All cash circulation in the Russian Federation is regulated by two instructions of the Bank of Russia in 2013 and 2014. And if the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3073-U dated October 7, 2013 is comprehensive and regulates cash circulation throughout the Russian Federation, then the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 is, in fact, a regulation of cash discipline at enterprises. It is this normative act that establishes the procedure for settlements with accountable persons. And it introduced innovations that greatly influenced the idea of accountable amounts.
Procedure for withholding accountable money
Funds that are issued to the employee as accountable funds are withheld from the salary in case of non-return by the employee. To do this, an order is issued to withhold accountable funds in free form. Such an order must be issued within a certain period, namely, no later than one month from the end date of the period that was set for the employee to report. These funds can only be recovered if the employee does not dispute either their amount or the basis. In this regard, it is necessary to obtain the written consent of the employee, in which he confirms that he is not against deductions. If there is no such consent, funds can only be recovered through the court (137 Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Important! The amount of deductions from an employee’s monthly salary should not exceed 20%.
Calculations with accountable persons
Current as of: August 21, 2021
Persons who have received accountable money from an organization and must make expenses or acquire property in its interests are called accountable persons. These are, for example, employees going on a business trip, or employees purchasing goods and materials for their employer. Although the accountant does not necessarily have to be an employee of the organization: money against the report can be issued, for example, to a person who performs work according to the GAP.
To streamline settlements with accountable persons, an organization can develop a Regulation on settlements with accountable persons or another similar document. A list of persons who have the right to receive money on account may also be approved. As a rule, for this purpose an order is issued, the form of which we have given in a separate material.
The basis for issuing money on account can be an administrative document of a legal entity (say, an order) or a written statement from the accountable (clause 6.3 of the Central Bank Instruction No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014). We talked in more detail about the grounds for issuing money on account in our consultation, where we also provided a sample of the corresponding order.
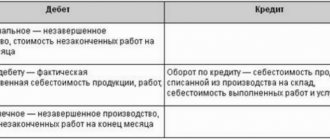
Synthetic accounting with accountable persons is maintained on account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). We talked in more detail about standard accounting entries for accounting for settlements with accountable persons.
Currently, the procedure for using cash register systems in settlements with accountable persons is of particular interest. We will tell you more about this in our material.
Deadline for return of accountable money
The legislation does not establish a deadline for issuing accountable funds; the employer must do this independently. This period is indicated in the employee’s application for the release of money for reporting. No later than three days after the established deadline, the employee must account for the funds received. If we are talking about money given to an employee on a business trip, then the report must be submitted within three days from the date of return from the business trip (Government Decree No. 749 of October 13, 2008).
If, when issuing accountable money, no deadline was set for providing an advance report, then the employee is obliged to provide it on the day the money is issued. However, it is better to ensure that such situations do not arise and there are no claims from the inspection authorities, to set a deadline for the report or return of funds.
Important! The size of the report and the period for which it is issued is determined by the employer. The employee must report on the funds issued no later than 3 days from the end of this period.
If an employee does not return unspent funds on time, this is a violation of cash discipline. But there is no liability for such a violation.
How to reflect an unreturned report in accounting
The accountant must return the unspent money within the period for which it was issued to him. If he did not do this, he will have to recognize them as unreturned.
Such means include:
- money for which an advance report has not been submitted or has been submitted but not reasonably accepted by the manager;
- the balance of funds has not been deposited at the cash desk, despite the fact that the advance report has been submitted.
We reflect these amounts in accounting based on the accounting certificate by posting Dt 94 Kt 71 .
Useful information from ConsultantPlus
So that the inspectors have no doubt that the money was taken on account and not misappropriated by the employee, we recommend establishing rules in the organization with clear deadlines for submitting a report on the amounts spent. Moreover, such reports must be accompanied by supporting primary documents (read more...).
Hold example
To the accountant of LLC "Continent" Petrova O.P. On February 1, 2021, an advance payment of 4,000 rubles was issued for the purchase of stationery for the accounting department for a period of 25 days. Petrova purchased stationery for only 2,500 rubles, for which she compiled an advance report, to which she attached supporting documents: a cash receipt and a sales receipt. Petrova did not return the remaining amount of accountable money - 1,500 rubles (4,000 - 2,500) on time, but wrote an application to recover this amount from her wages for February 2018.
Petrova’s salary for February is 35,000 rubles. The employee does not have children, so she is not required to provide a personal income tax deduction.
The maximum amount of deductions from wages per month is 20%:
35,000 x 20% = 7,000 rubles.
The amount that needs to be withheld from Petrova is less than 20% of the salary, so we can withhold it in full.
The postings will be as follows:
| Business transaction | D | TO | Amount, rubles |
| Funds issued for reporting are reflected as a shortage | 94 | 71 | 1 500,00 |
| Petrova's salary was accrued | 44 | 70 | 35 000,00 |
| Personal income tax was withheld from Petrova’s salary (35,000 x 13%) | 70 | 68 | 4 550,00 |
| An accountable amount was withheld from Petrova | 70 | 94 | 1 500,00 |
| Petrova's salary was transferred | 70 | 51 | 28 950,00 |
Advance report: what can be taken into account
The issuance of funds by an organization to a person in an employment relationship with it is standard business practice. The money that the company, with the participation of the accounting department, transfers for reporting is accompanied by documentation confirming its intended use. Documents are carefully reviewed by regulatory authorities. The main question that worries employees responsible for the expense report: both accountants and accountable persons - what can be taken into account? Despite the abundance of explanatory letters, guidelines, guidelines and instructions, many issues remain controversial. An employee whose “hands” are entrusted with accountable funds is constantly forced to think about how to collect documents confirming his expenses, and the accounting department has to check the submitted papers and checks line by line. In general, the following rules apply to advance money:
- Funds are issued for business and operational needs and travel expenses.
- The basis for issuing funds is the order of the manager. The manager makes a decision after the accountable person submits an application.
- After making the expenses for which the funds were allocated, they must be reflected in the report, attaching supporting documents.
- The accountable person must submit an advance report with justification for expenses to the accounting department within three days after the official date of return from the business trip. This date is considered to be the date indicated on the return ticket or waybill if the employee uses a car.
- If an employee receives money for business needs, then he must submit an advance report within the time limits established by a special order of the head of the organization. As a rule, such an order is issued in the form of an annex to the accounting policies of the organization.
- Employees of the organization must be familiar with all administrative documents relating to the procedure for issuing money on account and submitting advance reports confirming expenses.
What documents are officially accepted as justification for expenses?
This issue creates the greatest difficulties for all participants in checking advance reports: both for the checking workers and for the reporting ones. According to the current established practice of tax audits, supporting documents are:
- cash register receipt;
- passenger tickets, boarding pass;
- sales receipts/invoices;
- receipts, strict reporting forms (SSR) and other forms on the basis of which one can draw a conclusion about the validity of expenses.
In practice, for each item on the list, the accountant may have certain requirements, and accountable persons may have questions.
Here are some examples
- Documents compiled in a foreign language must be translated into Russian. Not all information specified in the document is subject to translation, but only that which is essential for accounting.
- Is it possible to indicate dates in the expense report that fall on weekends or holidays? If days on business trips are considered, they are indicated in the report as part of the total duration of the business trip, determined by the order and passenger tickets (waybills). For these days, daily allowances are paid as usual. If we consider the days when inventory items are purchased or any services are provided to the employee, then questions may arise related to the involvement of the employee in performing work duties on weekends. The procedure for working on weekends is established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is controlled by the labor inspectorate. Therefore, it is better to avoid completing documents on weekends and, as expected, take a break from work. It is not recommended to invite business partners to a representative dinner on a weekend or holiday.
- An organization can independently develop an advance report form and approve it in its accounting policies. The mandatory use of the unified form AO-1 has been abolished since 2013. In practice, many continue to use the old “verified” form, which has two sides (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 1, 2001 N 55). The first side (title side) is filled out by the accountable person and the accountant, approved by the manager. The second (reverse) side is filled out by the accountable person and confirmed by his signature. On the second side, in the free lines, the accountable person lists all the documents that are attached to support expenses.
- If funds were issued not in the form of cash (from the cash register), but via a corporate card to an account specially opened for such transactions, the procedure for filling out the advance report does not change. The legislation does not limit the amount of amounts that an organization can issue for reporting; they can be very significant, but even the smallest amounts issued must be taken into account in the advance report. At the same time, it is necessary to remember the legally established standards for cash payments between legal entities and individual entrepreneurs - no more than 100 thousand rubles under one agreement. If you need to purchase goods or materials in large quantities, the accountable person must take care in advance to agree with counterparties on the conclusion of contracts for each batch that does not exceed the specified limit for cash payments. This restriction does not apply to non-cash payments. In practice, restrictions on the issuance of amounts for reporting are established by corporate rules, which are defined in the company’s internal policies.
Cash and sales receipts - how to accept them?
Most often, reporting employees have difficulties with cash receipts - from stores, points of sale of tickets for public transport, gas stations (if you need to travel on company business by car). If other documents (invoices/sales receipts) are attached to cash receipts, then there will be no problems and they can be accepted for accounting. Any documents can be attached to the advance report. Moreover, these documents must confirm not only the fact of payment for material assets, but also the fact of their receipt. A cash receipt only confirms the fact of payment, so it is not enough to confirm the fact of purchase of goods (work, services). The regulations on cash registers determine that a cash register receipt is a primary accounting document printed by a cash register on paper, confirming the fact of a cash payment and (or) payment using payment cards between the user and the buyer (client), containing information about these settlements registered cash register software and hardware that ensure proper accounting of funds during settlements. Currently, the use of cash register technology is undergoing significant changes. The transition to a new order, modern and technological, will allow information about each purchase to be transferred online to the tax office, and buyers will receive and save cash receipts on their mobile devices. On July 1, 2021, the old order will cease to apply. At the same time, service sector enterprises, owners of vending machines, as well as persons applying patents and UTII, that is, for small businesses that were not obliged to use cash registers, will have another whole year to switch to the new procedure; for them it becomes mandatory from 1 July 2018. Thus, until mid-2021, there will be two procedures for issuing cash receipts: on old machines and new ones. Following the previous procedure, it is necessary to check the presence of the following mandatory details on cash receipts:
- name of company;
- TIN;
- serial number of the cash register;
- serial number of the check;
- date and time of purchase (service provision);
- cost of purchase (service);
- a sign of a fiscal regime.
According to the new rules, the mandatory details of a cash receipt will be checked automatically in the format established by the tax authorities. This will greatly facilitate the control of documents confirming payment. A mandatory element of the new cash register receipt is a QR code, thanks to which any buyer can check the legality of the purchase being made. It must be remembered that in some cases it is allowed to issue not a cash receipt, but a strict reporting form (SSR). The cash receipt and strict reporting form must contain, except in cases established by law, the following mandatory details:
- serial number for the shift;
- date, time and place (address) of settlement;
- name of the organization or surname, name, patronymic of an individual entrepreneur;
- taxpayer identification number;
- the taxation system used in the calculation;
- sign of calculation (receipt of funds from the buyer - receipt, return to the buyer of funds received from him - return of receipt, issuance of funds to the buyer - expense, receipt of funds from the buyer issued to him - return of expense;
- name of goods, works, services, payment, disbursement, their quantity, price per unit taking into account discounts and markups, cost taking into account discounts and markups, indicating the value added tax rate;
- the calculation amount with a separate indication of the rates and amounts of value added tax at these rates;
- form of payment (cash and (or) electronic means of payment), as well as the amount of payment in cash and (or) electronic means of payment;
- position and surname of the person who made the settlement with the buyer (client), issued a cash receipt or strict reporting form and issued (transferred) it to the buyer (client);
- registration number of cash register equipment;
- serial number of the fiscal drive model;
- fiscal sign of the document;
- the address of the website of the authorized body on the Internet, where the fact of recording this calculation and the authenticity of the fiscal indicator can be verified;
- subscriber number or email address of the buyer (client) in case of transfer of a cash receipt or strict reporting form in electronic form;
- the email address of the sender of the cash receipt or strict reporting form in electronic form in the event of transfer of a cash receipt or strict reporting form in electronic form to the buyer (client);
- serial number of the fiscal document;
- shift number;
- fiscal sign of the message.
The organization's posting of inventory items purchased for it by an employee is carried out on the basis of primary accounting documents, in particular an advance report, sales receipts, as well as documents confirming the fact of payment - KKM checks, receipts for a cash receipt order (see letter from the Federal Tax Service dated June 25. 2013 N ED-4-3/ [email protected] ). At the same time, part 2 of Art. 9 of Law N 402-FZ defines a list of mandatory details that any primary accounting document must contain. Namely:
- Title of the document;
- date of document preparation;
- name of the economic entity that compiled the document;
- content of the fact of economic life;
- the value of the natural and (or) monetary measurement of a fact of economic life, indicating the units of measurement;
- the name of the position of the person (persons) who completed the transaction, operation and is responsible (responsible) for the correctness of its execution, or the name of the position of the person (persons) responsible for the accuracy of the execution of the event;
- signatures of the persons provided for in paragraph 6 of this part, indicating their surnames and initials or other details necessary to identify these persons.
Invoices submitted for reporting must be drawn up on behalf of the organization, and not the individual employee, otherwise the costs for them will be difficult to attribute to the company’s costs. In 2016, the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation indicated (determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 03/09/2016 No. 302-KG16-450) that primary documents are recognized as executed in violation of the requirements of the law and are not accepted for accounting in the following cases:
- lack of information in them necessary to identify the persons who signed them;
- when the name of the purchased goods is not clearly indicated (for example, “household expenses, office supplies, household chemicals, building materials, expenses, children’s New Year’s gifts”);
- there is no date of compilation;
- The columns “quantity” and “product price” are not filled in;
- The seller's signature is missing.
If the transaction performed is subject to VAT, then invoices must be attached to the documents for the purchase of goods, works, and services. The type and content of invoices are regulated by Article 169 of the Tax Code and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 914 (dated February 2, 2000).
Business trip: what can be taken into account?
Documents that confirm the expenses of business travelers usually include:
- round-trip tickets for air, railway, and bus transport, cash receipts for the issuance of bed linen;
- confirmation of travel expenses to train stations/airports located outside cities, in hard-to-reach areas;
- documents from the place of residence - hotel bills, strict reporting forms or cash receipts;
- travel insurance policies;
- documents confirming payment of other travel-related fees;
- documents on payment for obtaining visas.
To confirm payment for the use of a passenger taxi, a cash receipt or receipt in the form of a strict reporting form is issued. The specified receipt must contain the required details:
- name, series and number of the receipt for payment for the use of a passenger taxi;
- name of the freighter;
- date of issue of the receipt for payment for the use of a passenger taxi;
- cost of using a passenger taxi;
- last name, first name, patronymic and signature of the person authorized to carry out settlements.
In the receipt for payment for the use of a passenger taxi, it is allowed to place additional details that take into account the special conditions for the transportation of passengers and luggage by passenger taxis. Thus, the driver of a passenger taxi is obliged to give the passenger at the end of the trip either a cash receipt printed by cash register equipment, or a receipt in the form of a strict reporting form, which must contain the established details.
Let's sum it up
The advance report is checked by the accounting department for the intended use of funds, the presence of primary documents confirming the expenses incurred, and the correctness of their execution. The verified expense report is approved by the head of the organization or another person with appropriate authority. Based on the data of the approved advance report, the accounting department writes off accountable amounts in the prescribed manner. BDO Unicon Outsourcing employees are always ready to tell you what difficulties you may encounter when filling out an advance report, what can be taken into account and how to draw up documents. The company offers a full range of consultations and professional services for personnel records and employee settlements.
When can you write off accountable amounts?
Accountable amounts can only be written off due to the expiration of the statute of limitations (ST). To do this, use the following procedure:
- Set the date from which the ID period is counted. It begins to be maintained from the day that follows the deadline for returning the report (191 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). For example, the employee had to return the unspent account by February 10; accordingly, from February 11 I begin counting the ID period. ;
- 3 years are counted from the beginning of the ID period. The term of ID is 3 years (196 Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The deadline for this particular case is not established by law, so the deadline for the ID is accepted. But it is necessary to take into account such circumstances that may cause the interruption of the ID. In this case, the ID countdown begins again.
Tax accounting
Issuance of money on account
does not lead to expenses for the organization, both general and special taxation systems (USNO and UTII). This follows from paragraph 14 of Article 270, paragraph 3 of Article 273, paragraph 2 of Article 346.17, paragraph 1 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code.
Returned unspent imprest amounts
do not increase taxable income, both when calculating income tax and the single tax under the simplified tax system or UTII. After all, accountable amounts do not become the employee’s property, but are his receivables until he reports on them and returns the unused amounts. The basis is Articles 41 and 346.29 of the Tax Code.
Uncollectible accounts receivable
in tax accounting is subject to write-off as non-operating expenses. If a reserve for doubtful debts is created for non-operating expenses, the amounts of bad debts not covered by the created reserve should be written off (subclause 2, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An organization using the general taxation system can do this.
Please note that the expiration of the statute of limitations is one of the criteria for recognizing a debt as bad and, therefore, taking it into account as expenses for corporate income tax purposes. To include amounts of receivables for which the statute of limitations has expired, documents confirming the expiration of the statute of limitations are required as expenses. This is stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 15, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/589.
An organization that applies the simplified tax system, regardless of the chosen object of taxation, does not have the right to reduce the base for a single tax by the amount of written off bad receivables (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13, 2007 No. 03-11-04/2/274).
The amount of written off bad receivables does not matter for organizations paying UTII. This follows from paragraph 1 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code.
What to do if the director does not account for the accountable money
Until recently, it was believed that it was necessary to withhold personal income tax on unreturned accountable amounts. But nowadays things are different. If the employee does not report, then the money cannot be recognized as his property; this debt will remain with him. It is necessary to withhold personal income tax and calculate insurance premiums only if the employee’s debt is forgiven. In this case, the employee receives income, and the company receives a loss. Therefore, with any employee, even with
director, it is worth agreeing to provide a report on advances issued. But if the company does not write off the debt and does not withhold it from the employee, then it can only be written off after the expiration of the ID period, which is 3 years (
Issuing an advance for a business trip
The procedure for issuing funds from the cash desk of an enterprise is determined by the Regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions, which was approved by the Bank of Russia No. 373-P dated October 12, 2011 (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations).
The advance is issued from the following funds:
- Receipts to the organization's cash desk for the sale of goods (Services, works).
- Received from the current account.
An advance is not issued from money received from citizens for payment in favor of third parties (for example, under an agency agreement in payment for communication services).
Important! A person who has no debt on previously received advances can receive money for a business trip on account.
Travel allowances are issued on the following grounds:
- If there is an order drawn up in form T-9 (collective form T-9a).
- Statements from the employee regarding the amount of the advance and the period of issue with the director’s visa.
Money is issued according to a cash receipt order, which is issued in one copy. In the “consumables”, the employee must write down the amount of money received by hand (rubles are written in words, and kopecks in numbers, for example, five thousand rubles 38 kopecks), and then sign the receipt. The money must be counted in the presence of the cashier, otherwise claims for missing amounts will not be accepted.
Registration of cash transactions
To carry out cash transactions, companies must organize a cash desk and appoint responsible employees. It is these employees who are responsible for the correct management of the cash register and registration of cash transactions.
When conducting cash transactions, companies are required to prepare cash documents. Such documents are an incoming cash order and an outgoing cash order. The forms of these forms are approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88. The Ministry of Finance of Russia in Information No. PZ-10/2012 emphasized that the PKO and RKO forms are mandatory for use.
When registering cash flow through the cash register, you should remember that the cash flow order is used when issuing money. A cash receipt order is used when funds are received.
Cash documents are signed by the cashier and the accounting employee, and are also recorded in the register of cash documents.
It should be remembered that cash documents must be drawn up without errors. If orders are issued in paper form, then corrections or additions cannot be made to their content. To eliminate errors, you should reprint the corresponding document and make the necessary entries in it.
Expenditure cash order forms are used when issuing wages, cash for reporting, and other cases of registering the expenditure of cash.
A prerequisite for the correct execution of cash transactions is maintaining a cash book. The form of such a document is approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
All cash transactions must be recorded in the cash book maintained by the cashier. Complete information is entered into form No. KO-4 in accordance with the receipt and expenditure orders. Any discrepancies are unacceptable.
At the end of the working day, the cash balance is indicated in the cash book, which is certified by the cashier’s handwritten signature.
It must be emphasized that all of the above forms should be used by companies in the case of transactions with monetary documents. A prerequisite for registration of such a movement is the affixing of the o.
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1 : What to do in a situation where an accountable person has not provided a report within the allotted 3-day period and needs to be given another accountable amount?
Answer : Until a person has reported on the previous amount, he cannot be given the next one, regardless of the amount of expenses, until the amount is reimbursed (deduction from wages or the employee returns the amount on a cash receipt order). An employee may refuse a business trip.
Question No. 2 : Is the employee paid per diem if a sick leave is issued for several days of a business trip?
Answer : Not paid, since the employee will receive temporary disability benefits.
Rules for drawing up an order
The employer is obliged to issue an order to deduct from the salary within a month after it becomes aware of the employee’s debt. If the specified deadlines are missed, then you will have to go to court to collect the amount of the debt, or the employee will first have to write an application for withholding.
The employee draws up an application to withhold accountable amounts in a free format.
The order should include the following information:
- Employer company name.
- Title of the document.
- Full name of the accountable person and his position.
- Date of issue of the order and place (city).
- Circumstances of issuing the accountable amount : when it was issued and for what purposes (for example, in connection with a business trip).
- Amount of funds subject to withholding.
- List of attachments (this may be a notice of withholding, an advance report, or a written statement from the employee).
In the order, the head of the company can appoint a person responsible for withholding money from wages. Usually this is an accounting employee who is responsible for payroll.
A sample order for deduction of imprest amounts from wages can be downloaded here. The employer has the right to approve its own standard format for an order to withhold funds from an employee’s salary. This is especially true when deductions are made quite often.
The deduction is made on the next day of payment of wages. It can be made from both an advance payment and a final payment. It is worth considering that even if there is a correctly executed order to withhold and the employee’s consent has been obtained, the employer is not always able to withhold the accountable amount that has not been returned to him at a time. This is due to the fact that the provisions of labor legislation limit the amount of deductions from the employee’s income.