Dividends are part of the profit remaining after taxation, which is distributed among participants, shareholders. The amount of dividends is calculated and paid in a certain order and within strictly established periods. For more information, see How to determine the amount and procedure for paying dividends.
Dividends can be issued in cash or in kind, that is, other property. Moreover, shareholders can only be paid in cash. For LLC participants - both through the cash register and to a bank account. This procedure follows from Article 28 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ and Article 42 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ.
Accounting and taxation of dividends also have their own peculiarities. Read about them in detail in this recommendation.
Situation: is it possible to transfer dividends to an account that does not belong to the shareholder or participant
Yes, you can, but only in limited liability companies.
In joint stock companies, dividends in cash are paid only by bank transfer and only to the shareholder’s account. If the recipient does not have an account, then the money is sent by postal order. This is stated in Part 8 of Article 42 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ.
But for limited liability companies there are no restrictions in the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ. Therefore, an LLC may transfer dividends at the direction of a member to the accounts of third parties, such as a spouse, relative, or organization. To do this, the participant must write a statement. In it, indicate the recipient and his account details.
Accounting
How to calculate dividends
In accounting, calculations for the payment of dividends should be reflected in a separate subaccount 75-2 “Settlements with founders for the payment of income.” Do this when making payments to shareholders and participants who are not on the staff of the organization. That is, in relation to those people with whom an employment contract has not been concluded, as well as in relation to other organizations.
On the date when the general meeting of shareholders and participants decided to pay dividends, make the following entry:
Debit 84 Credit 75-2 – dividends were accrued to participants, shareholders who are not on the staff of the organization.
If you are paying dividends to employee participants, use account 70:
Debit 84 Credit 70 - dividends were accrued to participants, shareholders - employees of the organization.
This follows from paragraph 10 of PBU 7/98 and the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 70, 75 and 84).
An example of how dividends accrued to people are reflected in accounting
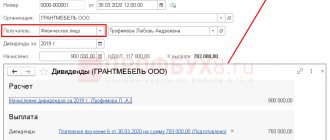
At the end of 2015, non-public Alpha JSC received a net profit of 266,000 rubles. On March 5, 2021, the general meeting of shareholders decided to use this amount to pay dividends.
The authorized capital of the company is divided into 100 ordinary shares:
- 60 shares belong to Alpha director A.V. Lvov;
- 40 shares are owned by Iraqi citizen R. Smith, who does not work for Alpha.
On March 5, 2021, Alpha’s accountant made the following entries in the accounting records:
Debit 84 Credit 70 – 159,600 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 60 shares) – dividends were accrued to Lvov;
Debit 84 Credit 75-2 – 106,400 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 40 shares) – dividends were accrued to Smith.
Russian organizations, when paying dividends, often must fulfill the duties of a tax agent. That is, calculate taxes, withhold them from payments and transfer them to the budget. This also needs to be reflected in accounting.
When you withhold personal income tax from dividends paid to individuals, you must also take into account whether they work for the organization or not. Depending on this, the entries will be as follows:
Debit 75-2 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax” - personal income tax is withheld from dividends of a participant, shareholder who does not work in the organization;
Debit 70 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax” - personal income tax is withheld from dividends of a participant, shareholder - employee of the organization.
If you pay dividends to a participant, shareholder - organization, then withhold income tax from them and document it with the following entry:
Debit 75-2 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - income tax is withheld from dividends of a participant, shareholder - organization.
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 68, 70, 75).
An example of reflecting personal income tax on dividends accrued to people in accounting
At the end of 2015, Alfa JSC received a net profit of RUB 266,000. Alpha did not receive income from equity participation in other organizations.
On March 5, 2021, the general meeting of shareholders decided to use all net profit to pay dividends.
The authorized capital of the company is divided into 100 ordinary shares:
- 60 shares belong to Alpha director A.V. Lvov;
- 40 shares are owned by a non-resident - Iraqi citizen R. Smith, who does not work for Alpha.
Dividends to the founders were transferred to their bank accounts on March 26, 2021.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in the accounts.
March 5, 2021:
Debit 84 Credit 70 – 159,600 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 60 shares) – dividends were accrued to Lvov;
Debit 84 Credit 75-2 – 106,400 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 40 shares) – dividends were accrued to Smith.
March 26, 2021:
Debit 70 Credit 68 subaccount “Personal Income Tax Payments” – 20,748 rubles. (RUB 159,600 * 13%) – personal income tax is withheld from Lvov income;
Debit 75-2 Credit 68 subaccount “Personal Income Tax Payments” – 15,960 rubles. (RUB 106,400 * 15%) – personal income tax is withheld from Smith’s income (there is no agreement concluded between Russia and Iraq on the avoidance of double taxation on personal income tax);
Debit 70 Credit 51 – 138,852 rub. (159,600 rubles – 20,748 rubles) – dividends were transferred to Lvov;
Debit 75-2 Credit 51 – 90,440 rub. (106,400 rubles – 15,960 rubles) – dividends were transferred to Smith.
How to record dividend payments
The method of payment of dividends also determines how to reflect this operation in accounting.
If dividends are paid in cash , then make the following entry in accounting:
Debit 75-2 (70) Credit 51 (50) – dividends were paid in cash.
When property is transferred to pay dividends , the accounting procedure depends on the type of these assets:
| Operation | Type of property | Debit | Credit | Base | |
| Calculation of dividends | Doesn't matter | 84 | 75-2 (70) | Clause 10 of PBU 7/98, Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 70, 75 and 84) | |
| Payment of dividends in kind | Doesn't matter | 75-2 (70) | 91 | Clauses 5, 6.3 and 12 PBU 9/99, Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 70, 75 and 91) | |
| Write-off of property transferred to pay dividends | Finished products and goods | 90-2 | 43 (41) | Clauses 5, 7 and 9 PBU 10/99, Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 41, 43 and 90) | |
| Materials | 91-2 | 10 | Clause 11 of PBU 10/99, Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 10 and 91) | ||
| Fixed assets | depreciation | 02 | 01 | Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 01 and 02) | |
| residual value | 91-2 | 01 | Clauses 11, 16 and 19 PBU 10/99, clause 29 PBU 6/01, Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 01 and 91) | ||
As you can see, the postings are due to the following. First, the amount of dividends is determined. Having transferred property against them, they determine the proceeds as if they were sold and take them into account to offset obligations to the participants. And, as when selling, the value of the property is written off.
Insurance premiums
When paying dividends, do not accrue:
- contributions for compulsory pension, social or health insurance (Part 1, Article 7 of Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009);
- contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases (clause 1 of article 20.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
The fact is that dividends are not remuneration for fulfilled duties under employment or civil law contracts. This means that there is no need to pay insurance premiums on them.
This procedure follows from the provisions of Part 1 of Article 7 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, paragraph 2 of Part 1 of Article 7 of the Law of December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ, subparagraph 1 of Paragraph 1 of Article 2 of the Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ, subparagraph 1 of part 1 of Article 10 of the Law of November 29, 2010 No. 326-FZ and paragraph 2 of the Explanations approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia of June 8, 2010 No. 428n.
The emergence of disputes between JSC and shareholders
If a company violates the rights of its members, the latter can file a lawsuit. This is usually true in cases where funds are not paid in full or not paid at all. During the period of non-payment, interest is accrued, which can also be recovered through the court. The corresponding requirement is indicated in the statement of claim.
Non-payment of dividends is usually equated to an administrative offense (according to Articles 15-20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). To assert your rights, you should go to an arbitration court, since an LLC is considered an entity conducting business activities. This rule is relevant even if the claim is filed by an individual.
IMPORTANT! If dividends were not received for a good reason (for example, the shareholder did not provide information about his current account), the participant can receive them within 3 years from the date of completion of payments.
Personal income tax
Personal income tax on dividends is paid by:
- residents, always;
- non-residents only when dividends are paid by Russian organizations.
In this case, the tax agent usually calculates, withholds and transfers personal income tax to the budget. And only when the income is received by a resident from sources abroad, the person himself must calculate and remit the tax.
Situation: which period should be taken into account when determining a person’s tax status when calculating personal income tax – the year for which dividends were accrued to him, or the year when they were paid to him?
Determine tax status based on the 12 months preceding the payment of dividends.
After all, a person’s tax status must be checked every time income is paid to him. Including dividends. At the same time, it is determined whether the person spent 183 calendar days or more on the territory of Russia over the next 12 consecutive months. This procedure follows from paragraph 2 of Article 207 and subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. A similar point of view is expressed in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 9, 2007 No. 03-04-05-01/326.
An example of determining the tax rate for calculating personal income tax on dividends
At the end of 2015, Alfa JSC received a net profit. On March 4, 2016, the general meeting of shareholders decided to use the entire amount of net profit received to pay dividends. Dividends were paid in the same month (March 24).
During the 12 consecutive months preceding the payment of dividends (from March 24, 2015 to March 25, 2021), one of the shareholders - A.S. Kondratiev - went on business trips abroad.
The period when Kondratiev was abroad was:
- in April – 13 days;
- in May – 16 days;
- in June – 19 days;
- in July – 20 days;
- in August – 18 days;
- in September – 24 days;
- in October – 15 days;
- in November – 17 days;
- in December – 22 days.
In January 2015, Kondratiev left Russia for an international conference for 16 days.
In February 2015, Kondratiev left Russia for treatment for 24 days.
In total, over the last 12 months preceding the payment of dividends, Kondratiev spent 180 days abroad (13 days + 16 days + 19 days + 20 days + 18 days + 24 days + 15 days + 17 days. + 22 days + 16 days). The period of Kondratiev’s stay in Russia is not interrupted by periods of his traveling abroad for treatment.
Kondratiev spent 186 calendar days in Russia over the past 12 months (365 days - 180 days). This period is more than 183 calendar days, therefore Kondratiev is a tax resident of Russia. From the dividends accrued to him for 2015, the Alpha accountant calculated personal income tax at a rate of 13 percent.
useful links
►Economic literature◄ ►Methodology of financial analysis◄ ►Forms of financial statements◄ ►The largest joint stock companies in Russia◄
The third section of the balance sheet liability “Capital and reserves” consists of the following items.
| III. Capital and reserves | Line code |
| Authorized capital (80) | |
| Own shares purchased from shareholders (81) | |
| Additional capital (83) | |
| Reserve capital (82) | |
| including: | |
| reserves formed in accordance with legislation | |
| reserves formed in accordance with the constituent documents | |
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) (99) | |
| Total for Section III |
The table presented above reflects the diagram of the third section of the balance sheet liabilities, indicating the accounts, the balances of which are reflected in the corresponding line of the balance sheet.
“Authorized capital” (line 410). This article shows the amount of the authorized capital (account balance 80 “Authorized capital”) in accordance with the provisions of the constituent documents. An increase or decrease in the authorized capital is made only after changes have been made in the prescribed manner to the constituent documents (charter) of the organization (organization).
The line “Own shares purchased from shareholders” shows the remaining value of the organization’s own shares that were purchased from shareholders, recorded on account 81 “Own shares (shares).”
“Additional capital” (line 420). This line shows the amount of increase in the value of the organization’s property reflected in the asset balance sheet, identified based on the results of their revaluation, as well as the amount of share premium of joint-stock companies (i.e., amounts received in excess of the nominal value of the company’s outstanding shares (minus the costs of their sale) ) and targeted financing received in the form of investment funds. Since the authorized capital is fixed in the constituent documents, it became necessary to take into account the increase in the equity capital of an economic entity. Account 83 “Additional capital” is intended for these purposes.
“Reserve capital” (line 430).
Personal income tax is paid by the person himself
Residents must calculate and pay personal income tax on their own only on dividends received from sources abroad. He will calculate the tax at a rate of 13 percent. He has the right to reduce personal income tax by the tax paid on income in the country of location of the foreign organization. True, he can use this right only if he has concluded an agreement with this country on the avoidance of double taxation. In this case, he will calculate the tax as follows:
| Personal income tax on dividends that a resident received from a foreign organization | = | Dividends that a resident received from a foreign organization | x | 13% | – | The tax that the resident paid at the location of the foreign organization in the country with which a double taxation agreement has been concluded (if there is one) |
If the calculation results in a negative value, then the resident has no right to reimburse the difference from the budget.
This procedure is established by the provisions of subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of Article 208, paragraph 1 of Article 209, paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, the tax agent must calculate, withhold and pay personal income tax.
How to reflect transactions with dividends to the recipient on the accounts?
The recipient's dividend transactions will be reflected in the accounting records as follows:
| Account correspondence | Contents of a business transaction | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| 76 | 91 | Income is reflected on the date of the decision to pay it |
| 51 | 76 | Dividends received |
Personal income tax transfers by tax agent
The tax agent must determine personal income tax on dividends separately for each taxpayer and for any payment. This is established in paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When calculating personal income tax, tax agents apply the following rates:
- 13 percent – when paying dividends to a resident;
- 15 percent – when paying dividends to a non-resident. This rate is applied if international treaties on the avoidance of double taxation do not establish a different rate.
This is established by the provisions of Article 7, paragraphs 2 and 3 of Article 214, paragraph 1 and paragraph 2 of paragraph 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
For information about who acts as a tax agent when paying dividends, see the reference table.
Situation: is it necessary to withhold personal income tax when paying dividends to a participant (shareholder) of a company who is an entrepreneur?
Yes need.
After all, the legislation does not provide for any exceptions in relation to the recipient of dividends - an entrepreneur. When paying dividends, the organization must fulfill the duties of a tax agent. Including withholding personal income tax. Therefore, when paying dividends to an entrepreneur, personal income tax must be withheld from him. This follows from paragraph 3 of Article 214, paragraph 2 of paragraph 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A similar position is reflected in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 10, 2008 No. 03-04-06-01/79 and dated July 13, 2007 No. 03-04-06-01/238.
Situation: is it necessary to withhold personal income tax when paying dividends to the heir of a shareholder (participant)?
Yes need.
This is explained by the fact that it is not the money itself that is inherited, but only the right to receive it. This means that the general rule according to which income received by inheritance is not subject to personal income tax does not apply. Therefore, when paying dividends to the heir of a participant or shareholder, personal income tax must be withheld. This conclusion follows from paragraphs 18 and 58 of Article 217, paragraphs 3 and 4 of Article 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A similar position is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 29, 2007 No. 03-04-06-01/363.
Situation: is it necessary to withhold personal income tax if a participant refuses to pay dividends (for example, in favor of an organization)?
Yes need.
After all, despite the fact that the participant did not formally receive the money, he disposed of it - transferred it to the organization. These amounts must be taken into account when determining the tax base, as well as those that were paid. This is directly indicated in paragraph 1 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, it is considered that the income was actually received on the date when the money was transferred to the accounts of third parties by order of the participant. But in this situation the money is not transferred anywhere. Therefore, the day when the participant refused dividends in favor of the organization is considered the date of receipt of this income (subclause 1, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, on a general basis, withhold personal income tax from these amounts (clause 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A similar point of view is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 4, 2010 No. 03-04-06/2-233.
Unpaid dividends: entries
On the date of expiration of the claim period, dividends not paid to the founders are returned to net profit. In this case the following transactions are made:
- Dt 75/Kt 84 - dividends not claimed by legal entities and individuals who are not employees of the payer company;
- Dt 70/Kt 84 - dividends not claimed by employees.
Thus, the balance of unused profit on account 84 will increase.
When calculating and paying dividends, the organization uses accounts and entries that will reflect business transactions actually performed by the company. Accounting must keep records of both accrued and paid amounts - in an analytical context for each founder, participant, and shareholder.
How can a tax agent calculate personal income tax at a rate of 13 percent?
When calculating personal income tax on resident dividends, apply a rate of 13 percent. When calculating your tax, consider whether your organization received dividends from other companies or not.
When the organization does not have such income, calculate the tax using the formula:
| Personal income tax on dividends (to be withheld) = Dividends accrued to a resident x 13% |
This procedure follows from the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of calculating personal income tax on dividends accrued to the founders. The organization did not receive income from equity participation in other organizations
At the end of 2015, Alfa JSC received a net profit of RUB 266,000. On March 5, 2021, the general meeting of shareholders decided to use this amount to pay dividends. Alpha did not receive income from equity participation in other organizations.
Alpha's authorized capital is divided into 100 ordinary shares. Of these, 60 shares belong to Alpha director A.V. Lvov, and 40 shares - to Iraqi citizen R. Smith, who is not a tax resident of Russia and an employee of Alpha.
On March 5, 2021, Alpha’s accountant made the following entries in the accounting records:
Debit 84 Credit 70 – 159,600 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 60 shares) – dividends were accrued to Lvov;
Debit 84 Credit 75-2 – 106,400 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 40 shares) – dividends were accrued to Smith.
The amount of personal income tax on dividends accrued to Lvov is: RUB 159,600. * 13% = 20,748 rub.
There is no agreement concluded between Russia and Iraq on the avoidance of double taxation on personal income tax. Therefore, the amount of personal income tax on income accrued to Smith is equal to: 106,400 rubles. * 15% = 15,960 rub.
If the company received dividends from participation in other organizations in the current or previous years, the procedure for calculating personal income tax will be different. It depends on whether dividends received from participation in other organizations are taken into account when paying participants. If taken into account, then calculate personal income tax in the usual manner.
Well, if, having received income from participation in other organizations, you have not yet paid dividends, then calculate your personal income tax as follows:
| Personal income tax on dividends (to be withheld) | = | Dividends accrued to a resident | : | Dividends to be distributed to all recipients | x | Dividends to be distributed to all recipients | – | Dividends received by the tax agent | x | 13% |
There is no need to withhold personal income tax only if the dividends your organization received are greater than or equal to those paid to the participant.
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 210 and paragraph 5 of Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When determining the indicator “dividends received by the tax agent,” take into account such income minus previously withheld tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/82).
Take into account receipts from both Russian organizations and foreign ones. And don’t take into account only dividends that are taxed at a rate of 0 percent (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2012 No. 03-08-05 and dated February 19, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/114).
Situation: at what rate (9 or 13%) should personal income tax be withheld from dividends paid in 2021, but distributed in previous years?
For dividends paid on January 1, 2021 and later, personal income tax is withheld at a rate of 13 percent. That is, according to the one that has been in effect since 2021. It does not matter for what period these dividends are for.
You can distribute profits for 2015 or earlier periods at any time. There are no legal restrictions for this. This conclusion follows from the provisions of Article 43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 28 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ and Article 42 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ and is confirmed by letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 20, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/133, dated April 6, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/235.
In any case, the tax rate must be applied to the one in effect on the date the income was received. And in the situation under consideration, such a date is considered to be the day when dividends were paid to the participant (founder). That is, this is the day when the money was transferred to the participant’s bank account, or the day when you issued dividends from the cash register. The date of dividend distribution does not matter here. Therefore, if the payment is dated 2021, then personal income tax will have to be calculated, withheld and transferred to the budget at a rate of 13 percent.
This procedure follows from the provisions established by subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 208, paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 210, paragraph 3 of Article 214, subparagraphs 1 and 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 223 and paragraph 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 16, 2015 No. 03-04-06/13962.
How to draw up minutes of a meeting?
The legislation does not establish any specific strict rules for the form of minutes of the meeting of founders or shareholders. The document is drawn up in free form, provided that it contains all the necessary details (number and date of the document, place of its preparation, what issues were considered, decisions on issues, signatures of those present).
If the organization has only one founder, then instead of the minutes of the meeting of founders, a participant’s decision on the need to pay dividends is drawn up. There are also no specific requirements for the form of the document, except for maintaining the necessary details. There is no need to show a detailed individual calculation of dividends for an individual recipient in the protocol or decision; it is enough to reflect the amount of the enterprise’s net profit that will be paid to the founders or shareholders.
The calculation of dividends for each participant is carried out in the accounting certificate. Its form should be developed at the enterprise, and the document should be fixed in the accounting policy. The issuance of dividends from the cash register is formalized by a cash receipt order, and when transferred from a current account - by a payment order.
How can a tax agent calculate personal income tax at a rate of 15 percent?
When calculating personal income tax on non-resident dividends, apply a rate of 15 percent. Do this only if the double tax treaty with the foreign country does not specify different rates. The list of such agreements can be found in the table.
Calculate personal income tax on non-resident dividends using the formula:
| Personal income tax on non-resident dividends (to be withheld) | = | Dividends accrued to a non-resident | x | 15% (tax rate), unless otherwise provided by international treaties |
Such rules are provided for in paragraphs 3 and 4 of Article 214, paragraph 3 of Article 224, paragraph 6 of Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of calculating personal income tax on dividends accrued to citizens. The organization received income from equity participation in other organizations
At the end of 2015, Alfa JSC received a net profit of RUB 266,000. It includes income from equity participation in other organizations in the amount of 150,000 rubles.
In March 2021, the general meeting of shareholders decided to use the entire amount of net profit received (RUB 266,000) to pay dividends. The authorized capital of the organization is divided into 100 shares. Of these, 60 shares belong to Alpha director A.V. Lvov, and 40 shares - to Iraqi citizen R. Smith (not a tax resident of Russia and an employee of Alpha).
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in the accounting records:
Debit 84 Credit 70 – 159,600 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 60 shares) – dividends were accrued to Lvov;
Debit 84 Credit 75-2 – 106,400 rub. (RUB 266,000: 100 shares * 40 shares) – dividends were accrued to Smith.
The Alpha accountant calculated the personal income tax on the founders’ income as follows:
– from Smith’s income (non-resident): 106,400 rubles. * 15% = 15,960 rub. (there is no agreement concluded between Russia and Iraq on the avoidance of double taxation on personal income tax);
– from the income of Lviv (resident): (266,000 rubles * 60%: 266,000 rubles) * (266,000 rubles – 150,000 rubles) * 13% = 9048 rubles.