From January 1, 2021, you will pay VAT at a rate of 20 percent (Federal Law dated August 3, 2018 No. 303-FZ). When managers signed a long-term contract with the buyer, they set the price including tax at a rate of 18 percent.
Sample additional agreement (Price including VAT)
Sample additional agreement (Price excluding VAT)
Now the new VAT rate has been approved. And suppliers have time to negotiate changes to contracts with buyers.
To do this, you need to conclude additional agreements to the contracts.
Some contracts may not be amended.
Firstly, if the contract provides for the seller’s right to unilaterally increase the price if legislators increase the VAT rate. But this is a rare situation. Typically, such a condition is not included in the contract.
Secondly, if the price for specific batches of goods of the company is established in specifications or other additional documents to the contract. Read on for another situation where it is not necessary to change the contract.
Warn managers so that in new contracts they immediately take into account the increase in the VAT rate.
If you sell goods taxed at a rate of 10 percent, there is no need to adjust the contracts.
Who will and will not be affected by the VAT rate increase?
Law No. 303-FZ dated 03.08.18 amends the VAT rate specified in clause 3 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. From January 1, 2021, the tax rate will increase from 18 to 20%.
The increase in VAT will not affect all taxpayers: there is a preferential list of goods, their sellers will remain working at a rate of 10%.
For whom the rates will remain the same
Sellers of “preferential” types of goods using a 10% rate.
This applies to goods and services listed in paragraph 2 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- food, except delicacies;
- children's clothing and footwear, except sportswear;
- books and periodicals, except advertising and erotic publications;
- medical products;
- domestic air transportation services.
Exporters and other businessmen using the 0% rate.
The list is given in paragraph 1 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- international shipping;
- supply of foreign diplomatic missions in the Russian Federation;
- transportation of gas, oil and petroleum products;
- customs processing;
- international electricity supplies.
For whom the rates will change
Taxpayers under the general tax regime
who operate in the domestic market and sell goods not included in the preferential list. For them, the rate will increase by 2 percent - from 18% to 20%.
The settlement rate applied in special cases will increase from 15.25% to 16.67%:
- Sale of an entire enterprise as a property complex (clause 4 of article 158 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- Provision by non-resident organizations of electronic services for individuals residents of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- advertising placement;
- services of electronic trading platforms;
- provision of domain names, hosting services, website administration and support;
- searching, storing and processing information via the Internet;
- granting rights to use books, audiovisual works and other information presented in electronic form.
| Natalya Tantsyura, head of the Dispute Resolution practice, United Consulting Group, explains how the rate increase will affect business: |
First of all, the change in the VAT rate will affect medium and small businesses, since changes in the price of monopolists’ products will not affect demand. A decrease in demand for the products of small and medium-sized businesses will “remove” many players who are still unstable. To avoid this, entrepreneurs will plan various maneuvers in the form of keeping prices at the same level to their detriment, various bonuses and premiums for customers.
The rate increase will also affect those companies that do not pay VAT (USN or patent) - since due to price increases by suppliers, they will also have to raise prices.
In general, an increase in VAT will lead to a slowdown in business processes and economic growth of many companies, including large ones.
The reality will be that the cost of the “tax increase” will fall on the end consumer.
A good solution for small businesses would be to switch to the simplified tax system.
Many will also save in illegal ways: lay off workers who are officially employed, or pay wages in envelopes.
Companies that work on government contracts will be forced to refuse contracts, since they also work with simplified companies. And the increase in VAT will fall on the shoulders of companies using the simplified tax system, their profitability will decrease significantly, which will lead to debt on current obligations and, in the future, to bankruptcies.
With this entire trend, there will be a decrease in the purchasing power of the population.
How the legislation on taxes and fees will change in 2021
The law signed by the president to increase VAT from 2021 to 20% maintains on a permanent basis the rate of insurance contributions to social extra-budgetary funds at 30%.
In addition, according to the document, all existing preferential VAT rates and the rights of automakers to receive deductions for VAT amounts paid for goods, works and services continue to apply, even if they were purchased through budget subsidies or budget investments.
Until 2025, there will be a zero VAT rate for air transportation to the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol, to the regions of the Far Eastern Federal District, and the Kaliningrad region. Currently, domestic air transportation is subject to VAT at a reduced rate of 10%. The exception applies to the Republic of Crimea, Sevastopol and the Kaliningrad region - zero VAT is established for them (for Crimea and Sevastopol - until January 1, 2021, for the Kaliningrad region - on an indefinite basis).
The adopted law maintains on a permanent basis the current contribution rate for compulsory pension insurance in the amount of 22%. The contribution rate remains at 10% for salaries in excess of the established limit. Until 2025, the validity of reduced insurance premium rates for compulsory pension insurance (20%), medical insurance and insurance against temporary disability and maternity (0%) has been extended for non-profit and charitable organizations.
Currently, the general rate of insurance contributions is 30% of the wage fund, of which 22% is a contribution to the Pension Fund, 5.1% to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, 2.9% to the Social Insurance Fund. It was assumed that from 2021 the general rate should increase to 34%, however, taking into account the adopted law, it will remain at 30%.
When to make changes to contracts
Sales, contracting and service agreements are often concluded for a long period of time, which is why they are taking over 2021 and 2021. In this case, businessmen have a question: do they need to make changes, and if so, what?
Changes are not needed if:
Example:
The price of the product per unit is 1,000 rubles excluding VAT. The total amount payable is determined based on the tax rate in effect on the date of shipment:
- until 01/01/2019: 1,000 + 1,000 × 18% = 1,180 rubles;
- from 01/01/2019: 1,000 + 1,000 × 20% = 1,200 rubles.
- The goods are supplied at preferential rates of 10% or 0%;
- The price for each delivery is agreed upon separately;
- The price is set without tax, and the wording “excluding VAT” is stated in the text of the contract;
- The terms of the agreement provide for “automatic” price adjustment when the VAT rate changes. The price is recalculated similarly to the previous option. The difference is that the total amount in the contract is indicated including tax.
In all other cases, an additional agreement must be included in the contract to separate the 2021 and 2021 shipments. This will help avoid disputes about the cost of goods with counterparties.
This mainly applies to existing agreements that were signed before the decision was made to increase the VAT rate - in the first half of 2021 and earlier. Agreements concluded later in most cases include this section. If a businessman forgets about this agreement, the contract can be supplemented. The main thing is that the agreement is dated 2021.
When concluding a purchase and sale agreement for goods at a price of 1,000 rubles per unit, include in the agreement an agreement with reference to the new edition of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
The price per unit of goods excluding VAT is 1,000 rubles. VAT is charged additionally at the rates established by clause 3 of Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely: until December 31, 2018 inclusive, the tax is calculated at a rate of 18%, starting from January 1, 2019 - at a rate of 20%
What needs to be specified in the additional agreement
At first glance, it may seem that there is no need for an additional agreement to change VAT by 20%. The value of the tax rate and the procedure for its application do not depend on the will of taxpayers and cannot be changed by them, because according to paragraph 1 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, GRU are determined without VAT, which is billed to the buyer additionally.
However, in practice there are many nuances, and a price increase that is beneficial to the seller is completely unprofitable to the buyer. In addition, there are situations where an additional agreement to change the VAT rate will help not only resolve the situation, but also avoid a conflict between taxpayers and inspection authorities.
The most common situations are when:
- the final cost of the product or service, including VAT, is fixed in the contract;
- the price of the goods is determined taking into account the estimated tax rate and the contract directly states: “including VAT”;
- in 2021, an advance payment is made for the goods and services sold in 2019.
Note! If the tax amount is not allocated in the agreement, VAT is determined at the calculated rate of 120/20 (110/10) or 16.67% (clause 4 of article 158, clause 5 of article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and the cost of the goods is determined by subtracting calculated VAT from the final cost.
Therefore, the question of whether it is necessary to conclude an additional agreement in 2019 on changing VAT is decided individually in each case.
An additional agreement to the contract is drawn up in the event of a change in the conditions specified in it or the circumstances in which the parties operate. It is drawn up in the same form as the main agreement, and after signing by the parties it becomes an integral part of it.
In the text of the additional agreement, only the clauses that have undergone adjustment are given with reference to their numbers in the main agreement, after which the text of this clause is stated in the new edition.
In addition, the document states:
- date of signing of the main agreement;
- numbers of the main contract and additional agreement;
- place of signing;
- names of the parties;
- Full name of the persons who signed the additional agreement;
- details of the parties and their signatures.
As a general rule, the additional agreement comes into force on the day of signing, but according to Art. 425 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the parties can change this date.
The form of the document has not been officially approved, so counterparties can develop their own sample additional agreement on increasing VAT, taking into account the provisions formulated in the main agreement.
Example
Since 01/01/2015, Polet LLC has been renting office space from Tsentralny LLC. The rent until December 31, 2018 was 11 thousand 800 rubles, including VAT 18% - 1 thousand 800 rubles.
After changing the VAT rate from January 1, 2019, the rent increased to 12 thousand rubles. including VAT 20% - 2 thousand rubles. The decision made was recorded in the additional agreement.
Additional Agreement No. 3
to lease agreement No. 215/04 dated 01/01/2015
01/10/2019, Moscow
Polet LLC, hereinafter referred to as the Tenant, represented by director P.N. Rozanov, acting on the basis of the charter, on the one hand, and Centralny LLC, hereinafter referred to as the Lessor, represented by director I.V. Mishina, on the other hand have entered into this additional agreement to the purchase and sale agreement No. 125/wholesale dated May 12, 2015 as follows.
Amend clause 4.3 of the above-mentioned agreement as follows:
- Set the rent amount from 01/01/2019 to 12,000 (twelve thousand) rubles, including 20% VAT.
This agreement is drawn up in two equal copies, one for each of the parties.
The additional agreement comes into force on 01/01/2019.
| ADDRESS | ADDRESS |
| and details of the Lessor | and details of the Tenant |
| Taxpayer Identification Number _______________________ | TIN ____________________ |
| OGRN_______________________ | OGRN ____________________ |
| Address:_____________________ | Address: __________________ |
| Check ______________________ | Check ___________________ |
| Bank: _____________________ | Bank: __________________ |
| BIC ______________________ | BIC ___________________ |
| Correspondent account ______ __________________________ | Correspondent account ____ _________________________ |
| E-mail: ____________________ | E-mail: __________________ |
| Tel. ______________________ | Tel. ____________________ |
| _____________________ Signature of the Lessor's representative | _____________________ Signature of the Tenant's representative |
| M.P. | M.P. |
An additional agreement to the agreement on increasing VAT is necessary to regulate relations between the parties to contracts for the supply of goods (performance of work, provision of services). In it, the parties determine a new procedure for setting prices for industrial goods and the amount of tax to be paid. The additional agreement is drawn up in writing and is an immediate part of the contract. We have provided a sample additional agreement on changing the VAT rate in this article.
The additional agreement on changing the value added tax rate should resolve all discrepancies that arose in connection with amendments to the legislation. In general, its structure looks like this:
- A title indicating the number and date of conclusion of the original document.
- Date and city of signing.
- Point to be reformulated.
- Its new edition.
- Effective date of the new provisions.
- Details and signatures.
More about VAT
- recommendations and assistance in resolving issues
- regulations
- forms and examples of filling them out
Get FREE access for 3 days to ConsultantPlus
We discussed above how to correctly specify the VAT rate in the contract. However, in the additional agreement it is advisable to do this as precisely as possible.
But there is another opinion. In accordance with it, during the transition period it is better to refrain from indicating the amount of tax liability. This applies to both percentage and monetary terms. It is better to simply refer to paragraph 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code.
The notice can inform the counterparty that:
- Due to the increase in VAT, the supplier is forced by law to increase the selling price of its goods.
- In accordance with the contract (indicating its details), the selling price of the goods from 01/01/2018 is so much, and in case of a change in the rate from 01/01/2019 it will be so much.
- Due to the fact that the shipment of goods (indicating their type and volume) occurs in 2021, the supplier is forced to request payment from the counterparty, taking into account the increased VAT (with clarification of the total amount payable). If an advance was received before, you must request an additional payment (indicating its amount).
- The supplier offers to renew the contract (with the specified details) and fix a new VAT rate in it. Or enter into an additional agreement.
Also, in the information letter about increasing the VAT rate, you can immediately propose a specific scheme for re-signing the contract (the simplest thing is to attach a copy of it to the notification, which the counterparty can sign and send by mail).
On January 1, a new rate of 20% came into effect. If the goods are shipped after this date, the new rate will need to be used in the documents, even if the supply contract was concluded in the previous year.
In order to avoid incurring losses due to claims from counterparties and disputes with the tax inspectorate, it is necessary to immediately audit the concluded supply agreements and make adjustments to them. This is usually done by concluding an additional agreement.
The following agreements need to be corrected:
- If the contract directly states that a rate of 18% is used, the additional agreement must indicate the cost of the goods without VAT and indicate that VAT is charged on top of this price at the rate in effect at the time of shipment;
- If the contract indicates only the cost of the goods without VAT, in such a situation it is not necessary to change the contract, but it is better to indicate in the additional agreement that VAT is charged on top of the price at the current rate. Thanks to this, it will be possible to definitely avoid disputes with buyers;
- The contract does not mention VAT at all - the additional agreement provides information that the contract price does not include VAT, and the tax is charged on top at the current rate.
There is no need to make changes to the following agreements:
- If the cost of goods or services is determined not in the contract itself, but in the documents attached to it (estimates, specifications, etc.);
- If the company sells work or goods that are subject to a 0% or 10% rate;
- If the contract contains a clause stating that the seller has the right to unilaterally increase the cost of goods or services when the amount of tax increases.
There will be no exception to the situation in which the buyer refuses to sign an additional agreement to increase the cost of the goods. In this case, the difference in price will be borne by the supplier company in the form of a reduction in the selling price.
The seller, of course, can sue and force him to sign an additional agreement based on a court decision. However, this judicial practice is just beginning to take shape, and therefore it is impossible to predict exactly what position the court will take.
Attention! It is worth noting that the tax inspectorate in its letter dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] indicates that it is not mandatory to enter into additional agreements. In any case, from January 1, 2021, a rate of 20% will apply, regardless of what is specified in the supply agreement.
The supplementary agreement does not have any special form, and is drawn up according to the principle of other documents in the style of a business letter.
First, the name of the form is indicated in the middle - “Additional Agreement”.
Further below you must indicate the name of the document to which the additional agreement is drawn up, its number and the date of signing.
Next, on a new line, on one side, the place of compilation of the form is written, and on the other, the date of compilation.
The following is an introductory part to the agreement. It must indicate each party to the contract, its designation further in the text (for example, “Supplier” and “Buyer”), the full name of the person who acts on behalf of each party and the document on the basis of which this person carries out activities.
Here it is necessary to note that the parties entered into an additional agreement to the supply agreement, and again indicate its details.
Next, the text of the agreement must be structured according to the following scheme.
In paragraph 1 it is necessary to indicate that the required clause of the supply agreement until December 31, 2018 is valid in the following wording. After this, you need to provide the specified text containing the price of the product or service and VAT in the amount of 18%.
Further, in clause 2 of the agreement, it must be stated that starting from 01/01/2019, the required clause of the agreement must be in force in the new edition. After this, you need to indicate the cost of the product, which uses the VAT rate of 20%.
Who will pay for the rate increase?
Who should pay the extra 2%? Seller or buyer? Depends on the terms of the concluded contract.
When the buyer pays for the increase
If the terms of the contract provide for a price adjustment when VAT increases, the buyer pays the difference of 2%. In this case, he will have to come to terms with the price increase, since the terms of the transaction will not allow this fact to be challenged.
If the price of the product was 1,000 rubles without VAT and 1,180 rubles with VAT, then from 01/01/2019 it will be 1,200 rubles with VAT.
As a result, the buyer will pay 20 rubles more or 1.7% (20 rubles / 1,180 rubles).
When the seller pays for the increase
If the price in the contract is indicated including VAT and does not provide for adjustment, it can only be changed by agreement of the parties. In this case, the buyer, guided by the principle of freedom of contract (Article 421 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), is not obliged to meet the seller halfway and may not agree to an increase in price.
Then the seller, starting from 01/01/2019, will be required to allocate VAT at a rate of 20% from the total sales price.
If the final price of a product unit is 1,180 rubles, then the price without VAT after 01/01/2019 will be equal to 1,180 rubles / 120 × 100 = 983.33 rubles.
The seller will lose 16.67 rubles. (1,000 rubles - 983.33 rubles) or 1.67% of the cost.
How the parties to the transaction can agree
When the buyer pays VAT, the seller may try to negotiate with him, citing the fact that the “additional” 20 rubles can be deducted on the declaration and reduce the amount payable to the budget. As a result, the buyer will lose practically nothing. The difference is that you will have to pay the supplier immediately, and the savings on VAT will arise at the end of the tax period (quarter).
If the buyer works under one of the special tax regimes and does not pay VAT, then he takes the entire amount into account as expenses and loses 1.7% “irrevocably”. In this case, the seller can offer a compromise - split the difference in half. That is, at a price of 1,000 rubles excluding VAT, increase the total amount not by 20, but by 10 rubles - up to 1,190 rubles.
| Olga Anatolyevna Shvedchikova, Deputy General Director for Economics of Market Line LLC, tells how the increase in VAT will affect businesses that pay tax at a rate of 10%. |
— How will the VAT increase affect your business?
— 98% of our sales come with a VAT rate of 10%, so the additional charge will be minimal, but deductions for work and services received will increase. Thus, the amount of VAT to be transferred to the budget will decrease, and the percentage of the tax burden will also decrease.
— What consequences do you expect/predict in your segment?
— Due to the reduction in the percentage of the tax burden, requests from the Federal Tax Service to justify the indicator will become more frequent. Financial results and cash flows are not expected to be significantly impacted.
— Will anything else change with the VAT increase (for example, the tax return, the form of sales and purchase books)?
- Yes, I think that the declaration form will be adjusted, the purchase books and sales books will also be added, fields will be added to reflect all rates: 10%, 18%, 20% - this is necessary during the transition period.
What do officials say about changes in the contract price when the VAT rate increases?
Government agencies provide clarifications that are unlikely to please sellers.
The Ministry of Finance, in information letter No. 24-03-07/61247 dated August 28, 2018, indicated that an increase in the VAT rate should not lead to a change in the price of government contracts. Therefore, sellers working under government contracts will, in most cases, have to compensate for the increase in the VAT rate at their own expense. An exception is large transactions, the volumes of which exceed the limits established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 19, 2013 No. 1186:
- 10 billion rubles for federal needs;
- 1 billion rubles for the needs of constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- 500 million rubles for municipal needs.
For all other categories of contracts, the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, in its letter dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] , comes to a similar conclusion. According to officials, there is no connection between the increase in the VAT rate and the need to amend the agreement.
However, in the same letter, Federal Tax Service specialists indicate that the parties retain the right to change the terms by agreement. If it is not possible to reach an agreement, all that remains is to rely on the court.
VAT - 20 percent: reasons for the increase
Increasing the VAT rate to 20% will bring the budget more than 600 billion rubles. additional income per year, notes Dmitry Medvedev.
According to the Prime Minister, the government has also decided to abandon the use of such an institution as consolidated groups of taxpayers in the future, due to the abolition of the requirement to control transfer prices within the country.
“The problem of so-called consolidated groups is not new. This mechanism has significant drawbacks. First of all, we are talking about the shortfall in regional budget revenues. Therefore, starting in 2016, let me remind you, we suspended the creation of new groups and prohibited the expansion of existing ones, and introduced a number of restrictive measures,” the Prime Minister noted at a government meeting. – And from 2023, this institution will be completely liquidated at the federal level. By making this decision in advance, we must ensure that both taxpayers and regional authorities have time to prepare for changes in tax rules regarding consolidated groups of taxpayers.”
The proposed tax measures will support economic growth and stimulate technological renewal and the development of small businesses and individual entrepreneurship. Medvedev proposed fixing the new tax configuration, if adopted, for the next six years.
This year, the government also plans to work out a decision on creating conditions to improve administration and reduce the administrative burden on business. This will reduce the tax burden on self-employed and individual entrepreneurs.
What will the court decide if the transaction partners do not agree?
Prospects for the trial are mixed. Clause 2 of Art. 422 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation determines that the terms of the contract do not change when legislation changes.
An exception is a direct indication in the law that obligations under previously concluded agreements are subject to adjustment. However, Law No. 303-FZ does not contain such provisions.
You can refer to Art. 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the adjustment of the contract in connection with significant changes in the terms of the transaction and consider the increase in the VAT rate as such. In this case, the seller will have to prove that he will suffer significant damage, knowledge of which would prevent the conclusion of the contract. However, the seller’s losses cannot be considered significant - they amount to less than 2% of the transaction amount.
A new arbitration practice on this issue has not yet been formed; court proceedings will begin next year. In a “mirror” situation, after the VAT rate was reduced from 20% to 18% in 2004, the courts indicated that the agreement could only be changed by agreement of the parties.
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated 07/08/2008 in case No. Ф09-4928/08-С5 - the lessee asked to reduce the price under the contract, since the VAT rate decreased by 2%. The court refused, citing the fact that the lease payment can only be recalculated by agreement of the parties.
The Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation adheres to the same position (clause 17 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2014 No. 33.)
Thus, there is practically no chance of winning the case in such a situation, and changing the contract unilaterally is unacceptable. The agreement can be terminated only if it specifies a change in tax rates as one of the conditions for early termination.
How to calculate VAT during the transition period
Let's consider “transitional” cases of tax payment from the point of view of both parties to the transaction. We are talking about a situation where the advance payment is transferred in one period, and the shipment is made in the next. Let's consider an advance payment, since if payment is received after shipment, its period does not affect the calculation of VAT.
The main criterion for determining the rate is the period of payment of the advance payment or sale (purchase) of the goods.
How to calculate VAT during the transition period
If the advance applies to shipment in 2021, then:
- it is more profitable for the buyer to pay an advance in 2021 in order to recoup 2 percentage points more;
- it is more profitable for the seller to receive an advance in 2021 in order to pay 2 percentage points less in tax.
After shipment, both parties to the transaction will have to pay the tax in full, but in the current period you can get a small savings.
How to calculate VAT when returning goods
In 2021, a buyer may want to return an item purchased in 2018. When the goods have already been accepted for accounting, they can only be returned if they are sold back to the seller with an invoice issued “on a general basis.” Then the situation will be “mirror” compared to that discussed above. If the parties do not agree on a price change, then the buyer “suffers”, who now sells the goods and is forced to charge additional VAT on return shipment.
When is a correction invoice needed?
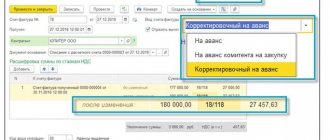
If the parties agree on an increase in price, the buyer pays the difference. When an additional payment is made in 2021, it should be accounted for using an adjustment invoice, which is generated in addition to the original advance invoice.
The adjustment invoice contains information about the change in the tax amount and total shipment amount compared to the original invoice. The letter of the Federal Tax Service dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] provides examples of an adjustment invoice.
Adjustment invoice
It happens that for some reason an invoice issued in 2018 was not taken into account on time. In this case, in order to determine the period for which the deduction is applied, the date of receipt of the document is important.
The invoice relating to the 4th quarter of 2021 will be received in 2021. This document includes VAT at the rate of 18%. Depending on the date of receipt of the invoice, the deduction is applied in the following order:
- If it was received earlier than the deadline established for submitting a VAT return for the 4th quarter of 2021 (i.e. before 01/25/19) - include a deduction on the invoice in this declaration (clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- If it was received after January 25, take into account the deduction in the declaration for the 1st quarter of 2021. Since the shipment took place in the previous period, there is no reason to increase the deduction - take VAT for deduction at a rate of 18%.
As of the date of writing this article (November 2021), no changes have been made to the VAT return form. But there is already a draft order of the Federal Tax Service, published on the Unified Portal of Draft Regulatory Legal Acts. In accordance with the project, lines will be added to section 3 reflecting increased tax rates. Due to the transitional situation, the declaration for the 1st quarter of 2021 will use old and new lines.
Draft new VAT declaration form
What to do with CCP
Federal Law No. 54 of 05/22/03, regulating the use of cash register systems (Article 4.7-1), provides for mandatory VAT information on the check. In 2021, the check must indicate a new rate of 20%. Order No. ММВ-7-20/229 dated 03/21/17 of the tax service, which contains all the details of the cash register check, should soon be changed in the part of the detail tag 1139. The amount of VAT is indicated here at the tax rate corresponding to the legislation. The draft amendments to the order have already been submitted for consideration and, presumably, will be considered before the end of the year.
Managers of organizations using cash register equipment should take care of changing its settings in advance. From 00:00:01 on January 1, checks must include the new VAT rate. This is especially important for retail outlets and stores that work intensively on holidays and at night. Re-registration of the cash register with the Federal Tax Service is not required.
On a note! On the issue of accepting tax deduction on the basis of a cash receipt, there is a contradiction between the position of the Ministry of Finance (letter No. 03-07-09/634 dated 12/01/18 and a number of others) and the position of the courts (decree of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 17718/07 dated 13 /05/08) remains the same for the coming year. The first source considers a deduction on the basis of a check impossible, and the second, on the contrary, asserts the right to receive a deduction when purchasing goods or services, works for cash, including on the basis of a cash receipt. At the same time, a number of Federal Tax Service officials are inclined to the possibility of receiving a deduction. So, on the tax authorities’ website you can find information from the Federal Tax Service of Altai about a 20% deduction based on a cash register receipt.