Business lawyer > Labor law > What are the working conditions: assessment system and classification
It is the employer's responsibility to create optimal working conditions for employees. Rational intensity of work and a comfortable environment make it possible to obtain improved results in all spheres of the economy. Failure to comply with legal regulations when organizing the work of a team not only reduces its productivity. It directly violates the rights of employees and can cause harm to their health or life. In this case, management risks receiving a fine from the Labor Inspectorate and judicial authorities, and in some cases even facing criminal liability.
Factors influencing labor intensity
The Labor Code allows you to understand what working conditions are like. In 2013, a separate federal law No. 426 was adopted. Legal acts approved acceptable standards, set out criteria for assessing working conditions, provided for the procedure for working in difficult and dangerous conditions and compensation for personnel for risks.
It is incorrect to assume that working conditions only include the creation of safe workplaces. The concept includes a whole range of requirements.
These include:
Schedule
- work schedules
- maintaining the balance of work and rest
- the correct level of intensity of work performed
- permission to work for employees based on their qualifications
- their certification in terms of special skills, ability to use equipment and knowledge of safety precautions
All these requirements must be observed and controlled by the management of the enterprise (Article 212 of the Labor Code).
Work intensity is one of the most important factors in determining working conditions. The indicator is calculated based on human resource costs per unit of labor time.
Description of the workplace
All working conditions must be specified in the employment contract without fail. The job description will largely depend on the employee’s field of activity.
So a job description for an office employee might look like this:
- The workplace is equipped with an ergonomic desk for the direct performance of job duties. In addition to the computer desktop, there should be a designated place for storing papers and office supplies (if they are necessary for work).
- The workplace should be equipped with an ergonomic chair that promotes free blood circulation in the body.
- Workplace equipment includes a computer or laptop, a set of office supplies, and a trash bin.
Nuances of monitoring
The assessment can be carried out per employee, per production group, or per average of all staff units of the enterprise within the reporting period (working hour, day, week, etc.).
The assessment is comprehensive and includes:
- expenditure of physical strength
- consumption of mental resources
- emotional background
- work environment
- the presence of motivation of a material and other nature
- convenience of work organization, etc.
The assessment procedure must take into account the intensity group to which the employee or the enterprise as a whole belongs.
There are four of them:
Increased physical labor
- Work that does not require physical labor.
- Light work.
- Work of average physical difficulty.
- Work under conditions of increased physical activity.
The first group mainly includes employees who perform sedentary work and engage in intellectual work. Light physical activity is used in the service segment or in production occupations where personnel monitor the operation of mechanized equipment. Factory and plant production, as well as agricultural enterprises, are classified as organizations of medium-sized physical labor. And increased loads are the norm in hazardous and heavy industries, for example, in the extraction of hydrocarbons and metals.
Monitoring criteria
Monitoring of work intensity should be carried out based on factors that directly influence the formation of this indicator:
- level of employment of each employee
- speed of work
- the size and severity of objects that the employee has to use during work
- volume of work performed
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards
For each of the criteria, there are maximum permissible values and standards approved at the state level.
Difficulty of work
In addition, the assessment takes into account:
- level of complexity of the technological process
- convenience of the workplace
- quality of the employee (gender, age, state of health, degree of fatigue, medical limitations, standard of living, social status, etc.)
Based on the number of factors that need to be taken into account, intensity monitoring is a multifactorial and complex process. It requires the development and application of special techniques that are capable of analyzing all the characteristics of the work.
Using the results
Intensity monitoring allows you to adjust your workflow and achieve planned results as efficiently as possible.
Violation of the intensity indicator has an inversely proportional effect on labor productivity:
- Optimal load generates optimal performance.
- By increasing the voltage during work, you can provoke a jump in productivity, but only for a short period of time.
- Long-term increased exploitation of employees will invariably lead to decreased productivity.
Despite the statistics, many managers try to increase productivity precisely by increasing the intensity of workers' work. Coercive measures are still in use, such as orders to work beyond normal limits under the threat of dismissal or refusal to sign an application for another vacation.
Worker wear and tear
It should be borne in mind that even if there is positive motivation in the form of additional bonuses or teamwork in emergency mode for the overall benefit of the enterprise, prolonged excessive workload has a negative effect on staff. Fatigue increases, physical endurance decreases, and illness and nervous exhaustion can be a side effect. As a result, an unfavorable climate is created in the team, employees go on sick leave and cease to achieve not only improved, but also standard results.
Experts recommend increasing productivity through the introduction of innovative technologies and optimization of technological processes. This is much more effective than using human resources in work “for wear and tear”. In addition, the latter option for organizing labor is legally limited and requires the management of the enterprise to pay numerous compensation expenses for employees.
Classification of working conditions
In the Law on Assessment No. 426, the classification of working conditions has a separate article. No. 14.
According to the document, 4 classes of working conditions are identified, depending on the level of harmfulness (hazard):
- Optimal ones, belonging to class 1, are the safest and cannot cause harm to the employee. Work in such conditions is recognized as the most effective, since there is no negative impact on the level of staff performance.
- Acceptable - the second class, in which the presence of harmful factors affecting the physical condition of a person is noted, but it is within the approved standards and is leveled out during the rest period.
- The third class is considered harmful, the impact on employees exceeds the standards, and there is a risk of disease.
This category is divided into subtypes: Injuries at work
- Grade 1 – recovery of the body after exposure requires time exceeding the rest period between work shifts.
- Grade 2 – the exposed employee runs the risk of permanent changes in physical condition that will lead to the development of occupational diseases in an initial (mild) form.
- Grade 3 – the level of exposure is extremely high, capable of causing illness from mild to moderate severity, up to a state of professional unsuitability.
- 4th degree – working in such conditions can lead to severe forms of illness.
- Hazardous conditions of the fourth class affect employees during work and even while partially at work; the likelihood of occupational diseases is especially high, and there is a threat to the lives of personnel.
The assessment method, specially developed and set out in the law, allows you to secure a class.
In addition, the legislation allows changing the class to a safer one if:
- use of certified protective equipment by personnel at work
- after assessment
- subject to expert approval
The opportunity is implemented with the permission of the federal executive bodies of labor protection, sanitary and epidemiological supervision and social and labor relations.
List of occupations classified as hazardous
The list of hazardous working conditions established by the state can be applied not only to individual professions, but also to entire industries. Namely:
ProfessionIndustryHarm received
| Engineer, geologist, surveyor, geophysicist, hydrologist, miner, fastener. | Mining | There is a possibility of being hit by a rubble. Additional factors: poor lighting and increased concentration of dust. |
| Crane operator, steelmaker, blast furnace operator, smelter, caster, heater | Metallurgy | There is a high chance of intoxication of the body. Also considered unfavorable conditions are high temperatures and harmful fumes. |
| Chemist, technologist, biochemist, laboratory assistant. | Chemical production | Constant exposure to toxic substances. The chance of severe burns or intoxication increases. |
| Designer, tester, gunsmith. | Ammunition making | There is a possibility of injury when interacting with firearms or explosives. Additional criteria: increased noise level. |
| Geologist, drilling machine operator, engineer. | Oil production | Systematic exposure to toxic fumes on the body. There is also a chance of getting burns when working with flammable liquids. |
| Flaw detector, electrician, installer, engineer. | Electrical engineering | There is a risk of serious injury when exposed to high voltage. There is a risk of death. |
| Carpenter, fitter, painter, installer, asphalt paver, slinger, foreman, crane operator, engineer. | Construction | The most dangerous class, which includes a number of unfavorable conditions: loud noise, presence of dust and chemicals, height, work with emergency structures. |
| Virologist, pharmacologist. | Healthcare | There is a chance of contracting some viral disease. |
| Layout designer, printing specialist, folder, cutter, technologist. | Printing | Systematic exposure to loud noise on the body. Additionally, there is contact with toxic substances. |
| Engineer, installer, designer, radiochemist, turner, milling machine operator, researcher, electrician. | Atomic industry | Constant contact with radioactive substances of increased danger. |
| Driver, flight attendant, mechanic. | Transport | There is a chance of serious injury, even death, in an accident. Sometimes working in this area involves poor lighting and increased noise levels. |
| Firefighter, Emergencies Ministry employee, diver. | Rescuers | High probability of causing irreparable harm to health. From time to time, negative factors such as elevated temperature, insufficient lighting, and evaporation of toxic substances may be observed. |
| Gas and electric welder | Welding work | Increased eye strain and contact with high voltage. |
As you can see, not all positions related to hazardous industries are hazardous according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, before applying for financial compensation, you should familiarize yourself with the table above.
Certification
Until 2014, labor legislation assigned enterprise managers the responsibility to certify workplaces. With the introduction of the special assessment system, certification activities did not disappear from legal documents, but became an integral part of the new program.
Employees' workplaces are checked according to several criteria, based on which the impact of working environment factors on personnel is assessed: physical, chemical, biological.
Physical impacts include:
Workplace certification
- indoor humidity and temperature levels
- workplace illumination
- noise level and air speed
- presence of radiation and its intensity
Despite the seemingly small degree of influence, physical factors can cause unpleasant sensations in employees. And with prolonged exposure it can create health problems for people.
Chemical factors include impacts from substances with which direct work is carried out (acids, paints and varnishes, alkaline solutions, gases, dust).
The influence of biological factors is relevant for those specialists who work with bacteria, viruses, infectious agents and other active organisms that can cause real harm to health.
Indicators are measured and compared with established standards. Based on the results, working conditions are assigned a class from 1 to 5.
Experts are not required to check every workplace. They can make an assessment based on the results of certification of a sample from similar working conditions.
At the same time, the law exempts from the need to check the workplaces of employees who work from home or remotely.
Assessment of working conditions
The state has established the obligation of the management of each enterprise to assess working conditions. Since 2014, a new procedure for its implementation has been introduced, enshrined in Federal Law 426. The document contains a detailed description of the procedure, the timing of its implementation and further application of the results. In addition to workplace certification, the assessment takes into account the intensity of the labor process, the availability of personnel permits (including medical examinations, safety training, etc.).
If previously management was allowed to carry out the assessment independently, now its implementation is assigned in 426 Federal Laws to individual organizations, which must be independent, accredited and entered into a special register approved by the Government. If a company was allowed to provide this type of service before the law came into force, then it has the right to conduct certification of workplaces without additional confirmation of authority.
Characteristics
The production process is the work of obtaining products from matter or raw materials. All stages of this activity are interconnected. The nature of the process is determined by type:
- Labor force used.
- Means of production.
- Source materials.
Having determined the main means of production, the type of process can be determined. Suppose we know that the main machine is a metallurgical plant. Then it will be clear that there is activity with metal and ore. The labor force will be metallurgists and steelworkers. From this it is possible to determine safety requirements and possible types of occupational diseases of employees.
Special assessment procedure
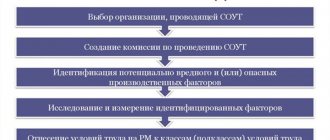
The assessment process is a coordinated work of accredited experts and responsible persons appointed by the management of the audited company from among its employees.
Main stages of the assessment procedure:
Creation of a commission
- Creation of a commission that will be responsible for organizing the work of third-party experts on behalf of the enterprise (the number of members must include an occupational safety specialist).
- Compiling a register of jobs.
- Approval of the appraisal work schedule.
- Selection and involvement of an accredited organization (the procedure is paid and based on contractual relations).
- Carrying out assessment work (determining compliance with standards, identifying harmful factors, etc.).
- Filling out and approving the report form.
- Informing employees, the Labor Inspectorate and the Social Insurance Fund about the results.
- Elimination of identified violations, taking into account the results of the commission’s work in the further labor process.
The legislation clearly delineates the powers of the parties and their responsibilities for the process of verification and registration of results in Federal Law No. 426.
Assessment deadlines
If workplaces at an enterprise were certified before the law was issued, the results remain valid for five years.
If, as a result of certification, a hazard class from 3 to 5 is assigned, then inspection of such workplaces by law must be carried out every five years.
The manager is required to conduct an extraordinary inspection at the following workplaces:
Need for assessment
- before commissioning, if they were organized from scratch (primary)
- if Rostrud inspectors have an order for unscheduled certification
- when changes are made to the technological process or fundamentally new equipment is supplied, which may change the indicators of the previous certification in terms of harmful effects or possible danger
- if the company has changed materials or raw materials
- when there was a high-quality replacement of special equipment designed to protect personnel from harmful influences
- if there are facts at the enterprise that are a consequence of the influence of working conditions on employees (accidents, occupational diseases)
- if the trade union insists on additional verification and its decision is justified
For unscheduled certifications, a period of six months to a year is established from the moment the basis for the inspection arises.
In addition to regular special assessments, working conditions can be checked by government agencies, according to Art. 216.1 TK.
The new procedure for assessing working conditions allows us to avoid formalism and the provision of fictitious reports by management. This has a beneficial effect on the diagnosis of the organization of work of citizens of the country at all enterprises, provides additional protection of their rights and enables people to receive the required compensation if their working conditions are not optimal.
Second commentary to Article 163 of the Labor Code
1. The contents of this article have been retained in the previous edition. Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation includes among the rights of the employer the right to demand that employees perform their labor duties and to bring them to disciplinary liability for violating labor discipline. The employer can exercise these rights only if they are provided with normal working conditions that allow the employee to fulfill labor standards within the established working hours.
2. Failure by the employer to ensure the good condition of premises, structures, machines, technological equipment and equipment, untimely provision of technical and other documentation necessary for work, as well as inadequate quality of materials, tools, other means and items necessary to perform the work, or their untimely provision the employee may become the reason for the employee’s failure to comply with labor standards and even downtime. In these cases, he has the right to the appropriate guarantees provided for in Art. 155 - 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (see comments to these articles).
3. The employer is also obliged to provide working conditions that meet labor protection and safety requirements. Articles 219, 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establish the right of an employee to refuse to perform work in the event of a danger to his life and health due to violation of labor protection requirements, failure to provide him with personal and collective protective equipment in accordance with labor protection requirements at the expense of the employer. Failure by the employer to comply with these requirements may also be the reason for the employee’s failure to comply with labor standards, entailing corresponding guarantees for him (see comments to Articles 155 - 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Employee compensation
The Labor Code provides material compensation only for those employees whose working conditions are dangerous or harmful to health (Article 219). In this case, compensation options must be reflected in contracts - labor and collective, as well as in local regulations of the company.
Compensation from the employer according to the law is:
- providing an employee with up to 36 hours of work weekly (Article 92 of the Labor Code)
- annual paid leave for a period of at least a week, in addition to the main one (Article 117 of the Labor Code)
- free medical nutrition, milk (Article 222 of the Labor Code)
- wages increased by 4% of the salary rate (Article 147 of the Labor Code)
In addition, employees have the right to preferential calculation of pensions, payment for recreation and treatment.
An employee can refuse some benefits by asking to replace them with material compensation. This category includes days of additional vacation, expenses for treatment and free food.
Mandatory compensation established by law can be supplemented at the request of the company's management. This is the practice of increasing wages for employees working in intensive work conditions. Municipal authorities can introduce their own benefits and coefficients that increase payment for work for personnel in hazardous and heavy industries in the reporting region.
A competent approach to assessing working conditions and the correct application of its results allow employers to effectively manage staff, avoid violation of their rights, and form a loyal attitude of employees towards the enterprise. Such organization of work will help maintain a decent level of labor productivity.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Another comment on Art. 163 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the employer’s obligation to ensure normal working conditions to meet production standards. Since production standards are a type of labor standards, the obligation to fulfill which is assigned to all workers, the law’s requirement for the employer to ensure normal working conditions should be extended to all types of labor standards. This means that the employer’s failure to fulfill this obligation, which led to the employee’s failure to comply with any labor standards, gives the employee the right to payment in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in an amount not lower than the average salary.