An employer may enter into various types of employment contracts, depending on the specifics of the employment or the nature of the work. When choosing the type of contract, it is important to follow a number of rules so as not to come to the attention of labor or tax inspectors.
Types of employment contracts according to their duration are divided into open-ended - for an indefinite period, and fixed-term - for a certain period of not more than five years.
Legislative justification for fixed-term contracts
The word “urgent” in the definition of this type of contract does not mean any additional speed of its execution; it comes not from “urgency”, but from “deadline”. This is how it is declared to differ from contracts that are concluded for an indefinite period.
In the usual form of employment contractual relations, the start date of work is precisely known, but the time of separation and the reasons for dismissal cannot yet be determined. But when the last condition is known to both parties, that is, both the employee and the employer know when they will terminate their cooperation agreement, it is advisable to formalize the relationship with a predetermined period - a fixed-term employment contract .
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation calls an employment contract mandatory when formalizing the “employee-employer” relationship (Article 56 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and the term is its essential condition. Options when an employer gives an employee temporary employment are defined in Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Their determining factor is an important circumstance: a fixed-term employment contract is legal only when, for objective reasons, it is impossible to conclude a permanent one.
NOTE! To conclude such an agreement, the will of the employer and even the consent of the employee are not enough; its execution must comply with the grounds given in the legislation.
Otherwise, if you have to deal with it in court, a fixed-term contract concluded on an illegitimate basis will be recognized as unlimited.
Working time and rest time
4.1. The employee is assigned [a five-day work week with two days off/a six-day work week with one day off/a work week with days off on a sliding schedule/a part-time work week].
4.2. The duration of daily work/part-time work is [value] hours.
4.3. The start and end times of work, the time of the break and its duration [in the case of providing days off on a sliding schedule - alternating working and non-working days] are established by the internal labor regulations.
4.4. The employee is granted annual basic paid leave of [value] calendar days.
4.5. The employee is granted an additional annual paid leave of [value] calendar days [indicate the basis for providing additional leave].
4.6. For family reasons and other valid reasons, the Employee, upon his written application, may be granted leave without pay, the duration of which is determined by agreement between the Employee and the Employer.
back to contents
The attractiveness of fixed-term employment contracts
The party that benefits most from entering into a fixed-term rather than an open-ended contract is the employer. The reasons are obvious:
- an employee on a temporary basis is more manageable;
- It is easier to motivate a “conscript”, since the extension of cooperation with him directly depends on the management;
- it is much easier to carry out the dismissal procedure;
- an employee dismissed at the end of his term cannot challenge such dismissal;
- In this way, you can get rid of any categories of employees, even the most socially protected ones.
For workers, as a rule, permanent employment is preferable, providing certain guarantees and confidence in their future. Domestic legislation and the International Labor Convention (ILO) adhere to the same position, seeking to minimize the number of workers employed on a temporary basis.
Procedure for filling out the document
The algorithm for filling out job information when applying is as follows:
- At the top, a continuous entry is made with the full name of the organization, or its stamp is placed.
- A line below, in the first column, enter the serial number of the entry.
- In the second column, divided into 3 columns, the date of employment is entered.
- The third contains information about which department and position the employee is being hired for. If the company has no divisions, its abbreviated name is indicated.
- The fourth contains the details of the order for appointment to a position (read more about how to draw up an order and what are the grounds for concluding a contract here).
ATTENTION : The date should not correspond to the time the order was issued or the contract was concluded, but to the first working day.
It is unacceptable to fill out a work book arbitrarily; the regulations for persons who have the right to make an entry comply with the law . The following are authorized to enter it:
- The head of the organization or individual entrepreneur - personally.
- An HR department employee who has these powers included in his functional responsibilities.
- A person from among the employees to whom this duty is imposed by a special order.
The recorded information must be endorsed by the person filling out the book; no other identification is required, including no stamp.
Features of a fixed-term employment contract
The determining factor in the choice in favor of the urgency of contractual relations is an important circumstance: a fixed-term employment contract is legal only when, for objective reasons, it is impossible to conclude a permanent one.
This reason must be indicated in the text of the contract.
The validity period of such an agreement cannot exceed 5 years. If the document does not indicate specific terms or an event that terminates the contractual relationship, it will automatically be considered a contract with an indefinite period. Likewise, if a period of more than five years is specified.
Termination of a fixed-term contract must be indicated in the text. This is possible in two ways:
- indicating a specific date when the contract will be terminated;
- designation of an event, the occurrence of which terminates the validity of the fixed-term contract.
The arrival of the final date does not mean immediate termination of work: the employee must be notified in writing 3 days in advance of the upcoming dismissal in accordance with its expiration. If this is not done, the dismissal can be challenged.
In the second case, prior notification is impossible, since the occurrence of an event automatically terminates the fixed-term contract, as provided for by its terms. Most often, such an event is the return to work of the main employee, instead of whom a temporary one was hired.
Responsibility of the parties
6.1. In case of failure or improper performance by the Employee of his duties specified in this employment contract and job description, violation of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as causing material damage to the Employer, he bears disciplinary, financial and other liability in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
6.2. The Employer bears financial and other liability to the Employee in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
back to contents
With whom can you enter into fixed-term employment contracts?
Employers formalize such relationships with those employees whose nature of work does not make it possible to determine the duration of the working relationship or, on the contrary, quite clearly indicates their end. Such categories of personnel include, for example, the following:
- seasonal workers;
- employees hired to complete a specific type of work by a specific date;
- employees who were sent to work abroad or to another branch of the organization;
- specialists hired from outside to perform work not provided for by the organization’s core activities;
- teachers who can work in the corresponding position only for the duration of the competition;
- replacing an employee on long-term sick leave or maternity leave, etc.
Final provisions
7.1. Disputes between the Parties arising during the execution of this employment contract are considered in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
7.2. In all other respects that are not provided for in this employment contract, the Parties are guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation governing labor relations.
7.3. The employment contract is concluded in writing, drawn up in two copies, each of which has equal legal force.
7.4. All changes and additions to this employment contract are formalized by a bilateral written agreement.
7.5. This employment contract may be terminated on the grounds provided for by current labor legislation.
back to contents
Transfer to a fixed-term employment contract from an open-ended one
As a rule, employees work under an open-ended contract. However, sometimes there is a need to transfer to a fixed-term contract. This can be done, but the procedure must comply with all the rules.
Reasons for transferring to a fixed-term employment contract
An employee can only be transferred to a fixed-term contract if there are sufficient grounds for doing so. If there are no such grounds, the agreement will be considered unlimited. An employer must not enter into fixed-term agreements for the purpose of deviating from providing employees with rights and guarantees. Let's look at the reasons why an employer makes a transfer:
- The employee is appointed to replace the temporarily absent employee. The latter retains his place of work.
- An employee is sent to temporary work abroad.
- The work involves a temporary expansion of production.
- The employee has a disability.
That is, transfer to a fixed-term contract is relevant in cases where the employee’s status changes. For example, he developed health restrictions.
Is it legal to transfer to a fixed-term contract?
The issue of the legality of transferring an employee to a fixed-term agreement is extremely controversial. If the employer initially signed the employee up to an open-ended contract, he must ensure compliance with the terms of this agreement. That is, the worker receives the right to work for an unlimited time.
The contract can be terminated only on the basis of the clauses established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For this reason, transferring an employee from an open-ended to a fixed-term contract is not legal. The employer cannot, for the purpose of transfer, simply enter into an additional agreement. The employee, if desired, can easily challenge this document.
Another significant mistake is drawing up a new agreement while the previous agreement is still in effect. According to the law, if two documents apply to an employee, the document with the most favorable conditions will be valid. In this case, the most advantageous would be an open-ended contract, since it provides a larger list of rights.
IMPORTANT! Many employers believe that entering into a new agreement automatically cancels the previous agreement. However, this is a wrong position. In order for only one act to be in effect, the old act must be legally repealed.
How to legally transfer a person to a fixed-term contract?
The only legal way to transfer an employee to a fixed-term contract is to terminate the previous agreement and draw up a new one. However, you need to take into account all the disadvantages of this path:
- The need to pay compensation for vacation that was not used.
- The accrual of length of service for vacation registration begins anew. In order for an employee to be able to legally go on vacation, he needs to work for 6 months. For example, an employee under the first open-ended contract worked for 5 months. That is, after a month he can go on vacation. However, if the previous agreement is terminated, another agreement is drawn up, the vacation will be legal only after 6 months.
- You will have to draw up cadastral documentation for the employee as a newly hired employee.
The legislation does not provide for a simplified procedure for dismissing an employee and rehiring him. The listed difficulties are related to preventing abuse.
Procedure for drawing up a new employment contract
Let's consider the legal procedure for transferring an employee to a fixed-term contract by drawing up a new agreement:
- The employer conducts a conversation with the employee and offers him new working conditions. Explains the translation scheme.
- The employee resigns at his own request or by agreement of the parties.
- A new employment contract with a limited duration is immediately drawn up. The manager issues an order to hire a person.
- The relevant information is entered into the work book.
This method of transfer is more complicated, but it is legal.
Rights and responsibilities of an employee
2.1. The employee has the right to:
— conclusion, amendment and termination of an employment contract in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- providing him with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— a workplace that meets state regulatory requirements for labor protection and the conditions provided for by the collective agreement [if any];
— timely and full payment of wages in accordance with their qualifications, complexity of work, quantity and quality of work performed;
— rest provided by the establishment of normal working hours, reduced working hours for certain professions and categories of workers, the provision of weekly days off, non-working holidays, paid annual leave;
— complete reliable information about working conditions and labor protection requirements in the workplace;
— training and additional professional education in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— association, including the right to create trade unions and join them to protect their labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests;
— participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, if any, and by the collective agreement;
— conducting collective negotiations and concluding collective agreements and agreements through their representatives, as well as information on the implementation of the collective agreement and agreements;
— protection of one’s labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests by all means not prohibited by law;
— resolution of individual and collective labor disputes, including the right to strike, in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- compensation for harm caused to him in connection with the performance of his job duties, and compensation for moral damage in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— compulsory social insurance in cases provided for by federal laws;
— [other rights provided for by the current labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations].
2.2. The employee is obliged:
— conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by the employment contract;
— comply with internal labor regulations;
— maintain labor discipline;
— comply with established labor standards;
— comply with labor protection and occupational safety requirements;
— take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees;
— immediately inform the Employer or immediate supervisor about the occurrence of a situation that poses a threat to the life and health of people, the safety of the Employer’s property (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property);
— [other responsibilities provided for by the current labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreement, local regulations].
back to contents
Legitimate reasons for urgency
The law provides for two legitimate reasons for concluding a fixed-term rather than an open-ended employment contract:
- Relationships are concluded strictly for a certain period, based on the nature of the work to be done and the accompanying circumstances.
- The urgency of labor relations is determined by the agreement of the parties in cases where this does not contradict current legislation.
The labor legislation of the Russian Federation (Part 1 of Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) allows the conclusion of fixed-term contracts arising from the nature of the work in the following circumstances:
- for a time when a full-time employee is absent from his workplace for objective reasons, whose workplace must be retained by law;
- the upcoming work will not take more than 2 months;
- to provide seasonal labor;
- for foreign forms of work;
- performing actions necessary for the company, but not related to its main activities (for example, installation work, repairs, reconstruction, etc.);
- work associated with a limited (usually up to a year) time period, such as expanding activities, increasing capacity, volumes, etc.;
- the company is specifically created for a short existence, providing a limited time for performing specific work;
- labor related to vocational training and internship of employees;
- election to a working elective body for a certain period;
- assignment to community service;
- additional cases provided for by Federal legislation (existing and possible to be adopted in the future).
A fixed-term employment contract, by agreement of the parties, can be concluded only on a limited list of grounds:
- the employer is a small business representative;
- employee - pensioner;
- a medical employee is allowed only temporary employment;
- work in the Far North and other equivalent territories;
- when elected through a competition to fill a vacant position;
- urgent work aimed at preventing and/or eliminating the consequences of emergency situations;
- with management, deputies and chief accountants of organizations;
- with creative workers (in accordance with the list of similar positions);
- with pupils or full-time students;
- with part-time workers;
- with those working on watercraft registered in the Russian International Register of Ships;
- other grounds consistent with federal laws (current and future).
Employer, remember:
- You cannot conclude a fixed-term employment contract on grounds not specified in Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- when dismissing an employee after the expiration of a fixed-term contract, do not forget to notify him in writing 3 days in advance;
- did not warn about dismissal - the contract will become indefinite.
Terms of payment
5.1. A piece-rate wage system is established for the Employee.
5.2. Salary is calculated based on [specify calculation method].
5.3. Wages are paid to the Employee [indicate specific dates of the calendar month]./Wages are paid to the Employee at least every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations.
5.4. When performing work outside the normal working hours, at night, on weekends and non-working holidays, when combining professions (positions), when performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee, the Employee is paid appropriate additional payments in the manner and amount established by the collective agreement and local regulations.
5.5. During the period of validity of this employment contract, the Employee is subject to all guarantees and compensation provided for by the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
back to contents
Features of calculating compensation for vacation
By law, every employed person is entitled to annual leave with vacation pay. If in the process of work not all days of a given rest are used by a person, then he is entitled to compensation.
Compensation payments are assigned to a fixed-term employee upon dismissal, regardless of the reason for termination of the contract. Even if an employee is dismissed for violations, the manager is obliged to pay for unused vacation days.
When dismissing, it is important to calculate how many unspent days the employee has left and pay compensation for these days based on average earnings for the annual period (or actual work time if the contract term is less than a year).
Online calculator for calculating average daily earnings.
Number of vacation days accrued for each full month worked in the organization:
- 2 working days – for seasonal fixed-term workers (Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- 2 working days – for a contract term of up to 2 months (Article 291 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- at least 2.33 calendar days (provided that there are 28 days per year) - in other cases.
A month in which half or more days are worked is considered full. Calculation of compensation upon dismissal for less than a month.
Important! The calculation of compensation depends on whether the vacation is provided in calendar or working days. The formulas for calculating average earnings in these cases are different and are prescribed in clauses 10 and 11 of Regulation No. 922.
In case of dismissal under a fixed-term contract, leave in working days is granted only in two cases: when a person is hired for the duration of the season, and when the term of the employment relationship is up to 2 months.
In other cases, rest is provided in calendar days.
Calculation of compensation for vacation provided in calendar and working days:
| Step 1 | Vacation period is calculated | Time worked from the date of employment to the day of dismissal, giving the right to leave (expressed in full months). | |
| Step 2 | The number of unused vacation days is counted. | The total number of vacation days allotted for the vacation period is determined, after which the days already taken off (if any) are taken away. Formula for calculation: Unused vacation days = (Annual vacation duration / 12) * Vacation experience – Used vacation days. | |
| Step 3 | The settlement period for compensation is determined | If the contract term is one year or more, then 12 months are taken before the month of termination of the fixed-term contract. If the period is less than a year, then the period of work in the organization is taken: from the date of employment to the last day of the month preceding the month of dismissal. If worked less than a month, then the actual working time. | |
| Step 4 | The total earnings accrued for the billing period are calculated | There is no need to take into account vacation pay, business trips, sick leave, various social benefits, and financial assistance. Only payments related to wages are taken. | |
| Step 5 | Time worked is counted | When granting leave in calendar days: A month has been fully worked if the employee went to work on all working days. If there were business trips, sick leave, vacations, time off, absenteeism, then the month is incomplete; the amount of time worked is calculated separately for it. Formulas for calculation: Worked for the billing period = Work days in full months + Work days in partial months. Working days in a full month = 29.3. Work days in an incomplete month = Actual work. cal days * 29.3 / Cal days in a month. | When granting leave in working days: The number of working days according to the six-day working week calendar for the time worked is taken. Days falling on business trips, sick leave, vacations, time off, and absenteeism are excluded. |
| Step 6 | The average earnings for one day of the billing period are calculated | Formula for calculation: Average salary. for 1 day = Total earnings / Days worked. | Formula for calculation: Average salary. for 1 day = Total earnings / (Number of working days for a 6-day work week - Excluded days) |
| Step 7 | The amount of compensation for vacation is determined | Formula for calculation: Compensation = Average salary. for 1 day * Number of unused vacation days. | |
Personal income tax of 13% is withheld from the accrued compensation and contributions are calculated at a general rate of 30%.
Calculation example if worked less than 1 month
If half or more days (15 or more) are worked in a month, then the employee is entitled to leave in the amount of:
- 2 working days – for an employment contract term of up to 2 months;
- 2.33 calendar days – for a period of more than 2 months.
If less than half a month is worked, no compensation is due.
When determining whether an employee has worked half the month or not, you need to take not the calendar month, but the month worked - from the date of employment to the date of dismissal.
Examples:
- The person was hired on October 18, 2021, and quits on November 5, 2021. In this case, he worked 19 days in the organization, which means he is entitled to 1 full month of vacation.
- The person was hired on October 23, 2021, and quits on November 3, 2021. In this case, 12 days worked - that’s less than half, and no vacation is allowed.
Input data for example:
An employment contract was concluded with Petrov for 2 months. The date of conclusion of the fixed-term agreement is September 10, 2021.
On September 30, 2021, Petrov retires early of his own free will.
For Petrov, a monthly salary was set at 30,000 rubles. How to calculate the amount of his compensation for vacation?
Calculation:
Petrov worked: from 09/10/2019 to 09/30/2019 inclusive - this is 21 calendar days, which is rounded up to a full month. Since the term of the employment contract is 2 months, Petrov is entitled to 2 days of vacation for the time worked.
The period for calculation (according to clause 7 of Regulation No. 922) is from 09.10.2019 to 09.30.2019, total earnings during this time = 21,000 rubles.
Average earnings are calculated taking into account clause 11 of Regulation No. 922, since vacation is provided in working days.
It is necessary to determine the number of working days according to the calendar for a six-day week. In the period from September 10 to September 30, 2021, this is 18 days.
Average daily earnings for compensation = 21,000 / 18 = 1166.67 rubles.
Vacation compensation = 1166.67 * 2 = 2333.33 rubles.
Example, if worked up to 2 months
A fixed-term employee who has worked for 2 months in an organization has the right to receive:
- 4 working days of vacation – if the term of his employment contract is up to 2 months;
- 4.66 calendar days of vacation - if the period is more than 2 months.
Input data for example:
Employee Petrov was hired under a fixed-term employment contract for 2 months - from 09/01/2019 to 10/31/2019. After this time, Petrov is fired.
His total salary for 2 months was 45,000 rubles. All their days are fully worked out.
It is necessary to calculate the amount of compensation that is due upon dismissal for vacation.
Calculation:
Since the contract period is 2 months, Petrova is entitled to 4 working days of vacation.
The billing period is from 09/01/2019 to 10/31/2019. Since the day of dismissal is the last day of the month, it is also included in the billing period.
For average daily earnings, the number of working days according to the calendar for a six-day period is calculated; for the period from 09/01/2019 to 10/31/2019 - this is 52 days.
Average daily earnings = 45,000 / 52 = 865.38 rubles.
Compensation = 865.38 * 4 = 3461.54 rubles.
Example, if worked for more than 2 months
Initial data:
Potapov was hired under a fixed-term employment contract for a period of 6 months: from July 10, 2021 to January 9, 2021.
From September 10 to September 16, 2021, Potapov was on sick leave.
His total earnings = 138,000 rubles. (salary for January 2020 and sick leave are not included in this amount).
Potapov did not go on vacation.
It is necessary to calculate what compensation should be paid to him upon dismissal.
Calculation:
Potapov worked for 6 months, for each he is entitled to 2.33 cal days of vacation. Total = 2.33 * 6 = 14 days for compensation upon termination of a fixed-term contract.
The billing period is from 07/10/2019 to 12/31/2019.
Days worked = 5*29.3 + (23*29.3/30) = 169 days.
Average daily earnings = 138,000 / 169 = 816.57 rubles.
Compensation = 816.57 * 14 = 11,431.95 rubles.
Example for a seasonal worker
Initial data:
Petrov was accepted under a fixed-term employment contract for the season as a waiter in a summer cafe for the period from 05/01/2019 to 09/30/2019.
On September 30, 2021, Petrov resigns.
Total earnings during work are 120,000 rubles.
In June, Petrov was sick from the 10th to the 15th. In September, from the 9th to the 10th, I was on leave.
Calculation:
Since Petrov is a seasonal worker, for every full month of work he receives 2 working days of rest.
Petrov worked for 5 months, during which time Petrov accumulated 10 vacation days for which compensation must be calculated.
The billing period is from 05/01/2019 to 09/30/2019.
Working days according to the six-day calendar in this period (minus Sundays and holidays) = 24 + 24 + 27 + 27 + 25 = 127.
Sick leave days: from June 10 to June 15 – these are 5 working days that need to be taken away.
Days off: from September 9 to 10 – these are 2 working days, which also need to be taken away.
Average daily earnings = 95,000 / (127 – 5 – 2) = 791.67 rubles.
Compensation = 791.67 * 6 = 4,750 rubles.
If a minor temporary worker is dismissed
If an employee under 18 years of age is hired under a fixed-term employment contract, then upon termination of relations with him, he is also entitled to compensation for vacation days.
The annual duration of rest for minors is 31 calendar days according to Article 267 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, for each full month (in which 15 or more days were worked) 31/12 = 2.58 calendar days are calculated.
Do the provisions of Article 291 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply to a minor employee, which states that for a contract period of up to 2 months or employment during the season, only 2 vacation working days are due for each month worked?
How many days of unused vacation must be paid if a minor is dismissed, hired for up to 2 months or for the duration of the season - 2.58 or 2?
All specified norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation apply to employees under 18 years of age. At the same time, the rights of a minor employee should not be deteriorated in comparison with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, therefore the amount of vacation compensation for both cases should be calculated and a larger amount should be paid.
Example of calculation for persons under 18 years of age
The minor worker Mukhin was hired for the season for 3 months: from 06/01/2019 to 08/31/2019. They fully worked out the specified time.
Total earnings for this period = 80,000 rubles.
To calculate compensation, we will carry out two calculations:
- Based on Article 267 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the annual rest period is 31 calendar days (2.58 calendar days per month).
- Based on Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which 2 working days are required for each month worked.
Next, we will choose a larger amount of compensation and pay it to Mukhin.
Calculation 1 based on Article 267 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as for a minor employee:
- Unused days = (31/12 months) * 3 = 7.75 days.
- Average daily earnings = 80,000 / 29.3*3 = 910.13 rubles.
- Compensation = 910.13 * 7.75 = 7053.47 rubles.
Calculation 2 based on Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as for a seasonal worker:
- Unused days = 2 * 3 months. = 6 days
- The number of working days according to the calendar for a six-day week in the period from June 1 to August 31, 2021 = 78 working days.
- Average daily earnings = 80,000 / 78 = 1025.64.
- Compensation = 1025.64 * 6 = 6153.85 rubles.
Thus, the amount of compensation for a minor = 7053.47 rubles. more than for a seasonal worker = 6153.85 rubles.
You need to pay a larger amount = 7053.47 rubles.
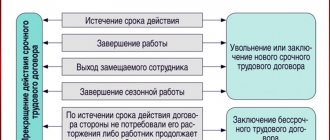
Expiration of the contract
A contract concluded for a short period of time may be terminated for the following reasons:
- all work specified in the contract has been completed;
- the agreement has expired;
- the season has ended if the subordinate was hired for seasonal work;
- The main employee returned to work, and a new worker was hired to replace him.
If the contract has expired, management can take the following steps to choose from:
- end the relationship with a subordinate;
- to extend the contract;
- sign a new contract with the worker for the same or a different period.
How to fire an employee at the end of the contract
If management decides to terminate the employment contract upon expiration, it is obliged to inform the worker about this three working days before dismissal. This is done in writing.
A notice of termination of an employment contract must contain the following information:
- name of company;
- Full name of the employee;
- reason for dismissal (expiration of the contract);
- the date from which the contract becomes invalid;
- date of document execution;
- compiler's signature.
The employee must be informed of his dismissal in advance
If a subordinate is not properly informed about the upcoming termination of employment, and his dismissal takes place, he may apply to the court for reinstatement.
An organization I know hired an employee under a fixed-term employment contract. After the contract expired, settlement was made with it. Thus, the dismissed person joined the ranks of the unemployed. However, the matter did not end there. A former employee of the organization filed a lawsuit demanding that he be given back the opportunity to work in the position he filled. In addition, the citizen demanded to recover from the employer a sum of money for the period of forced absence and compensation for moral damage. The court satisfied the plaintiff's demands because the boss did not inform the subordinate about the termination of his employment relationship.
If the contract was concluded for the duration of the work, then the dismissal procedure upon expiration of its validity period is initiated with the execution of an act of acceptance of work. To do this, you can use the unified form of document No. T-73.
The certificate of completion of work is drawn up according to the unified form No. T-73
Next, the HR department issues an order to dismiss the subordinate. The person being dismissed must familiarize himself with such an order.
At the last stage of termination of a fixed-term employment contract, the HR department draws up and issues an order to dismiss the employee
The dismissal of a pregnant woman after the expiration of the contract occurs somewhat differently. The boss is obliged to renew the contract if the employee presents a corresponding application and a doctor’s certificate that confirms her condition. The contract period will then last until the end of the pregnancy.
Dismissal may occur on the following days:
- on the day the maternity leave ends;
- on any day within a week from the day the employer learned about the end of the pregnancy.
However, there are situations when a woman in a position can be fired immediately upon expiration of the contract.
This is possible if:
- a fixed-term employment contract was concluded for the duration of someone’s duties;
- transfer of an employee with her consent to another job available to the employer and not contraindicated for her health reasons is impossible.
How to extend a fixed-term employment contract
The legislation does not contain a prohibition on extending a fixed-term contract. This means that, if desired, the parties can extend the employment relationship.
However, multiple extensions of a fixed-term contract turns it into an open-ended employment contract.
This poses a certain risk for the employer, because if the contract becomes permanent, some conditions of the labor process change.
If the employer decides to do this, the extension of the period occurs in the following order:
- The initiator of the contract extension contacts the other party in writing with a corresponding proposal.
- Next, the boss and subordinate sign an additional agreement, which specifies all the necessary changes.
- A corresponding order is issued.
The order to extend a fixed-term employment contract indicates the number of the expired agreement
The legislation makes it possible to extend the term of the contract with the following persons:
- pregnant women;
- university employees;
- athletes.
It is better to terminate the contract with the remaining employees and then enter into a new one.
Is early termination of the contract legal?
Early termination of a temporary contract is not prohibited.
The reasons for this may be:
- consent of each party to such an outcome of the case;
- employee's desire;
- employer initiative.
The management of the organization may decide to terminate the contract early if the following occurs:
- liquidation of the organization;
- reduction in the number of employees or staff reduction;
- failure of the employee to pass certification;
- change of owner of the company;
- violation of labor discipline by an employee, if there have already been other disciplinary sanctions, etc.
However, management does not have the right to dismiss all workers early.
I know of a case where the management of an organization tried to terminate an employment contract concluded with an employee for a certain time ahead of schedule. However, during the trial it was established that the employer did not have the right to do so. A worker cannot be dismissed early if he is replacing a permanent employee who retains his job.
How to fill out a work book
In conclusion, we note that the urgent nature of the employment relationship (for any of the reasons listed above) does not in any way affect the procedure for filling out the employee’s work book. Thus, it should not indicate that the contract was concluded for a certain period. After all, this is not provided for either by the Labor Code, or by the Instructions for filling out work books (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 10.10.03 No. 69), or by the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, producing work book forms and providing them to employers (approved by Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225).
If the employer enters into the work book information about the period for which the employment contract is drawn up, then this will be a violation of the procedure for maintaining work books, and may entail administrative liability under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.