Account 80 Authorized capital is used to account for the authorized capital that is created in joint stock companies (JSC) and limited liability companies (LLC).
Account 80 also takes into account the share capital created in general partnerships and limited partnerships, the authorized capital formed during the creation of a state or municipal unitary enterprise based on the right of economic management and contributions of partners, if the organization is a party to a simple partnership agreement (joint activity) and she is entrusted with keeping accounting records under the agreement (only in this case, account 80 will be called “Deposits of partners”).
What account is the LLC's management company reflected in?
The amount of the authorized capital reflected in the charter of a registered limited liability company must be taken into account in the accounting department of the enterprise.
In accordance with the Plan, account 80 is provided for accounting for the share capital of an LLC.
The posting for the formation of the management company is carried out once on the date of registration of the constituent documents by the tax authority.
Changes to Article 80 are made only in two cases:
- Liquidation of an organization - accounting when closing an LLC.
- Change in the size of the authorized capital (decrease or increase).
Making contributions when forming a management company
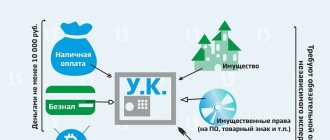
The authorized capital of an organization can be formed from monetary resources in cash and non-cash forms, as well as property or property rights. The simplest way for founders to contribute funds towards the formation of basic capital is a non-cash transfer of funds from the accounts of the owners to the account of the newly created company. It is also very easy to deposit cash funds through the cash desk towards the formation of the designated base capital.
It is much more difficult if the owners take part in the formation of these funds by contributing their property. In this case, it is necessary that the specified property be assessed by an independent organization, which will confirm that the value of the property corresponds to the declared share of participation.
More complex from a procedural point of view is the inclusion of property rights in the formation of a management company. Such a procedure requires not only an independent valuation, but also appropriate documentary support. In addition, such transactions have fiscal and legal risks. Both such rights and their assessment can, if there are compelling reasons, be challenged by both third parties and the federal tax service.
According to the requirements of the Civil Code, the minimum level of the authorized capital must be paid exclusively with monetary resources. And only that share that exceeds the minimum required level can be paid for with alternative assets.
Characteristics - subaccounts, what is accounted for as debit and credit?
In accordance with the Accounting Plan, account 80 is intended to reflect information about the amount of the organization’s authorized capital (share capital), its changes in the course of the enterprise’s activities.
The balance of account 80 must always correspond to the amount of the capital reflected in the constituent documents of the company. If the amount of capital changes, then information about the new amount must be reflected both in the charter of the LLC and in accounting account 80.
That is, at any point in time, the amount indicated on account 80 must be equal to the Criminal Code from the charter.
For an LLC, the minimum authorized capital is 10,000 rubles; the enterprise can, at its own discretion, form a larger charter capital.
Account 80 is passive - intended for accounting for liabilities - authorized capital. Its amount is always reflected on the loan; the balance of account 80 is always in credit.
Limited liability companies do not open subaccounts on account 80. The exception is production cooperatives, which can open the following subaccounts:
- 80-1 – Mutual fund;
- 80-2 – Collective fund.
Sub-accounts can also be opened by joint-stock companies:
- 80-1 – Common shares;
- 80-1 – Preferred shares.
Analytics for the 80-account can be organized by founders.
Introductory information
Judging by the number of links on the BukhOnline forum, the topic of accounting for authorized capital and transactions with it is very relevant.
This material for novice accountants outlines the basic information and rules that must be remembered when accounting for authorized capital. Authorized capital is an integral part of the enterprise's equity capital, which is widely used in assessing the financial condition of the enterprise. In particular, when assessing financial stability, business activity, and profitability.
The size of the authorized capital establishes the minimum amount of property of a business company, which is a guarantee of satisfying the interests of creditors. Depending on the form of ownership of the enterprise, the authorized capital is modified into share capital, mutual fund or authorized capital. I note that in the future we will mainly talk about the authorized capital of the LLC.
Accounting
Since the authorized capital is a liability, it should be taken into account as a credit to the passive account 80.
Accounting of the authorized capital includes the reflection of entries in account 80 in the following cases:
- formation of a management company upon registration of a company;
- increase in capital;
- reduction of the Criminal Code;
- closure of the company (liquidation).
All entries in account 80 are reflected on the dates of state registration of changes by the tax authority.
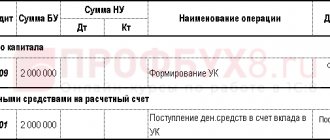
The first entry is reflected on the date of state registration of the company, while account 80 corresponds with account 75 “Settlements with founders”.
The wiring looks like this:
- Dt 75.1 Kt 80 – entry to reflect the founder’s debt on the contribution to the management company of the LLC.
Next, the accounting records reflect the entries for making contributions as they are received, depending on the method of payment for the share, account 75 corresponds from the asset account (property, money).
During the activities of the organization, postings to account 80 can only be reflected if its value changes.
This procedure is also carried out by the state. registration of changes with the tax authority. The posting can only be reflected on the registration date, not earlier.
The increase in capital is reflected by the following transactions:
- Dt 84 Kt 80 – authorized capital increased due to retained earnings at the end of the year;
- Dt 83 Kt 80 – the capital is increased due to additional capital;
- Dt 75.1 Kt 80 – The Criminal Code is increased due to additional contributions from the founders (current or new).
A decrease in the capital is reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 80 Kt 75.1 – Criminal Code is reduced by reducing the share of the LLC participant (or its repayment upon exit);
- Dt 80 Kt 81 – Criminal capital is reduced due to the repayment of the company’s own share;
- Dt 80 Kt 84 – Criminal Code reduced as required by law.
If no changes are made to the authorized capital, then the account 80 will only have to be encountered when closing the LLC. In this case, account 80 should be closed and the founders should be returned the value of their shares.
When liquidating an LLC, the following entries are reflected in the accounting records:
- Dt 80 Kt 75.1 – reflects the amount of the capital to be distributed among the founders of the LLC, is carried out for the entire amount of the authorized capital.
Postings
Below is a table showing typical accounting entries for account 80:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| When registering an LLC | ||
| The authorized capital of the LLC has been formed - the debt of the founders to the organization is reflected | 75.1 | 80 |
| With an increase in the Criminal Code | ||
| Reflected increase in capital at the expense of LLC property (profit) | 84 | 80 |
| The increase in capital due to the additional fund is reflected | 83 | 80 |
| The increase was taken into account due to additional contributions from the founders of the LLC | 75.1 | 80 |
| When decreasing the capital | ||
| The decrease in the capital due to the withdrawal of the participant and payment of his share is reflected | 80 | 75.1 |
| A decrease in the capital due to a decrease in the value of the founders’ shares is reflected | 80 | 75.1 |
| The reduction in capital due to the redemption of the LLC’s own shares was taken into account | 80 | 81 |
| Reduction of the capital due to compliance with the law (when the value of assets has become less than the capital or not all contributions are made on time) | 80 | 84 |
| Upon liquidation of an LLC | ||
| The organization's debt to the founders in connection with the liquidation of the company is reflected | 80 | 75.1 |
What should the balance be?
Account balance 80 is always a credit balance. Moreover, at any given time it must clearly correspond to the size of the authorized capital reflected in the charter of the LLC.
If the Criminal Code changes, changes must be made to the charter, which entail an adjustment to the balance of account 80.
Typical transactions for account 80
By debit of the account
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| An object of fixed assets was transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of an agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 01 |
| Property intended for rental is transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 03 |
| An intangible asset was transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of an agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 04 |
| Upon termination of the agreement on joint activity, the equipment is transferred to the participant of the simple partnership (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 07 |
| Investments in non-current assets were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 08 |
| Materials were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 10 |
| Animals are transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 11 |
| The costs of acquiring material assets upon termination of the agreement on joint activity were transferred to the participant in a simple partnership (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 15 |
| The amount of deviations in the value of inventories transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity was written off (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 16 |
| Work in progress was transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 20 |
| Semi-finished products were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 21 |
| Ancillary proceedings were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 23 |
| The servicing production was transferred to the participant of the simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 29 |
| Goods were transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 41 |
| Finished products were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 43 |
| Cash was transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 50 |
| Non-cash funds were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 51 |
| Funds in foreign currency were transferred to a participant in a simple partnership upon termination of a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 52 |
| Funds were transferred from a special bank account upon termination of a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 55 |
| Shares and debt securities were transferred to the participant of a simple partnership upon termination of the agreement on joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 80 | 58-2 |
| The debt for the return of deposits to the founders of the organization is reflected when the authorized capital is reduced (after amendments are made to the constituent documents) | 80 | 75-2 |
| Own shares purchased from shareholders were canceled (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 80 | 81 |
| The authorized capital was reduced to the amount of net assets (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 80 | 84 |
By account credit
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit |
| An object of fixed assets received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 01 | 80 |
| Property intended for rental, received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement, was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 03 | 80 |
| An intangible asset received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 04 | 80 |
| Equipment requiring installation received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 07 | 80 |
| Current assets received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement are taken into account (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 08 | 80 |
| Materials received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 10 | 80 |
| Animals received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement have been capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 11 | 80 |
| Inventory received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement was capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 15 | 80 |
| The amount of deviations in the cost of inventories received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement is taken into account (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 16 | 80 |
| An item of work in progress was received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 20 | 80 |
| Semi-finished products received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 21 | 80 |
| Part of the costs of auxiliary production paid by a participant in a simple partnership is counted towards the contribution to the joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 23 | 80 |
| Part of the costs of service production paid by a participant in a simple partnership is counted towards the contribution to the joint activity (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 29 | 80 |
| Goods received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 41 | 80 |
| Cash received as a contribution under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 50 | 80 |
| The funds deposited as a contribution under the joint activity agreement have been credited to the current account (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 51 | 80 |
| Funds in foreign currency deposited as a contribution under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) have been credited to a foreign currency account. | 52 | 80 |
| A contribution was made to a special account under a joint activity agreement (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 55 | 80 |
| Shares and debt securities received as a contribution under a joint venture agreement were capitalized (on a separate balance sheet of the joint venture) | 58-1 | 80 |
| The debt of the founders (participants) for contributions to the authorized capital is reflected (after state registration of the organization) | 75-1 | 80 |
| The authorized capital was increased due to additional capital (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 83 | 80 |
| The authorized capital was increased (after amendments were made to the constituent documents) | 84 | 80 |
Contribution of property to pay for the share
The monetary value of the property contributed to pay for shares in the authorized capital of the company is approved by a decision of the general meeting of participants. This decision must be made unanimously by the company's participants.
If the nominal value of a share (increase in the nominal value of a share), paid in kind, is more than twenty thousand rubles, an independent appraiser must be involved to determine the value of this property. The nominal value of a share (increase in the nominal value of a share) paid in non-monetary means cannot exceed the valuation amount determined by an independent appraiser.
By the way, overestimating the value of property contributed to the authorized capital can be fraught both for the participants of the company and for the independent appraiser. The fact is that they bear subsidiary liability for the obligations of the company in the amount of inflated value of such property.
Tax accounting of property received as a contribution
For tax accounting purposes, property received as a contribution to the authorized capital must be accepted at the value at which it was taken into account in the tax accounting of the transferring party. In this case, the value of the transferred property must be documented.
Forming the authorized capital with property in non-monetary form has its advantages: you can deduct VAT recovered by the owner (here an invoice is not needed), and write off the cost of such property as an expense when taxing. The main thing is that the primary documents are properly prepared and the cost of the accepted property is correctly formed. (For more information about the tax accounting of transferred property, see “How to register the transfer of property for related parties: contribution to the management company and contribution to property”).
Payment by the founders of their shares
Each founder of the company must pay in full his share in the authorized capital within the period determined by the agreement on the establishment of the company or, in the case of the establishment of the company by one person, by the decision on the establishment of the company. However, this period cannot exceed one year from the date of state registration of the company.
It is not permitted to release the founder of a company from the obligation to pay for a share in the authorized capital. At the time of state registration of the company, its authorized capital must be paid by the founders at least half.
After paying for the share in the authorized capital, the founder, losing ownership of the contributed property, receives the following rights:
- the right to receive net profit in proportion to the share of the founder;
- the right to receive the actual value of the share (in cash or in kind) in the event of withdrawal or expulsion from the company;
- the right to part of the company’s property after its liquidation;
- the right to participate in the management of the company, to receive information about its activities, etc.
Features of the management company
A management company is part of the total capital of a legal entity, which is associated with a fairly large number of requirements established at the legislative level:
- For state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises, the period for the actual formation of the management company is limited (no more than 3 months from the date of registration of the enterprise).
- Incomplete payment of management companies in PJSC, JSC and LLC prevents the payment of dividends and the issue of bonds. One of the options for limiting the total nominal value of all bonds issued by a business entity is the size of its charter capital.
- In the case of distribution of profits received by a PJSC, JSC or LLC among the owners, this is done in proportion to the shares of their participation in the management company. A different procedure may be established in HT.
- The formed and paid charter capital can then be increased or decreased in accordance with the established procedure. The reduction will only be possible after notification of all creditors.
- In economic societies and HT there is the possibility of leaving the participants. Including a refund of the cost of the deposit made.
- Owners of deposits in PJSC, JSC and LLC are responsible for losses from business activities only within the limits of the amounts of their deposits (even if these deposits are not fully paid by them) and are not liable for other obligations of business entities. The HT provides for additional liability of owners for the obligations of the partnership.
- Critical for the management company may be its comparison with the value of net assets (NA). If the value of the NA of a PJSC, JSC or LLC for 2 years in a row does not exceed the authorized capital, then the authorized capital must be reduced to the value of the AV. If at the same time the private equity becomes less than the minimum size of the capital company established by law, then the economic company must be liquidated. For state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises, this ratio is checked based on the results of each past year and the value of the authorized capital is immediately (if necessary) adjusted. If the NAV of a state unitary enterprise or municipal unitary enterprise turns out to be less than the minimum allowable capital and this situation is not corrected within 3 months after the end of the year, then the enterprise is subject to liquidation or reorganization.
For information on how to calculate the NAV value, read the article “The procedure for calculating net assets on the balance sheet - formula 2015”
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE WEEK
01/20/202111:18 Personnel
New labor protection rules – new responsibilities of the employer
21.01.202109:00
Litigation
How did a “penny” test purchase ruin an individual entrepreneur, a pensioner?
25.01.202114:58
Business organization
Debtors will retain a minimum income
25.01.202109:00
Personnel
The Ministry of Labor is considering indexing pensions for working pensioners
today at 09:0009:00
Taxes
Tax deductions can be obtained without 3-NDFL
PODCAST 4.12.2020
What has changed in taxes and reporting since 2021?
All episodes
Comments on documents for an accountant
Do I have to pay personal income tax if a company pays for the issuance of bank cards for employees?
01/26/2021 Payment by the employer of the bank commission for issuing and servicing employee salary cards is not…
Payment of income to a foreign company that does not have the actual right to it: tax consequences
01/26/2021 A foreign organization that directly receives income and is not a private income fund cannot claim...
Is the New Year bonus for employees not subject to insurance contributions?
01/25/2021 The court supported the Pension Fund of Russia, which fined an organization that paid bonuses to all employees and did not accrue...
‹Previous›Next All comments
Where is the authorized capital reflected in the financial statements?
Indicators counting 80 are used:
- When filling out the balance sheet. Line 1310 of the balance sheet corresponds to the amount of the authorized capital.
- Completing the capital flow statement.
Field 3100 reflects data for the year preceding the one before the reporting year. For example, if the report is for 2021, then the credit balance as of December 31, 2015 is shown.
The following fields reflect data for the year preceding the reporting year:
1. Credit turnover: 3210-3213 - increase in capital (now and further - only according to the accounting account of the authorized capital); 3214 — credit turnover within the framework of correspondence with account 75.1 (additional issue of shares); 3215 - credit turnover with accounts 83 or 84; 3216 - loan balance during enterprise reorganization.
2. Debit turnover: 3220–3223 - decrease in capital; 3224 - debit turnover with accounts 75 or 84; 3225 - debit turnover with account 81; 3226 - loan balance during enterprise reorganization.
The indicator for line 3200 is the sum of lines 3100 and 3210 minus the indicator for line 3220.
The following fields reflect data for the reporting year:
1. Credit turnover: 3310–3313 - increase in capital; 3314 — credit turnover on account 75.1; 3315 - credit turnover on accounts 83 or 84; 3316 - loan balance on the account of the affiliated company. 2. Debit turnover: 3320 - decrease in capital; 3324 - debit turnover with accounts 75 or 84; 3325 - debit turnover with account 81; 3326 - loan balance on the account of the selected company.
The indicator for line 3300 is the sum of lines 3200 and 3310, reduced by the value of the indicator for line 3320. ***
The authorized capital is formed on account 80. A credit shows its increase, and a debit shows a decrease. Turnovers and account balances are taken into account when calculating indicators for financial statements.
Source: "People's Adviser"
Account 80 of accounting is a passive account “Authorized capital”, it opens section Ⅶ “Capital” of the chart of accounts and serves to accumulate information about the state and movement of the authorized capital, in other words, the “airbag” of creditors. Let's consider the use of account 80 in accounting, typical entries and an example of increasing the size of the authorized capital.