The concept of “adjustment” itself implies a change in some data. We will look at changing data in VAT accounting in 1C 8.3 using the “Enterprise Accounting” configuration as an example.
There are two options here: using an “Adjustment Invoice” (CAI) or correcting erroneously entered data. In many ways, the user actions in these cases are similar, but we will look in detail at working in 1C with KSF, as well as how to reflect the direct correction of VAT errors.
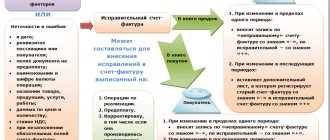
CSFs are issued by the seller to the buyer in the event of a change in the price and (or) quantity of goods (works, services). An important condition is that such changes must be agreed upon between the parties to the transaction. Then there is no need to submit updated VAT returns, and CSF (for example, adjustment documents for shipment) are reflected in accounting for the period when they were compiled (from the seller) and received (from the buyer).
There are two types of adjustments – increasing or decreasing the cost of sales. An accountant more often has to deal with a situation of decreasing value, for example, when applying retro discounts.
The accounting treatment is as follows:
From the buyer:
- Decrease in value - in the sales book;
- The increase in value is in the purchase book.
From the seller:
- Reducing the cost - in the purchase book;
- The increase in value is in the sales book.
Before the advent of Russian Government Decree No. 952 dated October 24, 2013, the Seller, when the cost of shipment increased, had to submit an updated declaration for the shipment period. Many sources on the Internet still advise this procedure, but it is no longer relevant. “Clarifications” on VAT are submitted if errors are discovered, and the agreed price change is now not an error.
Let's consider the process of reflecting CSF in the 1C accounting program, first from the buyer, then from the seller. If you still have questions, please contact our 1C system user support service, we will be happy to answer them.
Tax legislation requirements
Based on Article 81 of the Tax Code of Russia, an organization is required to submit an updated declaration only if errors and unreported data discovered after filing reports lead to an underestimation of the tax amount .
If the primary declaration contains unreliable or incomplete information that does not lead to an underestimation of the tax amount, then the taxpayer is not required to submit an “adjustment”, although he has the right to do so.
What threatens a company or entrepreneur who has filed an updated declaration? The mere fact of its presentation does not entail sanctions - it all depends on whether unreliable primary data caused an understatement of tax. If this is the case, then the arrears and penalties should be paid before submitting the “clarification”. In this case, according to paragraph 4 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer will be released from liability for incomplete payment of tax.
If the arrears are not paid before the tax service finds out about it, a fine may be imposed on the organization in accordance with Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Although the law does not require any explanatory documents to be attached to the updated declaration, it would still be useful to draw up a covering letter .
Moreover, when conducting a desk inspection, inspectors will still ask for clarification. The letter should indicate which tax declaration and for what period changes are being made, what erroneous (incomplete or unsubmitted) information is, in which sections and lines of the declaration they are located, as well as provide primary and updated indicators. If errors affected the tax base, a new calculation and tax amount should be provided. In case of payment of arrears and penalties, you should indicate the payment details and, together with the declaration and cover letter, send a scanned copy of it to the tax office.
How to fix your purchase book
How can an overstatement of VAT deduction occur?
Most often, this could happen due to the fact that an invoice was entered into the purchase book that did not meet the conditions for deduction. For example, if the purchase is not related to a VAT-taxable activity. They could also simply double the invoice data.
In such cases, you need to make changes to the purchase book and correct the erroneous invoice entry.
Resolution No. 1137 provides two options for making corrections to the purchase ledger.
If an error is found in the purchase book for the current period, then you need to cancel the invoice entries in the purchase book for the same period and indicate its cost indicators (columns 15–16) with a negative value.
Specific situations
Now let’s look at common situations in which it is impossible to avoid submitting an updated declaration to the tax service, and also when you can do without it.
Incorrect reporting period
What to do if there is an error in the code of the period for which the declaration was drawn up? The answer is clear - you need to notify the tax service about this error, and as quickly as possible. Otherwise, you can get penalties, and they can be imposed both on the organization (Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and on the official (15.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Is it necessary to submit a “clarification” in this case? This option is possible, although you may encounter misunderstanding on the part of the Federal Tax Service. They may simply not accept the document, since no primary declaration was filed during the specified period. Or consider the updated declaration as filed for the first time in violation of the deadline, and then the organization may be fined under Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
It's better to do this:
Declare in writing to the tax office that a return filed with an incorrect period code should be considered submitted for such and such a period (indicating its correct code).
Most often, the Federal Tax Service accepts such explanations and believes that the organization has reported without violations. But if penalties do follow, the organization has a chance to challenge it - in judicial practice there are examples when arbitrators decided such cases in favor of the taxpayer (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated July 30, 2009 in case No. A32-22251/2008- 12/190).
Late documents received
Often in practice there are situations when documents relating to a previous period are received from a counterparty. For example, an invoice for a December transaction can be received as early as January of the following year. In such cases, there is no need to submit a “clarification”, because you can include a “late” invoice in the purchase book in the current period. This rule was introduced at the beginning of 2015 by paragraph 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Based on it, you can claim VAT deduction for any period within three years from the date of receipt of goods, work or services.
However, this procedure applies only to deductions provided for in paragraph 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Other deductions of VAT (for example, paid as a tax agent, on prepayment, etc.) must be declared in the period in which the purchased goods were accepted for accounting, provided they were used to carry out activities subject to VAT.
There was an overstatement of VAT deduction
A situation in which an updated VAT return should definitely be submitted is when, due to an error that has crept in, the tax deduction has been inflated . Indeed, as a result, the amount of tax is underestimated, and this, as was said at the beginning of the article, imposes on the organization the obligation to provide “clarification”. Sometimes this happens due to the fault of the accountant - for example, he registered the same invoice twice or made a technical error when entering information into the accounting system. But this can also be a consequence of erroneous actions by the supplier’s accounting department. Let's say the initial invoice received in the reporting quarter was subsequently corrected and dated to the next period.
Regardless of whose fault it is that the deduction is inflated, an amended return will have to be filed. But before that, you need to correct errors in the purchase book - draw up an additional sheet and enter the correct data into it. Information that is subject to deletion must be written down with a minus sign.
Errors in the purchase book that do not affect the deduction amount
Sometimes in primary documents of past periods you can find technical errors that do not affect the amount of VAT. For example, erroneous indication of TIN, address, name of the counterparty.
By virtue of the aforementioned Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, their presence does not oblige the taxpayer to submit an updated declaration.
However, the tax authorities themselves still recommend doing this, because during a desk audit on VAT, when the data of invoices of counterparties for each transaction is reconciled, these errors pop up, and tax inspectors usually demand clarification.
Receive a corrected invoice
It happens that an accountant discovers errors in the received invoice and asks the supplier to correct them. The latter draws up an adjustment invoice and sends it to the buyer. However, there may be a time gap between these events, and the organization will receive the corrected document in the next quarter.
According to the Federal Tax Service, such an invoice should be registered in the period in which its correct version was received. The deduction previously claimed for it will have to be cancelled, VAT recalculated, its amount and penalties paid, and then an updated declaration submitted.
It is worth noting that this position of the tax service does not find unambiguous support from the arbitrators - they make their decisions both in favor of the Federal Tax Service and in favor of taxpayers.
It should also be remembered that not all erroneous data on invoices can lead to a denial of deduction. Paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly states that if errors do not interfere with identifying the parties to the transaction, the name and cost of the goods, the rate and amount of VAT, then there are no grounds for refusing a deduction on such an invoice. Therefore, before contacting the supplier for an adjustment document, you should make sure that it is necessary.
What is recorded in the purchase book
The rules for filling out the purchase book and an additional sheet of the purchase book are approved by Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011.
Supplier invoices are registered in the purchase book if the following conditions are met:
- purchased assets (work, services) were acquired for operations subject to VAT, including for resale, and were capitalized;
- the invoice is drawn up in the prescribed form and filled out in accordance with the rules set out in Resolution No. 1137.
Invoices, including adjustments, corrected ones, received on paper or electronically, are registered in a uniform manner as the right to tax deductions arises (Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You can record more than just invoices in the purchase ledger.
It registers tickets, hotel bills and other strict reporting forms that confirm expenses for employee business trips. It is only necessary that in these documents the VAT amount is highlighted as a separate line.
When returning goods sold at retail to individuals (that is, without issuing invoices), the seller can register in the purchase book the details of the cash receipts that he issued when returning the money to the buyer. This is possible if you have documents confirming the acceptance and registration of returned goods. In this case, the seller registers documents in the purchase book on the date of acceptance of the returned goods for registration.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
How to fill out a purchase book
What to do if you receive a request for clarification on your VAT return?
When receiving a letter from the tax office in the form of an electronic request for explanations, you must:
- Within 6 working days, send a receipt of its receipt in accordance with clause 5.1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If the receipt is not sent, then there will be sanctions - blocking of the account by virtue of clause 2, clause 3, article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- It is necessary to respond to such a requirement electronically within 5 working days by virtue of clause 3 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Codes are used to indicate errors regarding the requirements for providing explanations to the Federal Tax Service:
How to respond to the Federal Tax Service’s request for explanations
The form for the request for explanations and a response to the Federal Tax Service’s request was published in the Federal Tax Service’s letter No. ED-4-15/5752 dated 04/07/2015.
In response to the requirement to provide explanations to the Federal Tax Service, Appendices are attached in the form of tables duplicating the form of sections of the VAT declaration from 8 to 12, which indicate inaccuracies or errors. Requirements for other sections of the VAT declaration are presented in any form.
Additional sheet
If you discovered an overstatement of the deduction in the previous period, then you need to fill out an additional sheet of the purchase ledger. Its form is also approved by Resolution No. 1137, and the format for compiling in electronic form is approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 4, 2015 No. ММВ-7-6 / [email protected]
The extra sheet is almost the same as a regular shopping ledger sheet.
The difference is that it has a “Total” line. Here they indicate the total data of the purchase book for the period in which the error was made.
The subsequent lines of the sheet reflect the details of invoices subject to cancellation. And in the “Total” line, enter the difference between the “Total” line and the invoice amounts recorded in the additional sheet.
The additional sheet must indicate:
- serial number of this sheet;
- full or abbreviated name of the company;
- TIN and checkpoint of the company;
- the tax period in which the invoice was registered before corrections were made to it;
- the date when the additional sheet was issued.
For the quarter when the excess deduction was declared, you need to fill out an additional sheet in the purchase book. An erroneous entry about an extra invoice is canceled, that is, the numerical indicators of the erroneous invoice are recorded with a minus sign, and then the amount of deductions is displayed, which should be included in the declaration.
If, due to an overstatement of the amount of deductions, you underpaid VAT to the budget, then you must submit an updated VAT return for the quarter in which the error occurred. And do not forget to pay the arrears and penalties (clause 1, 4, article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Document Adjustment of receipts
Document Adjustment of receipt type of operation Correction of own error is used to correct own errors in 1C 8.3 made when entering primary data into the database:
- amounts of goods, works, services (GWS);
- details of the invoice (IF), namely: numbers,
- dates,
- INN/KPP of the counterparty,
- transaction type code.
The main ways to create a Receipt Adjustment :
- based on documents using the Create button based on : Receipt (act, invoice),
- Adjustment of receipts,
- Receipt of additional expenses,
- Returning goods to the supplier,
- Purchases – Adjustment of receipts.
Filling features:
- Main tab – basic settings and correction of invoice details in 1C;
- Goods tab – correction of the cost or quantity of acquired material assets;
- Services tab – correction of the cost or quantity of acquired intangible assets.
- Basis – the document being corrected or the primary document of the invoice being corrected;
- Old value/New value – registered data in the database and correct invoice data;
- Reflect the adjustment - where changes are made to correct receipts in 1C 8.3: In all sections of accounting - postings are generated for accounting, NU and movements in VAT registers;
- Only in VAT accounting – only movements in VAT registers are generated.
An error made when registering an invoice is a “technical” error in filling out the purchase book, therefore, when posting the Receipt Adjustment or by clicking the Register , a “technical” invoice is created to register the corrected data and correct the invoice in 1C.
Express check of VAT accounting in 1C 8.3
Errors in calculating VAT in 1C 8.3 will help to identify Menu Reports - Express check of accounting:
Using an example, we will consider the Express check of VAT accounting for the year, but you can also set the reporting period – quarter. It is necessary to check the boxes for maintaining the Sales Book and the Purchase Book for VAT. Perform check:
In 1C 8.3, a check is performed and data is output. In our example, errors were found:
Let's analyze errors in VAT accounting in 1C 8.3:
The error “Completeness of issuing invoices for sales documents” means, for example, that an invoice has not been issued. Or the invoice was issued in another program, for example 1C Trade and Warehouse, and was not entered into 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0:
Consequently, having submitted a VAT return, the organization’s counterparty, the buyer, will reflect an invoice that is not in the sales book. Accordingly, data on the VAT return will not be included. It is necessary to be attentive to such errors regarding VAT in 1C 8.3.
Especially, you need to look at the points related to VAT calculation:
Fines are not subject to VAT, and 1C 8.3 may contain an error. During the express check, you need to carefully monitor which transactions are reflected. Some errors may be in the form of a warning.
In the purchase book, you need to look at the compliance of VAT on account 19 with what is accepted for deduction:
Generating purchase book entries and sales book entries at the end of the year in 1C 8.3
In 1C 8.3, before an express check of VAT accounting, two regulatory documents must be generated - this is the formation of purchase book entries and sales book entries for December 31. Menu Operations – Regular VAT operations:
Documents are filled out according to the purchase book. If VAT deductions are carried forward to the next year, since the organization can do this within three years, then the line is deleted from the document. Account 19 will be reflected in both the balance sheet and the VAT register:
According to the sales book, a single entry is generated related to the restoration of advances. For example, when transferring an advance to a supplier, an advance invoice is received. According to it, VAT is accepted for deduction. Further, when the supplier supplies goods, works, services, it is necessary to restore the VAT at the previously accepted deduction from the advance payment. VAT recovery in 1C 8.3 is automatically carried out using a document for generating a sales book entry:
Express check does not detect all errors in VAT accounting. On the course on working in 1C: Accounting 8th ed. 3.0 we talk about triple VAT verification, analyze the correspondence of purchase and sales books and account turnover, and much more.