olegas 2 years ago / 250 Views
Competent selection of shares for investment involves conducting a preliminary analysis of the issuing company. Without this kind of assessment, buying shares, as the famous American financier and investor Peter Lynch aptly put it, can be compared to playing poker without looking at the cards.
The ultimate goal of this type of analysis is to determine the degree of investment attractiveness of the analyzed issuing company. Reading a company's balance sheet allows an investor to answer the question of whether its shares are worth investing in and what risk it might entail.
In this article we will look at the main criteria on which the analysis of a company’s balance sheet is based. In addition, we will give an example of an algorithm for such an analysis using the example of one of the companies representing the American stock market.
- Setting priorities
- Vertical analysis
- Horizontal analysis
- Current Assets
- Cash And Cash Equivalents
- Accounts receivables (Net Receivables)
- Inventory
- Liabilities of the company
- Stockholders' Equity
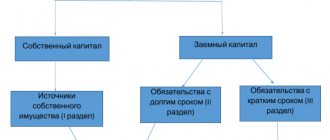
Brief description and composition of the enterprise’s capital
The capital of an organization can be monetary (i.e., in monetary terms, in money) or real, implying its expression in the means of production. This approach is considered the most optimal in terms of capital.
As is customary, money capital (MC), in other words, money is used by an organization for the purpose of purchasing means of production. At the same time, the funds that go to support households. activities can be either own or borrowed. Characterizing equity capital from this side, it should be noted that:
- it means the monetary value of property owned by the enterprise;
- it is taken into account as the difference between the book value of this property and the liabilities that the enterprise has at that moment;
Important! The value of the property includes, among other things, amounts unclaimed from debtors.
- its composition takes into account different sources, such as: profits from the results of its activities, authorized capital, share capital, as well as contributions and donations.
Thus, the composition of its capital includes the amounts of: authorized, reserve, additional capital (MC, RK and, accordingly, DC), as well as retained earnings (RE) and targeted financing.
Own capital (hereinafter also abbreviated as SK) gives the right to participate in the management of the organization. The sources of its formation can be external and internal, and the key area of its financing is long-term assets. Meanwhile, specific terms with terms of payment and return have not been determined.
How do short-term liabilities affect the amount of working capital?
The company's working capital indicator directly depends on the amount of current (short-term) liabilities. The greater the amount of current debts, the lower the working capital (with current assets remaining unchanged).
Presented in Section V, Current liabilities on the balance sheet are current liabilities (CL). The Current Liabilities section in the balance sheet is line 1510-1550. Current liabilities include: loans, debt to creditors, reserves for future expenses, expected future income, as well as other obligations. The other short-term liabilities indicated on page 1550 in the balance sheet are data on liabilities that are very significant for the enterprise, which were not taken into account on pages 1510-1540. For example, funds received from investors of a development company in the form of targeted financing.
The most important from the point of view of urgency of repayment are borrowed funds (1510): such debts must be repaid regularly, and late payment is fraught with additional costs in the form of fines provided for in loan agreements.
Accounts payable (1520) not repaid on time also entails negative consequences. For example, having a salary not paid on time (short-term obligations) will require additional material expenses, because you will have to find funds to pay compensation. Its size is calculated based on 1/300 of the refinancing rate for each day of delay, unless otherwise established by the collective agreement (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This money will have to be withdrawn from circulation, and there may not be enough funds to support current economic activities.
If a company has overdue tax obligations, it may also entail additional expenses for the payment of penalties and fines.
For information about what punishment a company will face if it transfers personal income tax to the budget late, see the article “What is the liability for non-payment of personal income tax?”
Long-term and short-term liabilities (Sections IV and V of the balance sheet) are sources of funds for the enterprise, with the exception of capital and reserves (Section III). Current liabilities include all debts that are due within a year, while long-term liabilities have a maturity of one year or more.
The more money is required to pay off short-term obligations, the greater the need for working capital to ensure current activities and, as a result, the lower the amount of working capital.
In the next section, you will learn how to calculate your own working capital using completely different balance sheet indicators.
The main components of its capital (MC, RK, DC and NP) in accounting. balance sheet
Own capital, or more precisely, all its components (MC, RK, DC and NP), are fully represented in the accounting. balance sheet No. 1. The current balance sheet form, corresponding to OKUD 0710001, was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 66n dated 07/02/2010. The latest changes to the wording of this order are dated April 19, 2019. The named components of the insurance company correspond to balance sheet lines 1310-1370. The insurance amount itself is written down on page 1300.
| Line by line distribution by book. balance | ||||
| UK | Revaluation of VA | DK | RK | NP |
| 1310 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 |
It should be noted that this balance sheet interpretation of the SC concept is traditional and most widespread. Moreover, this approach is used not only in domestic practice, but also abroad. In this regard, it is advisable to separately consider each component (MC, RK, DC and NP) of equity capital.
Authorized capital (AC) according to accounting. the balance sheet consists, literally, of “shared capital, authorized capital and contributions of partners.” In other words, this is the totality of all funds brought by the founders of an enterprise or organization into the property directly upon its formation. The sizes of these deposits, shares (other) are determined, as established, by the constituent documentation. Its corresponding value is subject to recording during state registration.
Reserve capital (RC) is a certain part of your capital. It is usually allocated from profit for the purpose of covering potential, expected losses. The size of the Republic of Kazakhstan and its features, the formation procedure are established by the legislation of the Russian Federation and the organization’s charter itself.
Additional capital (AC) is the price of property that was brought in by the founders of the organization after state registration of the size of the capital. These are already excess amounts generated from other cash receipts in the insurance company. Such an amount, for example, may arise as a result of a property revaluation, which revealed changes in the price of property.
Another important component of an enterprise’s capital is its retained earnings (RE). It is considered an absolute indicator of the effective performance of enterprises, reflecting retained earnings received for a specific period of operation. This part of the VP is after taxes are deducted and funds are transferred to other purposes.
The insurance company also includes investment and accumulated capital. The first includes the investments of the founders themselves, and the second, accumulated, includes that part of the capital that is formed and brought in above the first. The composition of SC can be shown schematically in the following way.
It is important to know and distinguish the terms listed above and their definitions, since they are involved in the formation and calculation of the insurance system.
Example of RNS calculation
The formulas for own working capital (WCC), discussed in the previous sections, are based on completely different balance sheet indicators, but lead to the same result. Let's consider both options for calculating the SOC using the example of the following balance sheet indicators:
| Indicator name | Code | As of December 31, 2020, thousand rubles. |
| Assets | ||
| I. Non-current assets | ||
| Fixed assets | 1150 | 430 |
| II. Current assets | ||
| Reserves | 1210 | 100 |
| Accounts receivable | 1230 | 20 |
| Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) | 1240 | 34 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 1250 | 90 |
| BALANCE | 1600 | 674 |
| Passive | ||
| IV. Capital and reserves | ||
| Authorized capital | 1310 | 10 |
| retained earnings | 1370 | 104 |
| V. Long-term liabilities | ||
| Borrowed funds | 1410 | 350 |
| VI. Short-term liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | 1520 | 210 |
| BALANCE | 1700 | 674 |
1st calculation option:
SOC = (100,000 + 20,000 + 34,000 + 90,000) – 210,000 = 34,000 rub.
2nd calculation option:
SOC = (10,000 + 104,000) + 350,000 – 430,000 = 34,000 rub.
In various sources, own working capital is called net working capital (NWC) or working capital (WK), since it shows the amount of funds remaining with the company after paying off current debts and is in constant circulation (work). In any case, own working capital is the most important characteristic of the capital involved in the current activities of the company.
Calculation of the SC value using the updated accounting form. balance
There are several ways to determine the amount of SC. The simplest and most understandable is the accounting calculation. balance. It is based on the summation of the values of those indicators that actually form the sum of the capital insurance (they were discussed above) minus line 1320 (shares purchased from shareholders).
We are talking about four values: UK, RK, DC and NP, which correspond to balance sheet lines 1310, 1340, 1350, 1360, 1370. The balance sheet calculation formula in this case will be as follows:
To get the amount of the capital account for the year, you should add the value of the capital account at the beginning and at the end of the required period (year). Calculation is made according to the formula:
Abbreviations in formula 2: SK - own capital for the whole year, SK n.g. – your capital at the beginning of the corresponding year, SK k.g. – your capital at the end of the same year.
In addition to the above calculation options, there is also another method used taking into account the instructions of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, presented in Order No. 84n dated 08/28/2014 (as amended on 02/21/2018). This regulatory document establishes the procedure for determining the value of net assets, which must be followed by LLCs, JSCs, state unitary enterprises, municipal unitary enterprises, industrial and housing savings cooperatives, as well as households. partnerships.
From the procedure established by the Ministry of Finance, the provisions that determine the composition of assets and liabilities taken into account in the calculation are applied in practice. So, according to the current procedure, when calculating the value of the SC, take into account:
- all assets (except for those that reflect the debts of the founders or shareholders for authorized contributions);
- all liabilities (except for income of subsequent periods, especially related to government assistance and gratuitous receipt of property).
Guided by these standards, when calculating, they take data from lines 1600 (assets), 1400 (long-term liabilities) and 1500 (current liabilities). The value is calculated using the formula:
Abbreviations in formula 3: DU - the amount of debt of the founders of the household. society, DBP - the amount of income of subsequent, future periods.
When calculating the insurance company, you should also take into account the basic formula, which is quite simple and looks like this:
The balance sheet currency is the total amount for all component accounts. balance. Moreover, the total amount of assets = the total amount of liabilities.
Where is it used?
Knowing the SOC indicator, we can calculate the share of the SK in the formation of the company’s OA:
DSC = SOK / OA
A value of this coefficient of at least 0.1 is considered acceptable. Comparison of this indicator over several periods (over time) will show an increase or decrease in the company’s dependence on external borrowings.
The capital agility ratio illustrates how much the firm's capital is involved in turnover and is calculated as follows:
KMK = SOK / SK
Another important indicator is the availability of inventory sources of financing. If the amount of inventories at the reporting date is less than the value of the SOC, the enterprise is characterized by absolute short-term financial stability. When calculating the supply ratio, the SOC value is divided by the amount of reserves. The normal value of this coefficient is 0.5.
What value of SC is considered optimal for enterprises?
The calculation result can be positive or negative (sum with a minus). In general, it is generally accepted that the SC value should be at least positive. The presence of a minus, negative amount indicates that the organization has serious problems associated with a significant credit burden and a shortage of highly liquid assets.
Rate fin. the state of the organization can be achieved by comparing the amounts of capital insurance and capital. It is generally accepted that the optimal value of the SC or NA should be equal in size to the amount of the Criminal Code or be greater than its value. The rationale for this standard is quite obvious. After all, any entrepreneurial activity must, firstly, pay off, and, secondly, maintain constant investment attractiveness. The organization should always feel an influx of new capital.
It follows that if the specified norm for the ratio of capital insurance and capital is not observed, i.e., the capital exceeds the value of the capital, then the organization may have two ways out of this problematic situation. First: start liquidation. Second: take appropriate measures to achieve the standard (i.e., to achieve the required ratio of CM and SC).
To summarize, we should once again pay attention to the fact that the value of the SC should be positive, and in the optimal case, also exceed the value of the UK.
Filling a line
Line 1150 indicates the residual value of all financial assets of the organization, formed at the end of the reporting period. To do this, from the primary price of the company's fixed income, reflected in account 01 in debit, it is necessary to subtract the amount of depreciation accumulated on them (accounted for in account 02 in credit). That is, this line records the difference between the debit balance of account 01 and the credit balance of account 02.
If additional equipment or reconstruction took place (as a result of which the initial price of the objects was increased), this must be stated in the appendices to the accounting. balance.
The same applies to the revaluation of property. As a rule, it is carried out once a year. It is carried out by indexing the current value of objects or by recalculating to the actual market price. The resulting differences increase the amount of additional capital.
One of the letters from the Ministry of Finance states that financial assets that are unsuitable for subsequent use must be written off. Their residual price is included in other costs.
Example 2. Calculation of the SC value using the general formula
Let's assume there is data from accounting. balance sheet for non-current, current assets (VA and OA), as well as long-term and short-term liabilities (DO and KO). The sum of assets equals the sum of liabilities (A=P). You should calculate the amount of the capital account using formula 4 (Balance sheet currency – Organization liabilities).
| Conditional data for calculation | Costing itself | Counting result |
| VA: 17,000 thousand. rub.; OA: 10,500 thousand rub.; BEFORE: RUR 1050 thousand rub.; CO: 9,000 thousand rub. rub. | First calculation. A = P = VA + OA = 17,000 + 10,500 = 27,500 Second calculation. SK = A(P) – DO – KO = 27,500 – 1,050 – 9,000=17,450 | Total, the amount of SC = 17,450 thousand rubles. rub. Therefore, on page 1300 they indicate “17,450” |
Results
Own working capital can be calculated in different ways using balance sheet figures. It characterizes the volume of the company’s own and equivalent funds aimed at financing current assets.
Analysis of the calculated amount of own working capital helps to take timely measures to optimize it and increase the efficiency of the company.
Sources: Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How is the initial price of an object formed?
Fixed assets are reflected in the balance sheet at their original cost - the sum of all expenses for the purchase of the object. Such costs include:
- Payment to the seller of the object;
- Transportation costs;
- Costs of consulting services related to the purchase of the property;
- Customs duties and fees;
- The amount of non-refundable taxes paid upon acquisition of the property;
- Expenses for state registration of property rights to the object;
- Payment for services of intermediary firms;
- Other expenses.
Conditions for classifying an object as a fixed asset
Accounting for fixed assets is regulated by the Regulations “Accounting for fixed assets”. In accordance with it, in order to recognize an object as a fixed asset, it must meet the following requirements:
- The object will be used in the production process or for the management needs of the company. Also, it can be intended for rental. It is worth noting that the price of objects purchased for rental is not reflected in the line “fixed assets in the balance sheet”.
- The company must use the facility for at least twelve months.
- The initial price of the object is at least one hundred thousand rubles.
- When a firm buys a property, it has no immediate plans to sell it.
- In the future, the object will bring profit to the organization.