General provisions
1.1. Inventory is carried out in each of the following cases (clause 1.5 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory, clause 27 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n, part 3, article 11, h 1 Article 30 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ, paragraph 38 PBU 4/99):
- before preparing annual financial statements;
- when changing financially responsible persons;
- when identifying facts of theft or damage to property, when it is necessary to establish the name and quantity of stolen (damaged) property;
- in the event of a natural disaster, fire or other emergency;
- upon liquidation or reorganization of an organization;
- in other cases when conducting an inventory is mandatory in accordance with legal requirements.
1.2. Checking the actual availability of property and the validity of existing obligations consists of performing the following actions:
- obtaining receipts from financially responsible persons in the relevant inventory records (acts) before and after the end of the inspection (paragraph 3, clause 2.4, clause 2.10 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory);
- entering into the relevant inventory lists (acts) missing information and technical indicators for objects that are not reflected in accounting or for which there is no data characterizing them (Instructions for the use and completion of forms);
- indication of the number of valuables (fixed assets, inventories, cash on hand, documentary securities, etc.), determined by physical counting, weighing, measuring (clause 2.7 of the Inventory Guidelines, Instructions for the use and filling out of forms );
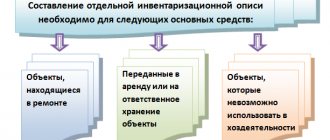
- Inspection of fixed assets for their further use. When identifying fixed assets that are not suitable for use and cannot be restored, the corresponding information is entered into a separate inventory list indicating the time of commissioning and the reasons that led these objects to unsuitability (damage, complete wear and tear, etc.) (clause 3.6 of the Methodological inventory instructions);
- Inspection of inventory items for their further use. When identifying unused or obsolete values, as well as values that have completely or partially lost their original quality or the further use of which is doubtful, the relevant information is entered into a separate inventory list (act) or a write-off act (clauses 3.25, 3.26 of the Methodological inventory instructions);
- confirmation of the presence of assets that do not have a tangible form (cash in bank accounts, intangible assets, financial investments, etc.) through documentary verification (clauses 3.8, 3.14, 3.43 of the Inventory Guidelines);
- confirmation of the balance sheet valuation of assets (taking into account valuation reserves);
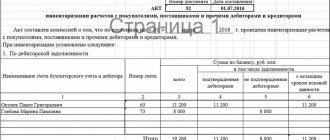
- determining the correctness and validity of the listed amounts of receivables and payables, estimates and other obligations by checking documents confirming the existence of an obligation or claim (clause 3.44 of the Inventory Guidelines).
1.3. The type of inventory carried out (continuous, selective) is determined by order of the manager. When conducting a selective inventory, the order indicates the types (groups, names) of individual assets and liabilities to be inventoried.
1.4. The following terms and frequency of planned continuous inventories are established (clause 2.1 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory, clause 26 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting):
| Inventory object | Periodicity | Planned timing of inventory 1 |
| Fixed assets | Once every three years, starting from 2015 (clause 1.5 of the Inventory Guidelines) | From October 1 to October 10 of the year of inventory |
| Unfinished capital construction | Annually before preparing annual financial statements 2 | From October 11 to October 20 of each reporting year |
| Intangible assets | Annually before preparing annual financial statements 2 | From October 21 to October 25 of each reporting year |
| Financial investments Provision for impairment of financial investments 3 | Annually before preparing annual financial statements 2 | From October 26 to October 30 of each reporting year |
| Inventories Reserve for reduction in the value of material assets 3 | Before preparing financial statements for the first half of the year 2 | From June 10 to June 25 of each reporting year |
| Before preparing annual financial statements 3 | From October 31 to November 15 of each reporting year | |
| Unfinished production | Before preparing financial statements for the first half of the year | From June 10 to June 25 of each reporting year |
| Before preparing annual financial statements | From October 31 to November 15 of each reporting year | |
| Future expenses | Annually before preparing annual financial statements 2 | From November 16 to November 20 of each reporting year |
| Cash in the cash register Forms of strict reporting documents | Quarterly | On the last working day of each quarter |
| Cash in bank account | Annually before preparing annual financial statements 2 As of December 31 | On the first working day of each calendar year |
| Accounts receivable Provision for doubtful debts 3 | Annually before preparing annual financial statements | From December 25 to December 31 of each reporting year |
| Accounts payable | Annually before preparing annual financial statements | From December 25 to December 31 of each reporting year |
| Estimated liabilities | Annually before preparing annual financial statements | From December 25 to December 31 of each reporting year |
| ||
1.5. Claims to the inventory commission are made in writing and sent to the head of the organization, who makes a decision on the procedure for satisfying it.
When to check
An order is usually drawn up by order of the manager in a planned or unscheduled manner. The person responsible for this is the chief accountant or another accounting employee, and if he is ill or absent, a person authorized to maintain accounting records.
Inventory is required in several cases (clause 27 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n):
- before preparing annual reports (you will need to inventory all assets and liabilities);
- when changing financially responsible persons, including those associated with the transfer of property to third parties;
- after emergency situations - fires, floods, other disasters;
- upon detection of theft or damage to property.
Receiving receipts from financially responsible persons
Before conducting an inventory, the commission collects the latest receipts and expenditure orders and reports on the movement of material assets (cash).
The chairman of the commission endorses all received orders with the indication “before inventory on “__________” (date).”
Financially responsible persons provide receipts stating that:
- receipt and expenditure documents were submitted by them to the accounting department or transferred to the commission;
- the assets that were their responsibility were capitalized;
- retired valuables are written off as expenses.
Inventory when preparing annual reports
The procedure, timing and list of objects are established in the accounting policy. On its basis, a sample inventory order is prepared annually before the annual report. List in it the composition of the commission, the name of the assets and liabilities being inventoried, the start and end dates, and state the reason:
the need to prepare annual financial statements.
Inventory deadlines
Russian legislation does not clearly establish the timing of inventory. But this does not mean that verification can be carried out at any time. The absence of a strict framework does not make it possible to abandon the inventory altogether.
The terms are set by the head of the enterprise. But he must pay attention to existing legislation. They are the ones who set the frequency of the inventory. This indicator depends on the inventory of what type of property the organization conducts. It also matters what obligations the company has. The manager of the enterprise must take these factors into account even before drawing up the inventory schedule.
In different organizations, the number of inventories and the timing of inventories are determined differently, but they must comply with existing requirements. Let's consider situations when an enterprise must conduct an annual inventory:
| Inventory objects | Frequency | Availability of specific features |
| MPZ | Every year | Carried out before preparing financial statements for the year |
| Capital investments | Before the start of drawing up a balance sheet and report for the entire year (inventory deadlines do not allow starting the check before December 1 of the current year) | |
| Major renovations currently underway | No | |
| Production not yet completed | Before the start of compiling annual reporting documentation, but not earlier than October 1 of the current year (in addition, the timing of the inventory in the organization is established by higher-level organizations) |
There are also objects that require more frequent inspections. If we are talking about accounts receivable or payable, then their inventory should be carried out 2 times a year - as of 01.06 and 01.12 of the current year.
There are research objects that require even more frequent checks. The procedure and timing of the inventory for them are determined by the manager. The following facilities must be inspected at least once a quarter:
- calculations regarding contributions to the budget;
- forms of waybills.
Every month the responsible person must take inventory of:
- materials;
- raw materials;
- money belonging to the enterprise;
- securities (we are talking about various monetary documents);
- strict reporting forms.
The manager must indicate in the accounting policy the frequency of the property inventory and the timing for each type of object. The main thing is not to break the existing rules.
An enterprise must conduct an inventory of settlements with its structural divisions that have their own balance sheet. This must be done every month on the 1st day.
An inventory of settlements with banks should be carried out as the relevant statements are received. The procedure and timing of the inventory are determined in this case situationally. Not only settlement accounts, but also other forms of enterprise accounts are taken into account.
Inventory may also be required in the event of bankruptcy of an enterprise. In this case, verification is mandatory in accordance with Russian legislation. It is necessary to inventory existing property. The timing of the inventory in bankruptcy proceedings is not precisely defined. It must begin at the moment the property is transferred to the jurisdiction of the bankruptcy trustee. The duration depends on the number of objects to be inventoried. Typically the procedure takes from 3 to 14 days.
How to draw up an order for inspection using form No. INV-22
Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88 approved form No. INV-22 - on its basis, a sample order for conducting an inventory 2021 was prepared. Form INV-22 must be used regardless of what the proceedings are related to, whether it is full or partial, whether it was planned in advance or carried out unexpectedly.
The order contains:
- the specific purpose of the conduct is an inventory of goods, fixed assets, assets, receivables, and all property;
- listing the divisions of the organization where the inspection will be carried out, for example, only in a warehouse or in another department, throughout the company;
- period and duration of the event - from what date to what date, when to provide the results of verification actions;
- composition of the commission, including full name its chairman - it is allowed to include not only company employees capable of assessing the state of property and liabilities, but also third-party auditors;
- information about the order: its date, number, information about the manager who signed the order.
Once the establishing document has been prepared, it must be recorded in a journal to record control over the implementation of such decisions. Take the corresponding register form from Goskomstat Resolution No. 88 - form No. INV-23. This is not necessary; companies are allowed to develop their own version of the magazine, but for convenience, use the template proposed by officials.
It is important that all employees listed in it are familiar with the order. They place their signatures directly on the sheet containing data on the upcoming inspection, or on a separate sheet for familiarization with the document, which is filed with the order.
The intention to compare goods, inventories, and valuables on paper and in reality must be notified and signed by the financially responsible persons of the department where the reconciliation is being carried out.
What to Inventory
The following are subject to inventory (clause 1, article 11 of law No. 402-FZ, clauses 1.2, 1.3 of the Guidelines):
- All property (assets) of the organization, regardless of its location. These are fixed assets, intangible assets, financial investments, inventories, finished products, goods, other inventories, cash and other financial assets, including accounts receivable. An inventory is also taken of property that does not belong to the organization, but is located in it (in custody, on lease, in processing), as well as property that is not taken into account for any reason.
- All financial liabilities (accounts payable, bank loans, loans and reserves).
About the need to carry out an inventory of property accounted for off-balance sheet, read the material “Is it possible to carry out an inventory for off-balance sheet accounts? ”
EXPLANATIONS from ConsultantPlus: During the inventory of fixed assets, it is necessary to check not only the presence of the objects themselves, but also their technical and (or) operational characteristics, as well as identify unused objects and the reasons why they are not used. Inventory of fixed assets has other features. They are related to the frequency of its conduct before the preparation of annual financial statements. Find out more about the nuances of conducting an inventory in the K+ legal reference system by receiving trial demo access. It's free.
Example: how to draw up an order for an inventory of material assets (2021 sample)
Step 1. In the appropriate fields, enter the name of the organization (IP), indicate OKPO, specify the order number and the date of its preparation.
Step 2. manta, specifying what event is being held and which of the employees is participating in it: the order for inventory contains the full name. employees, but when listing it is allowed to abbreviate their names and patronymics.
Step 3. We indicate what needs to be checked and in which department, we explain the reasons why it is necessary to compare real stocks, valuables, goods and those indicated in the documents. In our case, an example of the reason for inventory in the order contains the wording:
Detection of the theft of valuables from a warehouse by a security guard.
At the same time, we enter the start and end dates of the property condition analysis procedure.
Step 4. The last thing is to determine the last date for submitting the report based on the results of the reconciliation, and sign it with the manager who appointed the inspection.
This is what a completed order looks like.
Drawing up an order in any form
The order can also be drawn up in any form. But there is a list of information and details that must be indicated in an official document:
- company name;
- date of preparation and document number;
- objects and purpose of the inspection;
- list of departments involved;
- period;
- deadlines for providing results;
- composition of the commission indicating the last names, first names, patronymics and positions of each of its members;
- last name, first name, patronymic and signature of the manager.
Inventory and registration of its results
The verification consists of comparing and contrasting the actual volumes of values with those recorded in the primary documents. Therefore, first, the commission members get acquainted with the inventories of existing valuables, goods, and supplies. They then compare the property on hand to what is on paper.
At the end of the counting and comparison procedure, the commission members draw up documents containing the results of the inspection. Most often this is not one document, but several. Thus, the identified discrepancies are recorded in the results sheet. As a template for such a document, use form No. INV-26 from Goskomstat Resolution No. 26 dated March 27, 2000.
Documents for recording the results of the inventory are drawn up after it is completed. For example, if your organization carried out an inventory before drawing up annual reports in December 2019, then you are allowed to draw up documents based on its results as early as January 2021. If a discrepancy is identified between the actual data and accounting data, then they must be recorded in the reconciliation statement. A separate comparison sheet is drawn up for objects in custody or leased objects.
The accountant draws up a matching statement in two copies. One of them will remain in the accounting department, the second will be transferred to the financially responsible person.
Later, the results are discussed at a special meeting of the permanent inventory commission, which is the basis for drawing up a protocol. There is no approved form for the protocol, so the main requirements are to correctly indicate the data from the order on the initiation of control measures, about the members of the commission, and the discrepancies identified. If there are no discrepancies, this must be documented. At the same time, the commission puts forward proposals to capitalize, write off the identified surpluses (deficiencies), and reflect them on the balance sheet. In addition, it is permissible to record other initiatives in the protocol, for example, to strengthen security in order to avoid theft in the future. So, the list of final documents contains the following documents:
- a statement of records of the results identified by the inventory;
- comparison sheet of inventory results;
- a comparative statement of the results of the inventory of valuables owned by the organization;
- a comparative statement of the results of the inventory of rented objects;
- inventory list;
- explanatory letter.
Rules for conducting inspections at the enterprise
In order to accurately understand when and how to carry out an inventory, it is necessary to study the specifics of this issue. When taking up a position, the responsible person is obliged to thoroughly study the general rules for conducting inventory. This will help him avoid possible errors and inaccuracies.
Russian legislation clearly regulates when an enterprise is obliged to conduct an inventory check, and when it can do this at will. In both cases, the inventory commission must adhere to certain requirements. The inventory rules are:
- the head of the organization determines the timing and scope of inventory checks;
- when conducting inspections, MOTs related to property must be present;
- it is necessary to constantly monitor all situations that make inventory a mandatory procedure;
- to determine the amount of property an organization has, the general inventory procedure allows the use of counting, measurements or weighing, depending on the type of value;
- even before the completion of inventory activities, control checks can be carried out to determine the accuracy of the data obtained;
- if an organization has many types of valuables, then in the intervals between mandatory inventories it is recommended to conduct random checks of some categories.
The inspection rules are clear; all that remains is to figure out how to carry out an inventory at the enterprise.
Summarizing
After the commission has completed the inventory, a meeting is held. During it, the main results and identified discrepancies are determined. At the same time, the cause of the discrepancies and ways to correct the situation are determined. Based on the results, minutes of the meeting are drawn up. Typically this document has the following structure:
- name of the company indicating the organizational and legal form;
- the name of the unit where the inventory was carried out;
- name of the document - protocol of the inventory commission;
- list of commission members indicating surnames, initials and positions;
- description of the test results;
- list of speakers at the meeting;
- decision;
- conclusion of the commission;
- identified violations (if any);
- those responsible for the violation, indicating their surnames, initials and positions;
- information about measures to eliminate violations;
- signatures of the chairman and all members of the commission;
- applications.
As an illustration, we will give a variant of the protocol.
To easily draw up such a document, prepare the minutes of the meeting attached to the article.
The following documents are attached as appendices to the minutes of the meeting:
- acts and inventories of the inventory carried out according to INV forms for each materially responsible employee, facility, warehouse or division;
- list of products unsuitable for further use;
- a list of missing or excess products with an indication of price;
- explanatory notes from financially responsible employees or other officials.
We would like to add that at the meeting the commission must make the following proposals:
- on the timing and methods of eliminating shortages, on conducting internal investigations (if a shortage is detected);
- on the continued use of outdated and unsuitable products for subsequent use;
- other proposals regarding work with inventory items.
If no violations were found during the inspection, then there is no need to draw up an inventory protocol.
Based on such a protocol, the manager issues an order based on the results of the inventory.
Compiled by whom?
One person is not involved in drawing up the inventory report. A commission of at least 3 people is always appointed. The director or head of the company must indicate who will be among them in the issued order.
Typically the commission includes:
- Head of the enterprise;
- Accountant;
- Responsible for storing inventory and intangible assets;
- Professional auditors (optional);
- Employees of the organization.
This means that the act must contain the full names and signatures of all participants in the inventory. Members of the commission have the right to make written comments and clarifications. A mandatory condition is also the personal presence of the persons noted in the manager’s order. If someone is not present, as well as someone’s signature is not on the act, the event cannot be considered completed. And the report data may be considered invalid.
If there is a break in the work of the commission, it is necessary to limit access to documentation. It is usually placed in a safe or locker for safekeeping. An office or store premises may be sealed during a break (for example, at night). Outsiders should not have access to the results of the audit to avoid falsification of information.
Order based on inventory results
This document necessarily reflects the “reaction” of management to the proposals of the commission members and specific instructions on what needs to be done: conduct an additional inspection, punish the perpetrators, introduce additional security measures. The manager sometimes reserves control over the execution of orders. Let's take a closer look at the structure of the order. It, like a similar administrative document, is drawn up according to certain rules. Its structure must contain the following points:
- name of the organization and its legal form;
- details (it is convenient to use a letterhead);
- date and order number;
- preamble, which lists all the documents regulating the inventory (inventory acts, matching and accounting statements, audit protocol);
- order part.
The last part of the order reflects the following points:
- the results of the inspection are subject to approval;
- it is necessary to indicate the requirement to resolve discrepancies identified during the inventory and recorded in the relevant documents;
- an employee is appointed, usually from the accounting department, who is responsible for fulfilling the requirements of this order related to the elimination of discrepancies previously identified during the audit;
- an employee is appointed responsible for monitoring the implementation of the orders recorded in the provisions of the order on summing up the results.
After the order is signed by the first person of the company, the form is handed over to the responsible employee who is authorized to familiarize the designated employees with the provisions of the order against signature.
Check procedure
Before starting an inventory check, management draws up an appropriate order, which displays the stages of future work and their condensed characteristics. All employees are familiarized with this document, which makes it possible to quickly carry out all preparatory activities and ensure the accuracy and high quality of the final data obtained during the inspection. Inventory instructions determine the presence of the following characteristic features of the inspection:
- at the very beginning of the inspection at the enterprise, a special commission is created that operates throughout the entire inventory (such a commission is approved by the head of the organization);
- inventory begins after confirmation by the inventory commission of the receipt of reported values and the corresponding documentation;
- the commission is responsible for the accuracy, timeliness and clarity of the documentation compiled (knowing how to carry out an inventory, commission members must monitor the progress and correct recording of the results obtained);
- As the audit is carried out, its results are entered into the primary accounting documentation.
For more information on the formation of an inventory commission, read the article.
The correct implementation of all activities ensures the correctness and accuracy of the data obtained.