What is an advance under labor law?
The concept of an advance is not legally established. But in explanatory letters from representatives of regulatory authorities (in particular, in the letter of the Ministry of Labor of 2021 No. 14-1/B-725 or the letter of Rostrud of 2006 No. 1557-6), an advance is understood to be salary for the first half of the month.
Based on this definition, an advance as part of the salary (according to explanations of the Ministry of Labor of 2021 No. 11-4 / OOG-718) should include:
- A certain portion of the salary for hours worked.
- Allowances for harmful and dangerous working conditions , work in regions with difficult climates.
- Compensation for night work.
- Additional payments for replacement and combination.
- Similar compensation and incentive payments , except for those that are determined at the end of the month and which cannot be assessed at the time of issuance of the advance (for example, a bonus for fulfilling a monthly sales plan).
According to the requirements of the Labor Code, wages must be paid to the employee at least twice a month. This condition is specified in Part 6 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code. It follows from this that the employee must receive his salary at least twice. More frequent salary payments are allowed, but less frequent ones are prohibited by law.
In practice, employers divide wages into two parts: advance payment and final payment. Both of these payments are mandatory and cannot be ignored by the employer.
If the employer willfully refuses to pay the advance, he may be fined for violating labor laws under Part 6 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences. Liability under this article is 30,000-500,000 rubles. for legal entities and 1000-5000 rubles. for a company manager or entrepreneur.
In this case, the employer will bear responsibility even if the initiative to refuse the advance came from the employee, and he wrote a written application to transfer his salary once a month.
Normative base
Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 08/05/2013 N 14-4-1702
Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 08/10/2017 N 14-1/B-725
Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 05, 2004 N 1 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording labor and its payment”
Letter of Rostrud dated March 18, 2010 N 739-6-1
Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”
Almost always, in vacancies, instead of the salary that the employee will actually receive, the salary is indicated. And many people don’t even realize that salary and wages are not the same thing. And in order not to delve into the rules of how to calculate salary based on salary, the calculator on our website will help.
What percentage of the salary is the advance?
The legislation does not contain an answer to the question of what percentage of the salary is an advance. The employer is obliged to specify the amount of the advance payment in local regulations. He is not obliged to calculate it as a percentage of wages, but can use a fixed amount of the advance or take into account the actual time worked.
To simplify the procedure for calculating an advance to an employee, an advance is often set at 50% of the salary.
When determining the amount of the advance, the employer should take into account the provisions of the Resolution of the USSR Council of Ministers of 1957 No. 556, which has not lost its legal force today. It says that the amount of the advance is determined by the agreement of the administration with the trade union in the process of concluding a collective agreement, but its minimum amount cannot be lower than the tariff rate for the time worked.
The Ministry of Labor has repeatedly indicated in its explanatory letters that when determining the amount of the advance, the employer must take into account the time actually worked by the employee. A similar position is reflected in the Letter of the Ministry of Labor of 2021 No. 14-1/10/B-660 and of 2017 No. 14-1/B-725.
Thus, although this is not expressly prohibited by law, when determining the size of the advance, it should not be set as a percentage of earnings. This may cause claims from regulatory authorities, since the advance payment may be less than the employee earned during these days.
But if the amount of the advance, calculated as a percentage of the salary, turned out to be no less than the amount of wages calculated on the basis of the time actually worked by the employee in the first half of the month, then no claims will arise against the employer.
When determining the advance as a percentage, you need to take such a value that the advance received is as close as possible to what the employee would have received for the period actually worked.
The employer should not set an unreasonably low advance in a fixed amount. For example, in the amount of 5000 rubles. with a salary of 25,000 rubles. It is also unacceptable to use vague formulations such as “the amount of the advance is no more than 50% of the salary.” Local regulations must establish a clear algorithm for determining the amount of the advance.
Results
Newcomers must receive their first salary payment no later than 2 weeks after starting work. All subsequent payments are made within the time limits set by the company for issuing wages (every half month, taking into account the actual days worked).
In order to comply with the salary requirements of the law for newcomers, it is necessary in the local act of the company to provide for special deadlines for the payment of the first salary. Otherwise, the employer may be subject to disciplinary, material, administrative or criminal liability.
Sources:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to calculate
Let us give examples of calculating an advance payment using different methods of calculating it. The simplest method of calculation involves multiplying the salary by the advance interest rate.
For example, the advance payment was set at 50% of the employee's salary. The latter is 30,000 rubles. Accordingly, the advance payment will be 15,000 rubles.
When the actual time worked is used to determine the advance, then to calculate it you need to divide the salary for the full month by the number of working days in the month and multiply it by the number of days actually worked in the first half of the month. In this case, the day of payment of the advance is not included in the calculations.
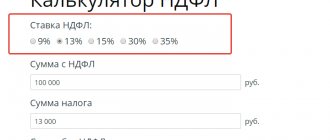
For example, an employee’s salary was set at 50,000 rubles. During the first half, he worked 10 days, and in total there were 22 working days in the month. The advance payment will be (50,000 / 22 * 10) = 22,727.27 rubles. The final payment is 20,772.73 rubles. (minus personal income tax 13%).
Another calculation option is also allowed, when the salary amount is initially reduced by personal income tax and upon receipt of an advance, the employee receives the amount minus personal income tax. In this case, the tax itself is withheld, but is not transferred by the employer until the final payment is made.
Taking into account the initial data in the above example, the advance calculation will look like this:
(50000 – 6500) / 22 * 10 = 19772.73 rubles.
Online calculator
You can simplify your advance payment calculations by using an online calculator.
To determine the amount of the advance, you need to indicate the number of days the employee worked in the first half of the month, as well as the amount of his salary for the full month. As a result, it will be possible to see exactly how much the employee will receive in advance, taking into account the actual period worked.
Taxation
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 223, art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated February 5, 2021 No. 14-1 / OOG-549, the first part of the salary (advance payment) is not subject to:
taxation;- deduction of insurance premiums.
Previously, employers hedged their bets and multiplied the advance by a factor of 0.87, but now this cannot be done.
All contributions are deducted from the last payment when the employer takes into account:
- actually worked time for the whole month;
- not only compensatory additional payments for the second two weeks, but also incentive bonuses for the entire month (bonuses, northern bonuses, etc.).
Advance payment terms
The employer must independently determine the timing of payment of advance payments to employees. This should be a specific date of the month that the employer must strictly adhere to. If the advance payment date falls on a weekend or holiday, the payment is transferred in advance. In other cases, it is not advisable to pay the advance ahead of schedule, as this may cause claims from inspectors.
For late payment of the advance, the employer faces financial and administrative liability. If the employer is late in payment, then along with the advance payment he must pay the employee compensation for the delay. It is determined in size in accordance with the provisions of local regulations adopted at the enterprise or according to the norms of the Labor Code.
Labor legislation states that the amount of such compensation is at least 1/150 of the Central Bank key rate for each day of delay. Compensation is paid even if the employer was not at fault for the delay (for example, there was a technical failure).
There are no statutory deadlines for advance payment. But taking into account the rules fixed here, wages must be paid for the period worked by the employee no later than the 15th day of the month that follows the payroll month. The time interval between advance payment and final payment is maximum 15 days.
Taking into account the above rules, the advance payment is due from the 16th to the last day of the month (it is undesirable to pay it on the last day of the month), and the final payment is due from the 1st to the 15th.
The employer is not allowed to use vague language when determining the terms of the advance: for example, the advance is payable “before the 20th of the month” or “from the 16th to the 20th”. This must be a specific date, otherwise legal requirements are violated.
Calculator for calculating compensation for delayed wages (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
If you have not been paid your wages, you can go to court to protect your rights. Along with the recovery of wages, you can demand payment of interest for delayed wages in accordance with Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as moral damage. Moreover, in order to collect interest, it is necessary to provide the court with a calculation of this interest.
Instructions for filing a claim for unpaid wages
If you are not paid your wages, and you work or worked officially, then in order to get your honestly earned money, you have to go to court. Let us immediately note that the statute of limitations for this category of cases is only 3 months from the day you learned or should have learned of a violation of your right. (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
What does it mean to miss the statute of limitations?
The essence of this concept is as follows: if you file a claim in court after missing this deadline and the defendant asks to apply the consequences of missing the statute of limitations, then the court will reject the claim (although in fact you were not paid wages).
Of course, you can hope that the defendant (your employer) will not come to court and write a review, but this is a huge risk and no lawyer will give you a guarantee of a positive court decision in this situation.
That is why it is necessary to file a claim, preferably without missing the statute of limitations.
Countdown of the limitation period
Let us explain a little that the date from which this period is calculated is determined by law as follows: when he learned or should have learned about the violation of his right .
That is, if you receive wages on the 5th and 20th of each month and on the 5th you were not given your next wage, this will be the beginning of the limitation period (you learned that you were not paid wages).
It should be noted that to protect your rights as an employee, you can contact the labor inspectorate and even the prosecutor's office , but unlike these structures, only a court decision can be enforced.
Therefore, if the labor inspectorate issues an order to the employer, which indicates the need to pay wages to such and such employees, then administrative liability will arise for the employer for failure to comply with this order, but the employee in this case remains unprotected.
Moreover, contacting the labor inspectorate does not extend the statute of limitations .
For example, you were not paid your wages on June 5 - you contacted the labor inspectorate.
After 2 months, we learned that an order had been issued against your employer indicating the need to pay you a salary, but the employer did not pay and after another 1 month did not pay.
As a result, when a person plans to go to court (since the employer does not pay wages), the statute of limitations has already expired.
Which court should I go to?
Currently, labor disputes fall under the jurisdiction of district courts . Moreover, the claim is filed at the location of the defendant (that is, the employer).
There is one exception to this rule : an application for a court order is submitted to a magistrate (also at the location of the defendant), if wages have already been accrued, that is, you have a pay slip indicating the amount of your salary for a given month, but you have not received it got.
Documents for filing a claim for unpaid wages
For this category of cases, the state fee is not paid, so the following documents are needed to file a claim:
- Statement of claim;
- Employment contract;
- Employment history;
- Calculation of collected wages;
- Interest calculation;
- Other documents (for example, confirming legal services, pay slips, etc.).
Let us add that the number of claims must correspond to the number of persons participating in the case.
For example, if we have 1 plaintiff and 1 defendant, then we make 3 copies: 1 for the court, the second for the defendant and, if desired, 1 for ourselves.
If the defendant has documents that you attach to the claim, then you can not make copies of these documents for the defendant, but simply write that the defendant has these documents.
The list of documents that are attached to the claim is established by Art. 132 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation
Filing a claim for unpaid wages in court
When the statement of claim is ready and all documents have been collected, you can go to court. The statement of claim can be submitted directly to the court (in this case, you will be given a mark indicating acceptance of the claim on your copy of the claim) or can be sent by registered mail with a list of attachments. After this, you will only have to wait for the court to notify you of the date of the court hearing.
Source: https://dogovor-urist.ru/calculator/236tk_zarplata/