- When is VAT paid?
Mandatory payment is divided into direct and indirect . The latter is included in the cost of goods and services; it includes excise taxes and value added taxes, fees on the sale of products and services.
Definition of indirect tax
What does indirect tax mean? A tax on goods and services imposed as a surcharge on the price or tariff. Their main feature is that the burden of payments is borne by the end consumer. Indirect taxes are mandatory and relatively easy to collect. This is explained by the fact that they are included by the manufacturer in the cost indicator of goods and services.
You can see which taxes are direct and which are indirect in the table of direct and indirect taxes.
Indirect taxes in the Russian Federation are divided into:
- individual: they are levied on a separate category of goods that are classified as highly profitable;
- general: they apply to all products, with the exception of some goods that are classified as socially significant.
Please note: in some cases, the type of fees in question can be passed on to the purchasers. An increase in the price of a product due to VAT levied on sales may lead to a reduction in consumer demand. In order to sell the goods, the seller is forced to reduce the price, but no one exempts him from payments. And in this situation, indirect collection acquires similar features to direct collection.
Net indirect taxes are fees paid to the Russian budget minus subsidies and benefits provided to certain legal entities in certain areas of their activities.
Results
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for a gradation of taxes into direct and indirect. Direct taxes are paid by the taxpayer on his income. Indirect taxes are included in the price of a product or service and are paid by the final buyer. And it is the responsibility of the taxpayer to timely transfer received indirect taxes to the budget.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What is considered indirect taxes in Russia - list
Speaker – Elena Minina, Senior Researcher at the Laboratory for Tax System Development, Institute of Applied Economic Research, RANEPA.
All taxes are divided into direct and indirect, there is no third option. Indirect taxes are taxes on goods, works and services and transactions with them, the most well-known of them are value added tax (VAT) and excise taxes. Direct taxes are taxes on income and property, the most famous of which are income tax and property tax.
Indirect taxes are actually levied not on the manufacturer, but on the end consumer, being included in the cost of the product, work or service, but the possibility of transferring the tax burden to the consumer depends on the elasticity of demand.
In Russia, all taxes are codified, i.e. all of them are defined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in its individual chapters. Thus, Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to VAT, Chapter 22 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to excise taxes, and Chapter 25.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to state duty. In an accessible form, information about the taxes that are payable by taxpayers can be found on the website of the Federal Tax Service www.nalog.ru. The list of indirect taxes is below.
VAT – Value Added Tax
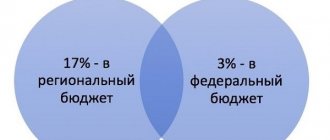
Indirect taxes include VAT. This indicator plays a big role in the seller's profit. The added value is subject to taxes. VAT is a type of indirect tax levied on the buyer. It accounts for 40% of the budget. This exceeds the percentage in the formation of the treasury when it comes from direct collections. VAT is paid for each transaction, it does not matter the number of intermediaries through which the products were sent. VAT is paid by the end consumer. All citizens and business entities pay it. VAT has rates that vary depending on what products are sold. Rates vary: from 20% to 0%.
A special feature of VAT is the fact that the tax is not levied on the entire cost of the produced product, work or service, but only on the added value that arose at a specific stage of the creation of the product, work or service. This means that the difference between the VAT billed to buyers and the VAT billed to sellers is paid to the budget. If the difference turns out to be negative, VAT is subject to refund from the budget, which leads to the emergence of tax schemes.
In accordance with Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in Russia, rates of 0%, 10% and 20% are applied. A zero VAT rate applies, for example, when exporting. A 10% rate applies to basic food products, children's products, most periodicals, a number of medical products, as well as domestic air transportation services for passengers and baggage. In other cases, taxation is carried out at a rate of 20%. Let us note that, for example, in Kazakhstan, another member country of the Eurasian Economic Union (which includes Russia), there is no reduced rate at all, but the VAT rate is only 12%.
When VAT is 0 percent:
- export of products;
- passenger transportation (some types);
- sales of manufactured products;
- provision of services in the housing and communal services sector.
Note that despite the fact that both Russia and the EU have VAT, in the USA, for example, there is no such tax. Instead, the United States applies sales tax, which is also an indirect tax, but simpler in nature in terms of calculating the tax payable to the budget.
Excise tax
An example of an indirect tax is excise tax. Excise taxes in Russia in accordance with Art. 181 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation taxes alcohol and tobacco products, ethyl alcohol, cars and motorcycles (with engine power over 112.5 kW (150 hp)), motor gasoline, diesel fuel and a number of other goods. Theoretically, excise taxes are imposed on goods that are harmful to health (increasing their value due to the excise tax should stimulate a decrease in the consumption of these goods), as well as goods that bring increased profits. Rates are distinguished by excisable goods; the rate can be ad valorem (as a percentage of the cost), fixed (in the absolute amount), combined (in the absolute amount plus as a percentage of the cost).
Note that historically direct taxes were the first due to the fact that they were easier to collect due to the obviousness of their presence, which concerns, for example, the real estate itself or linking the tax to the number of pipes or windows.
Examination
The taxpayer can check the fact of payment for all previous periods and the details of the accrual in his personal account on the tax service website.
In a separate article, we suggest reading in more detail about how to check and pay transport tax on a car.
About statute of limitations and amnesty
Individuals do not have to independently calculate transport tax - they are only required to make timely payments to the budget on the basis of a tax notice. In this regard, situations arise when the tax authorities did not send a notification for some reason or sent it to a non-existent address, and after several years they demand payment of tax for previous years. In this case, the decisive role is played by how much time has passed from the moment of non-payment to the present moment.
In the Russian Federation, the statute of limitations for paying transport tax is 3 years.
Consequently, during this time, the tax authorities (IFTS) can present their demands for collection of debt for non-payment of tax; after 3 years, the claims will be unfounded and should be appealed (how to find out and pay the debt?). In 2019, tax authorities can send payment notices not only for 2021, but also for 2021 and 2021.
You can find everything you need to know about the transport tax amnesty in another publication.
What is the difference between direct and indirect taxes - differences, examples
Director of the legal service “Unified Center for Protection” Konstantin Bobrov reports on the differences between direct and indirect taxes that: “Indirect taxes are actually paid by consumers, included in the cost of goods and services. They are not taxed on a specific object, while direct ones are established in relation to a specific object (vehicles, real estate, income). It is impossible to evade them: the consumer, when purchasing a product, pays this tax.”
What is the difference between direct and indirect taxes? VAT, excise taxes, customs duties are types of indirect tax collection. They differ from direct in that they do not depend on a person’s income. Indirect fees are paid by default by the end consumer, as they are included in the cost of goods and services.
Important: excise tax does not have a uniform rate and is set on an individual basis. That is, excise tax exists for each of the groups of products of the same name. His rate is approved for one year, and then for the next 2 years.
For example, property tax is direct, but not indirect, as is direct personal income tax. This fee is required to be paid to the budget only by the person who owns the property (property tax) or has income - personal income tax. If there is no property, you do not need to pay tax. And the same citizen will pay an indirect tax when purchasing goods in any case; the amount of the tax and the need to pay the indirect tax do not depend on his personal data.
The differences between direct and indirect taxes can be displayed in the table.
| indicators | straight | indirect |
| who pays | property owner pays | end-user |
| connection with the state | straight | mediated |
| taxable object | property: movable or immovable | service, product, sold |
| determining factors of bet size | amount of profit received | service and product |
| level of openness | a person or legal entity knows in advance how much he needs to pay | closed nature, the consumer does not know that the price of the goods includes a fee |
| calculations | complex | simple |
| dependence on factors | Yes | No |
All indirect fees are divided into 4 groups:
- Universal: surcharges included, with a few exceptions, in the cost of all goods and services. For example, VAT is an indirect, not a direct tax.
- Individual: they apply to individual products. For example, excise tax, or a fee associated with the purchase of jewelry.
- Fiscal: payment of a fee for obtaining permits. For example, for issuing business licenses.
- Customs duties: export and import duties. They are paid by exporters and importers of goods. They are actually included in the price of the product.
An indirect tax is customs duty. This is a payment paid by companies and individual entrepreneurs who import goods across the border. There is no fixed rate for the duty. The volume of payments is specified in agreements concluded between the Russian Federation and importing countries. Payments are made based on the declaration: it is generated by importers. If an entrepreneur imports certain products into the Russian Federation, the declaration is submitted no later than 15 days from the date of import.
Important: If an entrepreneur imports goods and services, he must write and submit to the tax authority an application for payment of indirect taxes. The document will confirm that the businessman is engaged in importing, which is important for deducting VAT upon import.
Who are taxpayers
A taxpayer is one who pays taxes. As you know, taxes affect almost every area of our lives, so it is impossible to find a person who does not pay them.
The calculation of taxpayers-motorists is made on the basis of information available about their transport. They go to the tax service after the car is registered with the traffic police. Legal entities must pay the duty and advance payment themselves, without waiting for the tax office to remind you.
Tax for individuals is calculated according to the formula - the tax base is multiplied by the corresponding rate. From this comes the cost that must be paid to the taxpayer.
For legal entities, everything is calculated differently. During the year, an advance payment is made, and the tax itself is calculated from it. When submitting a report, the organization must make a payment.
What taxes can be classified as indirect?
These are fees that go to the federal treasury and are created as a premium for goods and services. They are sold by the seller. It is his responsibility to include the surcharge in the product or as part of the payment. The tax is not added as income to the company selling the products, it is sent to the state budget. The seller is an intermediary between the state and the population, who pay indirect, but not direct taxes. The seller's income does not decrease, but does not increase either. And the state receives budget replenishment through indirect fees.
Transport tax, land tax, income tax are direct taxes, not indirect.
Entrepreneurs are the (formal) fee payers. Actual – third parties who act as final consumers of goods, services and works.
What can be considered an object of taxation?
If a citizen has at least one vehicle, regardless of its physical condition, then he is obliged to pay tax.
Almost all categories of vehicles are eligible for payment:
- Barge.
- Tractor.
- Minibus.
- Helicopter, etc.
- Water transport.
- Snowmobile.
- Motorbike.
- Tracked transport.
- A car.
Boats that have no more than 5 horsepower are not subject to tax. Therefore, you don’t have to pay it.
Advantages and disadvantages of indirect taxes
Advantages:
- efficiency of receipts to the budget;
- stability;
- there is no need for increased control over their entry into the treasury;
- increase in state revenues due to stable and timely receipt of indirect fees;
- For the consumer, these fees are convenient because they do not require the accumulation of funds, they do not have the nature of coercion, and there is no loss of time when paying;
- hidden nature: citizens may not even suspect that they are paying a fee.
Flaws:
- have fiscal significance;
- limit the income of entrepreneurs, since it is not always possible to increase the price of goods in proportion to the indirect collection, especially with an increase in tax.
Possible changes in legislation
In 2021, there is an active discussion about replacing the transport tax on cars with an environmental tax and introducing a new tax - recycling.
It is assumed that the amount of environmental tax will depend on:
- The volume of harmful emissions during vehicle operation (the more emissions, the higher the tax).
- Age of the car - the older the car, the higher the tax. The subtleties and nuances of paying tax on old cars can be found here.
- Eco-class vehicles - electric vehicles will be exempt from the tax (you will find the details of paying the transport tax on electric vehicles separately).
In this case, the amount of tax on a car that does not comply with the current environmental class in Russia will be multiplied by 1.5. If the car complies - 1, but if the car is completely new, and its eco-class exceeds the existing norm - 0.5.
The second potential fee is recycling . It will also aggravate the tax burden and applies to cars older than 5 years. Thus, for cars aged from 5 to 10 years, the basic road tax rate will be multiplied by 1.75, for cars from 10 to 15 years old - by 2, and by 3 - for cars over 15 years old.
What goods are not subject to indirect tax?
There is a group of goods that have preferential taxation:
- Products for children;
- press;
- medications;
- medical products.
Indirect tax VAT is not paid by certain business entities. These are companies that act as exporters, provide passenger transportation services, and the housing and communal services sector. VAT is not paid by educational institutions, research and scientific organizations, cultural institutions, and medical organizations.
Interesting fact: An example of a fee that is not an indirect or direct tax is a state duty. These are indirect payments to the Russian treasury. The state fee is charged to the user for the provision of legal services. Users contact government agencies, which provide them with services on behalf of the state. State duty is not always paid, that is, the fee is not mandatory. It only needs to be paid if a citizen or organization needs to perform a certain legal action. The amount of this fee is fixed.
How to become a taxpayer
Individuals and legal entities become taxpayers if:
- An object that arose as a “transaction” is fully taxed, that is, the payer will have to pay for it. An example is real estate and income generated from sales or services provided through this real estate.
- There is a status according to which a taxable object is formed. An example is imputed income. It is formed when the organization issues UTII.
- Uses any resources. For example, extracts minerals, or something else.
Direct tax is paid by both individuals and legal entities. They must deposit the amount themselves, without shifting their responsibilities to another person.