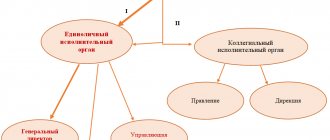
From the moment of registration of an LLC, a sole executive body, the director, acts on its behalf. Formally, this is the most important figure who bears administrative and criminal responsibility for the actions of the company. This situation provokes some founders to hire a person to whom all the property risks of the business can be transferred. Who is a nominee director, and is it worth transferring management of the organization to him? Find out about it in our publication.
Free consultation on business registration
Who is the founder
The activities of LLCs in the Russian Federation are subject to the requirements of Law No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/98. The current version states that a founder is a person:
- ratifying the organization's charter;
- contributing funds to the authorized capital;
- selecting management and appointing inspections of its activities;
- having the decisive right to vote when making decisions on the company’s activities.
The founder can be a legal entity or an individual. It is not necessary to have Russian citizenship; a non-resident can organize an LLC. Deputies, military personnel and a number of officials are not allowed to become organizers of an LLC.
Concept of limited liability
Many newcomers to business register an LLC in order to avoid personal liability when financial obligations arise. Indeed, Article 56 of the Civil Code states that a participant who has contributed a share to the authorized capital is not liable for the debts of the organization. But the company is not responsible for the owner’s personal debts. Therefore, most businessmen confidently answer that in the event of debt obligations, they will need to answer within the limits of the contributed share.
This rule applies if the company operates normally and regularly fulfills its financial obligations. In such a combination of circumstances, it is impossible to attract the founder to pay the company’s bills. The LLC acts as a completely independent entity bearing obligations to creditors. This creates the false impression that the financial risks for the organizer are zero.
But everything changes when the LLC ceases to exist, declaring itself bankrupt. In this case, participants may be required to fulfill financial obligations. But to do this, creditors need to prove that the company’s ruin was caused by the actions of the founders or the people they hired.
Article 3 of Law N14-FZ states: in the event of a company’s insolvency, the founders will be held liable if the company’s property is not enough to fulfill its financial obligations.
Why does a company need a nominee director?
It’s worth saying right away that it doesn’t make much sense for the founders to resort to such a management option as a nominee director. The real owner of the business, as the person controlling the debtor, will also be jointly and severally liable for the insolvency of the company.
But besides the desire to avoid possible responsibility, work as a nominee director can be offered by the founders in the following situations:
- the actual owner or manager of the business cannot or does not want to officially manage the organization (for example, he has the status of a civil servant or a disqualified person);
- several different enterprises are headed by the same person, which is a sign of the interdependence of these taxpayers and increases tax risks;
- the actual manager already manages another organization, and at the same time cannot or does not want to obtain the consent of its owners for parallel work for hire in the new LLC;
- it is necessary to split the business into several small firms in order to maintain tax benefits;
- to simulate competition when participating in tenders and government procurement, a director is needed.
Officially, there is no such thing as working as a nominee director, so the law does not establish responsibility for this. However, this situation carries risks for both parties.
Types of liability
The legislation provides for different options for the liability of the organizers of the enterprise:
- for the actions of the hired director;
- for your own actions.
Responsibility of a company director
In the first case, the management of the company is transferred to a third party, who provides management for a fee. It has certain legal and financial obligations to the owner of the company.
The hired director must monitor the state of current affairs, submit financial statements on time, and bear obligations before the law for his decisions. According to Art. 44 of Law N14-FZ , the director is liable to the owner for losses resulting from his erroneous actions or inaction.
The director will have to be responsible for:
- concluding obviously unprofitable transactions;
- concealing important commercial information from other founders;
- unjustified risks when concluding contracts and agreements;
- lack of due diligence checks on partners;
- deliberate destruction of financial and legal documents characterizing the company’s activities.
However, if the director proves that his actions were direct execution of the orders of the business organizers and they led to the liquidation and bankruptcy of the enterprise, then the financial burden will be borne by the founders.
1:07 – Fictitious bankruptcy and sanctions for it in the arbitration process? 3:12 – How can you remove assets from a company with debts? 7:04 – The founder denies that he knew about the conclusion of the agreement, what to do? 10:13 – The director’s actions led to the formation of debt, what should I do? 16:26 – Responsibility of the general director in an LLC? 16:49 – What does limited liability LLC mean? 17:21 – Can the founder of an LLC be fined for accounting errors? 18:05 – When agreeing with the organization’s debts, are the old founders responsible? 19:11 – How to hold the founder of an LLC jointly and severally liable? 20:20 – If the founder is a legal entity, why is the LLC at risk?
Responsibility of the founder and director in one person
If the founder himself acts as a manager, then it will not be possible to shift responsibility to an employee. If there are outstanding debts, he will have to take all possible measures to repay them. And if the company’s property is not enough, the founder will have to pay off debts from personal funds. The founder-manager is held accountable if he:
- exercised leadership incompetently;
- allowed an increase in debt on taxes and other areas of accounting reporting;
- used credit funds irrationally;
- chose unverified companies to work with.
Example from judicial practice:
The founder-director led a company that provided heat and water supply services. When holding a tender for servicing city property, he announced a new company with exactly the same name. The result of this action was that the former LLC lost the ability to provide services and was unable to repay the previously received loan.
The Arbitration Court recognized that the insolvency of the LLC was caused by the unlawful actions of the director, and ordered him to pay damages. The amount of damage amounted to 4.5 million rubles, and the founding director had to pay off the debt using personal funds.
Is the consent of the founders of an LLC necessary for the dismissal of a director?
The release of the director of an organization from his position is a procedure that is under the jurisdiction of two main areas of legislation: labor law and civil law (in fact, its corporate sub-branch).
From the point of view of labor legislation, the dismissal of a director on his initiative is carried out generally according to the same standards as the dismissal of any other employee of the enterprise. That is, the head of the company has the right, having written a statement of his own free will and having worked for the required period (30 days according to Article 280 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and this is one of the aspects of the difference in the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation governing legal relations with the participation of managers and ordinary employees of the organization), has the right to stop fulfilling his duties job responsibilities. The consent of the company's founders is not required here.
The procedure for registering the dismissal of a director at his own request by the HR department is described in detail in ConsultantPlus:
To learn more, get trial access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution.
From the point of view of civil law, a director is an official who is appointed to his position and dismissed from it by the decision of the founders of the organization. And if they do not agree to let him go, they can simply refuse to appoint a new leader. And even if the director, from the point of view of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is dismissed, he will nevertheless have to fulfill the duties assigned to him within the framework of civil law.
At the same time, in practice, a number of legal mechanisms can be identified that allow the director to resign without the consent of the owners of the company and, moreover, in full compliance with the specified categories of legal norms. Let's look at how a director can resign without the consent of the founders using these mechanisms.
Tax debts
The liability of LLC founders to the state is prescribed by law. Therefore, it is in the interests of the founders to monitor the actions of the director so as not to accumulate tax debts. Article 49 of the Tax Code states that if a liquidated organization lacks funds to pay off tax debts, including fines and penalties, the debt is collected from the founders.
An organization falls into the risk zone if the amount of tax debt reaches 300 thousand. If it is not possible to pay them, you must urgently declare bankruptcy. Otherwise, the tax committee will do this, but with a demand that the director and/or founders be found guilty.
You should not try to withdraw the company's assets to avoid paying debts. This will result in the founders being required to fulfill their obligations using personal funds.
Many people believe that it is difficult to hold the founder of an LLC accountable. However, since 2015, the Tax Code in some cases can use another tool - the initiation of a criminal case under Article 199 of the Criminal Code. As a result, the founders will not only be forced to repay the debt, but will also acquire a criminal record, which may negatively affect their future activities.
Actions before dismissal: transfer of documents
As soon as notifications of delivery of letters are received by the resigning director or are considered received upon delivery (Clause 1 of Article 165.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), the director can count the term of service.
Since the head of the company is a financially responsible person, before dismissal he should transfer documents and other corporate property to other competent persons. The list of such documents and types of property may include, for example:
- Reporting on entrusted amounts.
- Contracts.
- Powers of attorney.
- Keys, cards, digital signature.
- Seals and stamps, pre-sealed and stamped with the date of packaging. It is advisable to ask for witness signatures. This approach will help in the future to avoid accusations from the founders of illegal use of the seal.
In order to certify the fact of transfer of corporate property, it is necessary to draw up a special act.
For a sample of filling out the acceptance certificate when changing the director, see here.
If it is impossible to transfer these documents and property to the founders, they can be temporarily left with the notary (if he takes such things for safekeeping). Or leave it in your custody, issuing an appropriate order.
It is also useful to carry out the necessary communications with the credit and financial organization servicing the company's current account - by sending there, in particular, information that from such and such a date the director will terminate his employment relationship with the business company. As a consequence, the bank can cancel the digital signature and other instruments for the resigning director to exercise his powers (and this may additionally encourage the owners not to delay the appointment of a new head of the company - someone will need to sign financial documents).
What debts will you have to pay with personal funds?
The organizer of the company will be liable to the extent of his share in the authorized capital if it is not proven that bankruptcy was caused by his actions. Otherwise, some types of obligations will have to be fulfilled personally. This:
- Arrears on taxes and insurance payments to the budget. In bankruptcy, all tax debts must be eliminated. If the founder’s share in the management company is not enough, then he will have to pay with personal property.
- Debts to creditors. Debts will have to be paid off if it is proven that bankruptcy was caused by the actions of management. The order of repayment is determined in court.
- In case of illegal bankruptcy. If the founders or management maliciously brought the company into bankruptcy for personal gain, then they will be punished.
Punishment for malicious bankruptcy can be administrative, financial or criminal.
The claim against the employer has been considered: actions of the director
If the court sides with the plaintiff (it is possible that after several instances have been passed), the court’s decision to recognize the inaction of the company’s founders as illegal can be transferred to the Federal Tax Service as a basis for making changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
The main probable reasons for the court's decision in favor of the defendant include the director's failure to fulfill his duties after de jure dismissal under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The fact is that as long as information is recorded in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities that the plaintiff is the current director of the company, he is obliged to perform the duties of a director. If, due to his inaction, problems arise in the business, then his refusal to work may be interpreted by the court as a sign of abuse of the right to dismiss, which in this case may be carried out by the director intentionally in order to cause harm to the company.
In addition, the founders, in turn, can initiate a counterclaim against the resigning director as an official who allowed inaction, and recover damages from him due to problems arising in the business.
Vicarious liability
Vicarious liability is the obligation of a third party to compensate the balance of the debt of the principal debtor. There are three parties involved in the relationship:
- creditor;
- principal debtor;
- additional (subsidiary) debtor.
Subsidiary obligations arise if all measures to collect the debt from the main debtor have been exhausted. The circumstances under which the founders of an enterprise bear subsidiary liability for its activities and for the actions of its director are determined by law. With this option, the size of the share contributed to the authorized capital does not matter.
Amendments to the law on bankruptcy and LLC
Federal Law No. 488 of December 28, 2016 introduced significant amendments to the current law on LLCs and the law on bankruptcy recognition. These amendments greatly complicated the lives of those businessmen who created and deliberately bankrupted their companies. According to the adopted amendments, subsidiary liability remains for three years from the date of announcement of the liquidation of the company.
This law is aimed at protecting the interests of creditors. It expands the powers to collect debts from management and founders, as well as from persons who actually controlled the work of the company.
The scheme of work with the appointment of a “sic chairman” is also valid in modern realities. The director can follow the instructions of the owner, who has no official connection with the company's activities. The law defined the status of such “underground leaders”, calling them KDL (person controlling the debtor). They were extended the obligation to bear responsibility for the activities of the director, which led to the formation of debts. To establish the role of the CDL, testimony in court is sufficient.
When is subsidiary liability imposed?
If the company's assets allow it to pay off all its obligations, then there is no question of attracting additional debtors. Until the legal entity is liquidated, the founders are responsible only for shares in the management company and nothing more.
But after recognizing the financial insolvency of a legal entity, it becomes possible to attract personal funds from debtors. To impose subsidiary obligations, a number of conditions must be met:
- completed bankruptcy procedure or receipt by the court of an application from the debtor regarding financial insolvency;
- an established circle of persons who actually control the activities of the LLC;
- the presence of evidence linking the actions of management and the ruin of the company.
The persons involved may be:
- hired director;
- company founders;
- any persons exercising actual control of activities (KDL).
If the managers of the enterprise and the CDL are held vicariously liable, the concept of the presumption of innocence does not apply to them. That is, if you want to prove your non-involvement, you will need to do this yourself.
The founders of a limited liability company will be liable with their property for the company’s debts even if a personal bankruptcy procedure has been carried out. If the organizer leaves the LLC, then he may be required to repay debts that arose during the period of his participation. The possibility of attracting a former founder remains for two years after his withdrawal from the LLC.
Major changes in the law
Founders should familiarize themselves with the changes made to the law on liability for the activities of an LLC director:
- The circle of persons who can be involved in repaying debts has been expanded. In addition to the director and founders, it included KDL, persons who actually control the activities of the enterprise. Major shareholders, financial or technical directors and any other entities that have a significant influence on the company’s activities can be recognized as CDL.
- In Article 3 of the Federal Law No. 14 “On LLC”, a provision appeared that allows the creditor to collect debts from the director or founders if he proves the dishonesty or illiteracy of their actions. Previously, collection was possible only after bankruptcy.
- Creditors can make claims against controlling persons even if the LLC has been excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
These amendments significantly increased the ability of creditors to recover debts.
Dismissal of the director: we notify the owners
So, according to labor law, there are no particular difficulties with registering the dismissal of a director. Another thing is the exercise of the director’s right to dismissal, taking into account the norms of corporate law.
30 days in an LLC and 50 days in a JSC (we will look further at the rules of law that establish these terms) before terminating work as an employee, the director is obliged to notify the owners of the company of his desire to resign. During this period, their task is to issue local regulations on the dismissal of the previous director from his position, on the appointment of a new head of the company, and also initiate the necessary changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
The fact that the resigning director notified the owners of the company must be proven. For these purposes, he can send a registered letter to the founders of the company with notification and an inventory (which will reflect the presence of a resignation letter in the letter). This letter can be compiled in several copies and sent to:
- at the legal address of the company;
- at its actual address;
- at the home addresses of the founders.
Prosecution procedure
The founder's responsibility for the activities of the director appears in the bankruptcy process. If the LLC simply ceases to exist, having honestly paid all its debts, then no claims will arise either against the management or the organizers.
If the debts cannot be repaid, the law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” comes into force. This law describes in detail the procedure and outlines the conditions for holding accountable all involved persons - managers, owners and executive directors.
If the company's management does not timely file an application to declare the LLC bankrupt, the tax authorities will do it for them.
When considering a case of financial insolvency of a company, the director of the enterprise, founders, as well as persons recognized as beneficiaries are involved in the judicial process.
If the court recognizes the connection between the action (or inaction) of these persons and the inability of the enterprise to pay its debts, then penalties in the amount of creditors' claims will be imposed on both the company's property and the personal property of the persons involved.
How can self-bankruptcy affect you?
A business owner may fall under subsidiary liability for the activities of the director or his own mistakes, even if he begins bankruptcy proceedings on his own. Especially if deadlines were missed.
If debts cannot be repaid, then it is better to start the procedure for declaring bankruptcy yourself, without waiting for the tax authorities to do so. Advantages of self-bankruptcy:
- independent submission of documents without seizure;
- appointment of an arbitration manager of his choice;
- the ability to legally block creditors' claims.
However, even self-bankruptcy declared in a timely manner does not guarantee that you will not have to answer for debts with personal property. If the company's assets are insufficient, bringing the director and owners of the company to subsidiary liability is almost inevitable.
But it will be much worse if the bankruptcy procedure is initiated by the Tax Committee. Tax officials use every opportunity to raise funds to pay off debt, including seizing personal property and personal accounts.
Circumstances in which the owner’s guilt is recognized by default
The law provides for circumstances in the event of which responsibility for the activities of the director is assigned by default to the owner of the business. These are the following events:
- concluding a transaction by direct order or with the approval or insistence of the owner, provided that this transaction resulted in losses and led to bankruptcy;
- damage, loss or damage to accounting documentation for which the owner of the enterprise was responsible;
- actions that may be regarded as deliberate bankruptcy.
Additionally, the reason may be an unreasonable credit policy pursued by the owner and other errors leading to a violation of the property rights of creditors.
Options for protecting persons controlling the debtor
The adopted amendments treat CDLs quite harshly, denying them the presumption of innocence. However, there are situations in which the CDL has the opportunity to minimize the size of its financial obligations on the enterprise’s debts or avoid it altogether. To do this it is necessary to prove that:
- the person recognized as the controller of the debtor was not actually the controller, but the court must be provided with information about the real beneficiary;
- KDL acted as reasonably and conscientiously as possible, its actions were aimed at avoiding even greater losses;
- the amount of damage caused by the CDL is significantly lower than the financial obligations imposed on it.
These opportunities for CDL are recorded in Article 61.11 of Law No. 127-FZ in paragraphs 9, 10 and 11.
How to resign a CEO through court: claim against the employer
In fact, the manager withdraws his powers a month after notifying the business owners in accordance with Art. 280 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, in the state register the director will be listed as the sole executive body, and the department will only be able to change this entry with information about the new director.
If during the service period the founders have not appointed a new director of the company, the resigning director should initiate a judicial mechanism in order to exercise his right to be relieved of his position.
The founders of the company, who have not taken the actions necessary to appoint a new director instead of the resigning one, commit a violation that may be the subject of a claim in an arbitration court: as a result of their inaction, the rights of an employee holding the position of general director and wishing to be relieved of it are violated (subparagraph 2, paragraph 1 Article 29 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
In a statement of claim, from the point of view of labor legislation, a director who has resigned can indicate, in particular, that the founders of the company, first of all, violate his rights to freedom of work, unreasonably force him to perform duties, which is prohibited by the provisions of Art. 4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and clause 2 of Art. 37 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
The following must be attached to the application to the court:
- a copy of the resignation letter;
- postal documents confirming the sending of the application to the founders;
- a fresh extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, according to which the resigned director continues to hold his position;
- perhaps - the results of the plaintiff’s correspondence with employers (which reflects their reluctance to fire him).
conclusions
From all of the above, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- The obligations of the LLC organizers are not limited to the size of their share in the management company. If debts arise that cannot be repaid with company property, business owners will have to answer with personal funds. For this reason, it makes no sense to form an LLC just to avoid personal financial risks.
- It is somewhat more difficult to attract the owner of an LLC to fulfill financial obligations than an individual entrepreneur. But currently the number of such cases is in the thousands.
- If the company is run by a hired director, the owners should not completely remove themselves from running the business. It is necessary to introduce a control system that allows you to see the real picture. Otherwise, the director will have to bear personal responsibility for illiterate or dishonest actions.
- It is important to monitor the status of financial statements. Distortion of documents or their damage may become evidence of intentional bankruptcy and, accordingly, the occurrence of subsidiary obligations.
- Creditors have the right to demand repayment of debts not only from the enterprise, but also from its owner if the company is in the process of bankruptcy.
- Creditors need to prove that the cause of the company's ruin was the wrong actions or inaction of management, but in most cases there is a presumption of guilt, and there is no need to prove anything to those demanding repayment of debts.
- An attempt to divest a company's assets shortly before declaring bankruptcy is a reason to initiate criminal proceedings against the owners. Therefore, an attempt to hide part of the property may result in a criminal conviction.
- If it is impossible to fulfill financial obligations, it is better to initiate bankruptcy proceedings by the owner himself, without waiting for the Tax Committee or other competent authorities to do this.
It is recommended to begin the bankruptcy procedure with the involvement of highly specialized lawyers who have positive experience in handling such cases. Only in this case can you count on the successful completion of the process.
How to resign as a director: appeal to the Federal Tax Service and a possible lawsuit
There may be an alternative to going to arbitration with a claim against the inactive owners of an LLC - applying to the Federal Tax Service with a request to exclude from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities the entry that the director who resigned under the Labor Code continues to remain the head of the organization. For these purposes, the following documents may be submitted to the Federal Tax Service:
- form P13014;
- copies of the resignation letter, notice of convening a meeting of founders, postal documents.
In this case, the signature on form P13014 can be certified by a notary. We described how to fill out such a form here.
If the Federal Tax Service refuses to make changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities based on a corresponding request from the resigning director, he may initiate a lawsuit, the subject of which is the inaction of the department, expressed in the refusal to make changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Before this, it is also necessary to obtain clarification from a higher structure of the Federal Tax Service (clause 1 of Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), unless, of course, the department at the appropriate level does not satisfy the applicant’s request.
There is a possibility that the arbitration will side with the plaintiff - based on the fact that the information in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities that the plaintiff is the current director of the company will be unreliable, since he no longer works in the organization (decision of the Arbitration Court of the Lipetsk Region dated 09.11.2015 case No. A36-4738/2015).
However, it is worth noting that such precedents, by definition, are not very representative, since they are based on a fairly deep interpretation by the court of legal norms on state registration and, probably, will occur with the greatest frequency following the results of hearings in which the company itself will not be a third party and will not declare any claims.