What is transport tax?
Transport tax is a tax levied on vehicle owners. Transport means are: cars, motorcycles, scooters, buses, airplanes, helicopters, motor ships, yachts, sailing ships, boats, snowmobiles, motor sleighs, jet skis, motor boats and other water and air vehicles.
Not all vehicles are subject to taxation. For example, the following exceptions exist: - rowing boats, as well as motor boats with an engine power of no more than 5 horsepower - vehicles that are wanted, subject to confirmation of the fact of their theft (theft) by a document issued by an authorized body. The full list of exceptions is indicated in Article 358 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Payers of transport tax are both individuals and legal entities.
Transport tax in 2021: changes in Moscow Region and Moscow
In 2021, there were no changes in the size and structure of tax rates for transport in the capital and region. The only innovations introduced this year are a new form for filling out the declaration . Another innovation that affects exclusively legal entities is their receipt of notifications about the amount of the fee from the Federal Tax Service.
Previously, companies owning vehicles independently calculated the amount of contributions due to the local budget. Starting from the coming year, the Federal Tax Service will do this for them, sending a receipt with the amount due for payment.
How to calculate the tax amount?
The amount of transport tax is calculated based on the following parameters: — Tax rate
The tax rate is established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation per one horsepower of engine power.
Depends on power, gross capacity, vehicle category and year of manufacture of the vehicle. Tax rates can be increased or decreased by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation by no more than 10 times the rate specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. — Tax base
This parameter is set depending on the type of vehicle.
For cars, motorcycles and other vehicles with an engine, this is the engine power in horsepower - Ownership period
The number of complete months of ownership of the vehicle during the year.
— Increasing coefficient
For passenger cars with an average cost of 3 million rubles. a multiplying factor is applied. The list of such cars is available on the website of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation.
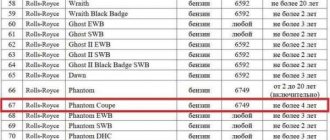
Transport tax rates in Moscow in the table
The rules for collecting tax fees for transport in the capital region are established by Law No. 29 of the Moscow Government. According to this regulatory document, the following rates are established, charged in rubles for each hp. engine:
| Bet size | Object of taxation |
| 7 | Motor vehicles with power up to 20 hp. |
| 12 | Passenger cars with engines up to 100 hp. |
| 15 | Motor vehicles with power from 20 to 35 hp. |
| 15 | Buses with engines up to 110 hp |
| 15 | Trucks up to 100 hp |
| 25 | Passenger cars with engines from 100 to 125 hp. |
| 25 | Other vehicles on wheels or tracks |
| 25 | Snowmobiles and motor sleighs with engines up to 50 hp. |
| 26 | Buses with power over 110 hp |
| 26 | Trucks with a power of 100-150 hp |
| 35 | Passenger cars with power from 125 to 150 hp. |
| 38 | Trucks with a power of 150-200 hp |
| 45 | Passenger cars with a power of 150-175 hp. |
| 50 | Passenger cars with a power of 175-200 hp. |
| 50 | Motor vehicles with a power of more than 35 hp. |
| 50 | Snowmobiles and motor sleighs with a power of more than 50 hp. |
| 55 | Buses with power over 200 hp |
| 55 | Trucks with power from 200 to 250 hp. |
| 65 | Passenger cars with power from 200 to 225 hp. |
| 70 | Trucks with power over 250 hp |
| 75 | Passenger cars with a power of 225-250 hp. |
| 150 | Passenger cars with power over 250 hp. |
When calculating car tax, in addition to the rate, you also need to take into account increasing factors. They apply to premium cars, the average price of which exceeds 3 million rubles. The list of such models is published annually on the website of the Ministry of Economic Development.
The value of the coefficient depends on the cost of the car and the year of its manufacture, ranging from 1.1 to 3 of the base rate.
Who is entitled to transport tax benefits?
At the federal level, the following categories of citizens are exempt from paying transport tax:
- Heroes of the Soviet Union, heroes of the Russian Federation, citizens awarded Orders of Glory of three degrees - for one vehicle;
- veterans of the Great Patriotic War, disabled people of the Great Patriotic War - for one vehicle;
- combat veterans, disabled combat veterans - for one vehicle;
- disabled people of groups I and II - for one vehicle;
- former minor prisoners of concentration camps, ghettos, and other places of forced detention created by the Nazis and their allies during the Second World War - for one vehicle;
- one of the parents (adoptive parents), guardian, trustee of a disabled child - for one vehicle;
- owners of passenger cars with an engine power of up to 70 horsepower (up to 51.49 kilowatts) inclusive - for one such vehicle;
- one of the parents (adoptive parents) in a large family - for one vehicle;
- owners of vehicles belonging to other preferential categories.
In addition to the federal list of preferential categories of citizens, there are regional benefits. For example, in some regions of the Russian Federation, pensioners pay only 50% of transport tax, or are completely exempt from it. The situation varies greatly depending on the region. For example, in Moscow there are no benefits for pensioners, and in St. Petersburg pensioners are completely exempt from paying transport tax for a domestically produced car with an engine power of up to 150 horsepower.
You can find out the availability of regional benefits on the tax service website, in the “electronic services” section. On this page you must select a subject of the Russian Federation, municipality (city), type of tax and year. After this, you will receive complete information about all types of transport tax benefits for individuals.
It is important to know that the tax authority does not have the right to provide a transport tax benefit based solely on age information. Benefits are of a declarative nature, as a result of which it is necessary to submit to the Federal Tax Service the taxpayer’s application in the prescribed form, which indicates the basis for providing the benefit (reaching retirement age).
Tax calculation and payment deadlines for organizations
Most regions of Russia provide for the need to make advance payments for payers from among legal entities. In Moscow there is no such obligation - legal entities pay tax in full at the end of the year. The last date by which funds can be transferred to pay off obligations is February 5.
The enterprise calculates the amount independently, taking into account the following factors:
- bid;
- the tax base;
- the share in the right;
- increasing the coefficient;
- holding period (number of months/12);
- benefit provided.
Payment is made without taking into account fractional shares of the ruble, using mathematical rounding rules.
Deadline for payment of transport tax for legal entities in 2021:
- for 2021 - no later than February 5, 2020
- for 2021 - no later than February 5, 2021
How to calculate the number of complete months of car ownership?
If a vehicle is delivered or deregistered during the year, then the transport tax is calculated with a certain coefficient. This coefficient is defined as the ratio of the number of complete months during which a given vehicle was registered to the number of calendar months in a year (12).
The procedure for determining the number of full months of car ownership is calculated in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Month of registration
It is considered complete if the vehicle
is registered
before the 15th day inclusive.
The month of deregistration is considered complete if the car is deregistered
after the 15th day. For example, if a car was registered after the 15th, then this month is not complete and is not taken into account when calculating the car tax.
Who is the tax payer?
Both citizens and legal entities are required to pay transport tax
. But in our article we will talk specifically about individuals. The person in whose name the corresponding vehicle is registered must pay the transport tax.
It is worth noting that a minor child can also be a transport tax payer. For example, if a child received a car as a gift from a relative (and legislation in Russia does not prohibit this). In this case, the transport tax must be paid by the parent of the minor child.
.
What is property tax?
Property tax is a tax on a residential building, apartment (room), garage, parking space, unfinished construction site, other buildings, structures, premises.
Residential buildings include residential buildings and houses located on land plots provided for personal farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture, and individual housing construction.
The property tax for individuals is a local tax; the tax itself and the tax rate are established by regulations of municipal authorities (in the federal cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol - by the laws of these constituent entities of the Russian Federation).
You need to know that paper tax notices are not sent to owners of taxable property in the following cases:
1) the presence of a tax benefit, tax deduction, other grounds established by law that exempt the owner of the taxable object from paying tax 2) if the total amount of tax obligations reflected in the tax notice is less than 100 rubles, except for cases established by law 3) the taxpayer is an Internet user - service of the Federal Tax Service of Russia - the taxpayer’s personal account and did not send a notification about the need to receive tax documents on paper.
There is a simpler and more convenient way - paying taxes online using our online service. Enter the document index in the field below the text (indicated in the notification with a list of tax charges), we will provide you with information about the charges and the opportunity to pay them with a card issued by any Russian bank.
Using the TIN number of the property owner, our service allows you to check the presence of debts on all taxes of individuals, including real estate tax, starting from December 1 of the year when the Federal Tax Service calculated the tax amount. Checking real estate taxes through our service does not require registration on the State Services portal.
Results
Transport tax rates changed slightly in 2017–2018. Many regions did not cancel the rates that were in effect in 2021 and 2021, respectively, and extended their validity. Several factors influence the calculation of transport tax. In addition to engine power, this is the class of the car, the year of its production, the purchase price, the number of months of ownership, environmental safety, scope of application, etc.
Read the articles from our section “Transport tax rates” to stay up to date with changes relating to this budget payment. And, apparently, there are a lot of them waiting for us.
Useful links on the topic “Property tax rates for individuals in Moscow in 2021 - 2021”
- Personal income tax 15%. Progressive scale
- Tax on interest on deposits
- Tax control of accounts
- Why are benefits declarative in nature?
- Personal income tax on inheritance
- Tax liability for failure to submit documents
- Living wage in Moscow
- Minimum wage in Moscow
- Personal property tax rates persons in Moscow
- Property tax benefits in Moscow
- Transport tax rates in Moscow
- Transport tax benefits in Moscow
- Transport tax rates in the Moscow region
- How to apply for a Moscow student social card
- How to apply for a social card for a student in Moscow
- How to pay for MGTS communication services on the MOS.RU portal
- Reference and legal information for Moscow and the Moscow region
- Children's benefits in Moscow
- Where to get a compulsory medical insurance policy in Moscow
- Moscow passport offices
- Consolidated plan for conducting scheduled inspections of business entities for 2014 - 2021 in Moscow and the Moscow region
- Addresses, telephone numbers, websites, details of Moscow tax inspectorates
- District courts of Moscow
- Territorial jurisdiction of Moscow district courts;
- Magistrates and court districts of Moscow;
- Territorial jurisdiction of Moscow magistrates
- The procedure for obtaining confirmation of the status of a tax resident of the Russian Federation
- When and what to report to the Federal Tax Service
- Convention on the International Exchange of Tax Information
- Taxpayer personal account
- Tax benefits for pensioners - procedure for provision and sample application
- How to pay taxes online
- Should children pay taxes?
- How to get a deferment (installment plan) for paying taxes
- Tax audits
- What should a complaint to the tax inspectorate contain?
Tax return
- Complete list (list) of persons who are required to file a tax return
- Sample of filling out the 3-NDFL tax return for 2021:
- title page, sections 1, 2
- income from sources in the Russian Federation (Appendix 1);
- calculation of property tax deduction for expenses on the purchase of real estate (Appendix 7)
- calculation of property tax deductions for income from the sale of property (Appendix 6);
- calculation of social tax deductions established by subparagraphs 4 and 5 of paragraph 1 of Article 219 of the Tax Code (calculation to Appendix 5);
- calculation of standard, social, investment tax deductions (Appendix 5);
Taxes
- UTII
- Land tax
- Personal income tax (NDFL)
- Income not subject to taxation
- Who are tax residents and non-residents
- Sale of an apartment by a tax non-resident of the Russian Federation
- The procedure for calculating and paying personal income tax upon the sale of a share in the authorized capital of an LLC, shares of an OJSC, securities
- Personal income tax on payments by court decision
- Tax on the sale of currency and income on Forex
- How to reduce personal income tax when buying and selling a car
- How to reduce personal income tax when selling and buying a home
- Procedure for paying personal income tax if an employee is on a business trip abroad
Tax deductions
- Property tax deductions
- How to get a property deduction when buying a home on credit
- How to get a deduction for improving housing conditions
- When can you get a deduction of 2,000,000 rubles when purchasing a room or a share of an apartment?
- Is a non-working pensioner entitled to receive a property tax deduction in connection with the purchase of an apartment?
- List of medicines for which social tax deduction is provided
- List of expensive types of treatment for which a social tax deduction is provided (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 19, 2001 No. 201)
Tax liability for:
- failure to provide documents
- failure to provide tax reporting;
- incomplete payment of taxes;
- failure to appear when called to the tax authorities
Tax payment period
In accordance with the provisions of the Moscow law on transport tax, taxpayer companies must transfer mandatory payments to the budget no later than February 5 of the year following the billing period. Organizations will not be allowed to make advance payments between financial periods. Citizen taxpayers must repay tax debts by the first of July of the year following the billing period. According to the law on transport tax of the city of Moscow, payment is calculated in rubles. If the amount of debt is indicated taking into account kopecks, an amount greater than fifty kopecks is rounded to the nearest ruble, and less is not included in the calculation.
Features of obtaining tax transport benefits in Moscow
To receive tax benefits on vehicles, individuals must submit a written application to the appropriate authority. It must be accompanied by a document confirming the basis specified in the application for canceling the annual mandatory payment. If Russian citizens have several preferential documents, they have the right to independently choose which document will be used to reduce the tax. You cannot use more than one paper to receive a 100% discount.
The benefits that are enshrined in Moscow Law No. 33 “On Transport Tax” do not apply to air or water vehicles, motor sleighs, and snowmobiles.
How to find out and pay property taxes?
Our service allows you to check and pay property taxes online.
Enter the TIN number or Document Index (indicated in the notification with a list of tax accruals) in the field below the text, we will provide you with information about the accruals. Using the TIN number of the property owner, our service allows you to check the presence of debts on all taxes of individuals, including real estate tax, starting from December 1 of the year when the Federal Tax Service calculated the tax amount. Checking real estate taxes through our service does not require registration on the State Services portal.
Tax benefits
Transport tax benefits are established by the law of the subject of the Russian Federation in which the car is registered (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 24, 2017 N 03-05-06-04/17112). For example, in the Smolensk region in 2018-2020, organizations were completely exempted :
- in relation to ambulances and sanitary vehicles, as well as fire engines;
- containing military-type automobile convoys and performing mobilization tasks - in relation to vehicles used to carry out mobilization tasks;
- religious organizations, public organizations of disabled people - subject to certain restrictions.
In addition, the tax rate in 2015–2019 was reduced by 30% for taxpayers carrying out regular transportation of passengers by public road transport in intercity, suburban and urban traffic, in relation to buses with a gas engine.
Reduction or complete exemption from payment of transport tax when paying into the Platon system
The Tax Code exempts organizations from paying calculated advance payments for transport tax in relation to a vehicle with a permissible maximum weight of over 12 tons, registered in the register (Platon system). This rule applies until December 31, 2021. In this case, the calculated transport tax based on the results of the tax period in relation to each vehicle having a permissible maximum weight of over 12 tons, registered in the register, is reduced by the amount of the fee paid in relation to such a vehicle in a given tax period. If the amount of tax payable to the budget takes a negative value, the amount of tax is taken equal to zero, i.e. The organization does not need to pay transport tax.
Attention! From 2021, a declarative procedure for providing benefits on transport and land taxes for organizations will be introduced. In other words, starting from 2021, organizations must report transport tax benefits with a special statement. The Federal Tax Service explained: you will have to submit an application only for tax periods starting from 2021.
All about transport tax: how to calculate, when to pay, possible benefits
There have been discussions about the abolition of the transport tax for many years, but so far this has not happened, car owners receive receipts for payment every year. Today we will find out who should pay it and for what, how to check the calculation of the tax, how rates differ in the regions, whether there is liability for non-payment and what the situation is with transport tax in other countries.
Owning a car is just an expense. When buying it, we pay a decent amount, it’s clear for what: ease of movement, drive, status and some other qualities individual for each. The car won't run without fuel, and so we put up with the cost of refueling. The benefits of insurance are also clear - in the event of an accident, you can count on compensation. But by giving money to the state, in fact, for what is generally recognized as the number two problem in Russia (the transport tax goes to the maintenance of roads), you begin to feel like the number one problem, that is, a fool. Well, at least because the state already receives money for road restoration from excise taxes on fuel. This fee looks more rational, since more transfers to the budget come from those who drive more, and it is not tied to the owner of the vehicle. So, in essence, our transport tax is a tax on car ownership.
Legal grounds for levying tax
The existence of a transport tax is stated in Chapter 28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The document defines the general provisions, payers, tax base and tax rate, but its application, territorial, environmental and age coefficients, benefits and other aspects are determined by the authorities of the subjects.
Taxpayers are all vehicle owners, with the exception of organizers of major sporting events such as the Olympics and the World Cup, and truck owners, who, according to the Platon system, pay the same or more for road use than the amount of the accrued tax.
The objects of taxation are cars, motorcycles, scooters, buses and other self-propelled machines and mechanisms on pneumatic and caterpillar tracks, airplanes, helicopters, motor ships, yachts, sailing ships, boats, snowmobiles, motor sleighs, motor boats, jet skis, non-self-propelled (towed vessels) and other water and air vehicles, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of article 358 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
There is no need to pay transport tax when owning a passenger car specially equipped for use by disabled people, as well as cars with a power of up to 100 hp, received through social security authorities.
Calculation of transport tax
The calculation of any tax is based on the tax base. For cars, this is the engine power in horsepower. Depending on their quantity, a certain rate is applied to vehicles. The Tax Code establishes five categories of rates for passenger cars, but they can be changed, and rates can be increased or decreased by the laws of the constituent entities, but not more than ten times. The only exception to the application of the restriction is a reduction in the rate for passenger cars with an engine power of less than 150 hp. pp.: the authorities of the constituent entities can even make it zero, as, for example, this happened in the Tyumen region. A couple of years ago there was a zero rate in Chechnya. Although today there are no more such “philanthropists” left.
Federal transport tax rates in 2017:
| Engine power, hp | Rate, rub. | |
| up to 100 l. With. inclusive | 2,5 | |
| over 100 hp up to 150 hp inclusive | 3,5 | |
| over 150 hp up to 200 hp inclusive | 5 | |
| over 200 hp up to 250 hp inclusive | 7,5 | |
| over 250 hp | 15 | |
The method for calculating transport tax comes down to the following formula:
Tax Rate x Horsepower x Number of Months of Ownership/12 x Multiplying Factor = Tax Amount.
The number of months of ownership is usually 12, but if the owner changes during the year, then full months are counted. Moreover, the exact date of purchase or sale does not matter: the full month is taken into account if registration was terminated after the 15th of the corresponding month or if the car was registered before the 15th inclusive. Accordingly, if a car is sold before or purchased after the 15th, then the tax is calculated based on the month preceding the sale or the month following the purchase.
Increasing coefficients are established in each region by the authorities of the subject. Usually this is a single value, but it can contain a combination of a territorial coefficient, a coefficient depending on the age of the car and/or its environmental class.
There are many calculators on the Internet that can be used to find out the amount of transport tax for a particular car, including taking into account the “luxury tax”. We recommend using the transport tax calculator Drom.ru , the relevance of which we regularly monitor.
Luxury tax
In fact, this is not a separate tax, but an increasing coefficient for the transport tax. It has been applied since 2014 to cars whose average cost is above 3 million rubles, and these vehicles are included in a special list of the Ministry of Industry and Trade. When the “luxury tax” was introduced, about 300 models were included in the list, but now this list includes almost 1,000 cars. The value of the coefficient varies from 1 to 3 depending on the cost of the car and its age (these parameters are defined in paragraph 2 of Article 362 of the Tax Code).
You must know the amount in order to check the calculation from the tax office. The fact is that the department receives information about changes in the tax base extremely slowly, especially if this leads to a tax reduction.
Most often, they “forget” to enter data about car owners who sold their car: the traffic police must report the change of owner to the tax authorities, but this data quite often “does not arrive”, and the invoice is issued for the full year. To correctly calculate the tax, you need to divide the annual amount by 12 and multiply by the number of months during which the vehicle was owned. If the amount received differs from that indicated in the payment slip, you must inform your tax inspector about this. Usually one call is enough, but a certificate from the traffic police about termination of registration may also be required. According to the rules, after checking the information, the inspector must issue a corrected invoice. But in practice, everything can be limited to a conversation on the phone: together you will recalculate the amount of tax that will need to be paid.
Features of taxation in different regions
As mentioned above, vehicle tax rates may vary depending on the region of registration of the car. Most regions simply apply the territorial coefficient, but some have their own characteristics.
Some examples:
• Moscow - tax is paid for eight categories of cars in increments of maximum power of 25 hp. • Kabardino-Balkaria - cars with a power of less than 100 hp are exempt from tax. or over 10 years old. • Primorsky Krai - for cars aged 3 to 10 years, the rate is almost two times lower than for new ones, and owners of cars older than 10 years and with a power of less than 100 hp. they pay three times less. • Novosibirsk region - the age of the cars is taken into account. The tax rate decreases depending on the year of manufacture of the vehicle. Age categories: up to 5 years, from 5 to 10 years and over 10 years.
Examples of transport tax amounts for 2021 for new cars in different regions, rubles:
| Region | Lada Granta 87 l. With. | Hyundai Solaris 123 l. With. | BMW 520d 190 l. With. | Toyota Land Cruiser 309 l. With. |
| Moscow | 1044 | 3075 | 9500 | 46 350 |
| Moscow region | 870 | 4182 | 9310 | 46 350 |
| Saint Petersburg | 2088 | 4035 | 9500 | 46 350 |
| Krasnodar region | 1 044 | 3075 | 9500 | 46 350 |
| Ingushetia | 435 | 861 | 1900 | 12 360 |
| Chechen Republic | 609 | 1363 | 4560 | 28 119 |
| Perm region | 2175 | 3690 | 9500 | 17 922 |
| Sverdlovsk region. | — | 1156 | 6213 | 30 653 |
| Novosibirsk region | 522 | 1230 | 5700/4275/2850 * | 46 350/34 763/23 175 * |
| Irkutsk region | 914 | 1784 | 6650 | 32 445 |
| Transbaikal region | 609 | 1230 | 3800 | 20 085 |
| Primorsky Krai | 392** | 923** | 7980/5320/2660 *** | 46 350/34 763/13 905 *** |
| Amur region | 1305 | 2583 | 5700 | 46 350 |
| Magadan region **** | 522 | 984 | 2280 | 11 124 |
| Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | 435 | 861 | 1900 | 9270 |
| Crimea ***** | 435/348/304/218 | 861/689/603/431 | 2850/2280/1995/1425 | 15 450/12 360/10 815/7725 |
* For cars aged up to 5 years inclusive/over 5 years up to 10 years inclusive/over 10 years. ** For vehicles whose country of manufacture is the Russian Federation, USSR, republics of the USSR, the tax on foreign cars of the same capacity will be 1566/731/522 and 3198/1919/1119 ** respectively. *** For cars aged up to three years inclusive/over three years up to 10 years inclusive/over 10 years. **** For 2021, rates are increasing and the tax will be 609/1230/2850/13,905 rubles. ***** For cars up to and including 10 years old/over 10 years old/over 15 years old/over 20 years old.
Privileges
Each region has its own list of beneficiaries who are exempt from paying transport tax either fully or partially. Typically, the first category includes veterans, participants in military operations, citizens affected by radiation, disabled people of groups I and II, large families or families with a disabled child. Heroes of the Soviet Union, Russia, awarded orders and medals, honorary citizens do not pay anything or pay only a part (usually 50%). In some regions, pensioners may not pay part of the tax; in some regions they do not pay if they own a low-power car; in others they do not have to work.
Car owners must prove their right to the benefit themselves. Typically, an application and documents confirming the relevant status must be submitted to the tax authorities at the taxpayer's place of residence, and updated if necessary.
In addition to standard categories, regions can set their own groups of beneficiaries for a specific period. Thus, in the Jewish Autonomous Region, the transport tax was canceled for a year for victims of floods, in Khakassia - from fires. Quite a lot of regions support agricultural producers and completely or partially exempt vehicles belonging to livestock or agricultural farms from transport tax. In Novosibirsk, only 10% of the established rates are paid by individual entrepreneurs and legal entities for vehicles using natural gas as fuel.
No care?
Some time ago, in order to reduce the amount of transport tax, it was “fashionable” to register cars in regions with minimal territorial coefficients: Adygea, Bryansk region, Dagestan, the Chechen Republic and several cities of the “Chernobyl zone”. But after regional coefficients rose, this scheme was no longer used. Another “saving” option is possible when registering a car for a beneficiary. But often they are subject to restrictions on power (no more than 100–150 hp), or on the number of vehicles owned (usually no more than one). But do not forget that upon the death of the beneficiary, the property recorded in his name will pass to the heirs, and they will have a completely legal right to take possession of it. Advice on registering a car for a minor is groundless, since his legal representatives must pay for the child. Schemes with fraudulent sales and purchase agreements and deregistered cars are impossible under the law and will have consequences in the form of a fine under Article 12.1. Code of Administrative Offenses “Driving a vehicle not registered in accordance with the established procedure...” - 500–800 rubles and 5,000 rubles for a repeated violation.
Payment period
Tax payment must be made once a year - no later than December 1 of the year following the expired tax period (calendar year). That is, in 2021, the tax is paid for 2016 at the rates established for 2021, and the tax for 2021 is paid until December 1, 2021.
In those regions where the age of the car is taken into account when calculating the tax, it (age) is determined in calendar years as of January 1. The starting point is the year of manufacture of the car. That is, if you bought a car in 2021, and it was released in 2011, then for the tax authorities it is already “five years old” and in the Novosibirsk Region and Primorsky Territory, reducing factors may be applied to it.
Car owners pay transport tax on the basis of a notification sent by the tax authority (clause 3 of Article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It could be a simple letter dropped into a box; registered, which must be received by mail; You can also arrange delivery of an email on the websites of the Federal Tax Service or State Services. If the notification didn’t arrive, that’s your problem. To solve them, you can calculate the tax amount yourself and pay it. If there is a larger error, the overpayment will be taken into account next year. Underpayment or unpaid tax will lead to certain consequences.
What if you don't pay?
For non-payment of transport tax, the current legislation of the Russian Federation does not provide for any separate punishment. The same sanctions apply to debtor car owners as to non-payers of any other tax.
The most harmless punishment is penalties for late payment. Their size is 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for each day of delay (at the rate effective from September 18, 2021, this is 0.0283%). If the tax on a gasoline 309-horsepower Toyota Land Cruiser of 46,350 rubles is not paid, the fine will be 13.13 rubles per day and will be accrued until the day of payment, but not more than 3 years.
After six months, a transition occurs to the next level - the imposition of a fine for violation of the payment deadline in the amount of 20% of the unpaid tax amount. The same sanction applies when the amount of tax paid is underestimated. If the tax is not paid intentionally, if the defaulter was aware of the illegality of his actions or inaction (the tax office must prove this), then the fine will be 40% of the entire amount. The obligation of everyone to pay taxes is stated in Article 57 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation limits the period for collecting transport tax to three years. That is, in 2021 you can only receive tax for 2014, 2015 and 2021, but not for 2013 and previous years. The same period applies to the limitation period for transport tax for individuals.
After six months from the date of payment and if the amount of unpaid tax exceeds 3,000 rubles, the inspectorate will begin to collect all debts forcibly (Article 48 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). On claims from tax authorities, courts can make decisions in a simplified manner - issue an order for collection without holding a meeting with summoning the parties. Tax authorities can write off money to pay off the debt on the main payment, late fees and fines from an account or deposit if there are any funds in them, and also receive cash, for example, from a safe deposit box or through the sale of seized property. If the car owner ignored the court order and does not pay the tax authorities, and there were no funds in the current account, then the case will be transferred to the bailiffs, who collect debts in accordance with the procedural code. First, enforcement proceedings are opened, which is mandatory to inform the debtor by mail, by telephone or in person. If after 5 days the debt is not repaid, then the bailiff has the right to write off money from bank accounts, seize property, receive money through the employer, impose restrictive measures in the form of bans on traveling abroad, processing real estate transactions, registering vehicles, etc.
Shifted burden
If 5 years ago the reason for non-payment of transport tax was the absence of a receipt from the tax office (the post office did not send it), and the courts made decisions in favor of car owners, now such an argument is not accepted. With modern technologies, receiving a payment depends only on the wishes of the payer. Moreover, since 2015, vehicle owners must themselves inform the tax authorities that they have movable property at their disposal. This can be done in the “personal account” on the Federal Tax Service website, or by mailing a free-form application and copies of the purchase and sale agreement, PTS and SOP, or by giving them during a personal visit. Concealing this information leads to a fine of 20% of the unpaid tax amount in relation to the tax object hidden from inspectors.
Russian legislation also provides for criminal liability for unpaid tax (Article 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). The case is initiated if over three years the debt has exceeded 900,000 rubles and the share of unpaid taxes, fees, and insurance premiums exceeds 10% of the amounts payable. The prescribed punishment can be either a fine of 100,000-300,000 rubles, or forced labor for up to one year, or arrest for up to six months, or imprisonment for up to one year. Serving a sentence does not relieve the culprit from paying off the debt.
What about them, or Motor Vehicle Tax
Not all countries have a transport tax in its pure form. Often, revenues to the road fund are included in fuel excise taxes, income from toll roads (the same as ours), and insurance. In many countries - there are 9 countries in Europe (Denmark, Ireland, Cyprus, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal and Finland) - the owner pays for owning a car when purchasing or registering it, and sometimes this amount is comparable to the cost of the car. For example, in Denmark, the purchase tax, depending on the price of the car and its environmental class, ranges from 105 to 180%. In Israel, the total tax, including VAT, reaches 117% of the nominal value of the car. In Turkey, in addition to VAT 18%, you need to pay a progressive tax (37% - for engines up to 1.6 l, 80% - from 1.6 to 2.0 l, 130% - more than 2.0 l), as well as local luxury tax for a car costing more than 40,000 liras ($10,500) - from 45% to 168%. Six countries (Austria, Belgium, France, Romania, Slovenia and Spain) use a one-time payment system. For the calculation, the manufacturer's data specified in the model characteristics is used.
An example is a one-time environmental tax for vehicles that were first put into service (new cars) in France after January 1, 2008:
| CO2 emissions (g/km) | Tax rate (EUR) | |
| level ≤ 135 | 0 | |
| 135 ≤ level ≤ 140 | 100 | |
| 141 ≤ level ≤ 145 | 300 | |
| 146 ≤ level ≤ 150 | 400 | |
| 151 ≤ level ≤ 155 | 1000 | |
| 156 ≤ level ≤ 175 | 1500 | |
| 176 ≤ level ≤ 180 | 2000 | |
| 181 ≤ level ≤ 185 | 2600 | |
| 186 ≤ level ≤ 190 | 3000 | |
| 191 ≤ level ≤ 200 | 5000 | |
| 201 ≤ | 6000 | |
| 350 ≤ | Tax must be paid annually | |
Spain
In Spain, the tax on motor vehicles is municipal and is set by the local authorities of each region. Rates depend on the volume of fuel consumption and the environmental safety of the car and vary from one locality to another. Great differentiation has led to the fact that a fifth of the country's vehicles are registered in several small cities.
Germany
In Germany, transport tax is paid annually and consists of two parts. The first is calculated based on engine volume - for every 100 cm³ of a gasoline engine you need to pay €2 per year, for diesel engines the rate is €9.5 for the same 100 cm³, and if it does not have a particulate filter - €10.7. The second part depends on the mass of harmful emissions, or more precisely, on CO2. This value is set by the vehicle manufacturer and recorded in the first part of the technical data sheet (Zulassungsbescheinigung), point V.7. The tax-free base is 95 g/km, and for each additional gram emitted per 100 km you need to pay €2 per year.
Sweden
Sweden has two parallel vehicle taxation systems. The new system applies to passenger cars registered from model year 2006 and depends on vehicle type, fuel and CO2 emissions. The old system is based on vehicle type, fuel type and vehicle weight.
Vehicle taxation system in Sweden (Swedish krona /≈ruble):
| Vehicle type | Basic tax | Tax on every gram of CO2 exceeding 117 g | Additional tax per 100 kg over 900 kg |
| New system (since 2006) | |||
| Alternative fuel cars | 360/2530 | 10/70 | |
| Non-diesel cars | 360/2530 | 20/140 | |
| Diesel cars | 1088,8/7652 | 46,6/328 | |
| Old system | |||
| Non-diesel cars | 801/5629 | 188/1321 | |
| Diesel cars | 2068/14 534 | 508/3570 | |
Electromobility in Europe
Incentives for electric vehicles are now being implemented in many countries, causing the number to rise to 1.26 million by 2015 (data from the International Energy Agency OECD). Of course, owners of electric vehicles do not pay excise taxes on fuel, but they are also exempt from emissions taxes for the entire time or the next 5-10 years. For hybrids, the eco-tax does not apply if the total emissions by performance characteristics are below a certain standard established in a particular state. Also, in some European countries, the state returns part of the money for the purchase of a new electric car or hybrid. In France, there is a premium of €750 for emissions between 61 and 110g CO2 per km, €1,000 for 21 to 60g and €6,300 for emissions below 20g/km. In Germany, electric cars are exempt from tax for 10 years, and when purchasing an electric car, the state returns €4,000 and €3,000 for plug-in hybrids. In Greece, electric and hybrid vehicles are exempt from registration tax, luxury tax and luxury lifestyle tax. But the leaders in the purchase of electric vehicles, Denmark and Norway, have lost interest in these vehicles. After the Danish government first reduced, and from 2021 completely abolished compensation for the purchase of electric cars, their sales decreased by more than 60%. By 2021, “electric trains” will be equal in taxes to cars with internal combustion engines. In Norway, due to failures in fees for the restoration of roads, which owners of electric vehicles do not pay, and this is almost a fifth of the country’s vehicle fleet, bonuses from the state that were previously issued upon purchase have been cancelled. From 2021, you will have to pay 50% of the transport tax, and in 2018 the so-called “Tesla tax” will appear - the fee for electric cars weighing more than two tons will be from 7,000 to 70,000 Norwegian kroner (from 50 to 500 thousand rubles), depending on their characteristics.
USA
In the US, the transport tax is included in the price of fuel - 18.4 cents per gallon (3.78 liters) for gasoline and 24.4 cents for diesel fuel go to the federal budget, and from 18 to 60 cents to local ones. The smallest fuel surcharge is in Alaska at 12.24 cents, while the largest is in Pennsylvania at 58.2 cents for gasoline and 74.7 for diesel. But 5,000 volunteers in Oregon and trucks in Illinois pay a VMT tax (Vehicle Miles Traveled): 1.5 cents are charged per mile, the distance is monitored by GPS trackers. The system works by analogy with our “Plato”, but, despite the positive effect proven over 10 years of the project’s existence in Oregon (collections from mileage exceed excise taxes by 20%), VMT is not being introduced everywhere due to the threat to “privacy” .
Japan
In Japan, the annual vehicle tax depends on the vehicle's engine size (for cars), its weight (for trucks) and passenger capacity (for buses). Quite a small expense compared to the fees for mandatory parking (in Tokyo, rent can reach up to $500 per month), mandatory insurance (approximately $300), and technical inspection, which becomes mandatory every year for cars older than two years ($500–$2,000) and a one-time payment when purchasing a car in the amount of 5% of its cost. If the vehicle meets the standard for improving fuel efficiency by 20%, as well as the standard for reducing emissions up to 75%, then the owner will receive a refund of ¥300,000 ($2,600) upon purchase. If fuel efficiency is only 10%, then ¥150,000 ($1,300) will be compensated.
| Engine capacity | Regular car tax | |
| Less than 1.0 l | ¥ 29 500 / $259 | |
| 1.0–1.5 l | ¥ 34,500 / $303 | |
| 1.5–2.0 l | ¥ 39,500 / $347 | |
| 2.0–2.5 l | ¥ 45,000 / $395 | |
| 2.5–3.0 l | ¥ 51,000 / $448 | |
| 3.0–3.5 l | ¥ 58,000 / $509 | |
| 3.5–4.0 l | ¥ 66,500 / $584 | |
| 4.0–4.5 l | ¥ 76,500 / $672 | |
| 4.5–6.0 l | ¥ 88,000 / $777 | |
| More than 6 l | ¥ 111,000 / $975 | |
China
China's transport tax is relatively low, with the highest annual rate ranging from 60 to 5,400 yuan. But the bulk of the burden is borne by buyers of new cars: the tax on local small cars (up to 1.6 liters) is 11.7% of the cost, and the fee for an imported car depends on the size of its engine - from 1% for an engine less than 1.0 liters, 3% with a volume from 1.0 to 1.5 l, 5% - 1.5-2.0 l, 9% - 2.0-2.5 l, 12% - 2.5-3.0 l, 25% - 3.0–4.0 l, 40% - more than 4.0 l. In 2021, a luxury tax of 10% was introduced on imported cars costing more than 1.3 million yuan ($190,000).
China Domestic Transport Tax:
| Engine capacity | Annual tax amount, yuan/$ | |
| Less than 1.0 l | 60–360 / 9–54 | |
| 1.0–1.6 l | 300–540 /45–82 | |
| 1.6–2.0 l | 360-660 / 54–100 | |
| 2.0–2.5 l | 660–1200 / 100–181 | |
| 2.5–3.0 l | 1200–2400 / 181–362 | |
| 3.0–4.0 l | 2400–3600 / 362–544 | |
| More than 4.0 l | 3600–5400 / 544–816 | |
It turns out that in Russia the transport tax is not all that bad. But it could have been better. For several years now, attempts have been ongoing to shift the tax burden entirely to fuel excise taxes and introduce an environmental tax. The first change seems quite fair. Those who drive more, buy more fuel, cause more damage to the roads and, accordingly, pay more. Well, a summer resident who travels several hundred kilometers during the season does not have to pay for the whole year. The environmental fee will depend on the class of the vehicle: the higher it is, the less harm is done to the environment and, therefore, its owner must spend less money to compensate for this damage.
But the expenses of our state are such that excise taxes are raised and the transport tax is not cancelled. Most likely, this will not happen in the near future either, since the authorities are afraid of the emergence of “lost revenues,” that is, money that the state cannot receive in the form of fees and taxes. While all the holes in the budgets are being patched, a new method of paying transport tax may appear, proposed by the director of the Institute of Transport Economics and Transport Policy at the Higher School of Economics, Mikhail Blinkin: to differentiate payment rates depending on the mileage of the car, which can be tracked using the GLONASS system. Its technical capabilities will be ready for this within a year.
PS What to do if the tax office incorrectly calculated the transport tax?
In the last couple of years, tax officials have been sending receipts demanding payment of tax for cars for which the tax has already been paid, or for cars sold several years ago. The reason is either a lack of information in the database or an attempt to increase budget revenues. At the same time, car owners themselves will have to defend a smaller tax base. As mentioned above, this can be done by visiting the tax office in person. The inspector will need to present either payment receipts or a sales contract, depending on the situation. Another way of informing is through your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website, then the tax authorities themselves will check the data in the traffic police and recalculate the tax, which can take up to 50 days (20 for consideration of the application and 30 for processing). But there may also be a situation where even in the traffic police database the disputed car is still listed as yours. In this case, you need to contact the department to terminate the registration on the basis of the purchase and sale agreement and obtain a certificate stating that the disputed car does not belong to you.