The head of an LLC is usually called the general director, but there are other options: director, president. Differences in the name do not affect its status - it is the sole executive body of the company. He represents the interests of the organization and signs documents related to its activities.
Let's consider how to appoint a person to the position of director of an LLC and what documents to formalize this.
Introductory information
The situation when a company is headed by its “founding father” is not uncommon in practice. Moreover, often such a manager is ready to perform his functions without receiving a monthly salary. There can be many reasons for this. There is a banal lack of funds, a desire to save on taxes and contributions, and simply a reluctance to “bother” with additional accounting and personnel issues. Unfortunately, regulatory agencies also play a significant role in this approach; they cannot decide whether the director, the sole founder, needs an employment contract. So such a manager works without a salary and an employment contract. But how safe is this approach for the company?
Responsibilities
The responsibilities of a director typically include:
- organization and effective operation of all structural divisions;
- increasing the profitability of the company;
- approval of the staffing table;
- establishing bonuses and allowances for employees;
- ensuring fulfillment of obligations to suppliers, creditors and customers;
- delegation of control of certain areas of activity to heads of divisions and branches;
- control over the operation of the enterprise structure;
- ensuring compliance with the regime of saving financial and labor resources.
The director's responsibilities also include:
- drawing up a master plan for the enterprise’s production and its development;
- development of the organization’s budget for the year, quarter;
- monitoring the accounting of expenditures and receipts of funds, use of materials;
- monitoring compliance with financial discipline;
- compliance with timely submission of reports to the relevant authorities.
Registration of a director - the sole founder: a brief history of the issue
The question of whether it is necessary to conclude an employment contract with the director, the sole founder of the organization, has been the subject of constant debate for more than twenty years. Let us briefly recall how the position of officials and legislators changed (for more details, see “Is it possible not to pay a director’s salary: new facts, previous conclusions”).
In 2002, a provision appeared in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stating that written employment contracts must be concluded with all employees, without exception. It followed from this that if the company’s staff list includes the position of director, then an employment contract must be drawn up with him.
But in a situation where the director was also the sole founder of the company, the conclusion of such an agreement raised questions. As a result, Rostrud issued letter No. 2262-6-1 dated December 28, 2006, in which it indicated that the sole founder cannot be an employee of the organization. The department referred to Article 273 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which states that the features established by the Labor Code for regulating the work of the head of an organization do not apply to the director, who is the sole founder. Therefore, the letter said, there is no need to conclude an employment contract with such a director. A similar point of view was expressed by the Ministry of Health and Social Development in letter dated 08.18.09 No. 22-2-3199.
But this approach soon enough led to the cessation of income to extra-budgetary funds from payments in favor of such managers. Therefore, the Ministry of Health and Social Development, in letter No. 428n dated 06/08/10, stated that in any case an employment contract is concluded with the director, even if he is the only founder. The ministry justified its new approach by the fact that only in this way can the manager be provided with social and labor guarantees.
In 2011, legislators noticed the described problem and tried to solve it by amending the laws on social insurance. They directly indicated that managers who are the only participants (founders) of organizations belong to the category of insured persons (clause 1, part 1 and part 5, article 2, article 13 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ , paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 7 of the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ, paragraph 1 of Article 10 of the Federal Law of November 29, 2010 No. 326-FZ).
True, these amendments were not very successful, since managers were not mentioned as a separate item, but were included in the general list of insured persons as follows: “those working under an employment contract, including heads of organizations who are the only participants (founders).” That is, instead of solving the problem, the amendments actually gave reason to believe that managers - the only founders - have the opportunity to choose: work under an employment contract and receive social protection, or not draw up a contract and not receive pensions and benefits.
Rostrud made the next move again. In letter dated 03/06/13 No. 177-6-1, officials again indicated that an employment contract with the manager - the sole founder - is not concluded. The rationale is this. An employment contract is an agreement between an employer and an employee, that is, a bilateral act. If one of the parties to the employment contract is absent, it cannot be concluded. The only participant in the organization must, by his decision, assume the functions of a manager, without concluding any contract, including an employment contract.
General Director: features of the position
To understand the difference between a general director and a director, let’s try to figure out what exactly this position is.
As we have already found out, the phrase itself is used to designate the main position in the management of a commercial organization. CEO is not necessarily the same as founding director. He may even be a hired employee and not participate at all in the share capital of the organization. Sometimes the title "CEO" is replaced by other terms. Usually this is the president. But this definition is most often used to name the head of a group of companies, while the general director is the sole head of a separate organization.
Position of the Ministry of Finance: there are labor relations, but there is no employment contract
And in 2021, the Russian Ministry of Finance became involved in resolving the issue of whether the director, the sole founder, needs an employment contract. In a letter dated 03/15/16 No. 03-11-11/14234 with reference to a fairly old court decision (determined by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 06/05/09 No. 6362/09), financial department specialists indicated that labor relations with the director - the sole founder - still exist . But they are formalized not by an employment contract, but by the decision of a single participant. This means that the manager is an employee of the organization and he needs to pay a salary. Thus, the issue of insurance premiums from payments to the director was resolved in favor of the budget, and at the same time the Ministry of Finance did not come into conflict with Rostrud (also see “The Ministry of Finance announced how to formalize labor relations with a director who is also the sole founder of the organization”).
But this approach, for all its apparent success, does not answer the main question: will a “manager without a contract” be an insured person? After all, the laws mentioned above clearly state that in order to fall into this category, a manager must have an employment contract. In addition, the conclusion of the Ministry of Finance directly contradicts the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which states that labor relations arise only on the basis of an employment contract. The only exception to this rule is the actual admission of the employee to work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer (it is clear that this exception does not apply to the situation under consideration).
Thus, we have to admit that the approach outlined by the Ministry of Finance cannot be applied in practice, since it contradicts the Labor Code. In addition, guided by the position of the Ministry of Finance, it is impossible to answer the question of whether it is necessary to charge insurance premiums on salaries that are paid to the director not on the basis of an employment contract. Finally, this approach calls into question the legality of including payments to a “manager without an employment contract” as expenses under the OSNO, under the simplified tax system or under the unified agricultural tax. Indeed, on the basis of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, labor costs include accruals provided for in the employment contract.
In passing, we note that the definition of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, to which the authors of the commented letter refer, was devoted to the question of whether the founder-manager has the right to social benefits. And this judicial act was adopted even before the approval of the above-mentioned amendments to the laws on social insurance. That is, the court’s conclusion, which officials refer to, is actually taken out of context. Therefore, it cannot be said with confidence that at present the arbitrators will support the approach proposed by the Ministry of Finance if a dispute arises about the right not to draw up an employment contract with the director - the sole founder.
If the decision is made by the general meeting of shareholders
What is a general meeting of shareholders?
According to Article 47 of the Law “On Joint Stock Companies” (No. 208-FZ dated December 26, 1995), the general meeting of shareholders is the highest management body of the company. Meetings of shareholders are divided into extraordinary, convened by the board of directors or director to resolve urgent issues, and regular (annual), convened once a year in the period from March 1 to June 30 to resolve the following mandatory issues:
- approval of annual financial statements;
- election of the board of directors;
- distribution of profits between participants, etc., provided for in Art. 47 of the Law.
The competence of this body includes solving key problems in the life of the company, including:
- making changes to the charter, increasing/decreasing the authorized capital;
- liquidation/reorganization of the company;
- appointment of a general director.
A complete list of actions within the jurisdiction of the meeting is contained in Article 48 of the Law and may be supplemented by the company’s charter.
A meeting of the general meeting is convened by its chairman. The quorum for this event must be at least half of the number of participants. Decisions at the meeting are made by voting. The company's internal documents may identify a person with a casting vote.
Minutes of the general meeting of participants on the change of director
Minutes must be kept at the meeting. According to paragraph 4 of Article 68 of Federal Law No. 208-FZ, it must be drawn up no later than three days after the event. The same norm regulates the content of the protocol. The following data is entered into it:
- place and time of its holding;
- persons present at the meeting;
- agenda;
- questions raised and voting results;
- decisions made.
This is important to know: How to appeal a decision to initiate enforcement proceedings: deadline for appeal
The document is certified by the signature of the chairman of the meeting. If during voting on any issue the rights of one of the participants were violated, and as a result a decision was made against which he voted, this person has the right to go to court to appeal the decision.
You can download sample documents at the end of the article.
Exception method: a contract is needed, but it cannot be civil law
So how do you formalize your relationship with a manager who is also the sole founder of the organization? In our opinion, in the current situation of legal uncertainty, it is possible (and necessary) to resolve this issue using the exclusion method.
Let us recall that relations regarding the management of an LLC are regulated by a special Federal Law dated 02/08/98 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies” (hereinafter referred to as the LLC Law). By virtue of paragraphs 1 and 4 of Article 40 of this law, the company’s relations with the sole executive body (that is, the director) are in any case formalized by an agreement. This law does not establish any exceptions for the manager - the sole participant of the LLC.
At the same time, from the analysis of the Law on LLC it follows that this agreement can be civil if it is concluded with a professional manager in the manner prescribed by Article 42 of the Law on LLC. Obviously, in this case, the person claiming to be the manager (that is, in our case, the sole founder) will carry out entrepreneurial activities in managing the LLC. This means that he will have to register as an individual entrepreneur (subclause 2, clause 2.1, article 32 of the LLC Law).
So, a civil contract is not suitable in the situation under consideration. We exclude him. And as a result we get the following. First, you need to conclude an agreement with the manager. Secondly, this agreement cannot be civil law. Thus, there is only one option left for formalizing relations with the director of the LLC - concluding an employment contract with him. The legislation does not yet provide for any other option.
How to draw up a document
You can issue an extract yourself or contact a company that specializes in providing such a service. If the document is drawn up independently, then it is advisable to adhere to the following procedure:
- the cover is formed: on a sheet of A4 paper, the entry “Extract from the charter of the LLC” is made, where “LLC” is the name of the company;
- a duplicate of the title page of the statutory document is made, and, if necessary, a copy of its first page;
- paragraphs, sections and chapters of the charter are copied for extract;
- at the end a copy of the last page of the statutory papers is inserted;
- the extract is signed by the person who issued the document, the position of this employee is indicated and the date is indicated.
- the pages of the statement are stitched (the procedure is optional, but some companies and authorities requesting the document require it).
The extract can be issued on the company’s letterhead or indicate the name of the organization at the top of the document. The binding indicates the number of pages of the document, the entry “correct”, the date of formation, the employee’s signature and the company’s seal, if available. If the extract is not bound, then certification must be made on each page by affixing a signature and seal.
Extract from the charter of the municipality (sample)
What to pay the founder-manager: salary or dividends
So, we have established that it is still necessary to conclude an employment contract with the manager - the sole founder. And if an employment relationship is formalized, then the employer must pay the employee wages (Art., Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The condition of remuneration is a mandatory condition of the employment contract (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, the absence of wage accruals in the presence of a concluded employment contract is a violation of labor legislation, which is punishable by at least an administrative fine (Part 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, it would be incorrect to say that the reward for a manager’s work may not be wages, but dividends. The fact is that a participant in an LLC has the right to dividends regardless of whether he manages the company or not (clause 1, article 8, clause 2, article 28 of the LLC Law). This means that dividends cannot be a substitute for wages.
Assignment of probationary period
In some cases, by agreement of the parties, a clause establishing a probationary period is included in the employment agreement.
Important! According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the duration of the trial period cannot be more than 6 months. The exception is cases when the registration of the general director occurs by transfer. A probationary period is not established for such employees.
When calculating the test period, the following periods are not taken into account:
- period of illness;
- being registered with the military;
- implementation of public events;
- absence of an employee from the workplace for other reasons.
Important! In accordance with the law, work performed by a candidate for a position during the probationary period is subject to payment on a general basis.
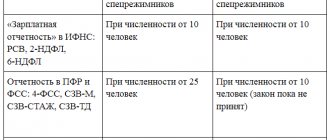
Calculation of insurance premiums and reporting: are there any options?
We will separately dwell on the question of whether it is necessary to accrue insurance premiums for payments to the director - the sole founder and to include information about him in the reporting on contributions. Naturally, in the case when the manager is paid a salary on the basis of an employment contract, it is necessary to calculate insurance premiums and provide personalized information. But in practice there are situations when the above question is not so clearly resolved. Let's consider such situations.
The first situation: an employment contract has not been concluded with the director and no payments are made in his favor (except for dividends).
In this case, it is obvious that the obligation to pay insurance premiums does not arise, since there is no taxable base (clause 1 of Article 419 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As for the presentation of reports, it must be taken into account that, according to the position of the Ministry of Finance of Russia (letter dated June 18, 2018 No. 03-15-05/41578), an organization that during the reporting (settlement) period did not make accruals at all in favor of individuals, all equally obliged to submit zero reports. As officials explained, the policyholder thereby declares the absence of payments and remunerations that are subject to insurance premiums, and, accordingly, the absence of paid contributions (see “The founding director does not receive a salary: is it necessary to indicate this information in the zero DAM?” ).
In addition, officials insist that for a director with whom an employment contract has not been concluded, the SZV-M form must be submitted (letter from the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation dated 03.29.18 No. LCH-08-24/5721 and the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 03.16.18 No. 17-4/ 10/B-1846; see “SZV-M for directors: the Pension Fund of Russia requires submission of reports even for those founding directors with whom there is no employment contract”). And although in both letters the reasoning used by the departments is not convincing enough, failure to submit reports will most likely lead to a conflict with inspectors. And how the court will look at this situation is almost impossible to predict, since initially the courts proceeded from the position that an employment contract should be concluded with the manager. Thus, in the event of a trial, the possibility cannot be ruled out that the arbitrators will take the side of the inspectors. In addition, the organization may have to pay a fine for the fact that an employment relationship has not been formalized with the director and his salary is not paid.
Therefore, comparing the possible risks, we believe that in the situation under consideration it is safer to submit both a zero calculation for insurance premiums and the SZV-M form in relation to the manager.
Fill out, check and submit the SZV-M for free via the Internet
Second situation: an employment contract has been concluded with the manager, but wages are not accrued to him
All the conclusions made above are also relevant for the situation when an employment contract has been concluded with the manager, but wages are not accrued to him. The difference in this situation will be the even more precarious position of the organization in the event of initiation of legal proceedings. After all, if there is an employment contract, salary calculation is mandatory (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
True, in 2021, a ruling by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 02/17/17 No. 309-KG16-20570 appeared, in which the judges recognized: if there is an employment contract with the director and in the absence of a salary accrued to him, contributions may not be paid (see “Supreme Court: if the organization does not pay the director a salary, she is not obliged to pay insurance premiums").
However, it is possible that inspectors will seek payments in favor of the director. And when they find it, they will try to justify that these payments are in the nature of remuneration for labor. If they succeed, the organization will be assessed additional fees, penalties and fines.
Third situation: the organization does not operate
This situation is a variation of the first or second situation, but with the condition that the organization does not carry out any activities (that is, we are talking about a “sleeping” organization).
Tax officials insist that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not relieve payers of insurance premiums from the obligation to submit calculations if they do not conduct financial and economic activities and do not pay remuneration to individuals during a particular settlement (reporting) period. Therefore, a “sleeping” company is obliged to submit the DAM with zero indicators (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 16, 2018 No. BS-4-21 / [email protected] ; see “The LLC does not pay salaries and does not conduct business: is it necessary to submit a zero DAM?” ).
And considering that we are talking about a manager with whom, according to the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Law on LLCs, it is necessary to conclude an employment contract, the chances of the organization defending the right to an “unaccountable” life are extremely small.
Peculiarities of a director’s activities in different areas of business
Despite the fact that every leadership position provides approximately the same powers, different areas of economic activity have their own characteristics. Therefore, in order to hold the position of director or general director in a particular area of business, you need to have some specific skills.
- In medical organizations, for example, it is impossible to do without special education.
- The general director in the field of trade or provision of services must thoroughly know the legislation in the field of consumer protection.
- The general director of a security company must have the opportunity to directly interact with the Ministry of Internal Affairs.
- In the housing and communal services sector, the manager must not only personally receive citizens, but also closely interact with suppliers of raw materials to provide the population with high-quality heat, water, electricity, and so on.
In general, everywhere has its own specifics, and the position of director or general director is not only a fancy word and a lot of authority, but also a huge responsibility. Moreover, the louder the word, the greater the responsibility.
Practical conclusions
In conclusion, we present some practical conclusions.
- Current legislation does not provide for any other option for formalizing relations with the director - the sole founder (who is not an individual entrepreneur), other than concluding an employment contract with him. Without an agreement, the activities of such a manager acting on behalf of the organization may be recognized as unlawful upon the claim of one of the company’s counterparties, which could jeopardize the business as a whole. Thus, an employment contract is needed, first of all, to protect the business, that is, the decisions that the manager makes and the documents that he signs.
- Labor relations, by virtue of the direct and repeated instructions of the Labor Code, imply the calculation and payment of wages. Violation of this rule is fraught with at least an administrative fine. Accordingly, if an employment contract has been concluded with the manager, the sole founder, then such employee must be accrued and paid wages in the amount specified in this contract. The law does not allow replacing wages with dividends.
- Concluding an employment contract with the manager, the sole founder, is a step that resolves numerous conflicts with regulatory authorities. Thus, such an agreement removes uncertainty regarding the calculation of insurance premiums (they must be calculated) and the reporting of contributions (they must be provided). In addition, the employment contract allows you to safely pay various social benefits to the manager. Finally, an employment contract makes it possible to include wages in expenses when determining the tax base for income tax, the unified “simplified” tax or the Unified Agricultural Tax, and in the event of claims being made, to successfully defend this right in court.
What is the difference between a CEO’s instruction and a simple director’s instruction?
If the structure of an enterprise requires the presence of both a general director and directors of areas, their job descriptions differ radically. The differences primarily lie in the delegation of authority and level of responsibility.
- The general director represents the interests of the enterprise as a whole, and the director only within the framework of his division and powers.
- The director in this case is appointed not by a decision of the Board of Shareholders, but simply by an Order of the General Director.
- If there is a general director, there may be several director positions.
- The general director controls and adjusts the activities of the entire organization as a whole, and the director controls only a separate area, for example, the financial part or sales.
General Meeting of Shareholders
The activities of joint stock companies are regulated by federal law, which contains a requirement to disclose information, including information about the holding of a general meeting, by publishing it on the Internet within 2 days
In case of violation of this norm, the company may be brought to administrative liability. The document itself must be drawn up no later than 3 days from the closing date of the meeting.
Publication does not deprive shareholders of the right to demand an extract, which the sole management body represented by the director is obliged to provide to him.
Order of conduct
As a rule, at a general meeting, decisions are made by majority vote:
- on the creation, reorganization, liquidation of an LLC;
- approval of the charter and amendments to it;
- participation in other legal entities;
- formation of executive bodies and elections of management bodies;
- approval of the annual report;
- appointment of an audit or audit.
The initiative to convene a meeting belongs to the executive body or a group of participants, numbering at least a certain percentage of their number according to the constituent documents. The procedure must meet the requirements of the law governing the activities of the organization and the charter. All members must be given advance notice containing the date, time, location and agenda.
In order to verify the legality of the meeting and the presence of a quorum, it is recommended to register those arriving with an identification document and affix the signature of the participant next to their last name.
The minutes must reflect its entire course, speeches of participants, debates, discussions of agenda items, voting and its results, decisions made :
- The introductory part indicates the start and end date of the meeting, the number of people taking part in it, the percentage of those who arrived to the total number of members of the organization, the presence or absence of a quorum, as well as the issues included in the agenda.
- The main part describes the sequence of consideration of issues, and you can draw up a short protocol with a record of the agenda item and the decision made, or a full one with a recording of the speakers’ speeches, remarks, and opinions.
At the end of the meeting, official minutes are drawn up based on the notes kept by the elected secretary. Its production time is usually from 3 to 5 days . The prepared document is signed by the presiding officer and the secretary and is stored along with all the documentation of the meeting: notification, registration sheet, draft notes on the progress of discussions.
Meetings of participants can be held by absentee voting, without convening all members of the organization. In such cases, the initiators notify in the usual manner about the convocation and the procedure for making decisions on the issues on the agenda. Voting is carried out by filling out ballots sent by the organizer within a certain period. Based on the results of counting the votes reflected in the ballots, a protocol is drawn up. This form of voting can also be used in regular in-person meetings in order to exclude the fact that a participant refuses to express an opinion.
For JSCs and LLCs, the legislation provides for notarization of decisions made . But if the charter establishes that the protocol must be signed by all participants in person or using an electronic signature that allows one to reliably establish the will of the voter, then there is no need to involve a notary.