Bookmarked: 0
What is revenue from product sales? Description and definition of the term.
Revenue from sales of products is one of the indicators of the characteristics of the enterprise. Revenue in its general meaning represents the amount of cash or other valuables that a company can receive during a certain period of its activity by selling goods and services. Do not confuse revenue with profit - profit is defined as revenue minus production costs. Revenue from product sales is one of the elements of the enterprise’s total revenue, along with revenue from financial and investment activities.
Let us consider in more detail what the term revenue from sales of products means.
Revenue (turnover, sales volume) is the amount of cash or other benefits received by a company for a certain period of its activity, mainly through the sale of goods or services to its customers. Revenue is different from profit because profit is revenue minus expenses (costs) that a company incurred in the process of producing its products. Capital gains resulting from an increase in the value of an enterprise's assets for some reason are not included in revenue. For charitable organizations, revenue includes the total value of cash gifts received.
Proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) include cash or other property in monetary terms received or to be received as a result of the sale of goods, finished products, works, services at prices and tariffs in accordance with contracts.
At the same time, the activity of the enterprise can be characterized in several areas:
- revenue from core activities coming from the sale of products (work performed, services provided);
- revenue from investment activities, expressed in the form of financial results from the sale of non-current assets, the sale of securities;
- revenue from financial activities.
Total revenue consists of revenue in these three areas. However, the main importance in it is given to revenue from the main activity, which determines the entire meaning of the enterprise’s existence.
What is revenue from product sales?
Revenue from product sales represents cash income received by an organization from customers for products sold. The indicator expresses the monetary relations between producers and consumers of goods. Revenue from sales of products is determined based on the quantity of products sold and their cost. For tax purposes, it is recognized as income from sales.
Revenue is not profit; a separate line is allocated for it in the “Income Statement”. The head of the organization must ensure the uninterrupted flow of revenue, since without this the business simply will not be able to function.
The following factors influence the amount of revenue from product sales:
- internal (production volume, range of manufactured goods, their quality and competitiveness, level of prices applied, cost, compliance with contractual terms, etc.);
- external (violation of contract terms, interruptions in transport, etc.).
Revenue and debt
Information about the company's borrowed funds is contained in sections 4 and 5 of the balance sheet. The relationship between this information and revenue is very weak, but it exists.
Borrowing money is a dangerous and burdensome operation. Dangerous because there is a possibility of not repaying the debt and even going bankrupt. Burdensome if paying interest on borrowed funds consumes all working capital, and there is no money left for current expenses. There is nothing to buy raw materials, nothing to pay wages and taxes, nothing to pay for electricity and heat, that is, the production process is under threat. As a result, disruptions occur in the supply of finished products to customers. And where there is no sales, there is no revenue.
IMPORTANT! Now companies do not need to standardize interest on borrowed funds for the purpose of calculating income tax (Law No. 420-FZ dated December 28, 2013). This is true for all debt obligations, except those that arose as a result of controlled transactions.
Calculation of revenue using the formula
Let's look at how to find revenue from sales of products using the formula. When making calculations, it is necessary to take into account the current sales volume and prices. The general formula for revenue from product sales looks like this:
B = Q × P
Here:
Q – number of goods sold;
P – selling price.
The formula can be used to evaluate an organization's performance and build long-term plans.
In practice, accounting for revenue from the sale of products, works and services is carried out using two methods:
- cash method (if the moment of sale is recognized as the fact of receipt of money to the seller’s bank account);
- accrual method (if the moment of recognition of income is the fact of shipment of goods).
Basic definition
It would seem that revenue is the amount received during the sale of goods. But this is far from true, since it depends on a number of nuances and characteristics. Previously, revenue was classified as one of the types of profit, but now there is controversy surrounding this issue. Today it is considered income from the company’s core activities, but at the same time, other areas can also generate profit.
The basic definition is: revenue is the total amount of money received during a certain period of activity from the sale or provision of services. It can take either a positive value or be equal to zero, but it will never take a negative value.
Receiving revenue is the final stage in the work of any commercial organization. It is the main overall indicator of the performance of a company or firm. This indicator is planned first, and on its basis the price of the product and its circulation are set. Based on revenue, all subsequent types of profit and income are calculated, and conclusions are drawn about the demand for a particular product.
In the absence of profit, the company inevitably suffers losses, which ultimately leads to its ruin and closure.
Examples of revenue calculation
Examples of calculating revenue from product sales in different ways are given below.
Example 1
LLC "Electrod" is engaged in the production of lamps. During the reporting year the following products were sold:
- lamp “Ella” – 700 pieces at a price of 250 rubles;
- lamp “Teresa” – 600 pieces at a price of 340 rubles;
- lamp “Miranda” – 400 pieces at a price of 600 rubles.
The annual revenue will be calculated as follows:
B = (700 × 250) + (600 × 340) + (400 × 600) = 619 thousand rubles.
Example 2
IP Petrov A.A. applies the cash method of accounting for income and expenses. On January 25, 2021, the entrepreneur delivered goods to the buyer for a total amount of 180 thousand rubles. On March 5, 2021, the individual entrepreneur agreed with the buyer on a mutual settlement in the amount of 106.2 thousand rubles. (including VAT – 16.2 thousand rubles). What revenue should an entrepreneur report?
As of the date of the offset agreement with the buyer (March 5, 2021), the individual entrepreneur is obliged to take into account income in the amount of the repaid debt (excluding VAT): 106,200 – 16,200 = 90,000 rubles.
Example 3
On February 12, 2021, Teplomash LLC shipped goods worth 600 thousand rubles to Ryabina LLC. Ryabina LLC paid off with Teplomash LLC on April 3, 2021, transferring money to its bank account. Teplomash LLC uses the accrual method when accounting for income, so all revenue will be displayed in accounting and tax accounting in February.
Estimation of enterprise profit
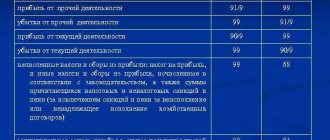
To see the profit, you will need to perform the operation of closing accounts 90 and 91 using the “Closing the month” procedure.
To do this, in the left “Operations” menu, select the “Month Closing” section. Set the period and indicate the name of the company. After performing this operation on the account. 99 will reflect the amounts from accounts 90 and 91.
If there is a debit result on account 99, this is a loss, if there is a credit result, this is a profit. Therefore, it is possible to generate a balance sheet according to the account. 99 and view the “Account Analysis” or “Account Turnover” reports.
Here you can see which amounts came from 90 and which from 91 accounts.
By clicking on the amounts, you can drill down into details. Accordingly, if the amounts came from the account. 90 – then this is profit or loss from the main activity. If from the account 91 - non-operating loss or profit. For those who use the simplified tax system, it is recommended to generate a report “Analysis of accounting according to the simplified tax system.”
Reflection in accounting
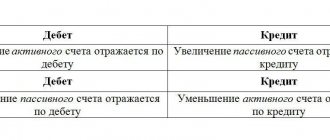
Account 90 “Sales” is used to record revenue from sales of products. The account consists of several sub-accounts. Postings for revenue from sales of products are compiled in order to determine the financial result from sales. The mandatory conditions under which revenue is recognized in accounting are given in PBU 9/99.
Example 1
Rubezh LLC sold spare parts for the amount of 354 thousand rubles. (including VAT – 54 thousand rubles). Revenue is recorded at the time of shipment. The cost of goods is 210 thousand rubles, sales costs are 35 thousand rubles. The buyer transferred the money to the seller.
The entries for revenue from the sale of finished products will be as follows:
- Dt 62 Kt 90 – revenue from the sale of finished products is reflected on the day of shipment - 354 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 68 - the amount of VAT is reflected - 54 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 43 - the actual cost of spare parts is displayed - 210 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 44 - sales expenses written off - 35 thousand rubles.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 – funds received from buyers for the products received amounted to 354 thousand rubles.
Calculation of financial results: 354,000 – 54,000 – 210,000 – 35,000 = 55,000 (rub.).
After the postings reflect the revenue from the sale of finished products, we take into account the financial result:
- Dt 90 Kt 99 - a profit of 55 thousand rubles was received.
Example 2
The organization sold spare parts in the amount of 354 thousand rubles. (including VAT – 54 thousand rubles). Revenue is recognized at the time of payment, and selling expenses are written off entirely to cost of goods sold. The cost of spare parts is 210 thousand rubles, sales costs are 35 thousand rubles. The buyer transferred 300 thousand rubles.
The postings will be like this:
- Dt 45 Kt 43 - the amount of the actual cost of goods shipped is written off - 210 thousand rubles.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 - buyers transferred money to pay for goods - 300 thousand rubles.
- Dt 62 Kt 90 - accounting records reflect the proceeds from the sale of finished products by posting - 300 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 68 – the amount of VAT is reflected. The calculation is as follows: (300,000: 118 × 18) = 45,762 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 45 - reflects the amount of the actual cost of products, the proceeds from the sale of which are recognized in accounting. The calculation is as follows: (210,000 × 300,000: 354,000) = 177,966 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 44 – the amount of sales expenses of 35 thousand rubles was written off.
Let's calculate the financial result: 300,000 – 45,762 – 177,966 – 35,000 = 41,272 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 99 – profit from sales of 41,272 rubles is reflected.
Results
To reflect the receipt of revenue into a bank account, accounting entries are made to the debit of account 51 “Currency accounts” (52 “Currency accounts”) and the credit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers.”
If cash proceeds are handed over to the bank by a cashier, account 50 “Cash” is credited in correspondence with account 51 “Cash Accounts” debited. When intermediaries (collectors, terminals) participate in the transfer of proceeds from the cash desk to the bank, account 57 “Transfers in transit” is additionally involved in the postings. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Revenue planning
The head of the organization or special services can plan revenue from the sale of products, works, and services. In an unstable economic situation, quarterly planning will be more effective than annual planning.
To plan revenue from product sales, the following methods are used:
- Direct counting method. Applicable in case of guaranteed demand. Products are produced in the quantities specified in pre-orders. Revenue is calculated by multiplying the volume of products sold by its price.
- Calculation method. It is used in conditions of uncertainty of demand for manufactured goods. The prospects for their implementation are taken into account.
Revenue and 1st section of the balance sheet
Almost every line of the first section of the balance sheet is associated with a revenue indicator. For example, if the residual value of fixed assets or intangible assets decreased sharply during the reporting period, it is possible that some of them were sold. In this case, we can talk about the company’s possible revenue from their sale. If information appears on the balance sheet about profitable investments in material assets, you can expect to receive revenue from an activity such as renting out property.
In the 1st section there are lines that, it would seem, have no connection at all with revenue, for example, financial investments. But it is not so. If a company operates profitably and is interested in its development, it will try to increase the money it earns. Financial investments are one such way. Of course, it is also possible to purchase securities or make contributions to the authorized capitals of other companies using borrowed funds. However, the main source in sustainable developing companies is profit, a significant part of which is revenue.
For information on the specifics of reflecting the company’s assets in the 1st section of the balance sheet, read the article “Procedure for drawing up a balance sheet (example)” .
Revenue analysis
Analysis of revenue from product sales allows you to solve the following problems:
- determine the validity of the business plan indicator for the sale of goods;
- determine the degree of plan fulfillment in terms of the volume and range of products sold;
- establish the influence of individual factors on the deviation of actual sales volume from the planned one;
- identify reserves for further increase in sales.
One of the effective methods of economic analysis is factor analysis of revenue from product sales. It helps to determine the influence of specific factors on changes in revenue. In the process of analysis, much attention is paid to the following factors: volume of sales of goods, selling prices, cost, structure of products sold.
Difference between basic concepts and definitions in trading
When carrying out actions related to the sale of certain things and products, employees have to operate with such concepts as revenue, income and profit. But you should understand the difference between each of these terms.
Net proceeds are often related to the concept of income. But income is a broader concept. Thus, income is considered to be an increase in economic benefits from the receipt of various funds and, as a result, an increase in the capital of the organization. But income can have several sources, not only revenue, but also payment of fines, sanctions, and interest from the bank. All this creates profit.
Money for the purchase of goods, taxes, payment of rent for premises, payment of wages to distributors - expenses. If you subtract this amount from the income received from the sale of goods and services, you can get a profit.
Naturally, revenue significantly affects the income and profit of an enterprise and is one of its main components, but equating revenue with these two concepts is fundamentally wrong.
Main functions
The main function that revenue performs is to reimburse the funds spent by the company on the purchase or production of goods. Its timely receipt into the company’s accounts ensures not only the stability of its work, but also the continuity of trade turnover and the company’s activities.
With the help of the proceeds received, bills of suppliers, both goods and materials, wages, and taxes are paid. In addition, the proceeds received can be used to purchase new goods or materials or expand the company’s activities.
If revenue arrives late, the company's activities suffer losses, as its profits decrease, penalties may be imposed, or contractual obligations related to the production of goods or payment of certain bills may be violated.