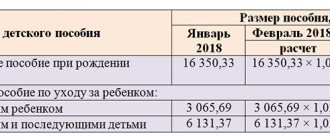
Insurance premiums are mandatory payments for individuals: employees and individual entrepreneurs. Contributions for employees are paid by employers, and individual entrepreneurs pay for themselves.
The global economic crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic has significantly worsened the situation of small businesses. And as one of the measures to support individual entrepreneurs and small enterprises, the Government decided to change the rates of insurance premiums for 2021.
In this publication you will find the latest news on the topic of insurance for employees and individual entrepreneurs.
Free tax consultation
Deduction rules
The updated Tax Code, namely Chapter 34 introduced in 2021, regulates the relationship between Russian employers and funds: the table of contributions to funds in 2021 will show their values and the BCC codes by which transfers are made.
The current fiscal legislation establishes that an employer, be it an organization or an individual entrepreneur, who uses hired labor in its activities, is obliged to calculate and pay insurance contributions to the state budget. Payments and taxes from wages in 2021, depending on their purpose, are sent to the corresponding extra-budgetary funds. The funds are then used as financing:
- pensions and pension savings of Russian citizens;
- free medical care;
- benefits and payments for temporary disability of workers, including maternity.
Let us note that employers must transfer contributions from accidents and occupational diseases to the Social Insurance Fund. The specifics of the application of this type of insurance coverage are enshrined in Law No. 255-FZ.
In addition to insurance coverage, employers calculate income tax on wages in 2021 to the Federal Tax Service. Personal income tax, or personal income tax, has a flat rate of 13%.
Where is it better to transfer money - to the Pension Fund or Non-State Pension Fund?
Future pensioners have a choice of where to send the funded part of their pension : to a state or non-state pension fund. Each has certain characteristics. However, the latter, against the backdrop of a difficult economic situation, are beginning to win in the eyes of the public.
The funded part of the pension in the Pension Fund
Before 2014, each person could keep some percentage of their retirement money in investment accounts as a savings portion. But then this part of the future pension was frozen. Now the former funded part goes into the insurance pension. The government uses this money to pay pensions to current retirees instead of allowing the contributions to sit in the owner's account.
Currently, the moratorium on the funded part has been extended until 2023. And it is unknown whether it will be unfrozen due to the difficult economic situation of the country. There are also plans to reform the funded pension, so it’s definitely not worth waiting for unfreezing.
Therefore, you should not expect that in the near future at least some income will be added to the “savings” part, as was originally planned.
Advantages of NPFs over Pension Funds
Non-state pension funds are becoming increasingly popular. They allow you to receive interest on the contribution, which can cover inflation and even provide a certain income. But this is not the only reason why citizens choose NPFs instead of the state pension fund. The former have a number of advantages:
- Transfer of savings by inheritance. You can withdraw money without unnecessary problems if its owner did not live to see retirement or did not receive all the accumulated money.
- Tracking the status of your retirement account via the Internet . All serious non-state pension funds have personal accounts in which the owner can see what is happening with his money: where it is invested, how it is spinning, what percentage of income, and so on.
- Predictability of interest growth . Every six months or a year, any self-respecting non-state pension fund publishes information on average profitability. This is exactly why you should choose a future fund for your pension.
- Guarantee of payments by the state. Even if the NPF closes, the state will be obliged to pay out the accumulated money for it. All funds from the account will simply be transferred to the Pension Fund.
At the same time, it is worth remembering that no non-state pension fund can guarantee profitability. Because it engages in investments that can be very risky and could result in you losing money. The Pension Fund of Russia is more stable and predictable in this regard. The amount an employee pays into it is what he will then receive as a pension. Therefore, it’s up to you to choose where you are willing to store your money until old age.
Objects of taxation
Despite the different concepts, many citizens believe that the payroll tax in 2021 is not only personal income tax, but also all insurance contributions. But officials quite strictly differentiated these terms.
Note that the key difference between personal income tax and insurance coverage is that income tax is withheld directly from the salary amount. But the employer pays insurance premiums to the budget from his own funds, that is, he accrues them “in excess” of the wages.
The object of taxation in both cases is the amount of remuneration for labor. For example, the payroll tax applies not only to official salary, but also to all types of compensation and incentive payments. For example, bonuses, extra pay for night work, payment for overtime hours and holidays.
General information
Before you figure out which funds deductions from salary go to, it’s worth finding out what payments in favor of an employee are from a legal point of view.
Wages are the remuneration that an employer provides to an employee for carrying out work activities.
It can be issued in kind. However, in most cases, the organization provides the employee with a cash payment.
Salary may include:
- salary;
- incentive payments;
- other transfers specified in current legislation.
The employer is obliged to comply with the deadline for providing wages.
Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that payments must be made at least 2 times a month.
The monthly salary is divided into two parts. Their size is fixed by internal acts of the organization or an employment contract.
In a number of situations, the employer may provide cash payments more often than the period established by law. However, if the company performs the action less than once a month, this will be considered a violation.
If the day of payment falls on a weekend or holiday, payment is provided the day before. Before going on another paid vacation, the employee also receives a cash payment.
The employer must make the transfer 3 days before the employee starts his vacation.
Rates and deductions
Currently, employers withhold personal income tax on all income of their employees at a flat rate. We noted the percentage of the 2021 payroll tax: personal income tax is 13%. Officials have provided a number of tax deductions for working professionals.
Thus, an employee has the right to claim a child deduction - the most common in Russia. Legislators also provided for professional, property, investment and social tax benefits. Read more in the article “How a citizen can get a tax deduction.”
Calculation procedure
Not all contributions are collected from the employee. Part of this is paid by the employer.
According to the rules, only 13% can be withheld from an employee's salary, levied as income tax. The remaining amount is taken from the wage fund. The employer must pledge it in advance.
Let's say an employee receives 10,000 rubles. In addition to this amount, the employer is required to pay a minimum of RUB 3,200. to funds and for the benefit of the state.
This amount consists of the following deductions:
- 2200 rub. to the Pension Fund;
- 310 rub. in the FSS;
- 510 rub. to the MHIF.
For this reason, the employer will have to invest not 10,000 rubles in the payroll, but 13,200 rubles. For the company, this figure will be the employee’s income.
Based on the above, in 2021 the employer is obliged to contribute at least an additional 30% to the payroll to make contributions to non-budgetary government organizations.
Read whether the thirteenth salary is paid upon transfer. What are the deadlines for issuing advance payments and salaries? Information here.
How to correctly write a power of attorney to receive a salary? Details in this article.
Some countries have a different payment method. The company provides the employee with the entire amount earned by him for a specified period, as well as a receipt with payments recorded in it that are to be made to various funds. The citizen pays taxes and current contributions on his own.
However, Russia took a different path. The amount of actual deductions is hidden. The employee only knows that he will have to pay 13% of the actual accrued wages as income tax.
Tax reduction
To reduce tax, the Tax Code provides for special deductions:
- standard (applied when there are children of a certain age);
- social (applies to the provision of documents for treatment or education);
- property (applied when purchasing housing).
The above deductions are issued to the Federal Tax Service or the employer. A deduction for children is provided upon application from the employer accompanied by the necessary documents.
The employer submits reports 2-NDFL (annually) and 6-NDFL (quarterly) to the tax office. Despite the fact that from 2021 the 2-NFDL is canceled, for 2021 it will have to be taken by March 1. The rules for filling out the form are described in Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2018 N ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
Read about the procedure for filling out form 6-NDFL in Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 14, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
Personal income tax (NDFL)
This type of accrual reduces the employee's salary. Today, the personal income tax rate for a citizen of the Russian Federation is 13% , for a non-resident (an employee who has citizenship of another country) – 30% . If an employee who is a resident is credited with 50 thousand rubles, then he will receive 43,500 rubles (50,000 – 6,500 = 43,500).
The list of conditions for exemption from paying tax or reducing the rate is established by Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (in particular, deductions are reduced if there are minor children dependent on the parents, but the law is applicable only to one of the spouses).
How are taxes calculated?
The wage fund is the basis for calculating accruals to extra-budgetary funds .
According to current legislation, a business entity is obliged to accrue and pay within the time limits specified by law the following contributions:
- to the Pension Insurance Fund (PFR);
- to the FSS (Social Insurance Fund);
- to the MHIF (Health Insurance Fund).
In turn, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are divided into two groups: contributions in case of temporary disability, and contributions related to injuries and occupational diseases. All listed contributions are charged to the accrued payroll of the enterprise (and fund) and are included in the cost of products (services).
Today the tariff in the Pension Fund is 22% , in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 5.1% , in the Social Insurance Fund - 2.9% . Social contributions for injuries are an indicator established for each enterprise individually, taking into account the type of activity.
The legislation provides for regulation of the amount of payments to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund. If the salary is more than 711 thousand rubles, then the amount exceeding this figure will be taxed at a rate of 10% . The Social Insurance Fund provides for zero contributions in case of excess of wages accrued in the amount of 670 thousand rubles.
Contributions are paid monthly , simultaneously with the payment of wages. The law provides for the payment of remuneration to employees twice a month , on days established by the enterprise (advance and settlement).
Reports to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are submitted quarterly , on an accrual basis. If payment deadlines or reporting deadlines are violated, administrative and financial penalties are imposed on the enterprise.
Let's look at an example :
The wage fund of Panorama LLC amounted to 215 thousand rubles in April 2015. Salary costs will be:
- Pension Fund – 47,300 rubles;
- in the Social Insurance Fund – 6235 rubles;
- in the Social Insurance Fund for injuries – 1290 rubles. (for the enterprise the deduction rate is set at 0.6%);
- in the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund – 10965 rubles.
All mandatory deductions are calculated by economists when forming the wage fund, and are included in the financial plan of the enterprise.
Basic, reduced, additional tariffs
Tariffs for insurance premiums for 2019-2020 are presented for clarity in the form of a table/diagram using information from the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for each type of contribution according to the following items:
- 425 (basic tariffs for the current year);
- 427 (reduced insurance premium rates);
- 428, 429 (additional tariffs).
Reduced insurance premium rates
| Policyholders | Rates |
| Organizations (IP) on the simplified tax system, the main type of activity of which is specified in subparagraph. 5 p. 1 art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation Pharmacy organizations (individual entrepreneurs with a license for pharmaceutical activities) on UTII Individual entrepreneurs using the patent tax system | During 2021 - 2021:
|
| Non-profit organizations (except for state (municipal) institutions) on the simplified tax system, carrying out activities in the field of social services for citizens, scientific research and development, education, healthcare, culture and art, mass sports (with the exception of professional) Charitable organizations on the simplified tax system | During 2021 - 2024:
|
| Business entities (business partnerships) that apply or implement the results of intellectual activity, the exclusive rights to which belong to their founders (participants) - budgetary (autonomous) institutions Residents of technology-innovation, industrial-production and tourist-recreational special economic zones | On OPS:
On compulsory medical insurance:
On OSS from VNiM:
On OSS from VNiM from payments to foreign citizens (stateless persons) temporarily staying in the Russian Federation (except for highly qualified specialists) - 1.8% |
| Russian organizations operating in the field of information technology | During 2021 - 2023: on OPS - 8.0%, for compulsory medical insurance - 4.0%, on OSS from VNiM - 2.0%, On OSS from VNiM from payments to foreign citizens (stateless persons) temporarily staying in the Russian Federation (except for highly qualified specialists) - 1.8% |
| Organizations that have received the status of a participant in the Skolkovo project | For 10 years, starting from the 1st day of the month following the month in which the project participant status was received:
The benefit can be applied for less than 10 years |
| Organizations (IEs) that received the status of participant in a free economic zone (FEZ) in the territories of the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol no later than three years from the date of its creation, that is, no later than December 31, 2021. | Within 10 years from the date of receipt of the status of a FEZ participant:
|
| Residents of the territory of rapid socio-economic development (PSED), who received the specified status no later than three years from the date of its creation. Residents of PSEDA in the Far Eastern Federal District - no later than December 31, 2025 (provided that the volume of investments is at least 500 thousand rubles) | From 08/03/2018, reduced tariffs apply only to individuals employed in new jobs. For residents of TASED located in the Far Eastern Federal District, this rule applies if legal relations arose from June 26, 2018. Reduced contribution rates apply for 10 years of residence:
|
| Organizations (IP) that received resident status of the free port of Vladivostok no later than December 31, 2025 (provided that the investment volume is at least 5 million rubles) | From June 26, 2018, reduced tariffs apply only to individuals employed in new jobs. Reduced contribution rates apply for 10 years from the date of obtaining resident status:
|
| Organizations included in the unified register of residents of the Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in the Kaliningrad region from 01/01/2018 to 12/31/2022 (inclusive) | Within seven years from the date of obtaining resident status (deadline - December 31, 2025):
|
Separate additional tariffs are provided for in Art. 429 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for social security of flight crew members of civil aviation aircraft and certain categories of employees of coal industry companies.
The completeness, correctness and timeliness of payment of the above insurance premiums are supervised by tax officials.
Groups of insurance rates
The insurance premium rate is the rate established by law by which the insurer’s obligations are calculated. Each type of contribution has its own tariff.
Conventionally, insurance premium rates can be divided into 4 groups:
- percentage - set as a percentage of the insurance premium base (for example: 22%, 5.1%, etc.);
- total - indicated in fixed amounts without reference to the base of insurance premiums (for example, fixed contributions of individual entrepreneurs for themselves);
- combined - are a combination of a percentage rate and a sum rate (for example, the rate of contributions for individual entrepreneurs for themselves with an income of more than 300,000 rubles).
Next, we will take a closer look at the insurance premium rates for 2019-2020.
Combined tariff formula for individual entrepreneurs
Tariffs for compulsory pension insurance (OPI) in 2019-2020:
- established in the form of a fixed payment (if the individual entrepreneur’s income does not exceed 300,000 rubles);
- are calculated in a combined way for income over 300,000 rubles. (fixed payment + percentage of excess income over the amount of 300,000 rubles).
In 2021, insurance premiums for OPS (SVOPS) are calculated as follows (subclause 1, clause 1, article 430 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
If D ≤ 300,000 rub. → SVOPS = 29,354 rub.
If D > 300,000 rub. → SVOPS = 29,354 rub. + 1% × [D – 300,000 rub.]
At the same time, SVOPS for the billing period cannot exceed 8 times the fixed amount of insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance.
In other words, if an individual entrepreneur’s income for 2021 did not exceed 300,000 rubles, he does not need any calculations. He will take the amount of insurance premiums for compulsory insurance from the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: 29,354 rubles. If the limit is 300,000 rubles. exceeded, it is impossible to do without calculation. For an example of such a calculation, see below.