Sales of goods (works, services) on the territory of Russia are recognized as subject to VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Goods (work, services) are considered sold if the ownership of them passes from the seller to the buyer (ownership of the results of work performed (services provided) passes from the contractor to the customer) (Clause 1 of Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The gratuitous transfer of ownership of goods (results of work performed, services provided) is also recognized as a sale and is subject to VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For more information about this, see How to calculate VAT when transferring goods (work, services) free of charge.
The transfer of property rights is also recognized as a sale. Consequently, such transactions are also subject to VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Individual transactions are not recognized as sales and, therefore, are not subject to VAT. The list of such operations is given in paragraph 2 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
VAT must be charged for payment to the budget in relation to all transactions recognized as objects of taxation, the moment of determining the tax base of which relates to the corresponding tax period (clause 4 of Article 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When is trade turnover taxed and when is it not?
Four main groups of trade turnover subject to VAT are presented in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- Paid or gratuitous sale of goods, services, labor, collateral in the Russian Federation, transfer of rights to property, to trade items on the basis of replacement of obligations by agreement of the parties or compensation, which is confirmed by paragraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code.
- Sales of goods and services to meet the needs of the organization, but not for the purpose of making a profit. Such transfer of products is subject to VAT if the costs are recognized as economically unjustified or such costs are included in the item of expenses not taken into account when calculating income tax. Art. 252, Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Carrying out construction and installation activities for your own needs. If an organization performs this type of work independently, then taxation is present (clause 3, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code). If the construction process is provided by a contractor, then there is no VAT.
- Import of trade items into the territory of the Russian Federation (clause 4, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 3, clause 1, article 2 of the “Customs Code of the Eurasian Economic Union”).
Revenue will not be subject to value added tax for manipulations that are not accepted as sales or are not subject to taxation. For example:
- Currency transactions (clause 1, clause 3, article 29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Transactions related to numismatics do not fall into this clause.
- Transfer of objects of ownership to the legal successor during the reorganization of companies (clause 2, clause 3, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Return of assets to a person who was a member of a business company as part of the initial contribution in the event of termination of the company’s activities or withdrawal of a participant from its membership (clause 5, clause 3, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Transfer of housing facilities, electrical networks, roads, etc. to authorities (clause 2, clause 2, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Sale of land or land shares (clause 6, clause 2, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Sale of property or rights to it in the event of bankruptcy of debtors (clause 15, clause 2, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
There is also a closed list of processes named in paragraphs 1-3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code . Their peculiarity is that, being objects of taxation, they are not recognized as subject to tax and are exempt from VAT.
Goods not subject to VAT include:
- Approved list of medical products (clause 1, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Food products for medical organizations and canteens of kindergartens, schools, etc. (subclause 5, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code).
- Residential buildings and shares of premises in them (clause 22, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Average monthly revenue
As part of the financial analysis of an enterprise's activities, third-party and internal analysts calculate various types of revenue. The goals of such analysis and division into types may vary depending on the activities of the enterprise or the preferences of the enterprise management. One example of an analytical calculation is the calculation of average monthly revenue.
where Save is the average monthly sales,
Sn – revenue for the nth number of months,
n – number of months.
What is this?
Revenue represents the income that an organization or enterprise receives over a certain period of time through the sale of a number of goods or services. This is the final stage of the company’s commercial or non-commercial activity, and the calculation is made by multiplying the price of the product by the number of units sold.
Net sales revenue is recognized as profit minus indirect taxes . It is an indicator of the organization's performance.
Revenue from the sale of sales objects is divided into two types:
- Gross revenue is the total amount including taxation (excise taxes, customs duties, VAT).
- Net revenue is profit from sales of products, works or services without taxation.
You will learn about how such sales revenue is calculated in a special material.
The tax calculation looks like this: let’s denote the amount by the letter C, then VAT=C*18/100. According to this calculation, with revenue of 100,000 rubles, VAT will be 18,000.
Including tax
To make such a calculation, the amount including VAT is designated Sn. The calculation turns out like this:
Сн = С + С*18/100 = С*(1+18/100) = С*1.18.
Then, with revenue of 100,000 rubles, the result will be 118,000.
In the Russian Federation, an invoice document is used to calculate value added tax . The law establishes clear rules for filling out this form and its format.
Without him
To calculate the value of profit without this indirect tax, the same formula is used as a basis. When designating N=18/100, it turns out that Сн = С+ N*С = С*(1+N).
Thus, C = Cn/(1+N) = Cn/(1+0.18) = Cn/1.18.
If difficulties arise when working with formulas, then specialized online calculators simplify the work of taxpayers .
With their help, data is calculated quickly and accurately.
On what account is it reflected?
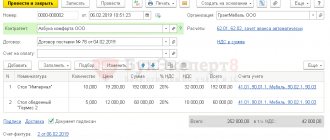
As a rule, this tax is calculated and reflected in the balance sheet once a quarter, that is, once every 4 months. VAT can be reflected in several invoices. It depends on what the income is related to. If income is received from the main activity of the enterprise, then the tax will be charged and reflected in the Sales account (90), but if proceeds are received from the sale of other property of the company (for example, the sale of fixed assets), then the tax is reflected in account 91.
We talked about which account in the balance sheet the revenue is shown in in a separate article, and you will find more information about how it is accounted for with and without VAT here.
Exemption from payment if sales volumes are less than two million rubles
Firms and individual entrepreneurs whose sales volumes are not high, according to the Code of the Russian Federation, have the right not to pay value added tax. This benefit comes into force if, for three calendar months, the total income from the sale of trade items or the provision of services (not taking into account tax) is less than 2 million rubles (clause 1 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Important! If, if there is a tax exemption, during the next three months the total profit (excluding tax) exceeds this amount, then the preferential right is canceled. The tax is restored and payable in the accepted manner, starting from the month where the excess occurred (clause 5 of Article 145 of the Tax Code).
We talked about the rules for displaying income of individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system here.
Calculation of the formula for return on sales
Return on sales is usually calculated by dividing operating profit by sales volume. Operating profit is that profit expressed before taxes. This type of profitability ratio shows whether the company's pricing policy is correct.
After all, it is necessary to have control over costs and expenses. This ratio is often used when assessing the operating efficiency of a company, but is not always applicable for comparing two competitive organizations.
Step-by-step instructions: how to plan sales income and costs in Excel
An Excel spreadsheet is used to plan revenue and production costs . The standard table for calculating efficiency has four fields:
- Tax rates (cell A1:B3).
- Income from the sale of trade items, expenses and debit VAT (A5:B7).
- Determination of value added tax for payment to the budget (A9:B10).
- Calculation of revenue and taxes on profit and turnover (A12:B17) (find out the main differences between revenue and turnover here).
Information is entered into the first two fields, and the next two fields process it.
- The type of calculation of the tax liability for VAT according to the table is as follows: =ROUND(B5*(B1/(1+B1));2).
- To calculate the amount of tax to be paid to the state treasury, you need to subtract the amount of the tax credit from the amount of tax liabilities (B10) = B9-B7.
- GP (gross profit) excluding VAT (cell B12) is calculated by subtracting the value of tax liabilities from the amount of revenue = B5-B9.
- Sales revenue is determined by subtracting costs = B12-B6 from the amount of VP.
- To calculate the turnover tax, VP is multiplied by the turnover tax rate = ROUND(B12*VZ;2).
- Revenue subject to taxation is the difference between the realized profit and the amount of turnover tax = B13-B14.
- Revenue tax is the product of the amount subject to taxation and the income tax rate, the result is rounded to the second digit = ROUND(B15*B2;2).
- Net profit is calculated by deducting the amount of income tax from taxable income = B15-B16.
Using an Excel spreadsheet is convenient because by changing the tax rate data, you can easily adapt to the current tax system. After changing the values of costs and sales amounts, the final result is immediately reflected. Excel offers various methods for entering data, in addition, formulas and a variety of functions provide additional possibilities for calculations.
We recommend that you pay attention to other publications by our experts, after reading which you will learn:
- How does revenue differ from cost, income and profit?
- How to calculate annual revenue?
- What are the reasons for the decline in revenue and how can it be increased?
Payment distribution
To distribute VAT on revenue, use the proportion of transactions subject to and non-taxable . The tax is deducted or included in the price of products and services (clause 4, clause 4, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If VAT is deducted, the proportion looks like this: ST (with VAT) / ST (total), ST (with VAT) is the price of products or services, the sale of which is subject to value added tax; ST (total) – the total price of goods or services sold in the tax period.
If the tax is included in the cost of products, then the following proportion is used : ST (excluding VAT) / ST (total), ST (excluding VAT) - the price of goods or services not subject to VAT; ST (total) – the total price of goods or services sold in the tax period.
The distribution of VAT on revenue does not include the following receipts:
- Interest on bank deposits and account balances.
- Profit on shares or shares in the authorized capital.
- Cash from payment of fines on loans and borrowings, violation of the terms of lending agreements.
- The discount rate charged by banks when purchasing bills of exchange.
- Cash received by subsidiaries from parent companies.
Attention! Expenses for the distribution of VAT include items of trade that participated in trade turnover on the territory of the Russian Federation. Production costs are necessarily taken into account in the cost of goods. The proportion must be drawn up strictly according to the regulations.
Value of revenue from product sales
The revenue of an enterprise plays a big role in the functioning of the enterprise. The revenue value is determined as follows:
- Determines the effectiveness and efficiency of the enterprise,
- The timely receipt of revenue determines the financial stability of the company, the state of its working capital, profit margins and timely payment of obligations (payment of wages to employees, settlements with banks on loans, with suppliers for work and services, etc.),
- With revenue, the enterprise covers its costs of production and sales of products, generating profit.
Discrepancy with VAT income and profit
Tax authorities always study income based on profit and VAT in order to identify non-taxable revenue. To do this, the information from both declarations is verified. Check line 010+020 (sheet 02) in Profit and line 010 (section 3) in VAT.
But additional factors influence the indicators, which complicates the task. For example, the value added tax base increases due to returns to suppliers, but revenue does not. Income decreases with returns from customers, but tax does not.
Therefore, it is quite difficult to understand the discrepancies between profit and VAT. The tax base is often violated due to accounting errors , so in practice equality between the values of two declarations is not respected.
Causes
The reasons for the discrepancy between VAT and profit may be as follows:
- Acquisition of property upon removal of fixed assets from circulation (Clause 13, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Detection of surpluses when comparing accounting and actual data (clause 20 of article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Positive differences in amounts and rates (clause 2, 11, article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Reconstruction of the cash reserve (clause 7 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Removal of loan debt due to the expiration of the statute of limitations (Clause 18, Article 250 of the Tax Code).
- Sales of trade objects whose sales area is not the Russian Federation (Articles 147, 148; Clause 1, Clause 1, Article 248; Clause 1, Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Acquisition of interest on loans issued or on the balance of money in the account (clause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code).
A number of transactions are taxable but do not generate revenue. This refers to the gratuitous transfer of trade objects or the provision of services for the needs of the organization itself. They are not included in the income tax return, but are reflected in lines 010 or 030 of column 3 (section 3) of the VAT return.
Reference! If an entrepreneur exports goods, then the data always diverges, since income from exported products is included in the declarations in different periods.
In the income tax return, proceeds are entered directly during the period of sale of trade items (clause 1 of article 249, clause 3 of article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and in VAT - after 180 days after shipment or during the preparation of papers proving the right to use a zero VAT rate.
Explanations from the Federal Tax Service
Explanations must be submitted to the tax office before the expiration of 5 days from the date of receipt of the notice (clause 2, 6, article 6.1, clause 3, article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is allowed to provide explanations in free form and always in writing, and the tax inspector must put a note about the receipt of the paper (the document must be handed over in person, and not by mail).
The note must contain the reasons for the discrepancies in the declarations, as well as links to articles of the Tax Code confirming the legality of their existence. If the reasons for the discrepancy in data are correctly compiled and justified, and provided to the tax inspectorate on time, then there is a possibility that in the future inspectors will not send similar requests.