It happens that the presence of a seasonal factor has a strong influence on the conduct of business by an entrepreneur. The simplest example, of course, is agriculture, or rather crop production - the season lasts about six months from May to October inclusive.
Another example is the work of a travel agency - it is quite obvious that the peak of work for managers and other workers occurs during the same summer period. The catch is that the first example can be considered seasonal work, but the second cannot.
Why this situation arises and when it is possible to sign an employment agreement with an employee only for a season will be discussed below, and an automatic online service will help you prepare the necessary documents.
Subject of the agreement
1.1. Under this employment contract, the Employee undertakes to fulfill the duties of his profession/position [indicate work by position in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty indicating qualifications; specific type of work entrusted to the employee] at [place of work, and in the case where the employee is hired to work in a branch, representative office or other separate structural unit of the organization located in another locality, the place of work indicating the separate structural unit and its location], and The Employer undertakes to provide the Employee with the necessary working conditions provided for by labor legislation, as well as timely and full payment of wages.
1.2. Work under this agreement is the main place of work for the Employee.
1.3. Working conditions at the workplace in terms of the degree of harmfulness and (or) danger are [optimal (class 1)/ acceptable (class 2)/harmful (specify the class and subclass of harmfulness)/hazardous (class 4)].
1.4. The employment contract was concluded for seasonal work.
1.5. The employee must begin work on [day, month, year].
1.6. The employment contract terminates at the end of the season [date, month, year].
back to contents
When is a contract for a season legal?
Let's start with what kind of work is recognized as seasonal according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This definition is given in Art. 293. This type of work includes those that, due to climatic conditions (or other natural reasons), can only be performed for a certain period (season), usually 6 months. I’ll say right away that 6 months is not a strict limit, the season can last a little more or less, it all depends on the conditions and the specific type of work.
The seasonality of work is determined by law; the entrepreneur himself cannot decide that the work he offers is seasonal. Where can I see a list of such works? There are several documents that need to be taken into account, we will highlight three of them separately:
- Resolution of the People's Commissariat of the USSR No. 185 of October 11, 1932 - the date of the document should not confuse anyone, it is still valid to this day.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 382 of 04/06/1999 is also a valid document approving the list of seasonal activities for which there is a deferment / installment plan for paying taxes.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 498 of 07/04/2002 - approves the list of seasonal industrial sectors, the enterprises of which have features in calculating the insurance period.
These lists are basic. When working in a specific sector of the economy, you also need to pay attention to the presence of industry (as well as inter-industry) agreements. They may also contain lists of work that are considered seasonal - in this case, the timing of the season is also established, since it can last more than six months. There are such agreements for organizations in the timber industry, housing and communal services, and automobile/urban ground transport (passenger transportation).
It turns out that you can sign an employment agreement with an employee for a season only when the work offered to him is truly seasonal - that is, included in any of the lists given above. The lists of seasonal work that we have named overlap in many ways. That is why work in crop production is recognized as seasonal, but summer work in a travel agency is not.
Rights and responsibilities of an employee
2.1. The employee has the right to:
— conclusion, amendment and termination of an employment contract in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- providing him with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— a workplace that meets state regulatory requirements for labor protection and the conditions provided for by the collective agreement [if any];
— timely and full payment of wages in accordance with their qualifications, complexity of work, quantity and quality of work performed;
— rest provided by the establishment of normal working hours, reduced working hours for certain professions and categories of workers, the provision of weekly days off, non-working holidays, paid annual leave;
— complete reliable information about working conditions and labor protection requirements in the workplace;
— training and additional professional education in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— association, including the right to create trade unions and join them to protect their labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests;
— participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws, if any, and by the collective agreement;
— conducting collective negotiations and concluding collective agreements and agreements through their representatives, as well as information on the implementation of the collective agreement and agreements;
— protection of one’s labor rights, freedoms and legitimate interests by all means not prohibited by law;
— resolution of individual and collective labor disputes, including the right to strike, in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
- compensation for harm caused to him in connection with the performance of his job duties, and compensation for moral damage in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— compulsory social insurance in cases provided for by federal laws;
— [other rights provided for by the current Labor legislation
and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, collective agreements, local regulations].
2.2. The employee is obliged:
— conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by the employment contract;
— comply with internal labor regulations;
— maintain labor discipline;
— comply with established labor standards;
— comply with labor protection and occupational safety requirements;
— take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees;
— immediately inform the Employer or immediate supervisor about the occurrence of a situation that poses a threat to the life and health of people, the safety of the Employer’s property (including the property of third parties held by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property);
— [other duties provided for by the current Labor legislation
and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, collective agreements, local regulations].
back to contents
Rights and obligations of the employer
3.1. The employer has the right:
— conclude, amend and terminate an employment contract with the Employee in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— conduct collective negotiations and conclude collective agreements;
— encourage the Employee for conscientious, effective work;
— require the Employee to fulfill his job duties and take care of the property of the Employer (including the property of third parties owned by the Employer, if the Employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees, and compliance with internal labor regulations;
— bring the Employee to disciplinary and financial liability in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws;
— adopt local regulations;
- create associations of employers for the purpose of representing and protecting their interests and join them;
— create a works council;
— [other rights provided for by the current Labor legislation
and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, collective agreements, local regulations].
3.2. The employer is obliged:
— comply with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, terms of the employment contract, agreements, collective agreement [if any];
— provide the Employee with work stipulated by the employment contract;
— ensure safety and working conditions that comply with state regulatory requirements for labor protection;
— provide the Employee with equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary to perform his job duties;
— provide the Employee with equal pay for work of equal value;
— pay the full amount of wages due to the Employee within the terms established in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the collective agreement [if any], internal labor regulations, and the employment contract;
— conduct collective negotiations, as well as conclude a collective agreement in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
— provide employee representatives with complete and reliable information necessary for concluding a collective agreement, agreement and monitoring their implementation;
— familiarize the Employee, against signature, with the adopted local regulations directly related to his work activity;
— timely comply with the instructions of the federal executive body authorized to exercise federal state supervision over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, other federal executive bodies exercising state control (supervision) in the established field of activity, pay fines, imposed for violations of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms;
— consider the submissions of the relevant trade union bodies, other representatives elected by employees about identified violations of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms, take measures to eliminate the identified violations and report on the measures taken to the specified bodies and representatives;
— create conditions that ensure the Employee’s participation in the management of the organization in the forms provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and the collective agreement [if any];
— provide for the Employee’s everyday needs related to the performance of his job duties;
— carry out compulsory social insurance of the Employee in the manner established by federal laws;
— to compensate for damage caused to the Employee in connection with the performance of his labor duties, as well as to compensate for moral damage in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation;
— [other duties provided for by the current Labor legislation
and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, collective agreements, local regulations].
back to contents
Employment contract with seasonal workers: how to draw up, sample
It should be noted that, on the basis of amendments introduced to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation by Federal Law No. 99 of June 30, 2006, work whose completion period exceeds 6 months can be recognized as seasonal, provided that the work is characterized by dependence on natural conditions, and its type is reflected in the intersectoral agreement In accordance with Chapter 46 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer engages workers in seasonal work on the basis of a fixed-term employment contract. When drawing up an employment contract for seasonal work, the employer should be guided by the basic norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note => Law of the Moscow Region of Regional Benefits for Payment for Major Repairs
Working time and rest time
4.1. The employee is assigned [a five-day work week with two days off/a six-day work week with one day off/a work week with days off on a sliding schedule/a part-time work week].
4.2. The duration of daily work/part-time work is [value] hours.
4.3. The start and end times of work, the time of the break and its duration [in the case of providing days off on a sliding schedule - alternating working and non-working days] are established by the internal labor regulations.
4.4. The employee is entitled to an annual paid leave of [value] days at the rate of two working days for each month of work.
4.5. The employee is granted an additional annual paid leave of [value] calendar days [indicate the basis for providing additional leave].
4.6. For family reasons and other valid reasons, the Employee, upon his written application, may be granted leave without pay, the duration of which is determined by agreement between the Employee and the Employer.
back to contents
Categories
Read in the article:
- What do the concepts of “seasonal work” and “seasonal worker” include?
- How to formalize labor relations and conclude an employment contract with a seasonal worker
- What guarantees are provided to seasonal workers?
- How to properly fire a seasonal worker and fill out his work book
WHAT WORKS ARE CONSIDERED SEASONAL?
Seasonal work has certain specifics and is usually used only in some industries. Legal regulation of labor relations with persons employed in seasonal work is carried out in accordance with the norms of Chapter 46 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Lists of seasonal work, including individual seasonal work, which can be carried out over a period (season) exceeding six months, and the maximum duration of these individual seasonal works are determined by industry (inter-industry) agreements concluded at the federal level of social partnership (Part. 2, Article 293 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Seasonal work has the following characteristics :
- Due to climatic and other natural conditions.
- Performed during a certain period (season).
- The work season has a certain duration, depending on which two types of work are distinguished:
- the duration of which does not exceed six months (general rule);
- may exceed six months.
The duration of seasonal work is approved by the order on the main activities of the organization, and the required number of seasonal workers is approved by the staffing table.
WE FORMULATE LABOR RELATIONS
An employment contract for seasonal work is a type of fixed-term employment contract (paragraph 4, part 1, article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), therefore, when drawing it up, special attention should be paid to indicating the basis (reason) for its urgency.
The sanatorium-resort institution Volzhskie Dawns LLC hired a physical therapy doctor, O. D. Mironova, for the period from May to September. How can I draw up a fixed-term employment contract with her for seasonal work?
Documenting labor relations with a seasonal worker is not much different from hiring a permanent employee - it is carried out according to general rules with the provision of all necessary documents (Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
However, it must be remembered that when concluding a fixed-term employment contract for a period of up to two months, a trial is not established, and when the employment contract is valid for two to six months, it cannot exceed two weeks (Part 6 of Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the duration of seasonal work is more than six months, the probationary period is established on a general basis and, as a rule, cannot exceed three months.
We conclude an employment contract
When drawing up a fixed-term employment contract with a seasonal worker, in accordance with Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to specify in the text of the document a condition regarding the period of its validity. Otherwise, the contract will be considered concluded for an indefinite period (permanent), and the employee will be considered hired for permanent work. In addition, on the basis of Art. 294 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to include in the employment contract a condition regarding the seasonal nature of the work (example 1).
We issue an order for employment
The content of the employer’s order (instruction) on hiring a seasonal worker must comply with the terms of the concluded employment contract. In the order, in the line “nature of work” you should indicate “seasonal” (example 2).
After concluding an employment contract with an employee, drawing up and signing an order for hiring him, it is necessary to make entries in the work book[1] and personal card.
WE PROVIDE GUARANTEES
The rights of seasonal workers, like other workers, are guaranteed by the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. One of these rights is the right to rest (paragraph 6, part 1, article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Employees engaged in seasonal work are provided with paid leave at the rate of two working days for each month of work (Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Vacation for a seasonal worker has some nuances:
- calculated in working days (annual paid leave provided to other categories of employees - in calendar days);
- A seasonal worker has the right to use annual paid leave on a general basis, that is, only after six months of continuous work. Most often this coincides with the expiration of the employment contract.
What to do in such a situation?
A seasonal employee can exercise his right to rest upon dismissal in one of the following ways:
- By agreement of the parties, before the expiration of six months of continuous work, leave may be granted to the employee in advance.
- At the end of the term of the employment contract, the employee can take leave with subsequent dismissal (the day of dismissal is the last day of leave (Part 2, Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)).
- An employee may receive monetary compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal.
NOTE
According to Part 2 of Art. 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, providing an employee with unused vacation followed by dismissal is the right, and not the obligation, of the employer, who has the right to refuse the employee.
WE FIRED A SEASONAL WORKER
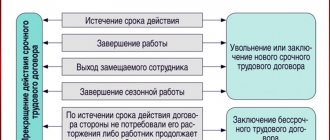
As a rule, an employment contract concluded to perform seasonal work during a certain period (season) is terminated at the end of this period (season) (Part 4 of Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), but it can also be terminated on the general grounds provided for in Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
According to Part 1 of Art. 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation about the termination of an employment contract due to its expiration, the employer must warn the employee in writing at least three calendar days before dismissal .
If an employee quits on his own initiative and wants to terminate the contract early, he must notify the employer within 3 days instead of 2 weeks.
The form of notification (warning) is not provided for by law, so it can be drawn up in any form (example 3).
After notifying the employee about the expiration of the employment contract, the employer issues an order for his dismissal (example 4).
The grounds for termination of the employment contract are entered in strict accordance with the wording of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
After the dismissal order is issued, an entry is made in the employee’s personal card and work book. The final payment is made on the day of dismissal, that is, on the last day of his work.
If the order to dismiss an employee cannot be brought to his attention or the employee refuses to familiarize himself with it upon signature, a corresponding entry is made directly on the document.
WE COMPLETE AN EMPLOYMENT RECORD
The employer maintains work books for both permanent and seasonal workers. For persons working part-time, work books are kept only at the main place of work (seasonal work can be both the main and part-time work for an employee).
Entries in the work book of an employee accepted under a fixed-term employment contract are made according to the general rules (example 5) - on the basis of the Instructions for filling out work books, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 69. In addition, the personnel employee must be guided by the Rules for maintaining and storage of work books, production of work book forms and provision of them to employers, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225 (as amended on March 25, 2013).
Entries made in the work book are certified by the seal and signature of the manager (or the person responsible for maintaining work books), as well as the signature of the employee himself.
On the day of dismissal, a corresponding entry is made in the book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them, and the dismissed employee signs in it to receive the work book in hand.
[1] For more information on filling out a work book, see below.
Terms of payment
5.1. A piece-rate wage system is established for the Employee.
5.2. Salary is calculated based on [specify calculation method].
5.3. Additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions deviating from normal conditions, systems of additional payments and incentive allowances and bonus systems are established by a collective agreement, agreements, local regulations and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms.
5.4. Wages are paid to the Employee [indicate specific dates of the calendar month]./Wages are paid to the Employee at least every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations.
5.5. When performing work outside the normal working hours, at night, on weekends and non-working holidays, when combining professions (positions), when performing the duties of a temporarily absent employee, the Employee is paid appropriate additional payments in the manner and amount established by the collective agreement and local regulations.
5.6. During the period of validity of this employment contract, the Employee is subject to all guarantees and compensation provided for by the current labor legislation of the Russian Federation.
back to contents
Shape and Features
An employment contract with a seasonal worker must be concluded in writing. There is no regulated form for its conclusion with seasonal employees.
The employer can use the standard form of the employment contract adopted by the organization. At the same time, he should indicate in such an agreement the duration of its validity and the nature of the work performed (seasonal, due to climatic reasons).
A sample fixed-term employment contract for seasonal work can be downloaded here.
Responsibility of the parties
6.1. In case of failure or improper performance by the Employee of his duties specified in this employment contract and job description, violation of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as causing material damage to the Employer, he bears disciplinary, financial and other liability in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
6.2. The Employer bears financial and other liability to the Employee in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
back to contents
Termination of the contract for the season
Since the contract for the season is a fixed-term contract, it expires upon expiration of the established period. The employee, according to the general requirement of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is notified in writing of the date of his dismissal at least three days before the end of his agreement with the employer.
An employee under a seasonal contract has the right to resign at his own request: in such a situation, he must notify the employer of his intentions three days (calendar) before the day of dismissal, and not 2 weeks, as in the standard case.
If the dismissal is due to staff reduction or liquidation of a legal entity, the employer is obliged to notify the employee 7 days (also calendar days) before the date of dismissal and pay a benefit equal to the average earnings for 2 weeks.
If you need an employment contract, you can download a sample employment contract on our website.
Final provisions
7.1. Disputes between the Parties arising during the execution of this employment contract are considered in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws.
7.2. In all other respects that are not provided for in this employment contract, the Parties are guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation governing labor relations.
7.3. The employment contract is concluded in writing, drawn up in two copies, each of which has equal legal force.
7.4. All changes and additions to this employment contract are formalized by a bilateral written agreement.
7.5. This employment contract may be terminated on the grounds provided for by current labor legislation.
back to contents
Test in the case of a fixed-term contract
The establishment of a probationary period for a fixed-term contract, as well as for an open-ended one, is not mandatory. But if there is an intention to install it, then it is necessary to remember that:
- it is not installed for a contract period of up to 2 months.
- it cannot be more than 2 weeks for a contract period of 2 to 6 months.
The condition for establishing the test must be fixed in the contract.
For those who cannot be given a probationary period when hiring, see here.