What is meant by a corrected invoice?
In ch.
21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the term “corrected invoice”, as well as “corrective”, is absent. Moreover, in both forms of invoice (both main and adjustment), proposed by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, there is a line for indicating the details of the corrections made to them. In addition, the preparation of an amended invoice is discussed in clause 6 of the Rules for filling out an invoice. Thus, it is implied that corrections are a thing that has a right to exist. Moreover, changes can be made both to the main document and to the corrected invoice.
However, it should be understood that an adjustment invoice and a corrected invoice are completely different documents:
- An adjustment invoice is needed when changes are made to the original data of the primary document (quantity and price), affecting the calculation of the final sales amount recorded in it and the associated VAT amount. Moreover, the adjustment does not mean that an error was made in the original version of the invoice. No, the issuance of an adjustment invoice can be caused by changes in the source data that occurred under the influence of some factors, most often documented (agreements on price changes, retro discounts, identification of shortages, defects or surpluses among the delivered goods).
Learn more about this invoice - “What is an adjustment invoice and when is it needed?” .
- The need for a corrected invoice arises when technical errors are discovered in the original document, which may have negative consequences for receiving deductions on it. However, not all errors result in the need to create a corrected invoice. If they do not affect the correct understanding of the information on the details in which they are included (even mandatory ones), then a deduction on such a document is permissible (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - therefore, there is no need for a corrected invoice.
See also “An error has crept into the invoice: should I draw up a corrected or corrective document?” .
The concept of a corrected invoice as an adjusted source document arose from the adoption of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137, i.e. since 2012. Previously, a significant part of the technical errors made in the preparation of an invoice could be corrected directly in the incorrect source document, having certified the corrections with the signature and seal of the originator. After the entry into force of this resolution, the amended invoice was given the status of an independent document, with all the ensuing consequences.
Error correction
If there is a technical error in the invoice (adjustment invoice), corrections must be made to the original document. That is, issue a corrected invoice. Do not prepare adjustment invoices in such cases. Even if an error is made when indicating the price (tariff), tax rate or cost of goods (work, services). This is stated in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 8, 2012 No. 03-07-15/102 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 12, 2012 No. ED-4-3/4143.
Corrections to invoices drawn up according to old forms are made according to the rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 No. 914. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 2 of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137 and the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 31, 2012 No. 03-07-15/11.
When correcting invoices (including adjustment ones) drawn up according to the forms approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, the seller (executor) must draw up new (corrected) invoices (adjustment invoices) . However, in the corrected invoice you cannot change the data on line 1 of the primary invoice. Instead, on line 1a you need to indicate the serial number and date of correction of the primary invoice. This is stated in paragraph 7 of Appendix 1 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
When correcting an adjustment invoice in a new copy of the adjustment invoice, changes to the indicators in lines 1 and 1b of the primary adjustment invoice are not allowed. In this case, line 1a is filled in, which indicates the serial number and date of correction.
The remaining details of the corrected invoice (including those initially not filled out or clarified), including changes in the initials of the authorized person who signed the invoice, are indicated in the general manner.
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 6 of Appendix 2 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
Example of making changes to primary and adjustment invoices
Torgovaya LLC (seller) and Alfa CJSC (buyer) entered into a purchase and sale agreement No. 18 dated February 16, 2021. According to this agreement, Hermes supplies Alfa with the following goods:
1. Powdered milk – 10,000 packets. The selling price of one package (excluding VAT) is 30 rubles/package. The total cost of the batch (excluding VAT) is 300,000 rubles. (10,000 packages × 30 rubles/package).
Powdered milk is subject to VAT at a rate of 10 percent (list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2004 No. 908). Therefore, the amount of VAT that Hermes presented to Alpha amounted to 30,000 rubles. (10,000 packages × 30 rub./package × 10%).
Thus, the total cost of a batch of milk powder (including VAT) is 330,000 rubles. (300,000 rub. + 30,000 rub.).
2. Sparkling water – 10,000 bottles. The selling price of one bottle (excluding VAT) is 15 rubles/bottle. The total cost of the batch (excluding VAT) is 150,000 rubles. (10,000 bottles × 15 rubles/bottle).
Carbonated water is subject to VAT at a rate of 18 percent (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, the amount of VAT that Hermes presented to Alpha amounted to 27,000 rubles. (10,000 bottles × 15 rub./bottle × 18%).
Thus, the total cost of a batch of sparkling water (including VAT) is 177,000 rubles. (RUB 150,000 + RUB 27,000).
Items were shipped on February 17, 2021. Hermes issued an invoice to Alpha for the shipped goods and registered it in the sales book.
Upon receiving the goods, it turned out that instead of 10,000 bottles of sparkling water, Hermes shipped 11,000 bottles. On February 20, the parties entered into an additional agreement to the contract, which recorded a change in the volume of supply.
On February 26, Hermes issued an adjustment invoice.
After completing the adjustment invoice, the Hermes accountant discovered that the invoices (both primary and adjustment) incorrectly indicated the address of Alpha (instead of “Mikhalkovskaya St., 20” it was indicated “Mikhalkovskaya St., d. 21").
On February 27, Hermes issued corrected copies of invoices (both primary and adjustment).
If, before making changes to the primary invoice, an adjustment invoice was drawn up for it, then in the amended invoice the indicators are given without taking into account the changes reflected in the adjustment invoice (clause 7 of Appendix 1 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137).
Only sellers (performers) have the right to make changes to previously issued invoices (including adjustment invoices). This follows from the provisions of paragraph 7 of Appendix 1, paragraph 6 of Appendix 2 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
The invoice (adjustment invoice) with the corrections made to it is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization or authorized proxies (Clause 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For more information, see Who has the right to sign an invoice.
Situation: what should a selling organization do if it erroneously issued two invoices for the same transaction? Did this come to light after filing your VAT return?
You will have to adjust the VAT tax base, recalculate the tax, and also notify the buyer of the error.
Due to the fact that the invoice was issued repeatedly for the same transaction, both the seller’s VAT tax base and the buyer’s tax deduction will be overestimated. Therefore, if you find such an error, you need to perform the following steps.
1. Cancel the reissued invoice in the sales ledger.
After all, it is on the basis of the sales book that the amount of VAT payable is determined (clause 1 of section II of Appendix 5 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). To do this, fill out an additional sheet to the sales book for the period in which the error was made, and reflect in it the amount of shipment and tax on the erroneously issued invoice with a minus sign (clause 11 of Section II of Appendix 5 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137).
2. Adjust the VAT tax base for the period in which the error was made.
Since the re-issued invoice was included in the total sales amount for the tax period, tax was excessively charged on this amount. This means that the organization has overpaid. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the tax base and recalculate the tax. And despite the fact that such an error led to an overpayment of VAT, in this situation it is necessary to submit an updated declaration to the tax office. It is not possible to adjust the tax base in the current period. This is explained by the fact that the general rules provided for correcting errors in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 81 and paragraph 1 of Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not apply to VAT.
Create an updated declaration based on the corrected sales book, taking into account the completed additional sheet (clause 5 of section IV of appendix 5 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). The resulting tax overpayment can be offset or refunded.
3. Notify the buyer of the discovered error.
It is clear that the buyer registered the erroneously issued invoice in the purchase book. And based on the data from such a book, he forms the amount of tax accepted for deduction (clause 1 of section II of Appendix 4 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). By reflecting an extra invoice there, the buyer simply overestimated the amount of the deduction. As a result, arrears arise, which is why organizations may be charged penalties and fines. Therefore, as soon as you discover that you have issued an invoice again by mistake, be sure to inform the buyer about this - send him a corresponding notification. Based on such a document, he will be able to make changes to the purchase book and also submit an updated declaration.
Situation: How to correct an invoice issued by a branch. The invoice incorrectly indicated VAT on tax-exempt services. Was the branch liquidated at the time the error was discovered?
A new invoice with the necessary corrections must be issued by the head office of the organization.
According to paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT payers, that is, organizations, must draw up invoices. The branch is not a VAT payer, so it issues invoices on behalf of the organization, but indicating its checkpoint. This is stated in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 13, 2012 No. 03-07-09/35 and dated January 26, 2012 No. 03-07-09/03.
If the invoice was drawn up with errors, and the branch that issued the invoice was liquidated, the organization, as a VAT payer, must issue a corrected invoice to the buyer. Issuing an invoice with an allocated VAT amount in the situation under consideration is an error and does not apply to cases where it is necessary to issue an adjustment invoice.
Paragraph 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, states that in order to correct an invoice, you need to draw up a new invoice with the correct indicators. In line 1a, indicate the serial number and date of changes. Since the corrected invoice is issued not by the branch, but by the head office of the organization, in line 2b indicate the checkpoint of the head office. In columns 7–8, put o (clause 5 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subparagraphs “g” and “h” of clause 2 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137).
In what cases is an invoice correction required?
So in what cases is a corrected invoice issued? It is needed when it becomes necessary to correct a technical error in the source document. For example, you may need to create a corrected invoice if there is an error:
- in the date, if the original document was mistakenly issued in a different month, year;
- details of the supplier or buyer, if they are written not just with a typo, but do not correspond to them at all (incorrect TIN, address, name, etc.);
- indication of the shipper and consignee, if they do not belong to the persons who actually sent and received the goods;
- details of the document for the transfer of the advance;
- name and currency code of the document;
- indicating the name of the product (work, service);
- indicating an incorrect price or quantity of goods;
- in the rate and, as a consequence, in the amount of VAT and the final amount of the document;
- or in the absence of data required to be filled in for imported goods (country of origin and registration number of the customs declaration).
It should be noted that most taxpayers, if an error is discovered in a timely manner and has not yet been identified by the tax authorities, prefer not to make a corrected invoice, but simply replace the defective document.
For errors that do not require correction, read the article “What errors in filling out an invoice are not critical for VAT deduction?” .
For information about what errors in the invoice should be corrected, read the article “We made a mistake in the invoice - what and how to correct it.”
What errors are encountered when compiling?
Despite a clearly defined maintenance procedure, errors in the preparation of invoices are not uncommon . Some of them do not prevent you from receiving a tax deduction; others should be taken seriously.
Let's figure out which inaccuracies are serious and which are completely acceptable.
- There is an error in the name of the buyer and the price in the invoice . Incorrectly indicated cost of goods and services, errors in the amount of VAT and names of goods (not to mention arithmetic errors) will become the basis for tax authorities to refuse a deduction (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2013 No. 03-07-09/19826, dated September 18. 2014 No. 03-07-09/46708 and dated 08/14/2015 No. 03-03-06/1/47252).
- Wrong currency . If line 7 “Currency: name, code” contains incorrect information, then identifying the cost of goods (work, services) and the amount of VAT will be difficult, and such invoices need to be corrected (letter dated March 11, 2012 No. 03-07-08/ 68).
- Using facsimiles . When preparing an invoice, you need to forget about facsimiles, because such documents are not the basis for deducting VAT (letters dated 09/17/2009 No. 03-07-09/48 and No. 03-07-09/31, dated 06/01/2010 No. 03 -07-09/33).
Some inaccuracies in the invoice book should not interfere with the VAT refund and disrupt your calm communication with the tax inspector.
- Numbering.
How to correct an advance invoice? Completed and advance invoices are numbered in chronological order (letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 10, 2012 No. 03-07-11/284 and dated October 16, 2012 No. 03-07-11/427). When using daily numbering of accounts, the deduction must be accepted in the usual manner (letter dated October 11, 2013 No. 03-07-09/42466). Important! Failure to indicate individual information on the invoice does not require any additional characters. The legislation does not specifically regulate the insertion of dashes (Letter of the Department of Tax Administration of the Russian Federation for Moscow dated 01/09/2004 No. 24-11/1046). - Error in address. When filling out line 2a, you must fully indicate all information about the taxpayer’s address (letter dated February 17, 2015 No. 16-15/013654). Neither abbreviations, nor punctuation marks (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 9, 2011 No. 03-07-09/41), nor even errors when indicating addresses are grounds for refusal to accept income tax and other taxes (letter dated June 7, 2010 No. 03-07-09/36, dated 08.08.2014 No. 03-07-09/39449 and dated 02.04.2015 No. 03-07-09/18318).
- Checkpoint.
The absence of a reason code, which is indicated in lines 2b and 6b of your invoice, does not affect the decision on VAT deduction (letter dated 08/26/2015 No. 03-07-09/49050). Moreover, large taxpayers are assigned two checkpoints at once - at their actual and legal addresses. In this case, when filling out invoices, it is necessary to indicate the checkpoint from the notice of registration as the largest taxpayer (letter dated 08.20.2015 No. 03-07-09/49236 and the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 09.07.2015 No. GD-4-3/15640 ).
Invoice Correction Form
There is no specific form for the revised invoice. It is drawn up in the same form in which the original document requiring correction was drawn up, i.e. main or adjustment. Both forms are contained in Appendices 1 and 2, respectively, of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137. In this case, the preparation of a corrected invoice can be carried out if it is necessary to correct invoices previously issued:
- for implementation;
- for an advance;
- for adjustments, including to several amended documents.
You can find the invoice form, including the one intended for correction, in the article .
Features of filling out an amended invoice
In both forms of the corrected invoice, under the main heading of the document containing its number and date, a line (or lines) is provided for entering the number and date of the correction:
- there is only one line in the invoice, and it is located directly under the heading;
- in the adjustment invoice—2: one is intended for information about the correction of the adjustment invoice itself, and the second is for indicating the details of the original invoice for which the adjustment invoice was drawn up.
There are no other features in the design of the corrected invoice. It is formatted in the same way as a regular one, only incorrect data in it is replaced with correct ones.
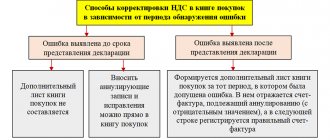
Features of registering an amended invoice
If the correction invoice is issued in the same quarter as the original invoice (adjustment invoice), then in the same quarter:
- The seller must register the corrected invoice in the sales book and re-register the erroneous invoice, but reflect all its numerical indicators with a minus sign.
ConsultantPlus experts have prepared an example of registering a corrected invoice in the sales book. Go ahead and get trial access to K+ for free.
- The buyer, if he has reflected an erroneous invoice in the purchase book, must register a corrected invoice in the purchase book and re-register the erroneous invoice, but reflect all its numerical indicators with a minus sign. If the buyer has not shown an erroneous invoice in the purchase ledger, he only records the corrective invoice.
An example of registering a corrected invoice in the purchase book is available in the ConsultantPlus system. Get trial access to the system for free.
In the diagram, we showed the procedure for the seller and buyer when the data in the invoice changes or if there are errors in it.
If the corrective invoice was drawn up in another (next) quarter:
- The seller must record the corrected invoice on an additional sheet of the sales ledger for the quarter in which the erroneous invoice was recorded. In the same additional sheet of the sales book, register the erroneous invoice, indicating all its numerical indicators with a minus sign.
- The buyer must draw up an additional sheet to the purchase book for the quarter in which he registered the erroneous invoice and, in the same additional sheet to the sales book, register the erroneous invoice, indicating all its numerical indicators with a minus sign. If the buyer initially did not reflect the invoice issued with errors in the purchase book, then the corrected one must register the corrected invoice only in the purchase book of the quarter in which this document was received.
Results
Changes to the invoice and adjustment invoice not related to amendments to the quantity, cost of goods (work, services) and tax obligations are made accordingly on the form of the invoice, adjustment invoice. When drawing up correction documents, it is necessary to indicate the details of the original document in which the error was made. The procedure for registering a corrective invoice depends on the period in which it was drawn up in relation to the erroneous invoice, and for the buyer also on whether he or she registered an invoice containing errors in the purchase book.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Tax legislation requirements
Based on Article 81 of the Tax Code of Russia, an organization is required to submit an updated declaration only if errors and unreported data discovered after filing reports lead to an underestimation of the tax amount .
If the primary declaration contains unreliable or incomplete information that does not lead to an underestimation of the tax amount, then the taxpayer is not required to submit an “adjustment”, although he has the right to do so.
What threatens a company or entrepreneur who has filed an updated declaration? The mere fact of its presentation does not entail sanctions - it all depends on whether unreliable primary data caused an understatement of tax. If this is the case, then the arrears and penalties should be paid before submitting the “clarification”. In this case, according to paragraph 4 of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer will be released from liability for incomplete payment of tax.
If the arrears are not paid before the tax service finds out about it, a fine may be imposed on the organization in accordance with Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Although the law does not require any explanatory documents to be attached to the updated declaration, it would still be useful to draw up a covering letter . Moreover, when conducting a desk inspection, inspectors will still ask for clarification. The letter should indicate which tax declaration and for what period changes are being made, what erroneous (incomplete or unsubmitted) information is, in which sections and lines of the declaration they are located, as well as provide primary and updated indicators. If errors affected the tax base, a new calculation and tax amount should be provided. In case of payment of arrears and penalties, you should indicate the payment details and, together with the declaration and cover letter, send a scanned copy of it to the tax office.