Tax deductions
Oksana Lim
Expert in tax and labor relations
Current as of February 22, 2019
Deduction codes are an important component of the 2-NDFL certificate. How to quickly and correctly select the required code from the code table? What are the nuances of reflecting a certain income code and the deduction code corresponding to it? We will answer all questions below.
general information
A tax deduction is a kind of benefit for an employee.
It is noteworthy that there are several types. The most popular are personal deductions for children. The first includes small amounts that are not taxed and to which war veterans, as well as disabled people of the first and second groups, are entitled.
The second broad group includes those amounts that are not taxed at a rate of thirteen percent due to the fact that the employee has children. Here the classification is quite large-scale, since the deduction code is affected by everything, from the presence of a second parent to what kind of child the child is.
There are more codes, since one deduction received two codes depending on who it is provided to. Until December 26, 2016, there was no such division.
- For example
, in the adjusted list, the deduction for the first child has two codes: - code 126 is assigned to the deduction for a child provided to the parent, his husband or wife, or the adoptive parent; - - code 130 indicates the same deduction, but already provided to the guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, his spouse.
The separation of codes was required because from 2021, the size of the deduction for a disabled child began to differ depending on who it is provided to. If the parent, his husband or wife, or adoptive parent, then 12 thousand rubles. If the adoptive parent, his spouse, guardian, trustee, then 6 thousand rubles.
In the same way, the amount of deduction for a full-time student, graduate student, resident, intern, student under the age of 24 years old, if he is disabled in group I or II, changes in the same way.
Deduction code
The deduction code reflects the amount by which a citizen’s tax base can be reduced. In accordance with tax legislation, there are several grounds for benefits. Citizens with one or more children are entitled to receive a standard deduction. And depending on which child the privilege is issued for, apply the appropriate code for this deduction in the individual’s income certificate. This type of benefit, unlike others, is calculated monthly until the children reach a certain age. The codes were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service No. MMB-7-11/ [email protected] dated November 22, 2016, the list is specified in Appendix No. 2.
Codes of deductions for children, features of their reflection in form 2-NDFL
Deduction codes imply various circumstances that determine the process of receiving benefits. They are necessary when contacting the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation and filling out the 2-NDFL certificate accordingly.
Single volume benefits have the following codes::
- Deduction 126 in the 2-NDFL certificate is typical for natural parents with one child. At the same time, deduction 126 is also applied for benefits for an offspring under 24 years of age with a disability who is undergoing contract training. Code 130 – under the same conditions, but reserved for guardians and trustees. Deduction code 126 in the certificate (the same as code 130) encodes a benefit in the amount of 1,400 rubles.
- Deduction code 127 is applied under the above conditions, but at the birth of a second child. Deduction code 127 in the 2-NDFL certificate also implies a preferential amount of 1,400 rubles. For guardians in the conditions under consideration, code 131 is used.
- If natural parents apply for a deduction for the third and subsequent children, it is necessary to indicate code 218 (for trustees - 132).
- If citizens are raising a disabled child, it is necessary to indicate code 129 (for natural parents) and 133 (for guardians) in form 2-NDFL.
In double volume, the deduction is encoded using the following ciphers:
- If there is one child, code 134 is applied for the only natural parent, 135 - for the only caregiver, 142 - if one of the natural parents refused the benefit, 143 - if the previous conditions are typical for caregivers.
- When the benefit is issued to the second offspring, code 138 is used for the only natural parent, 139 - for the sole guardian, 146 - if one of the natural parents voluntarily refused the benefit, 147 - if the previous conditions are typical for trustees.
- If the deduction being issued is assigned to the parents or guardians of a disabled person, code 140 is used for the only natural parent, 141 - for the only guardian, 148 - if one of the natural parents voluntarily refused the benefit, 149 - if the previous conditions are typical for trustees.
For example, Soboleva A.G. has three children for whom she applies for benefits. In this case, deduction codes 126, 127 and 128 are used.
Code 126, as well as deduction code 127 in the 2-NDFL certificate, are entered in the 4th section of the form, reserved for the benefits in question, where the corresponding amount is recorded. That is, there is enough space on the line for several designations. Therefore, deduction code 128 is indicated there.
128 deduction assumes a single benefit for the natural parent for the third child. All deductions are summed up, and on this basis Soboleva is given a deduction.
Thus, deduction codes are integral information for correctly filling out the 2-NDFL certificate. Their exhaustive list is given in Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ/7/11/387 dated September 10, 2015.
Personal income tax deduction codes for children in 2021: changes, table
As mentioned above, codes 114-125 were excluded according to order No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] Other encodings were approved instead.
Codes: standard personal income tax deductions in 2021 for children. Table.
| Deduction code | Who is entitled to | The amount of the deduction |
| To the parent, adoptive parent, parent's spouse: | ||
| 126 | For the first child | 1400 |
| 127 | For a second child | 1400 |
| 128 | For the third and next child | 3000 |
| 129 | For a disabled child under 18 years of age or a full-time student, resident, graduate student, student under the age of 24 who is a disabled person of group I or II | 12000 |
| To the caregiver, adoptive parent, guardian, spouse of the adoptive parent: | ||
| 130 | For the first child | 1400 |
| 131 | For a second child | 1400 |
| 132 | For the third and next child | 3000 |
| 133 | For a disabled child under 18 years of age or a full-time student, resident, graduate student, student under the age of 24 who is a disabled person of group I or II | 6000 |
| Double amount to the only parent or adoptive parent: | ||
| 134 | For the first child | 2800 |
| 136 | For a second child | 2800 |
| 138 | For the third and subsequent child | 6000 |
| 140 | For a disabled child under 18 years of age or a full-time student, resident, graduate student, student under the age of 24 who is a disabled person of group I or II | 24000 |
| Double amount to the sole caregiver, guardian, foster parent: | ||
| 135 | For the first child | 2800 |
| 137 | For a second child | 2800 |
| 139 | For the third and subsequent child | 6000 |
| 141 | For a disabled child under 18 years of age or a full-time student, resident, graduate student, student under the age of 24 who is a disabled person of group I or II | 12000 |
| To the parent, if the second parent refuses the deduction: | ||
| 142 | For the first child | 2800 |
| 144 | For a second child | 2800 |
| 146 | For the third and subsequent child | 6000 |
| 148 | For a disabled child under 18 years of age or a full-time student, resident, graduate student, student under the age of 24 who is a disabled person of group I or II | 24000 |
| To the adoptive parent, when the second adoptive parent refused the deduction: | ||
| 143 | For the first child | 2800 |
| 145 | For a second child | 2800 |
| 147 | For the third and subsequent child | 6000 |
| 149 | For a disabled child under 18 years of age or a full-time student, resident, graduate student, student under the age of 24 who is a disabled person of group I or II | 12000 |
Let's look at the changes in detail:
- code 114 changed to codes 126 and 130;
- code 115 - on 127 and 131;
- code 116 - on 128 and 132;
- code 117 - on 129 and 133;
- code 118 - on 134 and 135;
- code 119 - on 136 and 137;
- code 120 - on 138 and 139;
- code 121 - on 140 and 141;
- code 122 - on 142 and 143;
- code 123 - on 144 and 145;
- code 124 - on 146 and 147;
- code 125 - on 148 and 149.
Tax officials have broken down deductions into separate subgroups.
Where is the deduction code indicated in the 2-NDFL certificate?
Social, property and standard deductions are indicated in Section 4 of the form.
Deduction code
The deduction code reflects the amount by which a citizen’s tax base can be reduced. In accordance with tax legislation, there are several grounds for benefits. Citizens with one or more children are entitled to receive a standard deduction. And depending on which child the privilege is issued for, apply the appropriate code for this deduction in the individual’s income certificate. This type of benefit, unlike others, is calculated monthly until the children reach a certain age. The codes were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service No. MMB-7-11/ [email protected] dated November 22, 2016, the list is specified in Appendix No. 2.
Code 126 deduction: what is it?
Deduction code 126, according to the Appendix, reflects the amount that allows you to reduce the tax base for the first minor family member. The taxpayer's right to receive this benefit applies until the teenager reaches 18 years of age or 24 if he is studying full-time (undergraduate students, graduate students, cadets, etc.). Before the adoption of this law, the personal income tax reduction code was 114.
Tax deduction with code 126 indicates a personal income tax benefit for the first child. It is noteworthy that it can be used not only by those whose child is under eighteen years of age. If a certificate from an educational institution is provided confirming that the child is a full-time student, the benefit continues to apply until the child reaches twenty-four years of age.
It is also worth noting that this deduction code has been used since the end of 2016. Previously, it corresponded to code 114, which also applied to the first child who had not reached the age of majority or was receiving education, but only in full-time education.
The amount of deduction code 126 is 1400 rubles. This means that this particular part of the employee's salary is not subject to tax. That is, a monthly savings of 182 rubles.
We also must not forget that the deduction ceases to apply if the amount of wages for a calendar year reaches 350,000 rubles. In the month in which this amount was collected, deduction codes 126 and 127 will not be valid.
If a child is born: we carry documents
If an employee who works at an enterprise has a child, then he can immediately bring the entire package of documents to provide the standard deduction codes 126 and 127, and any other. It all depends on what kind of child appears in the family.
To do this, you only need two documents: a personal statement and a copy of the child’s birth certificate. However, nuances are possible. If a parent is raising a child alone, he also needs to provide documents that confirm this.
These include a certificate for single mothers in form number 25, a death certificate of the second parent, a certificate stating that he was declared missing. It is also worth bringing a copy of your passport, which indicates that after the death of a spouse or receiving the status of a single mother, the parent did not marry. This is necessary so that the accounting department knows which codes to use. Personal income tax deduction codes 126 and 127 apply only to those who are raising a child in a full family. For a single parent, these amounts will be doubled.
It is also worth paying attention to the change of surname. This is especially true for women. If the birth certificate contains the maiden name, and now the employee has other data, then it is also worth bringing a document confirming this. In this case, it will be a marriage certificate.
In your personal statement, you should indicate your details, which department the employee works in, as well as the child’s details, starting with last name, first name and patronymic and ending with date of birth. You should also sign and date the application.
There is no point in delaying the provision of documents, since even if the baby arrived on the 29th, the deduction will be provided for the entire month worked. Accountants should also take this into account. A tax deduction for a child is provided from the month of birth, subject to timely submission of documents
New place of work. What do you need?
If an employee comes to a new place of work and wants to receive a tax deduction, then in addition to the documents listed above, he must also provide a certificate in form 2-NDFL. This is necessary so that the accountant can enter information about the employee’s salary from the beginning of the year. This makes it possible to prevent you from taking advantage of the deduction upon reaching the threshold of 350,000 rubles.
Also, if an employee gets a new job in the same month in which he was fired from another organization, the accountant can check whether deductions have already been accrued to him for this month.
Deduction codes 126 and 127 in the 2-NDFL certificate can be seen directly under the column with the employee’s income. By dividing the amount of each of them by 1400, you can find out for how many months the deduction was provided. If the employee has already received his benefit for a given month, then the employer establishes deductions only from the next month. If there was a break between jobs, then no refund is provided for this period.
It is noteworthy that if an employee managed to change several places of work during the year, he will have to take certificates from each of them. Even if they worked there for several days. Income must be summed up and entered into the base in order to correctly calculate taxes.
Otherwise, for those who want to use tax deduction codes 126 and 127, you must bring a copy of the children's birth certificates, as well as a personal statement. It is also worth bringing certificates from places of study if the child is over eighteen years old.
Deduction code 127 in personal income tax certificate 2
Code 127 also applies to this type of compensation, but for the next child. To use the privilege, the same conditions remain - the child reaches 18 years of age or 24 if he is studying as a full-time student (graduate student, etc.). The deduction with code 127 replaced the previously used one - 115.
This means that every month an employee who is entitled to the benefit saves 182 rubles. The limit for using this deduction is the same as for the first child, namely 350,000 rubles.
Until the end of 2021, this code corresponded to the designation number 115; it had all the same parameters. This code is also used by those parents whose second child has reached the age of majority, but has not yet reached twenty-four years of age and is studying full-time.
Documents for deduction. Code 127
Tax deduction codes 126 and 127 are similar, therefore they have a similar set of documents. However, for the latter it will be somewhat wider.
If an employee has two children under eighteen years of age or full-time students, he must provide the following documents:
- Personal statement. You can fit both children into one at once.
- Birth certificates of both children, as well as copies of them. It is worth noting that even if the child already has a passport, it is the certificate that is provided, since this document contains information about the parents.
- Certificate in form 2-NDFL, if the employee gets a job.
It is also worth noting that if the first child no longer fits the category of persons for whom the deduction is provided, then a certificate for him still needs to be brought. This confirms the fact that the child for whom code 127 is used is the second.
Deduction code 128 in personal income tax certificate 2
Less common than 126 and 127, but in form 2 of the personal income tax you can find deduction code 128. The tax base is reduced due to the benefits provided for the third youngest family member who has not reached the age of majority or is under 24 years old, for those studying full-time at an educational institution. Before this, a different code was used in reporting – 116.
Subsidies
Withholding alimony and transferring it to the claimant If the writ of execution does not indicate the amount of alimony or its fixed amount, which is determined in accordance with the subsistence level, then they are calculated as follows:
- For 1 child - ¼ of the payer’s income.
- For 2 children - 1/3 of income.
- For 3 children or more - ½ income.
The total amount of alimony payments should not exceed 70% of the payer’s income minus personal income tax. In accordance with the law, the employer is obliged to transfer alimony to the recipient within three working days from the date of payment to the employee of wages or other amount from which they can be withheld.
For example, bonuses, vacation pay, temporary disability benefits. Withheld alimony and personal income tax must be reflected on the payslip so that the employee can understand how the amount paid to him is determined.
Child support Place of registration What is the validity period of the 2nd personal income tax certificate when submitted to the court for calculating alimony. read answers (1) Tags: Validity period of the certificate Statutory period Validity period I took the 2nd personal income tax certificate with a salary of 15,000 for alimony I received a letter from the bailiff to work for alimony and the accountant declares that he will pay alimony not from 15,000, but from 18,000, is this legal? read answers (2) Tags: Salary Get a certificate I owe a lot for alimony, the bailiff said to bring a certificate of 2 personal income taxes and we will recalculate the debt! The company where I worked no longerread the answers (1) Tags: Bailiffs Make a request Do you need a certificate 2 personal income tax from your ex-spouse to apply for alimony through the court?read the answers (1) Tags: Do you need a certificate Former spouses Filing for alimony My son and the cohabitant have a common child, she applies for alimony and requires a certificate of 2 personal income tax.
Family law Is alimony considered before or after personal income tax withholding? The legislation of the Russian Federation obliges each parent to provide for their children until they reach adulthood. If a child lives only with his mother or only with his father, then the other must provide financial assistance for his maintenance. In reality, children most often stay with their mother, so the father pays child support. Recipients of alimony often wonder whether the alimony they receive is income; alimony is withheld before the calculation of personal income tax or after.
Personal income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals. Its value is 13% and is withheld from the official income of the tax payer.
Also on the topic: Alimony is not paid in full and not regularly
Payments that are alimony in accordance with the Family Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to personal income tax. Despite this, in unusual situations, accountants are puzzled by the problem.
In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation 2021, amounts are first withheld to repay first-priority debts. These include alimony and the following requirements:
- For compensation for damage caused to health.
- For compensation for damage in connection with the death of the breadwinner.
- To compensate for the damage caused by the crime.
- On compensation for moral damage.
In the background are requirements related to payments to the budget. Then all other deductions are made. It is important to take into account that when collecting alimony for minor children and other first-priority claims, the total amount of withholding cannot exceed 70% of the debtor’s salary and other income. In other cases, you can retain no more than 50%.
How can you calculate your tax?
If an employee wants to check his tax himself, then he must know how to calculate it correctly. In general, the entire amount of his salary is multiplied by thirteen percent or by 0.13.
However, if an employee has the right to a tax deduction and has provided a full package of documents, then he should not be taxed on the entire amount of his salary, but only part of it.
Deduction codes 126 and 127 assume, for example, that an employee who has a first or second minor child has the right to a deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles. If there are two children, then the amount doubles. However, it is necessary to bring all documents for children on time. Otherwise, the lost amounts will have to be returned through the tax authorities and only for a certain period.
Practical example. Tax calculation
Employee Ivanova I.I. presented documents for her children. Deduction codes 126 and 127 apply to it, that is, for the first and second child, respectively. If Ivanova I.I.’s total earnings for the month amounted to 10,000 rubles, then without the benefit she had to pay the state 1,300 rubles.
But, since the employee has the right to standard tax deductions code 126, 127, then 1400 and 1400 rubles can be safely deducted from her salary when calculating the tax. In total, the amount of 7,200 rubles is taxed. The amount of tax transferred to the budget will be 936 rubles. This means that Ivanova I.I.’s benefit saved her 364 rubles.
Example
In the unified form of income reporting for an individual, the column reflecting the deduction code is in both the 3rd and 4th sections. Correctly indicate the amount in the part intended to fill out the provided compensation for various reasons:
We recommend additional reading: Is compensation for unused vacation subject to personal income tax or not?
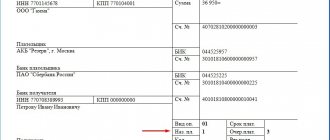
For example, this is what the reimbursement for the first and second child will look like in reporting 2nd personal income tax, indicating codes 126 and 127:
As a result, the citizen’s total income of 454,450 rubles is reduced by 14,000 rubles, and the tax is calculated from the balance. According to the sample, personal income tax compensation was not provided for the entire 12 months, but only until the amount of income did not exceed 350 thousand rubles.
It should be noted that compensation is reflected in the reporting on an accrual basis, no matter for what period the document was drawn up (quarter, 6 months or year).
How much to transfer alimony from and whether it is necessary to withhold personal income tax from it
It is easier to consider the calculation using an example.
The ex-spouse’s earnings are 40,000 rubles; the accounting department received a writ of execution to withhold 25% of the total income for the maintenance of one child.
The calculation will be performed by the accountant as follows:
- Personal income tax on earnings amounted to: 40,000 * 13% = 5,200 rubles;
- income that is accepted for calculating alimony: 40,000 – 5,200 = 34,800 rubles;
- therefore, the employee must pay alimony in the amount of: 34,800 * 25% = 8,700 rubles;
- The employee’s net income will be: 40,000 – 5,200 – 8,700 = 26,100 rubles.
Within three days, the accountant is obliged to transfer alimony to the ex-wife in the amount of 8,700 rubles.
What if the employee did not receive the benefit?
It happens that the employee did not know that he was entitled to any personal income tax benefit. It is likely that he either was not informed about this or did not provide documents in a timely manner. In this case, he can return the amount he overpaid to the tax authorities.
To do this, you need to provide a package of documents to the tax service. Deduction codes 126 and 127 in the 3-NDFL declaration will also have to be indicated if suitable deductions are made under this value.
It is also necessary to take a certificate from your place of work in form 2-NDFL, as well as copies of the children’s birth certificates, and, if necessary, a certificate from their place of study. It is worth remembering that you can only return amounts for the last three years. That is, in 2021 you can receive money for 2014, 2015, 2021.
Deduction codes 126 and 127 will appear in the declaration automatically if you specify them in a specific tab in the program provided by the Tax Service website. If the return is carried out over several years, then several declarations will have to be drawn up, separately for each year.
Tax refund deadlines
As practice shows, you will have to wait about 4 months for a refund from the date of application. There are cases when the wait lasted up to one year. This is explained by the deduction system:
- three months after filing an application, the tax service has the right to conduct an audit of the applicant;
- after a positive decision on the calculation of the deduction, the applicant receives a special notification about this by mail at the place of registration;
- compensation has the right to be calculated one month after receipt of the letter by the addressee.
Important! If the deductions arrived late, the applicant may demand that the Federal Tax Service pay a penalty, naturally providing evidence of the delay.
Scope of standard and social tax deductions for children
Once again, we focus on the period of granting the right to reduce personal income tax, because many taxpayers have a question about how, for example, compensation is calculated if a citizen is already 24 years old, but his studies have not yet been completed?
According to Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a reduction in the tax base is due to citizens for each family member under the age of 18, and up to 24, provided that he is a full-time student.
Early termination of the right to compensation may be caused by:
- death of a child;
- early termination of the agreement on the transfer of the ward to a family for upbringing.
When does the right to reduce personal income tax cease? According to the position of the Ministry of Finance, the benefit is provided to parents until the end of the year in which the child turns 18, not equal to the month of his birth. As for students, the period for providing a standard deduction is limited to the time of study, including academic leave.
That is, if the ward is 24 years old, and the period of study falls on this year, then the privilege of reducing the amount of personal income tax is granted to a full-time student until the end of the year. And if the period of study ends in the month before the end of the year in which the student turned 24, then starting from the next month, the reduction of the tax base in this way stops.
Are the personal income tax reimbursement amounts different for the first and subsequent children? According to Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the benefit amounts are different, but the amount of deduction for a disabled child is significantly higher:
| Who is compensated for? | Amount (rub.) |
| 1st and 2nd child | 1400 |
| 3rd and subsequent | 3000 |
| Disabled child I and II gr. | 12000 |
| 1st and 2nd child who is adopted or under guardianship | 1400 |
| 3rd and subsequent, adopted, under guardianship (trusteeship) | 3000 |
| For a disabled child adopted or taken into custody | 6000 |
Both parents have the right to use this privilege, each at their place of employment. Even if there is a child from the first marriage, the common child will be considered the second (third, depending on how many children both parties have from previous family relationships).
In accordance with the law, one of the parents can apply for a standard tax deduction for children in double the amount if the other party refuses to receive benefits at the place of work.
The limitation for receiving a deduction is that the taxpayer’s total income reaches 350 thousand rubles. (in a year). That is, when the amount of employee remuneration exceeds the specified limit, the reduction of the tax base by 1400 (3000, 6000, etc.) stops.
We recommend additional reading: How much is a 2nd personal income tax certificate issued in accordance with the law of the Russian Federation?
In addition to the standard deduction, parents have the right to apply for another type of compensation for a minor - social. The basis for granting such a privilege is the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which it is possible to return personal income tax for funds spent on education or treatment of a child. This is especially true if the child is studying on a commercial basis (which does not deprive his mother and father of the right to receive the standard deduction).
Personal income tax compensation for years of training or medical care is limited to the amount of costs incurred of 120 thousand rubles. But if we are talking about expensive types of treatment, the list of which is established by law, then compensation payments are made based on the entire amount of expenses. Including materials for the operation and medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Permanent disability: features of assignment
This type of disability is assigned to a citizen subject to the following conditions:
| Feature of disability | Assignment condition |
| Men > 60 years old | Malignant forms of cancer of various stages |
| Women > 50 years old | Benign brain tumor |
| Group 1 or 2 with unchanged condition or worsening for 15 years | Incurable mental defects |
| Disabled people of the Great Patriotic War or citizens who were disabled before participating in the Second World War | Diseases of the nervous system affecting motor skills and sensory organs |
| Military personnel recognized as disabled due to injuries received during the war | Severe nervous system disorders |
| Degenerative brain diseases | |
| Steadily progressing diseases of internal organs | |
| Absolute loss of hearing and vision | |
| Limb amputation |
However, if a citizen has been assigned permanent disability, it can be re-examined upon his application or upon the direction of the attending physician, who has noted changes in the patient’s health status.
List of documents required to apply for a child benefit
A standard deduction for children is issued by a tax agent for an employee, subject to writing an appropriate application and providing a certain package of documents. Knowing that some employees have children does not oblige the landlord to apply this basis for reducing the tax base; supporting documents are needed. Why? Because a tax deduction can be issued not only through the employer, but also through the Federal Tax Service or, for example, the second spouse receives a double deduction. To avoid illegal situations, confirmation of the right to reduce the amount of personal income tax for minors is required.
The application is written in free form, addressed to the manager, indicating the basis for the deduction, the full name of the children and the year of their birth.
The following package of documents is attached to the form:
- taxpayer passport;
- children's birth certificate or passport if they are over 14 years old;
- documents confirming the disability group;
- papers on adoption (adoption, guardianship, trusteeship)
- Students require a certificate from the dean's office confirming this fact.
The employer may require additional official documents, for example, to certify that the minor lives with the applicant.
At the same time, according to the letter from the Federal Tax Service, re-submission of documents if the situation in the family has not changed is not required. In most cases, the landlord only requests a document for the child and an application.