Every organization has household equipment: office furniture and equipment, stationery, tools, etc. This article will discuss the features of recording write-offs, i.e., transferring household equipment into operation.
You will learn:
- what document in 1C reflects the transfer of household equipment into operation;
- how to take these expenses into account in accounting and tax accounting;
- what cost item to choose to reflect expenses when transferring inventory into operation.
Components of household supplies and equipment
Accounting for inventory and household supplies (IHP) is carried out at the place of their storage and location. Typically, the following groups are used:
- Tools and devices that have universal use. They are used to manufacture a variety of products.
- Molds and similar items used for the production of certain types of products or to fulfill a single individual order.
- Containers that are used directly in the technological process.
- Production equipment.
- Household equipment.
- Instruments, laboratory equipment and automated installations.
- Working clothes and safety footwear.
- Other types of ICP.
Accounting for inventory and household supplies as part of the operating system
Those types of household equipment that are expected to be used for more than 12 months should be accounted for as part of fixed assets. When developing accounting policies, you should not miss the limitation of their cost. Within its boundaries, operating systems with a period of use of more than a year are taken into account among the inventories. The upper limit is 40 thousand rubles.
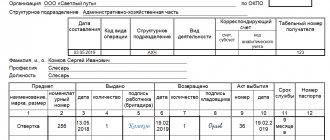
You can view the inventory card.
What else is important to know about how to write off materials in “1C: 8”
If the process is carried out according to invoice requirements, it is necessary that the goods and materials for production be operated to zero in the current reporting period. This ensures that their value is correctly written off as expenses. If they are not used up, then you need to move them from one warehouse to another, transfer everything to a special sub-account. You will have to write off expenses as an act, indicating the quantity actually used, etc.
In the program, you can enter information according to the form of the act adopted by the enterprise. It must be approved by the accounting policy. To do this, open the “Shift Report” document. It allows you to do everything manually or create a specification by unit (the latter is relevant when identical products are produced). The volume of blanks is calculated according to the required quantity of the finished product with clear data entry. The calculation will be done automatically.
If the user does not like how automatic postings are made for item items, then the settings can be found in the item accounts section.
Software for keeping records of warehouse operations can also be purchased from Cleverence. We offer various software that can be used to automate routine tasks. For example, consider "Sklad15" - software that helps you take inventory, work with cells, etc.
Accounting for inventory and household supplies as part of the inventory
ICP with a useful life of up to a year should be correctly considered as one of the components of the MPZ. For these purposes, the account is used. 10.9. The purchase of household equipment is formalized and reflected in accounting in the same way as it is provided for materials. Read also the article: → “Accounting for goods and products in the warehouse”
The main wiring used in the company:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation |
| 10.9 | 15, 23, 60 | IHPs are accepted for accounting at discount prices |
| 68, 70, 71 ,69 | Reflected the costs of purchasing IHP | |
| 20, 23, 29, 44 | 10.9 | Write-off of the full cost of industrial equipment that has been put into operation |
Example 1. I purchased household gloves from Rostok LLC in the amount of 58 thousand rubles. VAT – 10,440. Accessories were delivered by our own transport.
Subject to write-off:
- The cost of transport services is 8 thousand rubles;
- Travel allowances paid to the forwarder – 2.8 thousand rubles.
The following entries appear in the accounting:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation | Amount, rub. |
| 10 (11) | 60 | Gloves purchased from supplier | 58 000,00 |
| 19 (3) | 60 | VAT reflection | 10 440,00 |
| 10 (11) | 23 (3) | Write-off of transportation expenses | 8 000,00 |
| 10 (11) | 71 | Write-off of travel expenses | 2 800,00 |
| 60 | 51 | The debt to the supplier has been paid | 68 440,000 |
“Everything flows, everything changes...”
It’s not for nothing that a song was even written about this – in our world, everything really changes regularly. This is especially noticeable in the standards and rules of document flow. What was correct just a couple of years ago is now considered fundamentally wrong or an unoptimized approach. The changes also affected the definition of the concept of “inventory”, and with it household supplies. Everything was reviewed - what belongs to this category, how to take into account, how to control changes in the company’s property. Perhaps the most important thing based on the results of all the changes made is the main accounting rule, namely, the reflection should be made on account 1080.
Such a legal standard appeared quite recently. A few years ago, it was considered correct to keep a count of “Low value, high wear and tear items.” This included the entire inventory of the organization; it reflected the accessories used in the business activities of the company. New recommendations for proper accounting contain a rule for excluding such accounts. Since inventory still needs to be accounted for, it was moved to account 1080, making it one of the categories of materials.
Documentation of the movement of inventory and household supplies
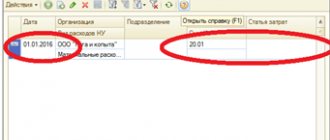
When household inventory is released from the warehouse, a demand invoice is issued according to f. No. M-11. It contains information about the department where the ICPs are issued, and the account number containing cost accounting for this department.
In the process of complete expenditure of household equipment, acts are drawn up reflecting its write-off. Based on such documents, the cost of the IPH is included in the costs.
Important! Write-off acts must be drawn up separately for different types of household supplies and equipment.
But in practice?
How it works? For example: a company has some special tools at its disposal. It is necessary for the full operation of the production workshop, so it is necessary to organize the transfer of positions. To do this, you will have to make changes to two lights: 2010 (debit), 1080 (credit). Products are written off from the account reflecting the main production and transferred to the one that shows the state of the enterprise's inventory.
Consider another example: the accounting department needs a new calculator. Let's assume that one has already been purchased, so you just need to pick it up from the warehouse by completing an operation. This is done like this: they use account 9420 (debit), which reflects the expenses of management positions, and from there the position is transferred to 1080 (credit), which shows the state of the items used in the company.
In order for the items currently used by the organization to be in order, it is important to correctly draw up account 014. It is classified as off-balance sheet and is responsible for reflecting items that have already been transferred for use to the organization’s personnel. All production premises and storage rooms used by personnel are reflected here. It is from here that positions are written off when they become unsuitable for normal use. And for this, as stated above, they appoint a commission, collect it, carry out write-off measures, and draw up an act of the standard standard within the company.
Using an inventory and household supplies card
A document called a card is a specialized form of primary documentation in the field of accounting. With its help, information about the industrial property received by the enterprise is recorded. The card takes into account IHPs whose useful life is more than one year.
Maintaining a card allows you to:
- receive prompt information about how well the organization and its divisions are provided with the necessary equipment;
- control the movement of each element of the ICP.
Important! An individual company or firm has the right to use the specified sample document or create it independently. But at the same time, all the necessary components must be preserved.
Before entering information into the card, household supplies and equipment must be collected according to one of the following criteria:
- Homogeneous purpose.
- Same price.
The form records the name of the property group and what its purpose is. The document is drawn up in a single copy for each employee who is assigned financial responsibility. Information about what inventory arrived or left is recorded on the card based on the data contained in the primary documents.
I twist and turn, I want to confuse
According to current regulations, an organization has the right to open accounts on its own initiative, where to take into account inventory, tools, and supplies necessary for business activities. The division into groups can be introduced at your discretion, focusing on the role of positions in the company’s work and the purpose of specific products.
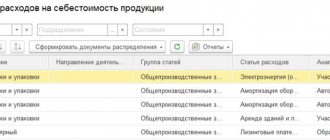
The price of inventory is included in the total production costs, which characterize the time period of transfer to operation from the warehouse.
The procedure for accounting for inventory and household supplies sent into operation
In order to control the movement of household equipment, the following is carried out:
- A record sheet of household supplies and inventory for all individual divisions of the enterprise.
- Accounting on off-balance sheet accounts.
You must select one of the above options and mark it in the company’s accounting policy. The Chart of Accounts does not contain an off-balance sheet account for those industrial enterprises that have been put into operation. However, it is put into operation in the company independently, designated, for example, as an account. 013.
When IHPs are transferred to work, the following records appear:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation |
| 25, 26, 44 | 10 (9) | Household equipment was transferred to household needs from the warehouse |
| 013 | IHP sent for household needs are taken into account |
If inventory is written off, the following entry appears:
Kt 013 inventory is completely written off
Accounting for an additionally established off-balance sheet account is carried out simply: without recording correspondence with another account.
The debit should reflect the presence of industrial property, their receipt by the company, and the credit should reflect their decommissioning.
There is no need to reflect data on this type of property in the financial statements, because:
- its value has been written off;
- such accounting does not in any way affect the correctness of information about the financial condition of the company.
Important! When household inventory is subject to disposal, this is necessarily documented in a write-off act, the structure of which the company employees develop independently.
Getting rid of unnecessary things
Some products listed in accounting records cannot actually be used as inventory or household supplies. This is due to wear, breakage, loss. In order for accounting to be correct and reflect the real state of affairs, it is necessary to regularly organize the write-off of materials. According to the current accounting rules, write-off is possible in the following cases:
- obsolescence of the product;
- expiration of operational life, storage time, shelf life;
- detection of loss, shortage, including situations provoked by accidents, natural disasters;
- detection of unaccounted positions.
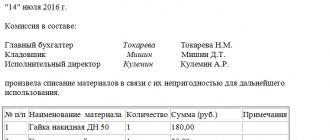
Write-off of inventory is completed using standard form 39P. In this way, you can write off any inventory or household supplies:
- special shoes, clothing;
- safety products;
- durable items.
If some items are classified as scrap and sent as such “junk” to the company’s storerooms, 39P is also drawn up. The act is prepared by the commission responsible for the write-off, established by an internal order of the chief executive. One copy of the document is sufficient. When the items actually end up in the storeroom, the documentation is sent to the Central Bank, having previously been signed by the storekeeper who accepted the items.
Features of accounting in a budgetary institution
The legislation does not clearly define what kind of property can be classified as inventory and household supplies (IHP). In accordance with established practice, IHP in budgetary institutions consists of:
- office furniture (cabinets, chairs, tables, bedside tables);
- electronic equipment (voice recorders and tablets, video cameras and cameras);
- devices for keeping rooms, workplaces and surrounding areas clean (mops, brooms, brooms, buckets);
- devices intended for lighting;
- things for toilet procedures (towels, soap, fresheners, sprays and gels);
- fire extinguishing equipment (fire cabinets, stands, fire extinguishers, shovels, hooks);
- household and kitchen appliances (refrigerators, coffee makers, microwave ovens, coolers);
- stationery
The criteria for classification as OS or materials are standard. The main one is SPI (useful life). When it is greater than 12 months, these non-financial assets are correctly reflected among fixed assets. Accordingly, those household supplies that will be written off in less than a year are inventories.
What accounting objects are classified as soft inventory?
The list of objects that are usually classified as soft inventory is presented in paragraph 118 of Instruction No. 157n, and it is open. This list includes:
– underwear (shirts, chemises, dressing gowns, etc.); – bed linen and accessories (mattresses, pillows, blankets, sheets, duvet covers, pillowcases, bedspreads, sleeping bags, etc.); – all types of clothing and footwear (suits, coats, raincoats, short fur coats, dresses, sweaters, skirts, jackets, trousers, boots, sandals, felt boots, etc.); – sportswear and footwear (suits, boots, etc.); – uniforms and other items of clothing functionally oriented towards civil defense; – special clothing and footwear, including safety equipment (overalls, suits, jackets, trousers, dressing gowns, sheepskin coats, sheepskin coats, various shoes, mittens, glasses, helmets, gas masks, respirators, other types of special clothing).
The specified property items are taken into account as part of material inventories, regardless of their cost and service life (clause 99 of Instruction No. 157n). The following does not apply to soft equipment:
– raw materials for its production (fabric, leather and other materials); – rags formed after the expiration of the life of clothing and linen; – costumes for theatrical productions, scenery, curtains; – tents, parachutes, carpets and other similar accounting objects with a service life of more than a year.
For your information:
the decision to classify objects as soft inventory items or another type of property (fixed assets, other inventories, etc.) is made by the institution’s commission for the receipt and disposal of assets at the procurement planning stage or upon receipt of objects.
Tax accounting under different taxation systems
Expenses on inventory and household supplies are not reflected equally in taxes
Companies with OSNO
In the process of calculating income tax when using OSNO, the write-off of the cost of industrial property occurs through the determination of depreciation charges. When household inventory cannot be recognized as property subject to depreciation, it is taken into account as part of the inventory. The company has the right to decide on the procedure for writing off IHP in the way it considers most appropriate, taking into account the length of time it was in use and other economic criteria.
For example, this can be done:
- in one go, one-time;
- evenly over not one, but several months.
When a company uses the accrual method, the tax base is reduced depending on the fact that the inventory is sent for use.
When using the cash method, the tax base is reduced after the transfer of the industrial property for use and the transfer of payment for its cost to the supplier company.
simplified tax system
In a company using the simplified tax system, costs are taken into account depending on which object of taxation it has chosen. If the object “income” is used, then the costs of economic property will not be able to reduce the tax base.
When the object is the same income, but minus costs, the tax base is reduced by the cost of purchased inventory and household property. The costs also include input VAT on these goods.
UTII
For such enterprises, expenses for household equipment do not affect the size of the tax base. The reason is that the object of UTII taxation is imputed income.
Combination of OSNO and UTII
When IHPs are used simultaneously in two types of company activities that are different from the type of taxation, the amount of expenses must be distributed. The calculation is carried out in direct proportion to the share of income from each type of activity. Indicators are determined for the period of time in which the inventory was purchased. The amount of VAT allocated in the invoice for the purchase of industrial property is also subject to proportional distribution.
How to draw up an act for writing off an instrument: sequence of actions
The standard form of the act is drawn up as follows:
- The resolution of the head of the organization “I approve” is placed in the upper right corner. Next, indicate the name of the organization, position and full name. its manager, date of approval.
- Next, indicate the full name of the document and the date of its preparation.
- The composition of the commission should be listed below. They write down the phrase “The Commission is composed of”, and then list the position and full name. its members.
- After this, you need to record the fact of writing off the instruments and indicate the reasons for their write-off.
- Information about unusable tools is usually displayed in the form of a table consisting of columns: tool name, quantity, unit cost and total amount. If the commission members have any comments on the items being written off, they can indicate them in a separate column.
- Below the table indicate the total cost of all inventory items.
After signing the act by all members of the commission and the financially responsible person, it is submitted to the head of the organization for approval.
Members of the commission are responsible for filling out the instrument write-off form. They must ensure that the procedure is carried out in accordance with legal norms and that only reliable data is displayed in the document. If financially responsible persons simply throw away unusable tools without carrying out the write-off procedure, the organization’s management may accuse them of theft. The director has the right to demand from them compensation for the cost of inventory items in full.
Supporting documentation must be attached to the act. These may be invoices confirming receipt of the tool, documents for internal movement.