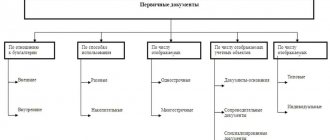
About managing personal affairs
The employer is obliged to maintain personal files of employees if this is expressly prescribed by regulations. For example, such a requirement is established for executive authorities. Those companies that are not subject to such acts have no obligation to maintain personal files of employees. However, sometimes employers begin to form them on their own initiative. In this case, they themselves draw up a list of documents that need to be included in their personal file. But it is important to comply with the law on the confidentiality of personal data.
So, for one reason or another, the company decided to create personal files for employees. First of all, you need to draw up a local regulatory act that will define important points and rules. This could be a standard or a position. It is advisable to reflect all the rules for registering personal files and the composition of documents.
The main rule: you should not collect unnecessary information about an employee in reserve - only what is really important. Otherwise, the principles of working with personal data will be violated.
Responsible person
Will the operator be held liable if he has not appointed a person responsible for the processing of personal data?
RKN will not be held administratively liable. But if such a fact is revealed during the inspection, the inspector will issue an order indicating the deadline for its execution. And if the operator does not eliminate the violation within this period, he will be brought to administrative liability under Art. 19.5 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Is it possible to appoint several persons responsible for processing personal data?
The notice of intention to process personal data must indicate only one individual responsible for the processing of personal data. Of course, the person in charge can delegate part of his functionality, but this needs to be indicated only in the operator’s local acts.
Is it possible to indicate in the notification the legal entity responsible for processing personal data?
Yes, if a legal entity is involved in the processing, it may be indicated in the notice of intention to process personal data in addition to the information provided for in Art. 22 of Law No. 152-FZ.
Protection of personal information
You can only collect information about an employee that meets the specific purposes for processing personal data . Otherwise, the organization may be fined under Article 13.11 of the Administrative Code in the amount of 30 to 50 thousand rubles . An official will receive a fine in the amount of 5-10 thousand rubles, and a citizen - in the amount of 1-3 thousand rubles.
What is the correct way to deal with employee documents? Let us turn to Article 65 of the Labor Code. It states that documents must be presented by an individual when applying for a job. In other words, the documents must be presented to the employer, after which they are returned to the employee. At the same time, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not say that the employer’s specialist has the right to make copies of them.
So, without the employee’s consent, a personnel specialist can only do the following: take the employee’s documents and enter information from them into his personal T-2 card.
In practice, employers often like to collect various information about their employees and store copies of their diplomas, SNILS, and passports. However, all these documents contain personal data of employees, which are protected by law. Collect personal information that serves a legitimate purpose. Moreover, the goal must be quite specific. For example, you cannot store an employee’s personal data in case the prosecutor’s office or the Bailiff Service suddenly requests it. As long as there is no such request, the employer does not need this information. Accordingly, if he collected it in advance and stores it, he thereby violates the law on the protection of personal data.
Important! The processing of a citizen’s personal data is permissible if it is necessary to fulfill an agreement to which he is a party. This is stated in Part 1 of Article 6 of the Law on Personal Data dated July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ.
GDPR and Russian companies
GDPR may apply to Russian companies in several cases:
- The Russian company has branches throughout Europe.
- The Russian company acts on behalf of the European company and is responsible to it for the processing of personal data.
- The Russian company operates not only in Russia, but is also aimed at European consumers. For example, an online store offers the sale of goods to Europe, and two conditions are simultaneously met:
- the site is available in the languages of EU countries;
- Payments in euros are provided.
If one of these conditions is not met, then the GDPR requirements do not apply to such a store.
Will Russian legislation be brought in line with the requirements of the GDPR?
According to Kontemirov, this is a debatable issue. Experts are studying the practice of applying European legislation, but how this will be implemented in Russia will be seen in the near future.
If the employee has given consent
It would seem that the problem can be solved simply - you can take a document from the employee stating that he allows the processing of his information. But in reality this is not enough. Even if the employee has agreed, this does not mean that there is a legitimate, specific purpose for processing the data.
Important! Employers need to remember a simple rule: if there is no purpose, then there is no right to keep copies of the employee’s personal documents.
The said law defines the principles for the protection of personal data. The point is this:
- There must be specific, pre-determined purposes for which a person's personal data is collected. Once these purposes have been achieved, the processing of his personal data must cease.
- Information may not be collected that is inconsistent with the purposes mentioned above.
- Only information that corresponds to the specified purposes is subject to processing.
- The content and scope of the data processed must correspond to the purpose of the processing.
Consent to the processing of personal data is stated in Article 9 of the law. It must again contain the purpose of processing, as well as a list of actions that can be performed with this data.
Conclusion: you can store copies of employee documents in personnel records only if it is needed for specific purposes.
For example, personal information may be collected for posting on the employer’s website (in the “Our Employees” section) or for issuing a voluntary health insurance policy. An example of a redundant purpose is storing personal data in case of a government request.
About the passport copy
A copy of the passport contains not only the name, date of birth and other information - it can be a source of biometric personal data .
In particular, in the photo you can notice the features of a person’s appearance. Such information is protected by law. Accordingly, it is necessary to store copies of employees’ passports, firstly, if there are adequate purposes and, secondly, after obtaining their consent to do so.
Conditions under which it is safe to store copies
In Art. 86 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation outlines the purposes for which employers are allowed to use and store employee data. They are used for:
- ensuring compliance with laws and other regulations;
- assistance in employment; providing education and career advancement;
- ensuring personal safety of workers;
- control the quantity and quality of work performed and ensure the safety of property.
In many organizations, not knowing what documents cannot be kept in an employee’s personal file, they keep copies of passports and other documents according to tradition. And sometimes even after dismissal. Meanwhile, the list of purposes for which employers are allowed to use employees’ personal data and the list of documents that are allowed to be stored in employees’ personal files are closed - copies cannot be used in any other way. For example, a photocopy of a passport will help fill out an employee card, maybe a couple more papers, but then it is no longer needed.