montesquieu argued: “Nothing requires so much wisdom and intelligence as to determine the part that is taken from the subjects and the part that is left to them.”
How are the expenses of an individual entrepreneur taken into account?
There are certain conditions that must be met in order for expenses to be taken into account when calculating personal income tax. The conditions are:
- Expenses must be paid in full;
- Expenses are associated only with the professional activities of an individual entrepreneur;
- There must be supporting documents, such as invoices, acts, invoices, etc.
There are cases when an entrepreneur cannot document his expenses, then he can take advantage of a professional deduction in the amount of 20% of the amount of income received.
Important. Documentary evidence and the 20% professional deduction cannot be taken into account at the same time.
According to Order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 13, 2002 No. 86n, expenses of an individual entrepreneur can be recognized under the following conditions:
| Recognition criterion | Description |
| Relationship between income and expenses | expenses can be taken into account as deductions for personal income tax only during the period of receipt of income with their help or subsequently |
| Expenses for the purchase of raw materials, materials, goods | These expenses can be included in the professional deduction only when they are written off for production, sales, etc. |
| Depreciation amounts | Amounts of depreciation can be taken into account as a professional deduction only when the property of an individual that is used in business activities must be owned. |
| Seasonal expenses | If the entrepreneur’s activities are seasonal, it is also necessary to observe the principle of the connection between expenses received and income. |
Zero declaration
A zero declaration is reporting that indicates that the taxpayer has no tax base and no tax payable in the reporting period. The obligation to represent it arises for the individual entrepreneur if the following conditions are met:
- its activities are carried out at OSNO;
- There was no such activity for the tax quarter.
The following must be filled out in the zero declaration:
- title page;
- first section.
Sections 2-12 are not completed, since there is no tax base for them.
Title page
On the title page the individual entrepreneur indicates:
- name, TIN code;
- Federal Tax Service number;
- code at the place of registration;
- adjustment number - “0” - for the first time during the reporting year, the next time - from “1”;
- tax period – quarterly codes “21-24”;
- activity code according to OKVED;
- current contact phone number.
Below you must indicate the number of completed pages in the reporting, the full name and position of the person who signed the declaration.
1 section
In section 1, the individual entrepreneur indicates:
Line 010: - code according to OKTMO;
Line 020: - KBK data;
Lines 030–050: — zeros, due to the lack of a base for calculating tax;
Lines 060–080: - are written if the code “227” is indicated in the line “code at the place of registration” on the title page. For other codes, zeros are entered.
The representative of the declaration certifies the section with a signature and indicates the date.
Feeding features
The zero declaration is submitted to the Federal Tax Service by the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter, exclusively in electronic form via TKS with the help of a special operator. Submitted on paper, it will automatically be considered invalid.
Penalties
Clause 1 of Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for liability, in case of failure to submit a zero declaration - a fine of 1,000 rubles. The same penalty is imposed for late submission.
Systematic violation of deadlines threatens to block bank accounts and stop electronic money transfers.
A situational plan of a land plot for gasification must be requested from the authorized body or a private organization. What is land demarcation and how is it carried out? Find out about this by reading our article.
KBK codes for land tax can be found here.
“Non-entrepreneurial” ways to reduce personal income tax
In addition to the professional deduction, an individual entrepreneur can reduce his expenses that arise in the course of business activities through social, standard and property deductions.
Take a concrete example of training costs:
Individual entrepreneur Sokolova T.O. two children.
One child attends a preschool institution, which costs 30,000.00 rubles per year. He also attends an art school - tuition fees are 25,000.00 rubles.
The second child goes to a sports school - tuition fees per year are 54,000.00 rubles.
In connection with production costs, individual entrepreneur Sokolov T.O. wants to claim a deduction for training expenses in the amount of 100,000.00 rubles (50,000.00*2), which will allow him to reduce the tax paid for the year by 13,000.00 rubles (100,000*13)
Note. The total amount of expenses for which an entrepreneur can be provided with a social deduction, with the exception of expenses incurred for expensive treatment and education of children, cannot exceed 120,000 rubles.
How to pay personal income tax
Since 2021, individual entrepreneurs on OSNO have been calculating advance payments independently based on income received, tax deductions and taking into account previously calculated advances - at the end of 3, 6 and 9 months of the current year. At the end of the year, you need to pay the final personal income tax according to the 3-NDFL declaration.
Calculation example:
| Period | Profit | Payment |
| 3 months | 300,000 rub. | 300,000 x 13% = 39,000 rub. |
| 6 months | 700,000 rub. |
|
| 9 months | 1,200,000 rub. |
|
| 1 year | RUB 1,300,000 |
|
We recommend reading: Declaration 4-NDFL for individual entrepreneurs on OSNO and advance payments.
FAQ
Question No. 1 What is OSNO?
Answer: OSNO is one of the types of taxation system, where an enterprise keeps full accounting records and pays all general taxes.
Question No. 2 What is the advantage of OSNO?
Answer: The main advantage of OSNO is the payment of personal income tax, so the amount of this tax is determined as a percentage of the difference between the expenses and income of the enterprise. And then the personal income tax turns out to be less than the income tax.
Answer: Expenses that reduce personal income tax on OSNO include material expenses, labor costs, depreciation, as well as other expenses that are associated with business activities.
Question No. 4 What conditions must be met in order to reduce personal income tax on OSNO? Answer: The conditions are very simple: payment of all expenses in full, you must provide supporting documents and the expenses are related only to business activities.
Question No. 5 Is it possible to simultaneously use a professional deduction and documentary evidence of expenses to reduce personal income tax?
Answer: Documentary evidence and the 20% professional deduction cannot be taken into account at the same time.
An individual entrepreneur faces certain difficulties when organizing his activities. Among other things, the question arises of which taxation system to choose and what are the individual entrepreneur’s expenses for OSNO. It all depends on the type of activity of the businessman, the amount of his income and the number of employees. Let's take a closer look at what the individual entrepreneur's expenses for OSNO are.
Results
The general taxation system for individual entrepreneurs is often considered not the most profitable due to the relatively high tax burden and the need to prepare numerous reports. However, the work of an individual entrepreneur on OSN can have undeniable advantages.
The fact is that many VAT payers try to interact only with those suppliers who also pay VAT in order to be able to receive tax deductions.
You can get acquainted with other remarkable facts about OSN in the articles:
- “How can an organization choose a tax regime: OSN, simplified tax system or UTII?”;
- “Can an entrepreneur who has switched to OSN reduce the income from the sale of real estate acquired by him on a simplified basis?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Advantages of OSNO
If an entrepreneur did not indicate the chosen taxation system during registration, then he automatically becomes a tax payer under the general regime with the ensuing responsibilities. You can switch to the simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax or patent with OSNO only from the beginning of the calendar year. This system of individual entrepreneurs is chosen very rarely, because in it, unlike the simplified one, the principles of accounting and reporting are more complex and require the application of certain efforts and time.
A businessman can maintain documentation independently, hire an accountant, use the Internet Accounting service, or seek help from a consulting company. In addition to paying taxes, an entrepreneur needs to pay a salary to an accountant or make contributions to a consulting company, which significantly increases costs.
Value added tax payable
If the VAT calculated on sales exceeds the tax deduction, the tax amount is subject to payment to the budget.
The tax is paid at the end of each quarter by the 25th
each of the three months following the previous period, in equal shares.
For example, according to the declaration for the 2nd quarter of 2021, VAT payable is equal to 90 thousand rubles. The tax will need to be paid by:
- July 25 – 30 thousand rubles (1/3);
- August 25 – 30 thousand rubles. (1/3);
- September 25 – 30 thousand rubles. (1/3).
Note
: tax can be paid in full in the first month after the end of the quarter. The main thing is to pay at least 1/3 of the tax amount by the 25th day of the first month after the previous quarter, otherwise there will be a delay in payment by this deadline.
Note
: if you are not a VAT payer, but you have issued an invoice with an allocated VAT amount, the tax will need to be paid in full
within 25 days after the end of the quarter
.
STS – simplified taxation system
Who is it suitable for: individual entrepreneurs that meet all the requirements of Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- number of employees up to 100 people,
- annual income or cost of fixed assets is not more than 150 million rubles,
- the business is not related to insurance, extraction of oil or other natural resources, sale of securities, operation of a bank or pawnshop.
How to switch: you can choose the simplified tax system within 30 days after registering an individual entrepreneur. If UTII was previously used, then within 30 days from the date of refusal of imputation. Other entrepreneurs can switch to this special regime from the beginning of the new year.
If you prepare a package of documents for registration as an individual entrepreneur using the free “My Business” service, then in addition to all completed documents you will also receive an application for transition to the simplified tax system. It is most convenient to submit the notification along with a package of registration documents.
What tax to pay: with the “simplified” tax system, you need to pay taxes quarterly, and submit a declaration only once a year. This is simpler than using the general taxation system, which is why many individual entrepreneurs choose the simplified tax system. Moreover, the list of restrictions is not as large as with other special modes.
The simplified taxation system is presented in two versions:
- The simplified tax system for the “Income” scheme is calculated using the formula: simplified tax system = Income * Rate 6%.
- STS according to the “Income minus expenses” scheme - according to the formula: STS = (Income - Expenses) * Rate 15%.
The rate is higher, but you can reduce the tax base by the amount of expenses (a list of eligible expenses is given in Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is advisable to choose this taxation scheme if the share of expenses in revenue is over 60%. If your expenses are more than this limit, then you can stay on this special regime, and if less, choose the simplified tax system at a rate of 6% of income.
Not everything is so simple. You need to look not only at the size of your expenses, but also at the regional nuances of applying the simplified tax system. By decision of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in a particular region and for individual entrepreneurs with different types of activities, rates can be reduced from 6% to 0% under the “Income” scheme and from 15% to 5% under the “Income minus expenses” scheme.
The more profitable option will be the special regime that provides reduced rates in your region. Of course, provided that your type of business is included in the list of beneficiaries. What benefits are available in your region can be found on the official website of the tax service.
Example:
In the Law of the Moscow Region of February 12, 2009 N 9/2009-OZ, the list of types of activities for which a reduced rate under the simplified tax system is not included does not include car repair. Let's calculate what tax our individual entrepreneur will pay under different simplified taxation systems at basic rates, without benefits.
- STS “Income” at a rate of 6%, but the amount of insurance premiums can be deducted from the tax amount (we calculated it earlier). It will turn out like this: 1,000,000 * 6% – 43,238 rubles. = 16,762 rub.
- STS “Income minus expenses” at a rate of 15%, while the tax base can be reduced by the amount of confirmed business expenses (200 thousand rubles) and by the amount of insurance premiums (43,238 rubles). Then the tax calculation will be as follows: 15% * (1,000,000 – 200,000 – 43,238) = 113,514.3 rubles.
Whichever option you choose, remember that you must also pay insurance premiums in addition to the calculated tax according to the simplified tax system.
Is personal income tax for employees included in expenses - 2021 - 2021 under OSNO and simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
An entrepreneur pays personal income tax not only for himself. When paying income to employees, he becomes a tax agent for payroll tax and is obliged to calculate, withhold from employees and pay this tax to the budget.
Both under the OSNO and under the simplified tax system with the object “income reduced by the amount of expenses,” an individual entrepreneur can take into account the amount of the transferred personal income tax - but not as an independent expense, but as part of the costs of paying employees with whom an employment or civil law contract has been concluded. In other words, the salary is accepted as expenses without reducing it by the withheld personal income tax. This is confirmed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia (letters dated December 15, 2015 No. 03-11-06/2/5880 and dated December 19, 2008 No. 03-04-05-01/464).
How an entrepreneur can keep track of expenses under the simplified tax system, find out in the material “How to properly keep track of income and expenses of an individual entrepreneur?” .
VAT exemption
Did you know that you can avoid paying VAT at all? Yes, Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that individual entrepreneurs may be exempt from paying this tax. You can use this right if for the three previous tax periods the amount of revenue of the enterprise was less than two million rubles. But do not count on such a privilege if you are selling excisable products. Alcohol, tobacco, fuel, some categories of cars - trade in all of this deprives the prospect of being exempt from tax.
Individual entrepreneurs may be exempt from paying this tax.
To obtain an official exemption from VAT, contact the tax office at your place of registration with a completed notice, an extract from the income-expenses book and a copy of the invoice registration book. Have time to submit your papers before the 20th of the month from which you plan to “become released.”
You must confirm your right not to pay VAT once a year. If the situation has changed and revenue has increased, you should notify the tax office yourself, otherwise the punishment will be fines and penalties. This also applies to cases where during the reporting period you sold excisable products.
Non-operating expenses
Non-operating expenses are not directly related to the company's activities. If there are no problems with determining production costs, then the identification of the second category is doubtful. These include (Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- costs of maintaining the leased property;
- interest paid on loans;
- negative differences in exchange rates;
- litigation costs;
- bank commissions;
- treaty sanctions;
- taxes and advances on them;
- any other reasonable expenses - that is, the list is not closed.
Losses in the form of bad debts, losses from downtime, shortages and losses from natural disasters also fall into this category.