As a rule, current control over the state of the assets of a company or organization is carried out through current accounting or management accounting. However, such control cannot cover every minute all the changes occurring in the material complex of the organization.
Because of this, a special procedure is provided for comprehensive and total accounting of material assets, known as “inventory of fixed assets,” which is carried out at certain intervals and according to the regulations established by regulations.
This article will talk about what an inventory of fixed assets is, on what legal basis it is carried out, what is included in the controlled assets, as well as who is responsible for its implementation and what documents are used to document the completion of the inventory.
What is it - an inventory of fixed assets (fixed assets) at an enterprise
First of all, this is a recalculation of the assets that the company has. With this action, it becomes possible to keep the company's property unharmed. Its main task is to compare real and virtual balances by checking the data specified in the accounting records. This is how money, equipment, buildings, debt obligations and much more are considered.
Using the census, you can monitor the correctness of information reflected in the organization’s accounts. Corrections are made as necessary to keep the reporting current.
The essence and meaning of inventory
Inventory is a method of monitoring the safety of the company’s property and obligations, as well as the accuracy of the reflection of information about them in accounting.
During the inventory, it is checked whether the actual availability of valuables corresponds to the data in the accounting reports. Also during its implementation, you can check whether all business transactions are reflected and executed properly. If necessary, clarifications and corrections can be made.
Due to certain circumstances, not all events are economic. activities can be registered at the same moment in which they were committed (for example, theft). Such transactions can only be identified during the inventory process. Based on the results of the check, you can register unaccounted transactions.
Business Solutions
- shops clothing, shoes, groceries, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
During the inventory, determine:
- are there actually objects that are indicated on paper and in the program;
- How correctly are inventory numbers assigned?
- Are accounting records maintained correctly?
- volumes of shortages/surpluses.
Terms, rules, frequency of inventory of fixed assets
According to the law, an inspection should be carried out at least once every 3 years at the enterprise. Library collections will not have to be counted and checked so often - once every five years. This is established on the basis of the Methodological Instructions.
Each company determines specific data for itself. This is usually done before the start of the annual report. But according to the law, there are cases when this should be done more often:
- as a result of an emergency;
- if reorganization or liquidation has begun;
- the property is going to be rented out or completely sold;
- The MOL or manager will change soon;
- annual reporting will be prepared soon;
- facts of theft, damage to property or abuse of authority were identified.
It is worth noting that if team members demand, then such a reconciliation is also carried out in the case when more than half of all participants in the contract leave.
By order of the owner or director of the organization, this can happen suddenly, at any time. There is a continuous inventory, when everything that is in the company is counted, and a selective inventory, when they count the assets in one division, branch or even office.
OS Inventory Rules
The main point of inventory is to determine the actual presence and condition of an object in order to adjust the existing accounting data if necessary. This is indicated by the rules for conducting OS inventory (pr. No. 49):
- An object not accepted for accounting, as well as in cases where incorrect data is indicated on it or data is missing, the commission must describe on the spot correctly and completely, include all technical indicators and other indicators for it in the inventory. Example: for buildings, indicate the materials of construction, purpose, measurements, area, number of floors (except for basements), date of construction.
- Market valuation must be applied to any unaccounted for items discovered. Wear is determined based on actual condition. To register such objects, a corresponding act is drawn up.
- In case of actual re-equipment (expansion, reconstruction, restoration), as a result of which the object is used for a different purpose, updated information is entered into the inventory.
- If the commission established that major work was carried out at the facility: premises were added, floors were completed; or a part has been scrapped or liquidated, pay attention to how the object is reflected in accounting. If the changes are not reflected, it is necessary to adjust the book value of the fixed assets based on the data from the primary documentation of the work. The inventory provides information about the changes.
As a general rule, machines, equipment, and transport are entered individually, indicating technical characteristics, manufacturer and other significant data. In some cases, the same type of inventory, machines and tools that have the same cost and are used in one division of the organization are taken into account in the inventory card of the appropriate form as a group. In the inventory they are reflected in one line indicating the actual number of objects.
Objects that have been temporarily removed from their parking areas, are in use, or are located outside the organization’s territory (for example, railway rolling stock, machinery, vehicles undergoing major repairs) must be inventoried in advance, prior to disposal. At the same time, it is advisable to inventory assets that are under repair by entering data into a separate form INV-10 (act). The commission inspects the facility under repair and compares the actual costs of repairs with the planned ones. The act reflects data on savings or overexpenditures, which are subsequently used for analysis and identification of economic reserves. The percentage of technical readiness of the object is indicated.
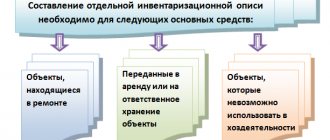
Separate inventories are compiled on the OS:
- unsuitable for use – completely worn out, damaged (the reason for unsuitability is indicated);
- rented and in safe custody (details of documents confirming rent, safe storage are indicated).
What is an inventory of fixed assets
This is a count of objects that are constantly used during production or for administration needs. This may include machines, equipment, equipment, including computers, various household equipment, livestock and plants.
The recount can be natural - when inspectors or authorities walk around the company and check the actual presence of assets. Another option is documentary, when they are reconciled only using accounting registers.
Legally, all this is formalized depending on what supporting documents were developed within the enterprise and secured by accounting policies through an order. A statement is a document that will be drawn up in 2 identical forms, because one is sent to the accountant, and the second remains with the MOL.
Commission for Inventory of Fixed Assets
The tasks of these people include inspection and verification of the correspondence of virtual balances to real ones. They record all the differences in the statement they have, write down inventory numbers, and monitor the characteristics.
They receive all relevant documents before starting their study. Who will be part of the inspectors fits into IVN-22. Financially responsible persons must mark that they hand over everything accountable.
Not only accounting sheets are subject to study and reconciliation, but also:
- information according to which it is possible to determine ownership of objects;
- technical passports;
- availability of documentation for natural resources owned by the company.
The need for an inventory
The purposes of conducting an inventory are for a number of reasons, the main of which are:
- conducting audits and audits;
- theft and abuse of organizational assets;
- various emergencies and natural disasters;
- at the request of investigative authorities;
- change of financially responsible employee;
- distrust of the financially responsible employee;
- identifying errors in accounting that can lead to material losses;
- change in the physical properties of values. This is due to the fact that some products change their physical properties as a result of natural loss.
Purpose and reasons for conducting an inventory of fixed assets
There are several reasons to perform such a study of warehouses and operating systems:
- it is possible to speak with certainty about the presence or absence of certain objects on the territory;
- it becomes easy to compare the actual data with those indicated in the accounting registers;
- it is allowed to correct the accounting document in accordance with the information revealed in fact.
When an inspection is carried out unscheduled, this usually happens due to discovered theft, the consequences of an emergency, or a change in management.
Nowadays it is allowed not to use strict reporting forms, but to develop your own accounting documentation. The main thing is to have all the details and positions. If you don’t have time to develop such templates, you can use standard examples in the program.
It is important that the software completely covers all tasks that arise in the enterprise. If this does not happen, then you can seek help from professionals, for example, at.
Thus, you can effectively check an enterprise’s OS using the “OS Inventory” software product.
This software allows you to use an information collection terminal with a built-in barcode reader to reconcile company fixed assets.
Each OS comes with a unique barcode label that can be printed using the driver. A standards-compliant, 100% readable barcode is automatically generated by the software based on the accession number.
The software allows you to upload information about the availability of a particular material from the 1C database, and then use the device to collect barcodes of real positions of fixed assets and balances and then load the received real information into “Inventory of fixed assets” or into “Entering balances of fixed assets and intangible assets” and for receiving availability and discrepancy reports.
The software also supports accounting by materially responsible persons (MRO) and departments.
Why do we need automation of OS accounting and inventory?
By automating fixed assets accounting and inventory, a company can achieve the following positive aspects:
- reduce the cost of time and money, since high speed of all operations will be achieved;
- increase the accuracy of inventory results, since its implementation will not be influenced by the human factor, which entails errors or inaccuracies in accounting;
- reduce the number of workers required to be involved when conducting inventory;
- identify and promptly restore markings if they are damaged or unreadable.
To automate accounting and inventory of fixed assets, two main types of technology are currently used: Barcoding and RFID.
The process of implementing automated accounting and inventory of OS based on barcoding involves the following steps:
- mark property items. To carry out this action, special adhesive labels are used, on which barcodes are printed. They are created by using special printers to print labels or tags. The type of labels for marking depends on the property to be accounted for. It is advisable to use polypropylene labels , since they are more durable and resistant to mechanical damage. In addition, labels can be either simple sticker tags or secure body tags;
- buy special equipment for reading information. For this purpose, special data collection terminals are used, which are mobile computers with a barcode scanner. In addition, companies can use both simple smartphones and data collection terminals at the same time;
- install inventory software. It is necessary for the operation of data collection terminals and transmission of information to an automated accounting system.
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
The program supports the simultaneous existence of multiple records on one TSD. In this way, you can conduct a check in several rooms/departments of the organization and then get several results at once in 1C.
Required accounting documents
The most relevant papers, without which an inventory of fixed assets (FA) cannot be carried out:
- inventory - INV-1 - here everything that matches or differs in the actual balances from the planned ones is written down, including inventory numbers and violation of operational features;
- INV-22 - an order that is drawn up before the start of the census;
- INV-18 – matching statement;
- INV-23 is a journal in which all recalculations must be reflected.
It is worth remembering that INV-18 must be drawn up in 2 copies, because one is given to the MOL, and the second goes to the accounting department.
GLAVBUKH-INFO
The inventory of fixed assets is carried out in accordance with the Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities, which must be applied taking into account the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.The inventory of fixed assets is carried out by a commission with the obligatory participation of financially responsible persons. Inventory of fixed assets consists of checking their actual availability in kind at their location or operation.
Before starting the inventory, it is recommended to check:
- the presence and condition of inventory cards, inventory books, inventories and other analytical accounting registers;
- availability and condition of technical passports or other technical documentation;
- availability of documents for fixed assets leased or accepted by the organization for storage.
If the commission documents are missing, it is necessary to ensure their receipt or execution. If discrepancies and inaccuracies are detected in the accounting registers or technical documentation, appropriate corrections and clarifications must be made.
When making an inventory of fixed assets, the commission inspects the objects and records their full name, purpose, inventory numbers and main technical or operational indicators in the inventory.
When making an inventory of buildings, structures and other real estate, the commission checks the availability of documents confirming the location of these objects in the ownership of the organization. The availability of documents for land plots, reservoirs and other environmental management facilities owned by the organization is also checked.
When identifying objects that have not been accepted for accounting, as well as objects for which the accounting registers do not contain or contain incorrect data characterizing them, the commission must include in the inventory the correct information on these objects.
Fixed assets are included in the inventory by name in accordance with the direct purpose of the object. If an object has undergone restoration, reconstruction or re-equipment and, as a result, its direct purpose has changed, then it is entered into the inventory under the name corresponding to the new purpose.
If the commission establishes that work of a capital nature (adding floors, adding new premises, etc.) or partial liquidation of buildings and structures (demolition of individual structural elements) is not reflected in the accounting records, it is necessary to determine the amount of increase or decrease in the book value of the object using the relevant documents and provide information about the changes made in the inventory.
Machinery, equipment and vehicles are entered into the inventory individually, indicating the factory inventory number according to the technical passport of the manufacturing organization, year of manufacture, purpose, capacity, etc. Same type items of household equipment and tools of the same value, received simultaneously in one of the structural divisions of the organization and taken into account in the standard group accounting inventory card, are listed in the inventories by name, indicating the quantity of these items.
Fixed assets that, at the time of inventory, are located outside the location of the organization (vehicles on long-distance voyages, sea and river vessels, railway rolling stock; machinery and equipment sent for major repairs, etc.) are inventoried until their temporary disposal.
For fixed assets that are not suitable for use and cannot be restored, the inventory commission draws up a separate inventory indicating the time of commissioning and the reasons that led these objects to be unusable (damage, complete wear and tear, etc.).
To reflect the actual availability of fixed assets at their locations and at all stages of their movement in the organization, the “Inventory List of Fixed Assets” is used in form No. INV-1.
The inventory list is drawn up in two copies and signed by the responsible persons of the commission separately for each place of storage of valuables and by the person responsible for the safety of fixed assets.
One copy is transferred to the accounting department for drawing up a matching statement, and the second remains with the financially responsible person or persons.
Before the inventory begins, a receipt is taken from each person or group of persons responsible for the safety of valuables. The receipt is included in the header portion of the form.
Inventories are compiled separately for groups of fixed assets (production and non-production purposes).
For fixed assets accepted for lease, an inventory is drawn up in triplicate separately for each lessor, indicating the lease term. One copy of the inventory list is sent to the lessor.
Inventory inventory data is used to compile matching statements, in which the actual inventory data is compared with accounting data.
Comparison statements are compiled when discrepancies are identified between accounting data and data from inventory records and acts.
To reflect the results of the inventory of fixed assets, for which deviations from the accounting data are identified, matching statements of form No. INV-18 “Matching statements of the results of the inventory of fixed assets, intangible assets” are used.
Separate matching statements are drawn up for fixed assets that do not belong to the organization, but are listed in the accounting records (those in custody, etc.).
The matching statement is drawn up in two copies by the accountant, one of which is kept in the accounting department, the second is transferred to the financially responsible person.
The results of the inventory of unfinished repairs of fixed assets are reflected in the inventory report of unfinished repairs of fixed assets in form No. INV-10.
This form combines indicators of inventory records (acts) and matching statements.
The act of inventory of unfinished repairs of fixed assets is used when inventorying unfinished repairs of buildings, structures, machinery, equipment, power plants and other fixed assets. The report is drawn up in two copies based on checking the condition of the repair work in kind. One copy of the act is transferred to the accounting department, the second - to the financially responsible person.
Acts and inventories are signed by members of the commission and financially responsible persons.
All business transactions and inventory results are subject to timely registration in accounting accounts without any omissions or withdrawals.
The results of the inventory must be reflected in the accounting and reporting of the month in which the inventory was completed, and for the annual inventory (carried out before drawing up the annual financial statements) - in the annual financial report.
When identifying surpluses or shortages of fixed assets, financially responsible persons must give appropriate explanations.
Discrepancies between the actual availability of fixed assets and accounting data identified during the inventory are regulated and reflected in the accounting accounts in accordance with the Federal Law “On Accounting”.
In accordance with the Federal Law “On Accounting”, identified surpluses of fixed assets must be accepted for accounting at market value on the date of the inventory and credited to the financial results of the organization (account 91 “Other income and expenses”).
Acceptance of surplus fixed assets for accounting is preliminarily reflected (as is any receipt of fixed assets) in the debit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”.
Operations to reflect in accounting an unaccounted item of fixed assets identified during inventory are documented with the following entries:
No.
| Contents of business transactions | Corresponding accounts | ||
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The market value of the unaccounted fixed asset is reflected. identified during inventory | 08 | 91-1 |
| 2 | The fixed asset is accepted for accounting at its original cost | 01 | 08 |
| 3 | The financial result (profit) was determined when an unaccounted fixed asset was accepted for accounting (as part of the final financial result) | 91-9 | 99 |
In accordance with the law, the shortage of property and its damage within the limits of natural loss norms are attributed to the accounts of production costs and/or sales expenses, in excess of the norms - to the account of the guilty persons.
If the perpetrators are not identified or the court refuses to recover damages from them, then losses from the shortage of property and its damage are written off to the financial results of the commercial organization.
The above norms of natural loss can be applied only in cases where actual shortages are identified and in the presence of approved norms of natural loss.
Since there are no approved norms of natural loss for fixed assets, all their shortages should be considered as excess and attributed to the perpetrators.
If there are no guilty persons, then this circumstance must be confirmed by relevant documents. The documents submitted to formalize the write-off of shortages must contain decisions of investigative or judicial authorities confirming the absence of the guilty persons or the refusal to recover damages from the guilty persons. Such decisions can be obtained both before, after or during the inventory.
After clarifying all the circumstances of the occurrence of shortages of fixed assets, the head of the organization makes a decision on the procedure for writing them off.
To write off shortages of fixed assets, subaccount 01–2 “Retirement of fixed assets” is used. The cost of the missing fixed asset is transferred to the debit of this subaccount, and the amount of accumulated depreciation is transferred to the credit.
The residual value of fixed assets identified in subaccount 01–2 “Disposal of fixed assets” is written off to the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.”
Subsequently, the identified shortage is recovered from the guilty party.
Collection is reflected in the credit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” and the debit of account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” (subaccount 73–2 “Calculations for compensation of material damage”) if there are guilty parties.
The market value of the missing fixed assets may be recovered from the guilty party.
When recovering from the guilty persons the cost of missing valuables, the positive difference between their value credited to account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” and their value reflected on account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” is credited to account 98 “Revenue” future periods" (subaccount 98–4 "The difference between the amount to be recovered from the guilty parties and the cost of shortages of valuables").
As the amount due is collected from the guilty person, the specified difference is written off from account 98 “Deferred income” in correspondence with account 91 “Other income and expenses” (subaccount 91–1 “Other income”).
The contribution of funds by the guilty person to repay the debt for damages is reflected in the credit of account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” (subaccount 73-2) in correspondence with the debit of account 50 “Cash”.
Example 1. Let’s assume that an organization has identified a shortage of a fixed asset item and there is a culprit. The guilty person voluntarily compensates for the damage caused by the shortage of the object, based on market prices in an amount exceeding the residual value of the object.
| No. | Contents of business transactions | Corresponding accounts | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The original cost of the missing fixed asset identified during the inventory was written off | 01-2 | 01-1 |
| 2 | The amount of depreciation accrued on the fixed asset at the time of write-off is written off | 02 | 01-2 |
| 3 | The residual value of the missing asset has been written off | 94 | 01-2 |
| 4 | The actual amount of damage is attributed to the guilty party | 73-2 | 94 |
| 5 | The excess of the amount of damage to be recovered from the guilty party over the actual amount of damage is reflected | 73-2 | 98-4 |
| 6 | Money contributed by the guilty party to pay off the debt for damages | 50 | 73-2 |
| 7 | The positive difference between the amount of damage to be recovered from the guilty party and the actual amount of damage (as the damage is paid off) is taken into account as part of other income. | 98-4 | 91-1 |
| 6 | Determined financial result (profit) (as part of the final financial result) | 91-9 | 99 |
In the absence of specific culprits, as well as in the presence of shortages of fixed assets, the collection of which was refused by the court due to the unfoundedness of the claims, the write-off of shortages and losses from damage to fixed assets is made to account 91 “Other income and expenses.”
Example 2. Let’s assume that an organization has identified a shortage of a fixed asset item in the absence of a culprit. In this case, the absence of a guilty person is confirmed only by a decision of the investigative authorities or there is a guilty person, but the court refused to recover damages from him due to the unfoundedness of the claims. In these cases, although the organization writes off losses as financial results, it does not have the right to reduce the taxable base for income tax, since such a right is given only when the trial has taken place, but the accused (guilty person) has been acquitted.
In this case, the amount of loss attributed to the financial results is reflected in the accounting records, but is not taken into account as part of the organization’s losses for profit tax purposes.
| No. | Contents of business transactions | Corresponding accounts | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The original cost of the missing fixed asset identified during the inventory was written off | 01-2 | 01-1 |
| 2 | The amount of depreciation accrued on the fixed asset at the time of write-off is written off | 02 | 01-2 |
| 3 | The residual value of the missing asset has been written off | 94 | 01-2 |
| 4 | Damage from the shortage of an asset was written off (due to the court’s refusal to recover damages from the guilty party due to the unfoundedness of the claim) | 91-2 | 94 |
| 5 | The financial result (loss) is determined (as part of the final financial result) | 99 | 91-9 |
Example 3. Let’s assume that an organization has identified a shortage of an item in the presence of a culprit, but in conditions where a trial has taken place and the guilty person has been acquitted.
In cases where there are such decisions of judicial authorities, the organization has the right to attribute losses from shortages, losses and thefts of property to the financial results of the organization and reduce taxable profit by the amount of losses incurred.
| No. | Contents of business transactions | Corresponding accounts | |
| Debit | Credit | ||
| 1 | The original cost of the missing fixed asset identified during the inventory was written off | 01-2 | 01-1 |
| 2 | The amount of depreciation accrued on the fixed asset at the time of write-off is written off | 02 | 01-2 |
| 3 | The residual value of the missing asset has been written off | 94 | 01-2 |
| 4 | The actual amount of damage is attributed to the guilty party | 73-2 | 94 |
| 5 | The shortage of an asset due to the acquittal of a guilty person was written off as financial results. | 91-2 | 73-2 |
| 6 | Financial result (loss) determined | 99 | 91-9 |
Shortages of valuables identified in the reporting year, but relating to previous reporting periods, recognized by financially responsible persons or for which there are court decisions to recover from the guilty persons. are reflected in the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” and the credit of account 98 “Deferred income”,
At the same time, account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” (subaccount 73–2 “Settlements for compensation of material damage”) is debited with these amounts and account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” is credited.
As the debt is repaid, account 91 “Other income and expenses” is credited and account 98 “Deferred income” is debited.
| < Previous | Next > |
What is the documentation of inventory accounting for unusual fixed assets (FPE)?
There are several situations in which actions will be slightly different from usual:
- if the inventory was under repair at the time of repair, then an INV-10 should be drawn up, which will reflect the total cost along with the costs of correction;
- for those objects that were leased, you will have to draw up your own documentation with confirmation from the counterparty;
- separate papers are needed for those materials that cannot be used further in business activities, and it is impossible to restore them - they are written off with an indication of the reasons.
In addition, if the material has changed its purpose after repair, it is important to enter updated, current data. This is especially true in cases where, after such reconstruction, the book value changes, which has not yet been reflected in accounting.
Inventory results. Discrepancies with accounting registers
[goo_mid] If the inventory commission identifies objects that are not suitable for further use, it must draw up a separate inventory. It indicates basic data about such an object and a general description of the reasons why this object is considered unsuitable.
Subsequently, based on the data from this inventory, management will make a decision on subsequent activities in relation to such a fixed asset.
If it is revealed that a fixed asset has changed its purpose as a result of restoration, reconstruction or re-equipment, then an entry about it is made in the inventory according to its new purpose.
If it turns out that the accounting registers did not take into account the work carried out on fixed assets that was of a capital nature, then the amount of change in the value of the fixed asset is determined based on the totality of data on the cost of such work. Data about such an object is entered into the inventory taking into account the calculated changes.
If objects are discovered that are not registered, or objects for which the accounting does not have complete data or they are indicated incorrectly, all available information on them is included in the inventory list.
Postings for displaying the OS inventory: example
Below we offer a sample of exactly what write-offs that occur due to the fault of employees and as a result of breakdown should look like.
- table
| Dt | CT | Amount, thousand rubles | Rationale | Documentation |
| When there are no guilty parties | ||||
| 01 (select) | 01 | 53 | The original price of the machine is written off | Write-off act |
| 02 | 01 (select) | 15 | Depreciation costs | Buh. certificates |
| 94 | 01 (select) | 38 | Remainder price | |
| 91 | 94 | 30 | Losses after write-off | |
| When there are culprits | ||||
| 01 (select) | 01 | 350 | The original price of the car is written off | Write-off act |
| 02 | 01 | 250 | Depreciation costs | Buh. certificates |
| 94 | 01 (select) | 100 | Remainder price | |
| 73 | 94 | 100 | The shortages were attributed to the culprit E.S. Erokhin. | |
| 73 | 98,4 | 25 | Difference between residual and market price | |
| 70 | 73 | 125 | The cost of the car was withheld from the salaries of E.S. Erokhin. | |
Capitalization of fixed assets identified during inventory
In accounting, fixed assets that were identified during inventory are accounted for at their current market value and are reflected as a debit to the fixed assets account in correspondence with the profit and loss account as other income (clause 36 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n).
As for tax accounting, the cost of fixed assets identified during the inventory period is included in non-operating income. This provision is enshrined in paragraph 20 of Article 250 of the Tax Code. At the same time, they are accepted for accounting at market prices and are subsequently subject to depreciation. This opinion is expressed by officials of the financial department in letters dated June 10, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/392, dated June 6, 2008 No. 03-03-06/4/42.
If a shortage is identified during the inventory, it can be reflected in one of the following ways:
- in non-operating expenses, if the guilty person has not been identified (as of the date of receipt of the relevant documents from government authorities confirming the absence of guilty persons (subclause 5, paragraph 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation));
- in non-operating expenses if the culprit is discovered. However, at the same time it is necessary to reflect the returned shortfall in non-operating income.
How to conduct an inventory of fixed assets: draw up an order
Each census begins with this document, which is prepared by the head of the organization. You can use the INV-22 form or create your own standard template for these purposes.
Certain points must be specified:
- Business name;
- the date on which the process will begin and end;
- who will be the chairman and members of the commission;
- how comprehensive the inspection will be (selective or complete);
- for what reason is it initiated;
- When should the documentation be submitted to the accounting department?
The executed order must be registered in the INV-23 journal, and then handed over to the chief inspector.
Before you start, you should check if you have:
- technical certificates for all objects;
- accounting cards;
- documents if the OS is leased.
Sample documents
Even having the opportunity to create their own accounting documentation forms, most accountants prefer to use ready-made samples. This, of course, has a double meaning: saving time and avoiding possible mistakes.
Inventory card for accounting of fixed assets
Maintaining analytical accounting of fixed assets is carried out for each object separately. All information about the asset throughout its “life,” its initial cost, year of manufacture and other characteristics is entered into the fixed asset accounting card.
The form, as in most similar cases, can be arbitrary, but with mandatory details indicated. In accounting departments today, the most often used form is the object inventory card OS-6:
OS-6
You can also see a sample of filling out in the sources, although maintaining this document, as a rule, does not cause much difficulty.
Inventory report
What this document is and why it is needed has already been written above. The form is a table topped with a “header”. It indicates the details of the enterprise, the grounds for conducting an inventory, and the lines list property, codes, units of measurement, cost and other data. A representative from the accounting department, who is required to participate in the process, will help the members of the commission understand these intricacies.
act
Inventory book
As is clear from the very name of this accounting tool, it is a collection of many sheets combined into a single book. There is no point in printing out forms - it is better to just buy it (form OS-6b) at an office supply store. The book is filled out in handwriting, and to ensure the reliability of the information, it is sometimes stitched and the thread is sealed with a mastic seal. The pages are numbered.
Each sheet contains ten columns in which data about fixed assets and persons responsible for their safety are entered, as well as documents on the basis of which the property was accepted for balance.
How to fill out a statement
How to make an inventory of fixed assets - count them and record all the different parameters. It is worth remembering that this is necessary not only to establish the correspondence of the number of units actually and according to plan. Other characteristics that must match the data on the card are also compared:
- performance;
- inventory numbers;
- what is it intended for;
- what it looks like externally, level of depreciation;
- presence/absence of defects.
When inspecting buildings, it is important to pay attention to:
- number of floors;
- year of construction;
- the material from which the room was built;
- total area and the share of useful space from it.
If a natural deposit is being studied, then its depth and probable length are of interest. For existing plants and trees, age and their presence on the site matter.
Why do you need a matching statement?
All this is recorded on a sheet, compared and approved. All detected deviations will be entered into accounting. This allows you to understand how much the enterprise in its reporting corresponds to what it actually is. You can work with up-to-date data and plan the further development of the organization.
Capitalization of identified surpluses
The so-called “surplus”, that is, fixed assets that are not listed in the accounting registers, but are actually available to the enterprise, is a very rare phenomenon. When surplus fixed assets are identified, they are assessed according to the rules applied to revalued fixed assets, and depreciation is determined by commission based on the actual condition. Such information is documented in separate acts.
Based on the acts drawn up during the inventory, during which surpluses were identified, accounting operations for registration are carried out. The accounting entries by which identified unaccounted for items are accepted for accounting are as follows:
| operation | correspondence | |
| Dt | CT | |
| Identified operating systems have been registered | 01 | 91-1 |
| Depreciation of previous years | 91-2 | 02 |
| Depreciation for all months of the current year | 20,25,26,44 | 02 |
The most important task in identifying and describing identified unaccounted for property is determining the actual date of its receipt. This is necessary for the most accurate reflection of depreciation amounts, the accrual of which for the object will also have to be restored. It should be taken into account that depreciation calculated for the entire period of operation until the beginning of the current year cannot be attributed to ordinary cost items. Reporting, both accounting and tax, for that period has already been compiled and submitted.
How to draw up an act based on the results
We have discussed in what cases an inventory of fixed assets is carried out. It is important to decide in what cases the document is drawn up. It is issued when it is discovered that a certain object no longer meets the required characteristics or does not work properly. In some cases, a write-off is made because the material is not available due to mis-sorting, theft or damage.
You must specify:
- MOL;
- the composition of the commission that revealed the inaccuracy;
- dates of statements, their numbers, comparative inventory data;
- when the census was started and completed.
All papers are attached to it, which reflect the discrepancy between accounting and the real picture.
How to assign an inventory number
To facilitate accounting and ensure safety, each fixed asset item should be easily recognizable among other property. A specialist understands the difference between, for example, an electronic frequency meter and a tachometer, but an accountant may not understand the instruments.
Therefore, all OS are equipped with inventory numbers applied in different ways: paint, engraving, permanent sticker, stamping and even welding (if the item is large and metal). The main requirements are clarity and uniqueness.
The following rules apply to inventory numbers:
- They are installed on all objects costing more than three thousand rubles. This is done at the time of balancing;
- The numbers do not change during operation;
- Assigned to objects consisting of parts with equal periods of use;
- The same number is not assigned to several objects;
- In library collections they are required for each copy;
- Do not change when moving within the same organization;
- A new accounting object can be assigned the same number 5 years after the old one is written off;
- For rented property, the number by which the property is registered by the owner can be used.
There are no legal regulations governing the inventory number system, so each organization uses its own method. Small companies do it simply by listing them in order, but in large companies it makes sense to develop some kind of system.
Example:
- The first two digits are the unit or department number.
- The rest are the number on the accounting sheet.
However, imagination in this matter is not limited by anything. The main thing is to be comfortable.
Special cases
It happens that an object is so small in size that the numbers simply do not fit on it. The physical properties of some accounted assets also sometimes do not allow any inscription to be placed on them. In this case, the rules for maintaining accounting documentation provide for the possibility of a detailed description of the item and indication of the inventory number only in the statement.
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
How to draw up the minutes that are drawn up at the final meeting
After the inventory is completed and all documents are filled out, the last council is assembled to sum up the results. A report on the work done is brought to the manager. This is not a mandatory process, but the record of its maintenance can become real evidence in court if a claim is filed for damage to the enterprise.
During the meeting, all changes, shortages, surpluses are read out, explanations from the MOL and expert opinions are listened to.
Finally, documentation is prepared that includes:
- results of the procedure performed;
- reasons why incorrect data was indicated in accounting;
- conclusions adopted by the commission;
- suggestions - how to eliminate all shortcomings and correct errors.
Everyone present signs it, then it is handed over to the manager so that he can make a final decision on all inaccuracies and inconsistencies.
The most effective solutions for automating asset accounting and inventory
For the effective implementation of automation of fixed assets accounting and property inventory, there is an excellent solution - the use of RFID (RadioFrequencyIdentification) technology.
RFID inventory is a technology based on the use of special self-adhesive and case-based radio frequency tags with a built-in identifier chip. Such a tag conveys information in encoded form about the property to which it is assigned.
The RFID tag transmits the identifier to the reader by a reflected signal. The use of RFID tags in the UHF range (860-960MHz) allows you to collect data at a distance of up to 5-10 meters.
The range depends on the power of the readers and the size and configuration of the tags. The anti-collision mode, implemented in this frequency range, allows you to simultaneously collect data from a large number of tags at the same time. According to the manufacturers of RFID readers, more than 100 tags per second. This allows you to carry out inventory many times faster than with technology using barcodes. Moreover, line of sight to the tag is not required for reading. For example, a tag placed behind a wooden or plastic partition is considered almost as good as one placed in line of sight.
The use of RFID technology implies the presence of the following elements:
- system database. It stores all collected information about property objects. Based on it, you can obtain information, summarize it in reports and use it to make management decisions;
- central database server. It represents the computing power necessary to process incoming information;
- administrator module. With its help, access rights to use the system are configured and the security and confidentiality of the system is ensured;
- system operator workplace. It is necessary to conduct the main activities of the system;
- control module for stationary tag readers. With its help, information is read and data is transferred to the system;
- data collection terminal module. It is used for mobile inventory of objects and is not tied to a stationary workplace.
Basic mistakes during inventory
There are several typical violations that many companies commit:
- an order appointing a commission is not drawn up;
- the UP did not specify the timing and order in which the inventory should be completed;
- hired an independent auditor who made errors in reporting;
- the order was filled out incorrectly - incorrect details, wrong full name;
- one of the inspectors was not present at the recount;
- everything was done only on paper, no actual calculations were carried out;
- violations were committed during weighing, measuring, etc.;
- the warehouse became accessible to everyone, and there was a risk of loss;
- A new MOT was chosen, but a census was not carried out before the old one left.
The essence of inventory
Inventory of real estate and equipment involves checking the reliability of actual and accounting information by comparing them with each other. This procedure must be carried out at least once a year, as indicated in special Methodological Instructions, and implies a valid census of individual items and accounting objects, their quantity and technical condition as a whole. As for animals in agriculture, they are inventoried quarterly, and, for example, library collections must be monitored at least once every five years. The frequency of inventory counts and their number, as well as other features, must be recorded in the company’s accounting policies.
The object of accounting and control during the inventory of fixed assets is an inventory object, that is, a fully equipped item with components and accessories, isolated, capable of independently performing certain functions.
Results
We examined the procedure for conducting and organizing an inventory of fixed assets (FPE), studied the sequence of its stages and documentation. With the help of recalculation, it becomes possible to understand which assets are reflected correctly in the accounts and which ones are not. We recommend that you carry out timely monitoring and complete postings. This is important for any enterprise, since without inspections it is impossible to determine the actual availability and shortage of objects, and this can result in problems, including with the tax service.
Documents for download:
Number of impressions: 3414
Main tasks of inventory
The main tasks of inventory are as follows:
- checking the compliance of the actual existence of property and liabilities with accounting information;
- checking the actual availability of fixed assets, money, valuables, debts, securities and work in progress;
- identification of valuables that have not been used for a long time or are in excess of norms for the purpose of subsequent sale;
- detection of valuables that have partially lost their quality and do not meet the established quality;
- checking whether the company complies with the conditions and rules for storing valuables and money, vehicles, special equipment and other assets;
- checking the real price of assets listed on the organization’s balance sheet; amounts of cash and non-cash money in hand and in accounts with credit institutions; money on the way; unfinished construction; costs of future periods; reserves for future costs; accounts receivable and accounts payable.