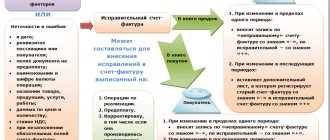
An invoice is a necessary document not only in accounting, but also in the office work of an organization in general. There are many nuances in filling out this document, ignorance of which can lead to problems with the Tax Inspectorate.
This is a form confirming the fact of shipment of goods or provision of services at a set cost. This is not the only function of this form. What is an invoice? An accounting form required to confirm the amount of VAT both on the sale of goods (services) and input VAT to prove the right to a tax deduction in order to avoid double taxation. The presence of an invoice is a prerequisite for crediting the amount of VAT on material resources (work, services) that were purchased by the taxpayer.
This is a very important document, often used in legal disputes, so it must be filled out correctly.
Accounting and legal services
Analytical accounting for account 62 in Stimul-2 LLC is maintained for each invoice presented by the buyer or customer, and for settlements in the order of scheduled payments - for each buyer or customer. The construction of analytical accounting provides data on debt secured by: bills of exchange for which the receipt of funds has not arrived; bills discounted (discounted) in banks; bills for which funds were not received on time.
Please note => Documents Necessary for Registration of Benefits for Utilities
Do you need a document?
In the terms of the contract, the parties to the transaction can agree on the rules for issuing certificates of completed work. To this primary document, which is the basis for reflecting work in accounting, and costs - when calculating income tax. In other words, the act of completion and the invoice are considered two non-fungible documents.
This means that in order to properly process the transaction, the supplier must provide an invoice and a signed certificate of completion of work.
It is worth noting that the above two documents can be replaced by one - a unified transfer document (UDD). We present a comparison of UPD and invoice here.
Important! The contractor, for the work provided, issues an invoice no later than five days from the date of drawing up the primary document (work completion certificate) addressed to the customer.
Invoice how many copies
- in line 1
- the serial number and date of issue of the invoice. When drawing up an invoice by the principal (principal) to the commission agent (agent) selling goods (work, services), property rights on his own behalf, as well as when drawing up in this case an invoice by the commission agent (agent) to the buyer in this line of such invoices a single date is indicated - the date the invoice is issued by the commission agent (agent) to the buyer; - in line 2
- the full and abbreviated name of the seller in accordance with the constituent documents; - in line 2a
- the location of the seller in accordance with the constituent documents; - in line 2b
- identification number and reason code for registering the taxpayer-seller; - in line 3
- the full or abbreviated name of the shipper in accordance with the constituent documents. If the seller and the shipper are the same person, then “he” is written in this line. Otherwise, the postal address of the shipper is indicated. When drawing up an invoice for work performed (services provided), property rights are marked with dashes in this line; - in line 4
- the full or abbreviated name of the consignee in accordance with the constituent documents and his postal address; - in line 5
- details (number and date of preparation) of the payment document or cash receipt (when making payments using payment documents or cash receipts, to which an invoice is attached).
When drawing up an invoice upon receipt of the payment amount, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights using a non-cash
form of payment, dashes are placed in this line. When drawing up an invoice by the tax agent specified in paragraph 4 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this line indicates the number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating the transfer of the tax amount to the budget.; - in line 6
- the full or abbreviated name of the buyer in accordance with the constituent documents; - in line 6a
- the location of the buyer in accordance with the constituent documents; - in line 6b
- identification number and code of the reason for delivery to the taxpayer-buyer's account.
Please note => Benefits for single mothers
Accounting for settlements with customers at Stimul-2 LLC
The invoice is drawn up in two copies.
The first copy is transferred to the buyer no later than 10 days from the date of shipment of the goods or receipt of an advance payment. The second remains with the organization that sold this product. Stimul-2 LLC issues an invoice, but does not keep a log of issued invoices and a sales book in the forms approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000. No. 914.
The journal for recording invoices issued to customers, in which their second copies are stored, records of invoices issued to customers are kept in chronological order.
The sales book is intended for registering invoices issued during transactions recognized as objects that are subject to value added tax, including those not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation).
Invoices issued for the sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services) to organizations and individual entrepreneurs for cash payment are subject to registration in the sales book.
Registration of invoices in the sales book is carried out in chronological order in the tax period in which the tax liability arises. When receiving funds in the form of advances or other payments for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), an invoice is drawn up.
In the case of partial payment for shipped goods (work performed, services rendered), when adopting an accounting policy for tax purposes, as funds are received, the seller registers an invoice in the sales book for each amount received as a partial payment, indicating the invoice details - invoices for these shipped goods (work performed, services rendered) and a note for each amount “partial payment”.
Registration of invoices with the same details in the sales book is allowed only in cases of receipt of funds in the form of partial payment, as well as shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services) against the received amount of advance or other payments with a corresponding adjustment (offset) of previously accrued tax amounts. payment.
The sales ledger is kept for a full 5 years from the date of the last entry.
It is allowed to maintain a sales book in electronic form. In this case, after the expiration of the tax period, but no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired tax period, the sales book is printed, the pages are numbered, laced and sealed.
Invoices that have erasures and blots are not subject to registration in the sales book. Corrections made to invoices must be certified by the manager’s signature and seal indicating the date the correction was made.
Stimul-2 LLC provides itself with invoice forms independently.
Stimul-2 LLC mainly uses invoices and payment orders for settlements with buyers and customers.
The payment order is issued simultaneously in several copies, which must be identical. The number of copies that must be submitted to the bank depends on how the payment is made; usually 3 or 4 copies are submitted (one copy each for the payer, payer's bank, buyer, buyer's bank). No corrections are allowed when filling out a payment order.
Before issuing a payment order, it is assigned a serial number, which is indicated in the corresponding field of the payment order form.
The payment order indicates the TIN; name and account number in a credit institution, bank identification code, etc.
The invoice is signed
- A participant in a simple partnership agreement received an advance or shipped goods (work, services) under such an agreement
- Trustee - received an advance or shipped goods (work, services) under such an agreement
- Commission agent (agent acting on his own behalf) - received an advance or shipped goods (work, services) of the principal (principal) - VAT payer
- An intermediary involved in settlements has shipped goods (work, services) to a foreign person who is not registered for tax purposes in the Russian Federation, or received an advance payment for them
Who is exhibiting?
An invoice is issued by the counterparty who performs certain work under the terms of the contract, who also has obligations to pay value added tax to the state budget. The same document, for the customer, becomes the basis for accepting the work provided, indicating the amount of VAT to account for its deduction.
More information about who issues the invoice can be found here.
In how many copies is the invoice issued?
Nowadays, all organizations use accounting programs and any document can be printed repeatedly. In this regard, there is a question that I haven’t found an answer to specifically anywhere: How many invoices issued should be printed when generating them? - one or two? It is clear that one copy is given to the buyer for VAT reimbursement. In general, do we still need copies of issued invoices? Of course, someone will say that this is a personal matter for each accountant, that this is stated in the accounting policy. But if we take the legislative component of the formation of issued invoices, are second copies of this document needed in the accounting department of the selling organization? At the same time, it is written everywhere that the Seller is obliged to generate an invoice and register it in the Journal of issued invoices. AND SHOULD
Should the seller keep a second copy with the signatures of the issued invoice?
=== That is Is it necessary to keep an invoice issued by the selling organization in paper form or is it enough to just register it in a journal? === It would be nice to receive an answer with a link to some regulatory documents.
Thank you all for your participation. Please note => Get Land in Crimea for Building a House for Free
Export of goods
Situation: is it necessary to issue invoices when selling goods for export?
Yes need.
Invoices must be issued for all transactions that are subject to VAT. There are some exceptions, but exporting is not one of them. This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, draw up an invoice, as usual, within five calendar days from the date of shipment for export (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Similar explanations are in letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 5, 2007 No. 03-07-08/180 and the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated September 19, 2003 No. 24-11/51717. And although the conclusions in them relate to the previous rules for issuing invoices, they are still valid today. Arbitration practice also shows that invoices must be drawn up when shipping for export (see, for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 5, 2005 No. KA-A40/8359-05).
An example of issuing an invoice for the sale of goods for export
JSC Alfa is engaged in the production of office furniture. On June 15, Alpha shipped 10 Office furniture sets to Ukraine. The buyer is the Dnepropetrovsk Switch Plant. The selling price of one headset is 150,000 rubles. (taxed at 0% rate). The total transaction amount is RUB 1,500,000. (10 pcs. × 150,000 rub./pc.).
Furniture sets are sold in accordance with the customs export procedure. Therefore, this operation is subject to VAT at a rate of 0 percent. Alpha submitted all the necessary documents confirming the fact of export on time.
Alfa presented the Dnepropetrovsk Switch Plant with an invoice for the cost of the shipped products. At the same time, when filling out line 6b “TIN/KPP of the buyer” of the invoice, the accountant took into account the fact that the accounting of Ukrainian organizations is carried out in accordance with the legislation of Ukraine. All Ukrainian organizations are included in the Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs and Organizations of Ukraine, and each of them is assigned an eight-digit OKPO number (analogous to the Russian TIN). It was this number assigned to the Dnepropetrovsk switch that was indicated in line 6b.
Situation: is it necessary to issue invoices if an organization exports goods, the sale of which in Russia is exempt from VAT?
No no need.
For transactions that are recognized as subject to VAT, but at the same time are not subject to (exempt from taxation) this tax in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is not necessary to issue invoices. This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, if an organization exports goods, the sale of which in Russia is exempt from VAT, then it should not issue invoices for the cost of these goods.
Actions after invoicing
Clause 3 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges the taxpayer to keep a journal record of issued and received invoices, books of purchases and sales. This procedure was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
Buyers maintain a log of received original invoices from sellers. Clause 8 of the Rules obliges to register received invoices in the purchase book as the right established by Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - tax deduction.
Tax rate
VAT deduction will be denied if an incorrect tax rate is indicated (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2011 No. 0307-08/124, Letters of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2008 No. 03-07-08/187, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2006 No. MM-6- 03/ [email protected] , Determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 26, 2016 No. 304-KG15-18260, Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated May 15, 2007 No. 372-O-P).
The peculiarities of applying the VAT rate during the transition period in connection with an increase in the tax rate from 18 to 20% are explained in detail in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-43/ [email protected]
In the said Letter from the Federal Tax Service, from January 1, 2021, it is recommended to issue the return of goods with adjustment invoices, regardless of whether the buyer accepted the goods for registration or not.
Moreover, if in column 7 of the invoice for which the adjustment invoice was drawn up, a tax rate of 18% is indicated, then in column 7 of the adjustment invoice the tax rate of 18% is also indicated. Instead of an invoice, organizations can issue a UPD, and instead of an adjustment invoice, accordingly, a universal adjustment document (UCD) (Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 21, 2013 No. ММВ20-3/ [email protected] , dated October 17, 2014 No. ММВ-20 -15/ [email protected] ).
If a UCD was issued during the initial shipment of the goods, the seller must issue a UCD when returning the goods. At the same time, in the received UCD, the buyer does not have to fill out line 12; in line 13, he can indicate the date of receipt of the UCD, and line 14 is optional.
Determination of the tax base and procedure for calculating VAT
As a general rule, according to paragraph 1 of Art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the moment of determining the tax base in our case will be the day of payment for the goods sold. The tax base should be determined on the basis of clause 2 of Art. 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, based on market prices.
VAT rates vary, depending on the type of products sold.
Table with VAT rates: (click to expand)
| Basic (discount) rates | Calculated | |||
| Main, 18% | Reduced, 10% | Special, 0% | 18%/118% | 10%/10% |
| – other goods not related to the application of the 10% or 0% rate (clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | -childen's goods; -medical products; -printed and book publications (clause 2 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | goods exported under the customs procedure (clause 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | In case of partial payment for goods sold, clause 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
When selling goods to individuals, a tax rate of both 18% and 10% can be applied, it all depends on the products sold.
The calculation of the tax amount is simple and is calculated using the following formula:
Tax amount = tax base * corresponding tax rate.
Step-by-step instruction
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
The organization entered into an agreement with Zolushka LLC for the supply of women's shoes (finished products).
On January 30, the first batch of women's shoes worth RUB 177,000 was shipped. (incl. VAT 18%):
- Women's sandals “Megan” – 150 pcs. at a price of RUB 1,180.
On February 15, the second batch of women's shoes worth RUB 236,000 was shipped. (incl. VAT 18%):
- Women's sandals “Megan” – 200 pcs. at a price of RUB 1,180.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Sales of finished products produced during the month of production | |||||||
| January 30 | 62.01 | 90.01.1 | 177 000 | 177 000 | 150 000 | Revenue from product sales | Sales (act, invoice) - Goods (invoice) |
| 90.02.1 | 43 | — | — | — | Write-off of product costs | ||
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 27 000 | VAT accrual on revenue | ||||
| Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer | |||||||
| January 30 | — | — | 177 000 | Issuing SF for shipment | Invoice issued for sales | ||
| — | — | 27 000 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
| Adjustment of cost of goods sold produced during the month | |||||||
| January 31 | 90.02.1 | 43 | 47 178,08 | 47 178,08 | 47 178,08 | Adjustment of cost of goods sold | Closing the month - Adjusting the cost of an item |
| Sales of finished products after cost formation | |||||||
| February, 15 | 62.01 | 90.01.1 | 236 000 | 236 000 | 200 000 | Revenue from product sales | Sales (act, invoice) - Goods (invoice) |
| 90.02.1 | 43 | 62 904,11 | 62 904,11 | 62 904,11 | Write-off of product costs | ||
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 36 000 | VAT accrual on revenue | ||||
| Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer | |||||||
| February, 15 | — | — | 236 000 | Issuing SF for shipment | Invoice issued for sales | ||
| — | — | 36 000 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
Find out first about Product release without planned prices (with subconto Products)
Errors when filling out the sales book
- Often the sales book includes codes that are not intended for it at all, for example, instead of code 26, which means that the seller has drawn up an invoice with summary data, when selling goods, works and services to persons who are not VAT payers, they put the code 02 “The seller received an advance from the buyer”
- Transaction codes intended for filling out the purchase book are used to fill out the sales book.
!!! Code 26 - applies only in cases of sale of goods to individuals; if there are doubts, then in this case it is necessary to enter code 01 .
Payers often ask the following questions when carrying out transactions involving the sale of goods to individuals:
- In what cases is it possible not to draw up invoices when selling products to an individual??
Answer: Invoices are not drawn up by taxpayers when carrying out transactions for the sale of goods to individuals, since these persons are not VAT payers, provided that the seller has issued the buyer a cash receipt or other document of the established form (clause 7 of Article 168 and clause 3 of Article 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In retail trade, what details are required in a cash receipt? (click to expand)
The cash receipt that the retailer (VAT payer) issues to the buyer must highlight the VAT amount and indicate the tax rate, as indicated by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter No. 03-01-15/25767 dated 04/27/17.
Sales of finished products after cost formation
Sales of finished products in the next month after their release are processed in the same way as sales of products during the month of production. The only difference is the correct reflection of the amount of expenses in the document entries.
Postings according to the document
If the sale of products is carried out after the formation of the actual cost, i.e. in subsequent months, then the amount for posting Dt 90.02.1 Kt will be equal to the actual cost of the product.
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 90.02.1 Kt - write-off of product costs using the Average (the write-off method is specified in the PDF accounting policy).
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1 - revenue from the sale of finished products: in accounting accounting, including VAT;
- in NU excluding VAT.
Control
Let's check the calculation of cost of goods sold PDF:
Study in more detail the formation of the cost of manufactured sandals “Megan”
Income tax return
In the income tax return, the amount of proceeds from the sale of products is reflected as income from sales:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 1:
- page 010 “Proceeds from sales - total”, including: page 011 “... revenue from the sale of goods (works, services) of own production.” PDF
The cost of goods sold is reflected in direct expenses:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2:
- page 010 “Direct costs related to goods sold (work, services).” PDF
Signatures on invoices and UPD
The invoice and UPD are signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization (Clause 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Appendix No. 3 to the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 21.10 .2013 No. ММВ-203/ [email protected] ).
Among the most common errors associated with signing documents are the following: the use of a facsimile signature, the invoice and UPD were signed by one person, but the transcript of the signature indicates another, the documents were signed by an unauthorized person.
Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 10, 2013 No. 0307-09/11863, dated April 23, 2012 No. 03-07-09/39 contain the following explanations: the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicate in invoices additional details (information), including the position of the authorized person , who signed the relevant invoice, is not prohibited.
If the invoice issued to the buyer is signed by some authorized persons, and the copy of the invoice remaining with the seller by others, then this is not a violation of the procedure for issuing invoices (Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 3, 2013 No. 0307-15/25437, dated July 19, 2013 No. ED-4-3/13161).
It should be noted that applying a deduction based on an invoice and UPD certified by a facsimile signature is illegal. This position is shared by regulatory authorities and courts (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 8, 2017 No. 0303-06/1/81951, dated August 27, 2015 No. 03-07-09/49478, dated June 1, 2010 No. 03-07-09/33, dated 17.09.2009 No. 03-0709/48, dated 17.06.2009 No. 0307-09/31, dated 28.04.2009 No. 03-07-09/24, dated 22.01.2009 No. 03-07-11/17, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated February 14, 2005 No. 03-1-03/210/11, Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 22, 2016 No. 307KG15-18124, Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated September 27, 2011 No. 4134/11, etc.)
In conclusion, we note that an ordinary desk tax audit, when “docking” indicators from the declarations of the taxpayer and his counterparties, is unlikely to identify the errors described above.
Nevertheless, you should not neglect the rules for preparing invoices and UPD, since no one is immune from in-depth desk and on-site tax audits.
| Egorova Olga Viktorovna, Tax Expert (Moscow) |
Back
Forward