Companies often enter into civil law agreements (CLA) with individuals: in this case, they can save a lot on costs. However, it will not be possible to completely avoid taxes and contributions in this case. Nikita Rozhentsov and Natalia Fedorova from Alliance Legal CG explained in detail what taxes need to be paid when working under GPC agreements in 2021.
Registration of relations with individuals through civil contracts is a common occurrence for many entrepreneurs. To perform one-time work or provide any service, it is not always advisable for an organization to hire an employee and bear associated expenses (personal income tax, insurance premiums), as well as provide the person with certain guarantees (annual paid leave, temporary disability benefits).
For such cases, the most optimal way out of the situation may be to conclude a service agreement or a contract with an individual. But for managers, the question of the fiscal burden immediately arises: how, how much and in what order to pay taxes and insurance premiums.
Civil law agreement taxes and contributions in 2020
If the citizen is not an individual entrepreneur and is an employee of an organization, there are a number of mandatory payments. Let's start with the fact that contributions to the Pension Fund are insurance contributions and payments, as well as other other remunerations that the payer accrues in the interests of the employee within the framework of labor or civil relations. And these relationships arise on the basis of contracts under which the employee performs certain services (employment contract or civil law). Also, the above agreements include copyright agreements, under which works of art, utility models, industrial designs, and so on are created for a fee.
What is a GPC agreement
This is a civil law agreement, also known as a civil law agreement, concluded between an organization and an individual. This includes, in particular, contracts:
- according to the norms of Article 779 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation for the provision of services;
- according to the norms of Article 702 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation for the performance of work, contract;
- according to the norms of Article 1288 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation - author's order;
- other.
After completion, the customer and the contractor sign a certificate of completion of work. On its basis, the citizen receives a reward, that is, money earned. This can happen either in stages or for the entire volume at once. Under agreements of this type, an individual acts as a performer of any work or services. In doing so, it can:
- have the status of an individual entrepreneur;
- do not have the status of an individual entrepreneur.
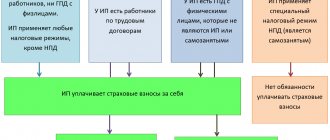
This is of decisive importance for the customer. Why is this so important? Because the obligation of an organization or entrepreneur to pay taxes and insurance premiums on remunerations paid to performers depends on this. In particular, under such an agreement with an individual entrepreneur, the customer of work or services does not have any such obligations; he must pay taxes on his own. But if the performer is an ordinary citizen, then the question of what fees are subject to a civil contract should be of interest to the management of the organization even before it is signed. Because if you underhold or underpay something, you can get a large fine from the tax authorities. But first things first.
Taxable income from contributions to the pension fund and social security
- performs a specific task for the customer or engages a subcontractor
- determines the procedure for performing the duties assigned to him
- can do assigned tasks at home or elsewhere
- receives not a salary, but a remuneration stipulated by the contract, which is paid in the manner established by the contract
- independently pays taxes, contributions to the pension fund and social insurance fund (unless this is specified separately in the contract)
- does not receive vacation and sick leave pay (unless this is specified separately in the contract)
Insurance premiums of performers for GPC
According to the norms of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the customer must, if he enters into GPC agreements with individuals, pay insurance premiums for:
- compulsory pension insurance (OPI);
- compulsory health insurance (CHI).
But only on the condition that we are talking about works or services. If the subject of the agreement is the transfer of ownership or other proprietary rights to property, as well as the transfer of property for use (rent), then insurance payments are not accrued (Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated June 18, 2018 No. 03-15-07/41602 and the Federal Tax Service dated June 25, 2018 No. BS-4-11/12184).
There is also no need to charge social insurance contributions for temporary disability and in connection with maternity, as well as “for injuries.” This follows from the provisions of Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, if insurance against occupational diseases and industrial accidents is expressly provided for in the GPC agreement, then payments to the Social Insurance Fund must be made (Clause 1, Article 20.1 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ of July 24, 1998). After all, if an accident occurs, the customer will be obliged to pay compensation to the contractor or pay sick leave.
Pension and medical fees for civil law relations are accrued at generally established rates:
- for pension insurance - 22%;
- for health insurance - 5.1%.
All benefits and the right to apply reduced tariffs that organizations have apply to GPC relations. Performers under such agreements are included in DAM reporting on a general basis.
Peculiarities of taxation of fees for compulsory medical insurance and compulsory medical insurance of contract agreements
Sometimes, by agreement between the contractor and the customer, in addition to direct remuneration for labor, payment to the contractor under the GPC is provided for reimbursement of expenses incurred by him related to the fulfillment of obligations. These may be costs for tools, raw materials, materials, and even travel to the place of work - everything that the contract itself provides for; There is no need to pay contributions for these amounts, as stated in paragraphs. 2 clause 1 of article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But personal income tax is still withheld from these amounts.
Moreover, all expenses of this kind must be supported by documents. This is necessary so that when conducting an audit, organizations do not charge additional insurance premiums for these amounts paid in favor of an individual.
For example
A company using the simplified tax system pays insurance premiums at reduced rates, since its income does not exceed 79 million rubles and the revenue from one of the preferential types of activities is more than 70% of the total income (clause 3, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2015 No. 17-4/10/OOG-1357).
And therefore, in relation to an individual contractor, the company also has the right to apply reduced tariffs, i.e. during 2021 - 2018, insurance premium rates for compulsory pension insurance will be 20.0%, for compulsory health insurance - 0%.
MAINTENANCE OF PERSONNEL RECORDS
Now let’s consider the question of when it is necessary to charge additional contributions to the compulsory pension insurance. Let us recall that the list of professions subject to additional contributions to pension insurance is contained in Article 30 of the Law “On Insurance Pensions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ.
According to paragraph 1, paragraph “a”, paragraph 1 of Resolution No. 537, when early assignment of an old-age pension to workers engaged in underground work, work with hazardous working conditions and in hot shops, List No. 1 of production, work, professions is applied, positions and indicators in underground work, in work with particularly harmful and especially difficult working conditions, employment in which gives the right to an old-age pension on preferential terms, approved by Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991 No. 10 (hereinafter referred to as text - List No. 1).
Labor agreement who pays taxes
I'm looking for a job. There is an offer that suits me practically with everything: location, schedule and salary. But they don’t apply based on a work book. They said that they do not pay sick leave (I have a small child and will have to take it sometimes), there is no vacation and vacation pay, i.e. the schedule will indicate that I worked these days. This confuses me. What other disadvantages are there when they don’t register according to the Labor Code? Pension not coming? And it also surprises me that despite the fact that they don’t register for work and don’t make deductions, their salary is white. How can this be?
Since all deductions provided for in Ch. 23 of the Tax Code are provided at the request of the taxpayer, then in order to exercise the right to a professional tax deduction, the contractor must provide the appropriate application and documents confirming expenses to the tax agent.
RSV filling mechanism
The DAM must be filled out in rubles and kopecks, and all indicators must be entered from left to right, starting from the very first cell. In calculations submitted electronically or when created through a computer program, dashes are not placed in empty cells (Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 10, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/551).
The field “Last name ________I.___O.___” is intended to be filled in by individuals who are not registered as individual entrepreneurs and have not indicated their TIN in the DAM. Organizations do not fill out this field.
Results
An employer who has entered into a contract with an employee has the right not to pay contributions for disability and maternity insurance on payments accrued under this contract, and to accrue contributions for injuries only if this is expressly provided for in the contract.
It is for this reason that the possibility of reclassifying such a contract into an employment contract should be excluded. Accrual of other insurance premiums (for compulsory health insurance and compulsory medical insurance) is carried out at generally established or reduced (if there is a right to apply them) rates. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Income tax
Expenses incurred for the payment of remuneration under civil contracts must be recognized as of the date of signing the act of provision of services. These expenses are taken into account in labor costs (if the contractor is not an individual entrepreneur/self-employed) or in other expenses (when the contractor is an individual entrepreneur or self-employed).
Note: the entrepreneur is required to confirm the expenses incurred with documents (agreement, acts of completion of work/provision of services, in some cases - reports on the work done, and so on). Failure to fulfill this obligation, as well as failure to confirm the actual completion of these works/provision of services, may serve as the basis for claims from the tax authorities and lead to additional assessment of income tax, as well as penalties and fines.
How the tax office checks the RSV
The tax office checks whether the amount of pension contributions for the 2nd quarter matches the personal accounting information. If there is a discrepancy, it is necessary to correct the error (clause 7 of Article 431 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax officials also check the consistency of the individual information provided with the Federal Tax Service database. If there are errors, the RSV must be retaken.
In order to determine the correctness of calculation of insurance premiums, inspectors add the amount of calculated contributions for the 2nd quarter to the amount for the 1st quarter. If the result is less than the total amount, you need to look for and correct the error.
Regulatory framework for 2021
The main regulation for this type of relationship is the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In Art. 702 states that a work contract acts as a transaction for the contractor to perform certain works that are paid for by the customer. Based on the terms of a specific agreement, in practice the following types of work contracts :
- Household (performing work to meet the customer’s household needs). The standard used is Law No. 2300-1 of February 7, 1992 “On the Protection of Consumer Rights,” as well as the Rules for Consumer Services in the Russian Federation.
- Construction (carrying out construction work and everything connected with it - capital, installation, reconstruction work). The standard is Federal Law No. 39 of February 25, 1999 “On investment activities in the Russian Federation” and Federal Law No. 160 of July 9, 1999, as well as the Land and Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation.
- Design and survey (the customer prepares documents based on the results of the work performed - the results of economic, natural research, technological, constructive, architectural solutions).
- Public (the purpose of creation is to meet state or municipal needs).
In Art.
432 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that an agreement is considered concluded from the moment an agreement is reached on significant issues. The subject of the transaction is described in Art. 743 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The work performed is recognized as it. As for the cost for the work, it is considered significant if it was agreed upon by the parties in advance, in accordance with the provisions of Art. 709 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Why do they enter into a GPC agreement with employees? The answer is in the video below.
Temporary employment contract with an employee for individual entrepreneurs without paying taxes
For example, an individual entrepreneur makes a summer cafe in the warm season, he needs waiters, cooks, cleaners, but for the period from May 1 to September 30. Or a businessman needs people to repair a warehouse. He can enter into an agreement with any company performing such work, or hire citizens under an employment contract valid until the renovation of the premises is completed.
And also if an employer employs a pensioner (due to restrictions or age), or if a person goes to work for an entrepreneur who employs less than 35 people. The last paragraph of individual entrepreneurs can be used as the basis for drawing up a fixed-term contract with each employee.
How to apply
A GPC agreement with an individual does not have a unified form.
However, when drawing up a document, it is important to indicate some aspects and nuances of cooperation:
- Preamble indicating:
- Full name and other data of the customer and contractor;
- other authorized persons.
- An item indicating a specific expected result after completing a given task. For example, the subject could be building a house. In this case, it is important to describe the main characteristics of the structure, materials used, colors, etc.
- Deadlines for completion, without which the document cannot be considered legally valid. The GAP must specify the start and end dates of work, as well as the period of intermediate inspection. It is not necessary to indicate a specific date. Typically a time period or condition is used. For example, the term is the fact of completion of construction.
- Quality of work. Quality is determined according to the criteria specified in the contract. It also indicates the warranty period during which the contractor undertakes to correct defects if any are discovered.
- The procedure for performing work or providing services. Here are the basic requirements for cooperation and links to regulations. It is important to indicate which party provides materials, tools, equipment, etc.
- Amount and procedure of payment. Payment is set based on results, tariffs or time spent at the discretion of the parties. This also includes the cost of materials and the nuances of paying taxes. The payment procedure is established - in cash or by transfer to an account, as well as terms.
- Responsibility. The section lists sanctions for failure to fulfill the obligations of the parties to each other. It is advisable to indicate the amount of fines or other sanctions.
- Change or termination. This part lists the conditions under which the agreement may be terminated or become invalid. They also establish the possibility of making changes.
- Conclusion. The final part indicates the validity period of the agreement, contact information and signatures of the parties.
A sample contract is available.