On October 1, 2021, a new edition of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation came into force. 68 amendments have been made to the code, which relate to an increase in state duty, the procedure for determining the tax base for VAT, the application of a zero VAT rate for exports, as well as other issues related to the application of value added tax.
The edition of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has been amended by several new laws since October 1, 2021:
- Federal Law of August 3, 2018 N 303-FZ;
- Federal Law of August 3, 2018 N 302-FZ;
- Federal Law of August 3, 2018 N 301-FZ;
- Federal Law of June 27, 2018 N 159-FZ;
- Federal Law of June 4, 2018 N 143-FZ;
- Federal Law of June 4, 2018 N 143-FZ.
For the most part, all amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are related to VAT. In particular, the conditions for applying the zero rate were determined, an updated procedure for determining the tax base was established, and the responsibilities of tax agents were clarified. In addition, one change concerns the state fee.
Government duty
The wording of Article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has been changed, a new subclause 138 has been added to its paragraph 1. Its norms establish a state duty for the issuance of federal special and (or) excise stamps with a two-dimensional bar code for labeling alcoholic products. Its size is 0.16 rubles for each stamp.
According to the norms of the new edition of Article 333.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when applying for a legally significant action specified in the new subparagraph 138 of paragraph 1 of Article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payment of the state duty must be made after submitting the application and documents for such an action, but before the issuance of federal special stamps and excise stamps marks.
Refund of state duty
On October 25, a new procedure for the return of state fees when concluding a settlement agreement in court will be introduced (Federal Law dated July 26, 2019 No. 198-FZ).
According to the new rules, when concluding a settlement agreement before the court of first instance makes a decision, the plaintiff is returned 70% of the state duty paid by him. The same applies to cases of refusal of a claim and recognition of a claim.
If a settlement agreement is concluded in an appellate court, 50% of the state fee is refundable. If in the court of cassation - 30% of the state duty. Let us remind you that now the maximum amount possible for refund is 50% of the amount of the state duty paid.
The procedure for determining the tax base for VAT upon receipt of an advance payment
In accordance with the new edition of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when assigning a monetary claim arising from a contract for the sale of goods (work, services), transferring property rights to residential buildings or residential premises and shares in them, garages and parking spaces, and receiving for this prepayments, the tax base is determined according to new rules. In particular, the following paragraph was added to the article:
When the taxpayer receives payment, partial payment on account of the upcoming transfer of property rights in the cases provided for in paragraph two of paragraph 1 and paragraphs 2 - 4 of Article 155 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base is determined as the difference between the amount of payment, partial payment received by the taxpayer on account of the upcoming transfer of property rights rights, and the amount of expenses for the acquisition of these rights (the size of the monetary claim, including future claims), determined based on the share of payment, partial payment in the cost at which property rights are transferred.
In this case, VAT paid on prepayment can be deducted according to the new edition of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and in the manner prescribed by Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The new five percent rule
Currently, paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code requires separate accounting of input VAT on the acquisition of goods, works or services that are used in taxable and non-taxable activities. At the same time, the taxpayer has the right not to comply with this rule, that is, not to keep separate records of transactions, if the share of costs allocated to operations not subject to value added tax does not exceed 5% of the total amount of expenses. All VAT charged by suppliers is simply accepted for deduction.
With the introduction of new amendments, the situation with such leading VAT will change from 2021. The right to deduct the entire amount of input VAT, subject to the 5 percent limit, will remain, but you will still have to keep separate records of taxable and non-taxable transactions.
New tax agents
Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has been supplemented with a new clause 5.1, according to which Russian railway carriers are recognized as tax agents when providing railway rolling stock or containers on the territory of the Russian Federation on the basis of contracts of assignment, commission or agency agreements. This provision applies to services provided starting from October 1, 2021, and does not apply to cases of provision of services:
- on international transportation of goods;
- transport and forwarding services;
- services for the provision of railway rolling stock or containers for transportation,
but only on condition that the point of departure and destination are located on the territory of Russia.
Salary increase
From October 1, the salaries of public sector employees will be increased (Order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated March 13, 2019 No. 415-r). Salaries of employees of federal government, budgetary and autonomous institutions financed from the budget will be increased by 4.3%.
The salaries of employees of federal government bodies, civilian personnel of military units, institutions and divisions of federal executive authorities will increase by the same amount.
Zero VAT rate
The new norms of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Tax rates” provide for the possibility of applying a zero VAT rate from October 1, 2021 for:
- provision of services for domestic air transportation with a point of departure or destination in the Far Eastern Federal District (until January 1, 2025);
- carrying out, without a license for the use of subsoil, the production of precious metals from scrap and waste;
- sales of goods exported from the territory of the Russian Federation to the territory of a member state of the Eurasian Economic Union, in cases provided for by the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union of May 29, 2014;
- provision of services for the provision of sea vessels, mixed (river-sea) navigation vessels and services of crew members of such vessels for use for a certain period of time on the basis of contracts for chartering a vessel for a time (time charter) for the purpose of transportation (transportation) exported outside the territory of the Russian Federation or goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation.
Taxes 2018: important changes. Part two: VAT
Separate VAT accounting
The following clarifications have been made to the Tax Code:
- compliance with the 5 percent rule allows, as before, to accept “input” VAT for deduction in full. However, it is necessary to keep separate records;
- it is stipulated that the 5 percent rule does not work when the product is used only in VAT-free transactions. Previously, this point of view was expressed by the Ministry of Finance, the Federal Tax Service and the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation.
Refusal of zero VAT rate
Amendments have been made to Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which allows, from January 1, 2018, to abandon the application of the 0% rate when selling goods exported as part of the export procedure, as well as when performing certain types of work or services in relation to such goods. Among them:
- services for international transportation of goods;
- works and services performed and provided by oil and petroleum products pipeline transport organizations for the transportation, transshipment or reloading of oil and petroleum products; services for organizing pipeline transportation of natural gas.
Cancellation of VAT deduction when purchasing through subsidies
But the changes that will affect taxpayers purchasing goods, works or services from budget funds are unlikely to please. Let us remind you that until 2021 the following rules were in force. If the taxpayer has accepted VAT as a deduction on goods (works, services), and later the costs of purchasing them or paying import VAT are compensated by subsidies, then the tax must be restored. From January 1, 2021, the tax will also have to be restored when receiving budget investments. The rules for such restoration have been clarified (clause “c”, paragraph 12, article 2 of Law No. 335-FZ):
- VAT is restored regardless of whether it is included in subsidies (budget investments) or not;
- in case of partial reimbursement of costs, the amount of VAT is restored in the share, which is determined based on the cost of goods (work, services) excluding VAT, acquired through subsidies (budget investments), in the total cost of purchased goods (work, services) excluding VAT. Previously, in such a situation, regulatory authorities recommended restoring the tax in relation to the subsidies received (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 19, 2012 No. 03-07-11/15).
The legislator did not limit himself only to the restoration of VAT, but prohibited, from January 1, 2021, from declaring deductions for goods, works and services (including fixed assets and intangible assets) acquired through subsidies or budget investments (clause “b” of paragraph 12 Article 2 of Law No. 335-FZ).
VAT that has not been deducted can be included in income tax expenses if two conditions are simultaneously met:
- expenses for purchased goods, works and services are taken into account as expenses when calculating profit, including through accrued depreciation;
- Separate accounting of VAT amounts is maintained for goods, works and services purchased through subsidies or budget investments.
Since the changes come into force on January 1, 2018, we do not recommend claiming a tax deduction for those goods purchased (shipped by the seller) using subsidies (investments) after January 1, 2021.
Updating the VAT return form
The change in the form of the VAT tax return (approved by Order No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] , 2014) is due to the introduction by Federal Law No. 463-FZ of December 28, 2016 of amendments to Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which Services provided within the framework of arbitration are not subject to VAT.
New formats for VAT documents
In the new year, tax authorities will update the electronic formats of the invoice journal, purchase book and sales book, as well as additional sheets for them. The change in current formats is due to the approval, from October 1, 2021, of new forms for the journal of received and issued invoices, the purchase book, and the sales book. From this date, amendments to the forms of VAT documents have already come into force (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 19, 2017 No. 981). In 2021, VAT documents will need to be prepared using new formats.
Payment of VAT by Unified Agricultural Tax payers
Federal Law No. 335-FZ dated November 27, 2017 recognizes agricultural producers on the Unified Agricultural Tax as VAT payers. According to the authorities, this is a necessary measure in order to smoothly integrate agricultural producers into economic relations with VAT payers. In addition to changes in the part of VAT for Unified Agricultural Tax payers, it is proposed to apply the exemption from property tax only to the part of property used in business activities in respect of which this special tax regime is applied.
Expanding the list of tax agents Federal Law No. 335-FZ dated November 27, 2017 assigns the functions of tax agents for VAT to buyers of certain types of products. Thus, in 2021, buyers as tax agents will be required to pay VAT on the purchase of raw animal skins, scrap and waste of ferrous and non-ferrous metals, secondary aluminum and its alloys. Only individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs are not recognized as tax agents. These tax agents are required to calculate and pay VAT to the budget, regardless of whether they themselves are VAT payers or not. This, in turn, will raise the question of software with functionality that provides the necessary accounting and reporting.
Contact us and we will answer them, 8(804) 333-16-02
Best regards, e-office24 team!
Share with your friends!
The procedure for confirming the zero VAT rate
According to the norms of the new edition of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is now possible to confirm the zero VAT rate for exports, among other things, by a contract (a copy of the contract) with a Russian organization for the supply of goods to its separate division, which is located outside the EAEU. Moreover, if such contracts were previously submitted to the Federal Tax Service to justify the application of the zero tax rate for VAT or to justify exemption from excise duty for previous tax periods, their resubmission is not required. Instead, it is necessary to submit a notification indicating the details of the document with which the specified documents were submitted and the name of the tax authority to which they were submitted.
Also, taxpayers now may not submit to the Federal Tax Service of Russia copies of transport, shipping or other documents with marks from the customs authorities of the places of departure confirming the export of goods outside the Russian Federation. When exporting to the EAEU, it is possible not to submit these documents if the list of applications for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes is presented in electronic form. But if the tax authority discovers an inconsistency in the information provided by the taxpayer, or its absence, the tax authorities have the right to request copies of documents confirming the export of goods outside the Russian Federation. These rules begin to apply to operations for the sale of goods (works, services) carried out starting from October 1, 2021.
When compensating tax amounts, participants in the “tax free” system must submit a register to the Federal Tax Service, which indicates information from documents (checks) for compensation of the tax amount, containing a mark from the customs authorities of the Russian Federation confirming the export of goods outside the customs territory of the EAEU and information about the compensated amount VAT. This register must contain information about the size of the tax base to which the taxpayer applies a zero tax rate.
Consequences of change: ↑
Organizations will continue to have questions for a long time related to innovations that appeared thanks to the adopted Federal Law No. 238-FZ of July 21, 2014.
The government tried to take into account all the nuances and weaknesses of the previously existing legislation.
With the entry into force of the innovations, the conduct of commercial activities has become easier for both selling organizations and purchasing enterprises.
pros
Among the advantages of the adopted changes it is worth noting:
- simplification of document flow;
- reducing the number of indicators in the purchase book (there is no need to note the price without VAT);
- determining the date of sale of real estate;
- reducing the formation of inconsistency in financial transactions;
- elimination of double taxation. This innovation will have a beneficial effect on enterprises that open or have representative offices or branches abroad;
- partial abolition of keeping journals on the movement of invoices.
The advantages of the adopted changes are quite noticeable for organizations operating both in the domestic market of Russia and abroad. However, every law adopted has its own weaknesses.
Flaws
The activities of each enterprise are very specific. After all, an organization can be called a living organism that changes daily.
Modern companies must work efficiently and respond instantly to various external and internal factors.
The authorities are constantly adopting and amending current legislation. Business managers are required to take into account innovations, especially those related to the taxation system.
The changes brought about by Federal Law No. 238-FZ of July 21, 2014, adopted in the summer, should have a positive effect on the activities of organizations.
Perhaps due to the implementation of some specific operations, some companies will feel the disadvantages of the introduced changes. Time will tell.
Practical examples
A sales company operating under the OSNO (general taxation system) provided services to a company using the simplified taxation system (USN).
According to the legislation that was in force until October 1, 2014, the seller must issue an invoice with allocated VAT.
However, the organizations entered into an agreement not to issue invoices. In this case, the seller has the right not to issue an invoice to the buyer.
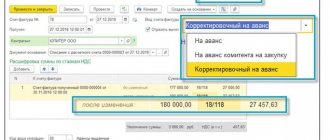
Next example. The seller received an advance from the buyer in the amount of RUB 118,000. and from this amount I paid VAT 18,000 rubles to the budget.
The purchasing company accepted this amount as a deduction. The seller transferred products in the amount of 94,400 rubles. (including VAT RUB 14,400).
How to pay VAT on advances issued, read the article: VAT on advances. What is the VAT rate in Russia, see here.
Find out how to fill out the VAT return quarterly here.
According to the concluded agreement, only half of the advance payment is offset against payment for shipment, that is, 59,000 rubles, where VAT is 9,000 rubles.
Thanks to the adopted innovations, the seller, having completed the first shipment, has the right to claim a deduction, and the buying company must restore the tax that falls on 59,000 rubles, that is, 9,000 rubles.
The seller will deduct the amount of the remaining advance VAT, and the buyer will recover it when the advance is offset against the completed shipment.
Payment of excise taxes
According to the provisions of Article 198 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the minimum amount of taxes paid by an organization for exemption from excise duty when re-exporting without providing a bank guarantee has been reduced from 10 billion to 2 billion rubles. Similar amendments have been made in relation to the amounts of taxes paid by the guarantor. At the same time, the amount of obligations under guarantees increases from 20% to 50% of the value of net assets.
The new version of Article 203.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that a bank guarantee is not provided by taxpayers - organizations that produce excisable goods on the basis of an agreement for the processing of customer-supplied raw materials, if the owner of the raw materials (materials) has a total amount of taxes paid of at least 2 billion rubles.
Changes in air transportation and airport services
Subclause 22 of clause 2 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation exempts from VAT aircraft maintenance services that are performed at airports and in Russian airspace. However, there is no indication of specific types of services in the Code. From January 1, 2021, the Government has the right to determine such services ; it must formalize their list in a separate document.
In addition, a zero VAT rate has been introduced for domestic air transportation of passengers and baggage in the Kaliningrad region since the beginning of this year.
General issues
Repeated request for documents from the Federal Tax Service
In the current version of paragraph 5 of Article 93 of the Code, there is a rule prohibiting tax authorities from repeatedly requesting those documents that were previously provided by taxpayers. From September 3, 2021, this ban will be lifted. In other words, the Federal Tax Service specialists will be able to request documents for verification again.
The taxpayer will retain the right not to submit such documents, but the Federal Tax Service must be notified of this in a timely manner . The notification should indicate that the requested documents were submitted to the inspection (which one), and also provide the parameters of the document under which they were transferred or to which they were attached. The notification must be submitted within the deadline specified in the requirement to submit it.
However, if inspectors request original documents that have already been submitted to the Federal Tax Service and were returned to the taxpayer, then the latter will not be able to refuse to submit them. The same applies to documents lost by Federal Tax Service specialists due to force majeure circumstances. You will have to submit the requested papers again.
Registration of the results of additional control measures
Also, from September 3, Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation will be changed, namely, clause 6.2 will be added and clause 6.1 will be adjusted. These rules affect the results of additional tax control measures.
As part of the inspection, it may be necessary to request documents, conduct an examination, or call a witness for questioning. Such events are appointed by decision of the head of the inspection, which indicates the timing of their implementation. There have been no changes in this part.
The amendments affected the results of such checks, or rather, their execution. Previously, nothing was said about this in the Tax Code. But from September 3, 2021, the following rule will come into force: the results of the mentioned measures must be documented in the document “addition to the tax audit report” . It must be completed within 15 days after the event takes place. In the document, inspectors must reflect the start and end dates of the event, a description of the essence of the event, as well as the evidence collected during the event.
The addition to the act, and along with it the materials received, are transferred to the taxpayer within 5 working days . If the audited entity does not agree with the conclusions set out in the document, it will have 15 working days to object in writing. Please remember that you have 10 working days from the end date of the event to file an objection.
The above changes will take effect on September 3, 2018 and will apply to decisions on reviews completed after that date.
Extending the deadline for providing transaction documents
As you know, tax officials can request documents not only during an audit. This happens, for example, when they collect information about a specific operation. On September 3, 2021, a new version of paragraph 5 of Article 93.1 will come into force. 10 working days will be allotted for the provision of documents from the date of receipt of the request, and not 5, as before. If there is nothing to answer the tax authorities - there is no requested information or documents - you need to report this within the same period.
The new deadline does not apply to the provision of documents and information received during the “counter” inspection. As before, such requests must be satisfied within 5 business days .
Changes in controlled transactions
Several changes will be made to Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, dedicated to controlled transactions:
- A new criterion for classifying a transaction as controlled will appear. This is the application by the parties of different income tax rates to the income from such a transaction. The exception is the rates at which dividends, certain types of debt obligations, as well as the income of foreign organizations operating in Russia without representative offices are taxed.
- The criterion regarding exemption from income tax is stated differently. In the new edition, it reads like this: one of the parties to the transaction is exempt from the taxpayer’s obligations for income tax. Previously, a transaction was considered controlled if one party is exempt or applies a zero rate and the other is not.
- One of the criteria for classifying a transaction as controlled is abolished. Namely, the fact that one of the parties is a resident of a special economic zone or a participant in a regional investment project.
- The cost of controlled transactions is changing. It will be possible to recognize a transaction as controlled only if it meets some criterion and the income of its participants exceeds 1 billion rubles per year. In other words, if one of the criteria is met, but the transaction price is lower, it is not controlled. In the old version, exceeding the price threshold of 1 billion rubles was an independent criterion for classifying a transaction as controlled. Changes have been made both in terms of value and for transactions equated to transactions between related parties. This refers to transactions involving third parties who are nominal - do not take on any risks, do not perform functions, do not use assets. Such a transaction will be considered controlled provided that the amount of income of the participants from it exceeds 60 million rubles per year.
These changes will be taken into account when determining the tax base for 2021 and beyond. It does not matter when exactly the parties entered into the agreement.
Consolidated groups of taxpayers will disappear
Soon there will be no such entity as a consolidated group of taxpayers. It was decided to completely abandon it by 2023 . Groups that were created in 2018 will be considered unregistered. The same CGNs that were formed before the beginning of this year will be valid only until the end of 2022.