Issues discussed in the material
:
- What is the authorized capital of a company?
- Why does a company need a large authorized capital?
- What risks are associated with having a large authorized capital?
- How to properly increase the authorized capital of an LLC
One of the mandatory actions of companies starting their work as a limited liability company is the formation of an authorized capital, because it plays the role of a guarantee for future partners. In this case, you need to decide what is better: specify a minimum amount or form a large authorized capital. Next, we will talk about the pros and cons of a large authorized capital.
What is authorized capital?
In the Russian Federation, engaging in any type of business without registration with a government agency is prohibited.
There is a fine for any type of commercial activity that is not registered. An LLC is a form of establishing a legal entity. The procedure for this establishment and all legal issues affecting the activities of a limited liability company are regulated by Federal Law No. 14.
The state also provided that up to 50 founders can organize a limited liability company. The format of the organization obliges these people to issue and approve the charter - a legal document that carefully reflects all information about future activities, as well as the structure of this organization.
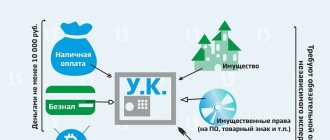
In addition, the founders need to create a special fund, which in the future will be called the authorized capital (displayed in documents as “UK”).
So: authorized capital is cash, as well as material assets expressed in monetary terms, created for the authorized capital of a company engaged in commercial activities.
Important! UC is a conditional value expressed in rubles.
But, it must be said that the rule for creating a management company is not only the direct responsibility of the LLC. In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, other commercial and non-profit organizations must also have authorized capital:
- partnerships of any kind, type and form, they are required to have share capital;
- cooperative organizations and companies: create mutual funds;
- unitary organizations (exclusively state and municipal bodies): form, in turn, the authorized capital.
Practice of resolving disputes related to non-payment of authorized capital
Failure to fulfill the obligation to pay the authorized capital in full is a rarity and the only consequence of this oversight is the forced liquidation of the legal entity. Basically, judicial practice is faced not with non-payment as such, but with the recognition as invalid or void of contracts and other documents through which payment was made.
Thus, when creating a cinema, real estate was transferred in payment for the authorized capital, “external decency” (appraisal and registration) were observed, while the legislation on privatization and a number of other legislative acts were significantly violated, the transaction was declared invalid, and the consequences of recognizing it as such were applied to it and liquidated the company (Resolution of the Sixth AAS N 06AP-2078/2017).
In practice, cases of LLC liquidation due to non-payment of authorized capital are rare.
An independent demand for liquidation of a company is not always subject to satisfaction due to the fact that it is necessary to prove the fact of a significant irreparable violation committed during the creation of the company. To confirm the presence of this fact, most often it is necessary to put forward an independent demand, for example, about the invalidity of a transaction, about the restoration of a violated right, about invalidating the registration of a company, and others. Before receiving a decision confirming the presence of a significant violation, the courts are inclined to refuse the forced liquidation of the company (Resolution of the Seventh AAS No. 07AP-10580/2015).
Why do you need authorized capital?
The authorized capital is a kind of protective cap for the company, a kind of guarantee. If an organization goes bankrupt, the first money received in the bankruptcy of a legal entity will be paid to investors and creditors.
After which the company’s property is sold, and if these financial resources are not enough, then the formed management company of this organization will be taken away.
In other words, it is necessary:
- to calculate the value of the created limited liability company;
- the conviction of partners, counterparties and creditors that the company is a solvent market participant;
- safety option;
- understanding the distribution of the company's future profits.
Functions and significance of the organization's authorized capital
- Distribution.
The Criminal Code reflects which individual or legal entity owns the property and assets of the LLC and to what extent.
Example: Trust LLC is created, where the authorized capital is 100,000 rubles. There are two participants in this organization, one individual owns a share with a nominal value of 70,000 rubles, and the second one owns a share of 30,000 rubles. The distribution functionality will be that one participant owning a larger share will own 70% of the votes in the company, and his partner will own 30%.
Owning unequal shares will indicate unequal rights in a given organization. However, some aspects of ownership of rights can be regulated by the company’s charter or collective agreement.
- Warranty.
The legislation of the Russian Federation determines the company's capital as the minimum amount of its property. Then, in the event of bankruptcy, the organization will be able to answer for its obligations to creditors or investors. The company is obliged to maintain “net” assets that are an order of magnitude higher than the amount available in the charter capital.
The size of the so-called net assets is very simple to calculate: you need to subtract the total amount of all debts, loans and liabilities in monetary terms from the book value of all tangible and intangible assets of the organization.
If the value of “net” assets for a long time is less than the authorized capital, then the limited liability company is obliged to do the following: reduce the capital or liquidate the company.
- Reputational.
Example: the first counterparty’s capital is 150,000 rubles, and the other LLC’s is 4 million rubles. It is more reasonable to assume that it is safer to work with a second legal entity, since it has assets that it values. Practice shows that the large size of the management company is not a 100% guarantee of the honesty and reliability of the counterparty.
Management structure
The authorized capital of a limited liability company consists of shares of all participants. Each share has its own value, which is nominal.
The total nominal value is equal to the amount of the authorized capital.
Minimum authorized capital
In the Russian Federation, it is legally established that the authorized capital of an LLC must be at least 10,000 rubles. This is the minimum threshold when creating a company. But the maximum has no legal boundaries.
Important! The larger the size of the company's authorized capital, the more opportunities the company itself has, for example, when obtaining a credit line from a bank or additional licensing of its activities.
Types of authorized capital
The management company is proposed to pay with financial resources, property, securities, shares of any other companies or associations, government bonds. Other types of assets may also be considered, for example: intellectual property rights, copyrights or patent agreements.
Reference. It doesn’t matter how and by what means the charter capital of your company will be formed, as required by current laws, you will still be required to contribute a minimum amount in monetary terms to the authorized capital.
Deadline for payment of authorized capital when creating an LLC
If you want to engage in commercial activities, you will need to top up the authorized capital balance no later than four months after registering the company.
Before depositing funds, a participant in a limited liability company will not be able to vote, unless otherwise stated in the organization’s charter.
Important! Before the contribution, the founder, according to current laws, bears full subsidiary liability for all obligations of the company, that is, funds can be recovered from him for these obligations.
There may also be other consequences associated with late payment of funds - this is the transfer of the unpaid share to a limited liability company.
The founder of the company cannot fail to pay the authorized capital.
Contribution of authorized capital
The legislation suggests that the contribution can be implemented in several ways. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Depositing the capital into the current account by non-cash method.
Funds can be deposited into the company's bank account. To do this, in the payment purpose field, it is indicated that funds are being contributed to the share of the management company, in accordance with the general decision on the establishment of such and such a participant, in the amount necessary for this participation.
- Depositing the capital through a bank cash desk.
In this case, the general director of the company creates a cash receipt order. The purpose of this order indicates the following: which founder and in what amount paid for the share in the management company. Next, the participant pays for this order, the money appears in the company’s current account.
- Payment for the management company with property.
The founders may provide in the company's charter and agreement for the possibility of contributing funds to the management company in non-monetary means, that is, property.
If this is stated in the conditions, the founders can vote to approve the monetary value of the property contributed to the authorized capital instead of cash, under the guise of a contribution. To correctly calculate the value of deposits over 20,000, an independent expert is invited to evaluate the value of the property. Afterwards, according to the transfer and acceptance certificate, the property is entered on the company’s balance sheet.
Important! It is necessary to keep all documents about each payment to resolve possible conflicts. There is no requirement to notify the tax authorities of the payment.
How to calculate and account for a share at its actual value
Calculation of actual value (VA) is done using the formula:
DS = NS / UK * CHA , where:
- NS – the value of the share at par, the initial contribution of the participant. It is prescribed in the Charter and fixed in value terms.
- UK – mouth. capital.
- NA – net assets.
Net assets (NA) are determined:
NA = IIII + DBP - ZUK , where:
- IIII – “total” of the 3rd section in the balance sheet.
- DBP – deferred income.
- ZUK - the amount of debt in the authorized capital of the organization's members.
Accounts:
- D81 K75 - the actual value of the departing participant’s share is recorded.
- D75 K68 - income tax is withheld from the value of the share of the departing participant (if an individual).
- D75 K51 - payment.
Payment can be made not only in one cost option, but also in property, no later than 3 months from the date of acceptance of the application. The procedure, according to the Charter, may be different, but the maximum payment period should not exceed one year.
Important
- A participant in an LLC has the opportunity to leave it of his own free will, but exit from the LLC also occurs for other legal reasons.
- The members of the LLC are the first to buy out its share.
- The actual value of a share can be expressed in monetary form and act as property.
- If the former participant is not satisfied with the calculation of the actual share value, he can appeal to the judicial authorities.
- Calculation of the actual value must be done taking into account the market prices of the assets.
- The issue of determining the last participant in the reporting period before leaving has not been fully regulated. It is recommended to use data from the previous year.
- If an organization takes into account interim reporting data (quarter, month), it is recommended to specify this point in the accounting policy.
- The actual value of the share is determined by the share of the authorized capital multiplied by the net assets of the company.
Shares of participants in the authorized capital of the company
There are several important nuances in the share distribution of an organization’s capital that should be well understood.
- Real and nominal price of shares in the authorized capital.
Shares contributed to the authorized capital are always calculated at a nominal price, regardless of their actual value.
Example: the authorized capital of Romashka LLC is 100,000 rubles. The sole founder of this company decided to sell 20% of his enterprise for 5 million rubles. The buyer's actual expenses will amount to 5 million rubles, but purely legally, he receives a nominal share of 20% of the 100,000 rubles of the authorized capital.
Important! For the real (actual) value of a share, the total value of assets, which are proportionally equal to this share, is taken into account.
- Alienation of shares.
The transfer of one share or part thereof to another participant is called alienation. Typically, such transfers of shares occur during any transactions or on the basis of succession or inheritance.
- Sale of shares in the management company.
Here all the subtleties are focused not on how this or that share is sold, but to whom it is sold.
If a transaction occurs through the sale of a certain share to another participant in the organization, then a purchase and sale agreement is concluded between the seller and the buyer. Such a transaction is registered in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. If the share is transferred to a third party who has no relation to this company, it is necessary by law to comply with the pre-emptive right of purchase by internal participants of the company according to the company's charter.
- Donation of shares.
The donation of a particular share is regulated on the basis of a document of donation. Preemptive rights do not play a role here.
Problematic issues when calculating the cost of a share
The actual value of the share is equal to the value of net assets, calculated in proportion to the participant’s share in the authorized capital. Net assets are identified according to the balance sheet (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 84 N dated 08/28/14).
Attention! If the actual value of the share is higher than the net assets reduced by the minimum authorized capital, the cost of the share is paid in part. A bankrupt organization, as well as one that may become so as a result of payments, are exempt from the obligation to make payments (Federal Law No. 14, Article 23-8).
In practice, some assets are reflected in accounting registers, differing significantly in value from market prices. An example would be fixed assets, specifically real estate. Even its regular revaluation often does not reflect changes in prices on the market; they are more mobile and usually show an upward trend.
What value of the share must be paid when a participant leaves the LLC if the actual value of the share is less than the nominal value ?
A retiring member of the Company may not agree with the calculation of his actual share based on accounting data or decide that market prices were applied incorrectly, to the detriment of his interests.
Next, there are two possible scenarios for the development of the situation:
- calculation based on a mutual compromise between the outgoing participant and other members of the LLC;
- the outgoing participant's appeal to the court, with the appointment of an independent examination.
Judicial practice in these cases allows us to draw an unambiguous conclusion: the market value of assets (real estate) must be taken into account in calculations.
Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court 16191/11 dated 04/17/12 was adopted by arbitration courts (for example, decision A40-8084/2012 dated 08/11/16 of the Moscow Arbitration Court and a number of others, similar).
Attention! VAT recoverable (account 19) is included in the calculation of net assets, but VAT on assets sold is not included, and does not increase net assets (resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court 3744/13 dated 10-09-13).
What reporting period should you take?
According to Federal Law No. 14 (Articles 23-6.1, 25-2), the actual part of the share is calculated based on the last reporting period before the one in which the participant left the organization. Note that the very concept of “reporting period” causes considerable controversy, including judicial ones. Until 04/11/18, the organization had an obligation to provide interim reporting (month, quarter), according to Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34n (clause 29). This provision has now been canceled. The reporting period is a year, at the same time, Federal Law No. 402 “On Accounting” does not prohibit organizations from preparing interim reports (Article 13).
The organization has two options:
- be guided by the balance sheet data of the previous year when calculating;
- prescribe the preparation of interim reporting in the accounting policy and be guided by data for the quarter or year closest to the participant’s exit date.
Judicial practice has not formed a unified position on the issue:
- Resolution of the AS SKO No. A53-17251/2013, 03-12-15 speaks of a monthly reporting period.
- Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District No. F09-4725/12, 03/17/14 states that the pre-exit quarter should be taken as a basis.
- Resolution of the 9th AAS No. A40-209925/2014, 02-02-16. declares the reporting period to be a one-year period.
Changes in the authorized capital of LLC
- Increase in capital.
There are two options for increasing the authorized capital of a company: through the company’s movable and immovable property or through additional contributions.
But the Criminal Code will change only after full payment of the increase.
- Reducing the Criminal Code.
By decision of all participants in a limited liability company, the size of the authorized capital can be changed downward, but not below the minimum threshold. In this case, the shares change in proportion to the size.
Important! The tax service should be notified of all types of changes in the Criminal Code. She enters the necessary information into the state register.