Transport tax rates for cars in the Moscow region
Benefits for paying transport tax in the Moscow region
The procedure, rates and deadlines for paying transport tax in the Moscow region for 2020-2019 are determined by the Law of the Moscow Region dated November 16, 2002 No. 129/2002-OZ (with appropriate amendments and additions in force in 2021).
It applies to all cities in the region. The administrative center is Moscow. Large cities of the Moscow region: Balashikha, Bronnitsy, Dzerzhinsky, Dolgoprudny, Domodedovo, Dubna, Yegoryevsk, Zhukovsky, Zvenigorod, Ivanteevka, Kashira, Kolomna, Korolev, Kotelniki, Krasnoarmeysk, Lobnya, Losino-Petrovsky, Lytkarino, Mytishchi, Orekhovo-Zuevo, Podolsk , Protvino, Pushchino, Reutov, Roshal, Serpukhov, Fryazino, Khimki, Chernogolovka, Elektrogorsk.
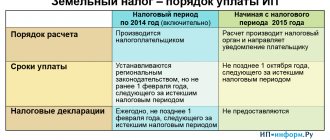
Procedure and deadlines for tax payment
Taxpayers-organizations of the Moscow region pay advance tax payments no later than the last day of the month following the expired reporting period.
Tax payable upon expiration of the tax period by taxpayers who are organizations is paid no later than March 28 of the year following the expired tax period. For more information about the procedure for paying taxes by legal entities, read the article at the link.
Deadline for payment of transport tax for legal entities in the Moscow region in 2021
- for the 1st quarter of 2021 - until April 30, 2020;
- for the 2nd quarter of 2021 (6 months) - until July 31, 2021;
- for the 3rd quarter of 2021 (9 months) - until October 31, 2021;
- for the 4th quarter and the whole of 2021 - March 28, 2020
For reference. Transport tax for 2021 is paid by organizations until March 28, 2021.
Taxpayers who are individuals (citizens of the Russian Federation) pay transport tax on a car on the basis of a tax notice sent by the tax authority. The amount of tax on a car is determined by the tax authorities on the basis of information submitted to the tax authorities by the authorities carrying out state registration of vehicles on the territory of the Russian Federation. Federation.
Deadline for payment of transport tax by individuals
Starting from 2021, the deadline for paying car tax for individuals has changed - now the tax must be paid before December 1 (previously, the payment deadline was set until October 1).
Individuals must pay transport tax in the general manner no later than December 1 of the year following the expired tax period. That is, the car tax for 2021 must be paid before December 1, 2021, for 2021 - before December 1, 2020, and for 2021 - before December 1, 2021. If December 1 is a non-working day, the payment deadline is postponed to the next working day.
The deadline for paying transport tax on a car in the Moscow region in 2021 is until December 1, 2021.
There are cases when the tax office does not send a tax notice about tax payment or it is not received for some reason. For information on what to do if the notification is not received, see the television program “Taxes” in the video below.
Transport tax rates in the Moscow region
Transport tax rates in the Moscow region are established accordingly depending on engine power, jet engine thrust or gross tonnage of vehicles, category of vehicles per one horsepower of a vehicle engine, one kilogram of jet engine thrust, one registered ton of a vehicle or unit of vehicle in the following sizes:
Transport tax rates in the Moscow region
Name of the object of taxation
| Tax rate (in rubles) for 2018-2019, 2020 | |
| Passenger cars with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 10 |
| - over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 34 |
| - over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 49 |
| - over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 75 |
| - over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 150 |
| Motorcycles and scooters with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 20 hp (up to 14.7 kW) inclusive | 9 |
| - over 20 hp up to 35 hp (over 14.7 kW to 25.74 kW) inclusive | 16 |
| - over 35 hp (over 25.74 kW) | 50 |
| Buses with the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture, up to 5 years inclusive, with engine power (for each horsepower): | |
| - up to 200 hp (up to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 27 |
| - over 200 hp (over 147.1 kW) | 56 |
| Buses with the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture, over 5 years, with engine power (for each horsepower): | |
| - up to 200 hp (up to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 50 |
| - over 200 hp (over 147.1 kW) | 100 |
| Trucks with the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture, up to 5 years inclusive, with engine power (for each horsepower): | |
| - up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 20 |
| - over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 25 |
| - over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 33 |
| - over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 45 |
| - over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 58 |
| Trucks with a number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture, over 5 years, with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 25 |
| - over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 40 |
| - over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 50 |
| - over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 65 |
| - over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 85 |
| Other self-propelled vehicles , pneumatic and tracked machines and mechanisms (with each horsepower) | 25 |
| Snowmobiles, motor sleighs with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 50 hp (up to 36.77 kW) inclusive | 25 |
| - over 50 hp (over 36.77 kW) | 50 |
| Boats, motor boats and other water vehicles with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 100 |
| - over 100 hp (over 73.55 kW) | 200 |
| Yachts and other sailing-motor vessels with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 200 |
| - over 100 hp (over 73.55 kW) | 400 |
| Jet skis with engine power (per horsepower): | |
| - up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 250 |
| - over 100 hp (over 73.55 kW) | 500 |
| Non-self-propelled (towed) ships for which the gross tonnage is determined (for each registered ton or gross tonnage unit if the gross tonnage is determined without specifying the dimension) | 200 |
| Airplanes, helicopters and other aircraft with engines (per horsepower) | 250 |
| Airplanes with jet engines (per kilogram of thrust) | 200 |
| Other water and air vehicles without engines (per vehicle unit) | 2000 |
In order to calculate the transport tax in the Moscow region yourself, you need to multiply the vehicle power (in hp) by the tax rate (second column of the table).
Please note that when collecting car tax, increased transport tax coefficients are applied to expensive cars costing more than three million rubles.
Attention: due to the fact that the final tax amount depends on the category and make of the car, its power, we do not recommend using online calculators. The most accurate calculation is achieved by simply multiplying the car's power by the tax rate (taking into account increasing factors for expensive cars).
Transport tax rates in the Moscow region
For a year
| Name of taxable object | Rate (RUB) for 2021 |
| Passenger cars | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 10 |
| over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 34 |
| over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 49 |
| over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 75 |
| over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 150 |
| Motorcycles and scooters | |
| up to 20 hp (up to 14.7 kW) inclusive | 9 |
| over 20 hp up to 35 hp (over 14.7 kW to 25.74 kW) inclusive | 16 |
| over 35 hp (over 25.74 kW) | 50 |
| Buses with the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture, up to 5 years inclusive | |
| up to 200 hp (up to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 27 |
| over 200 hp (over 147.1 kW) | 56 |
| Buses with the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture exceeding 5 years | |
| up to 200 hp (up to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 50 |
| over 200 hp (over 147.1 kW) | 100 |
| Trucks with the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture, up to 5 years inclusive | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 20 |
| over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 25 |
| over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 33 |
| over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 45 |
| over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 58 |
| Trucks with a number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture exceeding 5 years | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 25 |
| over 100 hp up to 150 hp (over 73.55 kW to 110.33 kW) inclusive | 40 |
| over 150 hp up to 200 hp (over 110.33 kW to 147.1 kW) inclusive | 50 |
| over 200 hp up to 250 hp (over 147.1 kW to 183.9 kW) inclusive | 65 |
| over 250 hp (over 183.9 kW) | 85 |
| Other self-propelled vehicles, pneumatic and tracked machines and mechanisms | 25 |
| Snowmobiles, motor sleighs | |
| up to 50 hp (up to 36.77 kW) inclusive | 25 |
| over 50 hp (over 36.77 kW) | 50 |
| Boats, motor boats and other water vehicles | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 100 |
| over 100 hp (over 73.55 kW) | 200 |
| Yachts and other motor-sailing vessels | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 200 |
| over 100 hp (over 73.55 kW) | 400 |
| Jet skis | |
| up to 100 hp (up to 73.55 kW) inclusive | 250 |
| over 100 hp (over 73.55 kW) | 500 |
| Non-self-propelled (towed) ships for which gross tonnage is determined (from each registered ton of gross tonnage) | 200 |
| Airplanes, helicopters and other aircraft with engines (per horsepower) | 250 |
| Airplanes with jet engines (per kilogram of thrust) | 200 |
| Other water and air vehicles without engines (per vehicle unit) | 2000 |
FILES
Note to the table: the values in the Moscow region are given for 2021, 2021, 2021, 2021, 2021, 2021. To select rates for a specific year, use the selector. These rates are applied in the cities: Aprelevka, Balashikha, Bronnitsy, Vidnoye, Volokolamsk, Voskresensk, Golitsyno, Dzerzhinsky, Dmitrov, Dolgoprudny, Domodedovo, Dubna, Yegoryevsk, Zheleznodorozhny, Zhukovsky, Ivanteevka, Istra, Kashira, Klimovsk, Klin, Kolomna, Korolev, Kotelniki, Krasnoarmeysk, Krasnogorsk, Krasnozavodsk, Lobnya, Losino-Petrovsky, Lukhovitsy, Lytkarino, Lyubertsy, Mozhaisk, Mytishchi, Naro-Fominsk, Noginsk, Odintsovo, Lakes, Orekhovo-Zuevo, Pavlovsky Posad, Podolsk, Pushkino, Pushchino, Ramenskoye, Reutov , Sergiev Posad, Serpukhov, Solnechnogorsk, Stupino, Fryazino, Khimki, Chernogolovka, Chekhov, Shatura, Shcherbinka, Shchelkovo, Elektrogorsk, Elektrostal, Yakhroma and other settlements of the Moscow region.
In the Moscow region there are fewer registered transport tax payers than in Moscow. However, more than in other regions of the country - 2 million 150 thousand citizens and legal entities. All of them make payments to the budget, guided by the requirements of Law No. 33 of July 9, 2008.
What to pay attention to
Contrary to expectations, only the interest rate will be increased, and not the entire tax system. It should also be taken into account that in different areas of the region, collection percentages may differ significantly from each other. This is due to the lack of a unified regulatory mechanism. It is important to understand that if a car is registered, say, in Saratov, but is operated mostly in Moscow, then the tax will be charged in accordance with Saratov tariffs.
Basic Concepts
Transport tax is a gratuitous payment to car owners for the operation of vehicles, which is mandatory. The amount of tax is established in accordance with Chapter 28 of the Tax Code by regional bodies of the legislative assembly.
They determine:
Comprehensive information on transport tax rates in the Moscow region in 2021 can be found on the tax service website.
The object of taxation is any vehicle (water, air, land), the registration of which was carried out in accordance with the procedure established by federal law.
I would like to clarify the situation around vehicles that, due to certain circumstances, are not in use (theft, faulty technical condition, etc.). The fact of registration of a car or other transport is the basis for charging a tax fee.
As long as the vehicle is registered, its owner is obliged to repay the debt in a timely manner. The exception is stolen cars, but only if the crime is confirmed. Significant evidence is a document issued by the relevant law enforcement agencies.
The method of calculating the tax base directly depends on the type of transport:
In accordance with legislative norms, payers are the persons to whom the objects of transport taxation are registered. This is stated in Article 357 of the Tax Code, however, this statement is controversial, since when interpreted literally, the mentioned article does not indicate the exact circle of taxpayers. There is no other law obliging people to pay taxes. It turns out the following: this tax fee is not established by domestic legislation, which indicates that its repayment is not obligatory.
Contrary to the provision of Article 357 of the Tax Code, the circle of taxpayers remains uncertain to this day, since vehicle registration is supervised by the Ministry of Internal Affairs. This fact indicates that the circle of taxpayers is determined by the executive branch, not the legislative branch. This is a direct contradiction to Article 57 of the Russian Constitution.
As one of the options for legal evasion of transport tax, you can send a well-written letter to the Federal Tax Service at the place of permanent registration, in which you must indicate this legislative oversight, referring to the Constitution of the Russian Federation, as well as the Civil and Tax Codes. In addition, at the end of the appeal, you should request that this letter be attached to the package of other documents when transferring the case to court.
The tax period for transport fees is a calendar year - 365 days. This is indicated in provision 360 of Article NK. Reporting periods: 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarters.
Payment deadline: November 1 of the year following the expired tax period. The fee is paid on the basis of the previously received notification by the payer (no later than 01.10).
Basics of calculating payments
All the details of the transport tax are indicated in Article 28 of the Tax Code. In accordance with its content, taxpayers are defined as legal entities and individuals in whose names vehicles are registered.
It is important to understand that ownership is not a determining factor, unlike the fact of registration. For example: a car may belong to a commercial organization on the basis of a leasing agreement. In this case, the vehicle is registered to the company, and the leasing company remains the owner.
Both self-propelled and towed vehicles are subject to transport taxation. For the most part, this point affects motor transport. It is important to know the list of cars to which this law does not apply.
These include:
The basic rates for transport tax are established and described in Article 28 of the Tax Code of Russia.
The amount of tax depends on the car. The calculation is made by multiplying the engine power by the interest rate. You can calculate it yourself using a calculator.
When registering a car or deregistering it during a billing year, a coefficient is applied that reduces the tax levy in proportion to the proportion of months of vehicle ownership during the year. A full month is considered to be one in which the car was purchased before the 15th or was sold out after the 15th.
Regional authorities are empowered to make the following amendments to the Tax Code at the local level:
These powers determine the importance of knowledge of Article 28 of the Tax Code and regional laws on transport tax for taxpayers. Private enterprises that have vehicles on their balance sheets are responsible for calculating the tax collection on their own. For individuals, this procedure is carried out by the tax service.
Legal entities have the right to repay debt through advance payments, or on the basis of an annual declaration through the CBC. For individuals there is only a one-time annual payment for the past period.
What does the tariff depend on?
As mentioned earlier, transport tax rates vary significantly depending on the region of registration of the car.
In addition to motorists, owners of such vehicles as:
Specific rates are established within the framework of the law by decision of local authorities and depend on such indicators as the welfare of citizens in a certain region and the total number of vehicles registered.
The key factor when calculating the tax fee is the engine power and the category of vehicle. The more powerful the engine, the more expensive it is to maintain. This principle helps motivate citizens to purchase more environmentally friendly cars.
In addition, an important factor is also the so-called increasing coefficient provided for cars worth more than 3 million rubles. Like a number of other factors, it is calculated purely individually and largely depends on the region of registration.
Nuances of forming the amount
The Federal Tax Service calculates the amount of transport tax for individuals taking into account all three reporting periods. The final amount is obtained by multiplying the regional rate by the tax base. For legal entities the procedure is identical. Representatives of commercial organizations must calculate the tax using the same formula independently.
The deadline for submitting the transport tax return for 2021 is indicated here.
Essentially, the tax base is a measure of each transport:
Perhaps soon the following aspects will also be taken into account when calculating tax:
This project is already being considered by the relevant legislative structures.
Betting overview
The table below will allow you to familiarize yourself with the size of tax rates in the Moscow region:
Tax calculation and payment deadlines for organizations
In the Moscow region, as in the vast majority of regions, taxpayers from legal entities make advance payments based on quarterly results. Tax for the entire year is paid in full at the end of the year. The payment deadline is March 28. When calculating, the amount is rounded to the nearest ruble according to mathematical rules: if there are more than 50 kopecks in the amount, they are paid as one ruble, less - kopecks are not taken into account.
Deadline for payment of transport tax for legal entities in 2021:
- for 2021 - no later than March 28, 2020
- for the 1st quarter of 2021 - no later than April 30, 2020
- for the 2nd quarter of 2021 (6 months) - no later than July 31, 2021
- for the 3rd quarter of 2021 (9 months) - no later than October 31, 2021
- for the 4th quarter and the whole of 2021 - no later than March 28, 2021
Table with increasing coefficients for 2020
The increasing coefficient, or the so-called “luxury tax,” was introduced in 2014 and applies exclusively to owners of expensive cars.
That is, when calculating the final amount, it is taken into account exclusively by the owners of cars whose value is more than 3 million rubles. The list of vehicles subject to the increased tax can be seen on the website of the Ministry of Industry and Trade.
The list is regularly updated as the number of expensive cars on Russian roads is growing rapidly.
The size of the increasing coefficient depends on the cost of the car and the year of its manufacture. Based on these characteristics, the car owner can independently determine his luxury tax using the numbers from the table:
| Cost, million rubles | Number of years in operation (counting from the year of manufacture) | Coefficient |
| 3-5 | Until 3 | 1,1 |
| 5-10 | 3-5 | 2 |
| 10-15 | 5-10 | 3 |
| 15+ | 10-20 | 3 |
When calculating the age of a car, it is necessary to take into account both the year of its manufacture and the period for which the tax is paid.
Important! The increasing factor is applied only if all conditions are met. The absence of a car on the website of the Ministry of Industry and Trade or its operation exceeding the number of years allows you to avoid an increased payment, despite the cost of the car.
Rules and deadlines for paying taxes for individuals
Citizens also do not make advance payments, but they do not need to make payments themselves. All the necessary information for paying taxes for the past year is received by residents of the region in the form of notifications from the territorial divisions of the Federal Tax Service. Letters are sent to the place of registration of the individual. If the place of residence has been changed, and due to circumstances the tax authority has not been notified about this, you can use the taxpayer’s Personal Account on the tax service website.
Individuals are required to pay invoices no later than December 1 of the same year in which the notification is received. Failure to pay taxes on time will result in a fine.
Deadline for payment of transport tax for individuals in 2021:
- for 2021 - no later than December 1, 2020
- for 2021 - no later than December 1, 2021
Please take into account: in accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 6.1. Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if the last day of the period falls on a weekend, then the day of expiration of the period is considered to be the next working day following it.
Procedure
Here are all the instructions on the procedure for applying for benefits for your personal transport:
- Prepare an application form online.
- Provide the service with all necessary documents. It is better to find out about them by calling the service in advance. Although the main documents are indicated in the presented material.
- Contact the Federal Tax Service and submit an application. This can be done both on the Internet and in real life.
- Get your result; in case of refusal, they will simply write to you that you do not fit the required category, and if you successfully receive the benefit, you will be given a document providing the benefit.
Benefits for individuals
A number of residents of the region may qualify for transport tax benefits:
- heroes of the USSR, Russian Federation, as well as full holders of the Order of Glory;
- veterans and disabled combat veterans, incl. WWII;
- disabled people (disability group 1, 2);
- citizens who were captured by the Nazis as minors during WWII;
- victims of radiation as a result of the Chernobyl accident;
- guardian of a disabled child, one of the parents in a large family;
- victims of radiation during the accident at Mayak, as well as those exposed to radiation during testing at the Semipalatinsk test site;
- citizens who were at risk during nuclear weapons testing, as well as those who suffered from radiation sickness during such tests;
- guardian of an incapacitated citizen;
- owners of vehicles with engines less than 70 hp.
FILESOpen table of transport tax benefits in the Moscow region
It is important to know
Transport tax is paid for a vehicle registered with the traffic police. And the owner specified in the vehicle passport (PTS) pays the tax.
To receive transport tax benefits, you must independently provide the tax office with documents confirming that a citizen or organization belongs to a preferential category.
You will learn the tax rates and more detailed information from the Moscow Region Law N 129/2002-OZ “On transport tax in the Moscow Region” (03/05/2020)
Your opinion
Please rate how satisfied you are with the transport tax benefits in the Moscow region.
How to pay taxes online
Transport tax is regional - this means that benefits for it can be established both by Chapter 28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation on transport tax.
In the Moscow Region, transport tax benefits are established by the Law of the Moscow Region dated November 24, 2004 No. 151/2004-OZ “On preferential taxation in the Moscow Region”, according to which: