The services of banks are used by all organizations and entrepreneurs carrying out economic activities. Most of the services are provided by credit institutions on a paid basis; the fee for such services is called a bank commission.
In order to attract clients, financial institutions are constantly expanding their range of services, offering not only financial intermediation, but also software products in the form of personal accounts with a set of accounting functions and reporting forms.
The most popular services of credit institutions include:
- settlement and cash services for ruble and foreign currency accounts;
- remote management of settlement operations through a client bank;
- currency control;
- accepting and issuing cash;
- cash collection;
- SMS notifications about payment transactions;
- acquiring operations for accepting card payments;
- issuance and servicing of payment cards;
- factoring operations;
- provision of bank guarantees.
In accounting, expenses associated with servicing in credit institutions are classified as other expenses (clause 11, paragraph 6 of PBU 4/99 “Expenses of the organization”) and are reflected in account 91.02 “Other expenses and income.”
From the point of view of accounting entries, the list of the most common bank services can be divided into two types of operations: not subject to VAT and subject to VAT.
Let's look at the accounting entries for each type of transaction.
Bank commission: grounds for its calculation
The basis for charging commissions are agreements for maintaining a current account, servicing a deposit or issuing a loan. Within the framework of these agreements, the terms of the relationship between the organization and the bank are stipulated.
The following list of services for which commissions are paid can be distinguished:
- Ongoing maintenance of the current account with subsequent installation and maintenance of the Client-Bank program.
- Cash collection.
- Transactions of purchase and sale of foreign currency.
- Providing and maintaining a credit line.
- Property management on a trust basis.
- Rent of deposit boxes.
- Use of leased property.
For each type of banking services provided to the client, a separate agreement is drawn up, which details the conditions for the provision of these services, the amount and procedure for paying the bank commission.
What determines financial relations with a bank?
When working with a banking organization, a legal entity enters into a relationship with it with certain obligations of both parties. In order for cooperation to begin, it needs to be documented. These obligations are governed by the agreement signed between the parties:
- to open a bank account (Article 845 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- for placing a deposit (Article 834 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- to receive credit funds (Article 819 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- factoring (financing against the assignment of a claim on funds);
- other financial relationships permitted by the Charter of the credit organization and the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Question: Is it possible for a developer to take into account the costs of bank services for sending an equity participation agreement to Rosreestr under the simplified tax system? View answer
Reflection of bank commissions on accounting accounts
In accounting, bank commissions can be displayed in two ways:
- The first method is based on the use of current accounts 60 or 76 with the corresponding sub-account “Settlements with the bank”. Both of these accounts are suitable for accounting for banking services - the procedure for their use can be regulated in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
- The second method is more practical, since the commission is displayed without “intermediate” accounts, but directly to account 91.
Please note, according to the instructions for using the chart of accounts, correspondence of 91 accounts does not provide for payment for the services of credit institutions.
In practice, the second method of accounting for banking services is most often used.
Features of bank operations
All non-cash payments carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation are carried out through banks. Based on a banking service agreement, an enterprise can open a bank account and carry out all necessary operations with its help.
The main banking operations carried out by enterprises include:
- payment for goods, services, works received;
- crediting funds from buyers, customers;
- payment of wages to employees;
- issuance of funds on account for travel expenses and business needs;
- placement of funds in a deposit account;
- credit line servicing;
- transactions related to the use of a checkbook.
It should be noted that operations with the issuance and crediting of funds can be carried out both in cash (through the cash register) and in non-cash form.
The bank carries out all operations on the current account only after the order or receipt of the consent of the organization that owns the account. Exceptions are cases provided for by law (collection of fines, penalties, tax obligations).
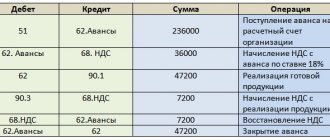
Accounting entries for bank commissions
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| Postings to the bank when using an “interim” account 60/76 | ||||
| 60 (76) | 51 | 1 450,00 | A bank commission has been debited from the company's current account (date of debit from the account) | Bank agreement, bank statement |
| 91-2 | 60 (76) | 1 450,00 | Bank commission is included in expenses | Bank agreement, bank statement |
| Bank commission is subject to VAT | ||||
| 60 (76) | 51 | 5 000,00 | Bank commission (including VAT) is written off for credit servicing | Bank agreement, bank statement, invoice |
| 19 | 60 (76) | 762,71 | VAT charged | Check |
| 68 | 19 | 762,71 | VAT displayed | Check |
| 91-2 | 60 (76) | 4 237,29 | Bank commission is included in expenses (excluding VAT) 5000 – 762.71 = 4237.29 | Bank agreement, account |
| Bank commission – “direct” display method | ||||
| 91-2 | 51 | 8 700,00 | Bank commission written off | Bank agreement, bank statement |
| Uniform write-off of bank commissions (within clearly defined time frames) | ||||
| 60 (76) | 51 | 9 450,00 | Bank commission paid (date of transfer) | Bank agreement, bank statement |
| 97 | 60 (76) | 9 450,00 | Inclusion of paid commission into deferred expenses (by date of transfer or evenly) | Banking agreement. Order on the accounting policy of the enterprise |
| 91-2 | 97 | 9 450,00 | Bank commission is included in expenses | Order on the accounting policy of the enterprise |
| If in tax accounting this commission is recognized as an expense at a time, and in accounting - evenly over a specified period, then a deferred tax liability arises | ||||
| 68 | 77 | 1 890,00 | Deferred tax liability accrued9450 * 20% (income tax) = RUB 1890. | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 77 | 68 | 1 890,00 | Reducing deferred tax liability (we uniformly reduce the amount of bank commission accrued in the current period on account 91-2) | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| Retention of bank proceeds credited through the POS terminal | ||||
| 60 (76) | 90-1 | 35 000,00 | Revenue deposited through the POS terminal is displayed | POS terminal control tape |
| 90-3 | 68-VAT | 5 338,98 | VAT is charged on the sales transaction | POS terminal control tape |
| 91-2 | 60 (76) | 630,00 | There is a fee charged for servicing the POS terminal. | POS terminal control tape, agreement |
| 51 | 60 (76) | 34 370,00 | The proceeds received through the POS terminal (minus bank commission) 35,000 – 630 = 34,370 rubles are credited to the company’s current account. | Electronic journal, bank statement |
Accounting for expenses for banking services
Banking fees are a common expense item for a company. However, their accounting is not as simple as it seems at first glance. We will help you figure it out.
T.N. Kovaleva, expert of AG “RADA”
The company pays the bank for services for opening an account, debiting and crediting funds, issuing cash, etc. The cost of all types of services and their specific list are stipulated in the agreement between the company and the bank. For example, in a bank account agreement (agreement for cash settlement services).
The payment schedule for bank services is also fixed in the agreement. The bank may charge the firm every day for account transactions or debit a set amount once a month.
At first glance, it is not difficult to classify the costs of paying for banking services. However, in practice this turns out to be a serious problem for many accountants. This is due to the fact that accounting and tax treatment of these expenses are different.