Salaries must be paid twice a month - in advance and in the main payment. But every company can go through difficult times in which salaries will be accrued but not paid.
Even in this case, it is necessary to fill out tax reports, but this is done according to a slightly different principle; the specific filling method has been clarified by the Federal Tax Service. It turns out that in case of non-payment of money to employees, it is necessary to fill out only 1 section, which is present in the 6-NDFL report.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
8 (800) 700 95 53
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
In this case, 6-NDFL in case of delayed wages is still calculated in the same way as the amount due for payment as wages is indicated, but at the same time zeros are placed in the lines for indicating tax indicators. But still, when filling out the declaration, you need to adhere to some features, for example, you must indicate data for half a year, but leave the remaining sections untouched.
6-NDFL: wages accrued but not paid
Section 1 of Calculation 6-NDFL is filled out “incrementally” from the beginning of the reporting year, and Section 2 covers transactions of the last 3 months of the reporting period.
The Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation explains: accrued but not paid wages in the reporting period, as well as personal income tax calculated from them, are included in lines 020 and 040 of Section 1. In Section 2, the amounts of delayed wages and taxes are reflected only starting from the period when they were paid to employees (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 24, 2016 No. BS-4-11/9194). How to fill out 6-NDFL when wages are delayed - let's look at examples.
Example 1
The salaries of the company's employees were calculated in the amount of:
- For January 2021 – 100,000 rubles, personal income tax 13,000 rubles,
- For February 2021 – 112,000 rubles, tax deduction 4,000 rubles, personal income tax 14,040 rubles,
- For March 2021 – 110,000 rubles, personal income tax 14,300 rubles.
The salary payment day is the 5th day of the month following the billing month, but the company only received funds to pay it in the 2nd quarter:
- January salary was paid on 04/02/2018.
- Salary for February and March – 04/16/2018
Section 1 of the 6-NDFL calculation for the 1st quarter of 2021 reflects the following amounts:
- Line 020 – 322,000.00 (accrued income for January-March);
- Line 030 – 4000.00 (since negative amounts in 6-NDFL are unacceptable, deductions are indicated without the minus sign);
- Line 040 – 41 340 (personal income tax from January-March income).
In Section 2 of the calculation, all rows will be zero.
When filling out 6-NDFL for the first half of 2021, you need to include the same indicators in Section 1, and on line 070 reflect the tax withheld from your January-March salary:
- Line 070 – 41 340.
Section 2 in the semi-annual calculation is filled out taking into account the following provisions (clause 2 of Article 223 and clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): the date of actual receipt of “salary” income (line 100) regardless of whether it was paid on time or not - this always the last day of the month for which salaries are accrued. Personal income tax is withheld on the day of payment of salaries to employees (line 110), and the day following this is the deadline for transferring the tax (line 120).
The January salary issued to employees in April will be reflected in section 2 as follows:
- Line 100 – 01/31/2018;
- Line 110 – 04/02/2018;
- Line 120 – 04/03/2018;
- Line 130 – 100,000.00;
- Line 140 – 13,000.
Although the salary for February and March was paid on the same day, it must be reflected in separate blocks - according to the date of actual receipt of income.
February salary:
- Line 100 – 02/28/2018;
- Line 110 – 04/16/2018;
- Line 120 – 04/17/2018;
- Line 130 – 112,000.00;
- Line 140 – 14,040.
March salary:
- Line 100 – 03/31/2018;
- Line 110 – 04/16/2018;
- Line 120 – 04/17/2018;
- Line 130 – 110,000.00;
- Line 140 – 14,300.
Example 2
Only on 04/02/2018, the organization transferred the salary for December 2017 (RUB 70,000). At the same time, the employer, along with the December salary, paid compensation for each day of delay in the amount of 1/150 of the current Central Bank ref rate (according to Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Section 1 in 6-NDFL for 2021 will include the amounts of salary accruals and personal income tax on lines 020 and 040:
- Line 020 – 70,000.00;
- Line 040 – 9100 (70,000 x 13%).
6-NDFL for the 1st quarter of 2021 will not reflect the indicated amounts at all. And in 6-NDFL for the first half of 2021 you need to indicate:
- line 070 – 9100 (personal income tax withheld in April from the December salary);
- line 100 – 12/31/2017;
- line 110 – 04/02/2018;
- line 120 – 04/03/2018;
- line 130 – 70,000.00;
- line 140 – 9100.
Compensation accrued for wages not paid on time does not need to be reflected in 6-NDFL at all, since it is not taxed.
Section 1 calculation
Officials recalled that section 1 of the 6-NDFL calculation is filled out with an accrual total for the first quarter, half a year, nine months and a year.
Line 070 “Amount of withheld tax” of Section 1 indicates the total amount of tax withheld as of the reporting date, cumulatively from the beginning of the tax period. On line 080 “Amount of tax not withheld by the tax agent” - the total amount of tax not withheld as of the reporting date, cumulatively from the beginning of the tax period (taking into account clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 14 of Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
In the situation under consideration, tax on wages accrued for the first three months of 2021, but paid in April, must be withheld in April directly upon payment of income. Accordingly, “0” is entered in lines 070 and 080 of section 1 of the 6-NDFL calculation for the first quarter. And when filling out the 6-NDFL calculation for the six months, the amount of tax withheld from the salary paid in April must be reflected in line 070 of section 1.
The total amount of wages accrued for January-March, as well as the amount of tax calculated on such income, are reflected respectively in lines 020 and 040 of section 1 of the 6-NDFL calculation for both the first quarter and the half-year.
Late income and ensuing troubles for the employer
The Labor Code directly obliges the employer to pay wages in full and within the time limits specified in:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- collective agreement;
- internal company labor rules;
- labor contracts.
The consequences of late payment of wages can be very different. Firstly, this will be of interest to both tax authorities (personal income tax) and labor inspectors (the fact of the delay). Secondly, most workers have every right to leave their job altogether, having warned their superiors about this, if they have not seen their salary for more than two weeks (Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, no one can deprive such persons of their average earnings for the entire period of waiting for their “hard-earned money”.
Moreover: in the event of a delay in transferring income to employees, the company will have to fork out for appropriate monetary compensation. Its calculation is tied to the key rate of the Bank of Russia. And that's not it.
The inspectors will probably threaten fines under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. And in very egregious cases of delayed wages - and criminal prosecution under Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, partial non-payment of wages (from 50%) also falls under it. Until recently, the latter measure was used extremely rarely due to the imperfection of the laws, but now investigators have become more energized in this regard and have begun to actively use it.
Example and sample of filling out 6-NDFL in case of salary delay
Form 6-NDFL for the first quarter at Primer LLC will be filled out as follows:
Section 1
- line 010 – 13 tax rate, %;
- line 020 – 270,000 rub. The total amount of accrued income to employees;
- line 030 – 0 rub. The amount of deductions provided to employees;
- line 040 – 35,100 rub. Amount of calculated tax;
- line 070 – 23,400 rub. Amount of tax withheld. Tax is withheld upon actual receipt of income, in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 226. In our example, the payment of wages for March was not in the current reporting period, therefore we reflect only the amount of tax withheld for the month of January and February:
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
Section 2
- line 100 – 01/31/2017, the last day of the month for which the salary was accrued, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, regardless of whether it was paid or not;
- line 110 – 02/06/2017 date of actual receipt of salary, in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- line 120 – 02/07/2017 working day following the day of actual receipt of salary, according to paragraph. 1 paragraph 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and paragraph 7 of Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- line 130 – 90,000 rub. The amount of actual salary received;
- line 140 – 11,700 rub. Amount of payroll tax withheld:
When filling out the 6-NDFL calculation in the second quarter, we reflect the payment of delayed wages for the month of March:
General requirements for filling out the report
6-NDFL must be filled out based on accounting data for income accrued and paid to individuals, tax deductions provided to them, as well as calculated and withheld personal income tax. All this data is contained in tax registers.
Report 6-NDFL includes:
Title page - contains the details of the tax agent, the Federal Tax Service - the recipient of the calculation, as well as the calculation number and the period for which it is submitted.
The first section reflects the total value for all individuals:
- income (on line 020), incl. dividends (on line 025);
- tax deductions (on line 030);
- taxes (on line 040), incl. from dividends (on line 045);
- fixed advances for tax on income of foreigners (on line 050).
This section is completed for each income tax rate separately (line 010) - 13, 15, 30 or 35 percent.
Lines 060-090 - the number of individuals who received income, tax withheld and not withheld, tax returned - are filled in throughout the organization, so their values are indicated only on the first sheet. The second section includes all taxable income (salaries, sick leave, vacation pay, bonuses, etc.) paid during the reporting period. This section deciphers the date of receipt of income, withholding tax and transferring it to the budget. Let's look at filling out the section line by line using the example of wages.
Line 100 is the date when the income was actually received. When paying salaries, the last day of the month is indicated.
Line 110 is the date when tax is withheld from income. According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax must be withheld on the day the income is paid, i.e. on the day the individual actually received the money. For example, if a payment for July is made on August 5, then the tax is withheld on August 5.
Line 120 is the date when the withheld tax must be transferred by the tax agent to the budget. As a general rule, no later than the day following the day of salary payment.
Lines 130 and 140 - the amount of income and the tax withheld from it, respectively.
Let's look at specific examples of how wages are reflected in 6-NDFL.
What are the consequences of delaying payment of wages to an employer?
The employer is obliged to pay wages to employees in full and within the approved time frame, in accordance with Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the collective agreement, and the employment contract. Delay of wages entails an administrative or criminal violation, as stated in subparagraph 1.4 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. An employee who has not been paid wages on time for more than two weeks has the right to leave his job by notifying his boss or manager, in accordance with Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the manager is obliged to pay average earnings for each day of downtime.
It is important to note that if wages are delayed, the employer is obliged to pay monetary compensation to employees, in accordance with Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But in the calculation of 6-NDFL, the amount of monetary compensation is not reflected, since it is not subject to personal income tax, according to paragraph 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Form 6-NDFL is submitted quarterly by an entrepreneur who hires employees and pays them income. The responsibility to calculate personal income tax from income falls on the employer, since he assumes the status of a tax agent. The reporting shows when and in what quantity payments were provided to employees, as well as what tax was withdrawn from them. Sometimes it happens that an employer cannot pay wages on time. How to fill out 6-NDFL when wages are delayed, we will consider below.
6ndfl.jpg
Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges employers to pay wages not only in full, but also on time. At the same time, situations where an employer does not transfer wages to its employees on time are not a rare occurrence. The reason for delayed payments is most often financial difficulties in the company. Wages not paid on time raise many questions when filling out reports. We will explain below how delayed wages are reflected in the calculation of 6-NDFL.
How to show a delay in 6-NDFL
In order to avoid difficulties in the future, it is worth considering in detail filling out 6-NDFL when wages are delayed.
The date of the month on which salaries are calculated is the date on which the employee actually received income. This indicator does not depend on whether the employer made the payment on time or not.
Late payment of wages will affect the time of calculation and transfer of tax to the treasury. The tax can only be calculated at the moment when the payment is actually made.
The transfer of the tax amount will take place on the working day following the day the employee actually receives wages.
For example, wages for April were accrued. The actual payment according to the law should take place on April 30, but due to the prevailing circumstances it was made on May 14. In this case, there is no place to withdraw the tax amount from earlier than May 14, because the employee had no income at all during this time.
And it is also not possible to transfer the tax amount to the treasury earlier than May 15, which will be reflected in 6-NDFL.
A conscientious employer may charge compensation for delayed wages. If this happens, then this procedure is not indicated in 6-NDFL, since compensation is not subject to personal income tax and is not even included in the list of deductions.
Employer's payment obligations
The Labor Code, in order to protect workers who are hired to perform work on contractual terms, obliges the employer to pay wages. Moreover, he must pay it within a strictly specified time frame.
The amount of the salary, as well as the timing of its payment to the employee, are stipulated in the contract signed by the employee, in the rules within the corporation, in employment contracts, as well as directly in the Labor Code.
An employee who has not received the income due to him for work performed for 2 weeks in a row may notify the employer of the suspension of work. Moreover, the wait for the due payments must also be paid. The calculation will be based on the employee’s average earnings.
6-NDFL in case of delayed wages, this fact reflects what tax authorities, and then labor inspectors, will probably be interested in. The employer will be legally obliged to:
- Pay compensation to employees.
- Pay fines to the tax office.
- In complex situations, criminal liability is possible.
Therefore, paying your employees for their work is entirely in the interests of the employer himself. Delays in payment of wages occur for the following reasons:
- Difficult financial condition of the hiring company.
- The employer has doubts about the quality of the work performed.
- Due to other considerations of the employer or deliberate non-payment.
It should be noted that some not entirely honest employers, having paid 50% of wages, believe that this way they will be able to get rid of responsibility. This is wrong. Partial non-payment of wages may also result in criminal liability, as can complete non-payment.
So, 6-NDFL is designed to display all the income that is received by employees, as well as the timing of their receipt and the timing of withholding taxes from them, which is directly reflected in the 6-NDFL form.
Reasons for delay in payment
From a legal point of view, there can be no valid reasons for partial or complete delay of wages. Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the obligation to pay a penalty for delay in payments to each employee for each working day, even if the failure to pay was the fault of the bank. It is assumed that the employer must seriously assess the risks and calculate all possible unpleasant situations, and in particular, delays or failures in the banking system also place a financial burden on the employer.
Despite this, there are many reasons why salaries are not paid on time, for example:
- Irresponsible attitude towards company affairs.
- Intentional delay.
- Untimely calculations made by the accountant.
- The data was submitted to the bank on time, but he was unable to transfer it due to some internal problems.
- The company does not have the funds to pay.
For employees who do not receive their salaries on time, it does not matter who is at fault. For this reason, the management of the organization is obliged to ensure payment of the penalty, and only then look for those responsible for the hitch and, if possible, recover from them the losses incurred.
Main nuances
Notes on the law
According to the explanations of the Federal Tax Service under paragraph two of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents must send calculations of personal income tax to the tax authorities at the place of registration. persons who were calculated and withheld for a certain period. Such periods are considered to be the first quarter, six months, and nine months, and the filing deadline is set at the last day of the month that follows the reporting month.
In this case, the report must be submitted in a form approved by the Federal Tax Service. It is called 6-NDFL, which was introduced in 2021. The first section contains general data on a cumulative basis, and section 2 contains information on the dates of payments and transfers of taxes.
If the tax agent indicates an operation in one period, but completes it in another, then it must be entered into the declaration after completion. This also applies to situations where wages were delayed. If wages were accrued on March 3, and the tax on them was paid on March 4, then this is reflected in the first section of 6-NDFL for the first quarter.
At the same time, the agent most often does not indicate such information in the second section. It will be indicated when paying salaries to employees based on the results of the six months. According to the Tax Code, the date of actual receipt of income is the last day of the month in which income was accrued, but not necessarily its payment.
According to the Code, tax agents must withhold accrued tax from the taxpayer’s income itself at the time of actual payment. And the transfer of amounts of withheld tax is made when paying wages, no later than the next day after that. The same applies to disability benefits, caring for a sick child, as well as vacation funds.
Possible problems
According to the Labor Code, the employer is obliged to pay out the money earned in full, observing the deadlines.
Specific payment time frames are indicated in:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- collective agreement;
- internal rules of the enterprise;
- employment contracts.
For the employer, the result of late payment of funds may be quite unpleasant; for example, regulatory authorities may be interested in the reasons for this. Moreover, the question is possible both with regard to personal income tax from the tax authorities, and to the observance of the rights of workers from labor inspectors.
In the event of a delay in wages, employees can stop the work process, having previously given a warning to their superiors, after two weeks of non-payment, which is guaranteed by Article 142 of the Code. But even if the employee takes such measures, he will receive his average earnings for the entire time he is waiting for the debt.
Also, after the debt, the company will need to pay monetary compensation, which is calculated at the rate of the Bank of Russia. And inspectors can expect fines related to violation of Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code. And if the delay in wages has reached a critical level, criminal prosecution under Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code is possible.
Partial non-payment of money may also result in criminal liability. Since the laws are imperfect, this measure was unpopular, but recently it has become increasingly common in court decisions.
How to fill out 6-NDFL when wages are delayed
In any case, the calculation in form 6-NDFL is submitted to the tax office no later than October 31, but it is necessary to understand which columns and what information to fill in if there is a delay in paying money to employees.
Section 1 indicates accruals on an accrual basis, starting from the beginning of the year.
In this case, the fact that funds are paid to employees does not matter:
And in section 2 there are amounts that have already been paid to employees, or were transferred as tax for the period.
If the salary was accrued but not issued, then you should indicate in the lines:
As an example, let's take a situation in which wages for March were paid in May. In line 100, you should indicate 03/31/2017, in 110 - the date of issue of money, for example, 05/6/2017, then 05/7/2017 is entered in line 120.
There is also a situation where wages were accrued but not paid throughout the entire quarter. In fact, employees have income, because the date of receipt is the last day of the month in which it was accrued.
In this situation, accrued money and the tax on it are shown in lines 020 and 040 in section 1, and column 060 indicates the number of employees. The tax will be withheld only upon payment, so field 070 is set to 0, because the salary payment operation has not yet ended. And section 2 is left empty.
Features of filling out section 2
The data for the second section of Form 6 of personal income tax should be reflected when the company issues wages, in that reporting period. For the situation described above, income was transferred only in April, which means that section 2 should be filled out only in the half-year report.
These positions are regulated in the Tax Code:
- For page 100 – article 223;
- for page 110 – art. 226 paragraph 4 and art. 226.1. paragraph 7;
- for page 120 – art. 226 clause 6 and art. 226.1. clause 9.
Things to remember
Employer Responsibilities
While providing protection to workers, the Labor Code imposes an obligation on the employer to pay wages. And the issuance of money must be carried out within the time limits specified by law. The salary itself and the terms of payment are stipulated in the employee’s contract, as well as in corporate rules, employment contracts and the main document - the Labor Code.
As mentioned above, if wages are delayed by more than two weeks, the employee can notify the manager about stopping work. The waiting period for money is paid according to the law and is calculated based on average earnings.
Indication of salary arrears in 6-NDFL will certainly arouse the interest of tax and labor inspectors.
Moreover, in this case, the employer will have to:
- pay compensation to employees;
- pay off fines from the tax office;
- Criminal liability is also possible for the person responsible for the delay.
That is why full payment of earned money within clear deadlines is the main interest of the employer.
But it should be noted that salary delays still occur for the following reasons:
- financial difficulties at the enterprise;
- doubts about the quality of the work performed;
- deliberate non-payment.
Some employers try to avoid liability by paying only half the salary. But such a step does not in any way relieve one from responsibility, especially since the article of the Criminal Code also implies such an offense.
Sample of filling out form 6-NDFL in case of delayed wages
Where to contact
If an employer withholds wages, an employee whose rights are thus violated may seek legal protection. After all, at the level of legal norms there are no grounds for non-payment of money.
How excess daily allowances are reflected in 6-NDFL - you will be told at the link.
And if a violation of rights does occur, the employee can:
- stop work;
- request payment of interest as compensation;
- ask for help from the Labor Dispute Commission by filing a complaint about negligent management;
- send a complaint to the Labor Inspectorate;
- contact the prosecutor's office;
- file a claim in court.
Most often, the employer issues compensation, especially if the employee intends to continue working. Complaints to regulatory authorities, and even more so to the court, are extreme measures taken when other methods cannot be used.
Enrollment without payments
The example of filling out form 6-NDFL indicated above suggests differences in filling out some lines, but the filling out method does not change radically. As an example, let's take a situation where the salary was still accrued, but was not paid for several months.
As an example, from the beginning of 2021, for 5 months the company was not able to pay its employees. The situation changed only in the summer, in June, when on the 26th the debt was finally paid, and at the same time the personal income tax was transferred to the budget.
In this case, the declaration lines for the 1st quarter must be filled out as follows:
In this case, the half-year declaration will look like this:
Monetary compensation and fines
If the salary was delayed and the employee needs to be provided with compensation, this issue is dealt with by the accountant who is responsible for the salary.
During the calculation, the following nuances must be taken into account:
- the legal norm, which is at the level of one hundred and fiftieth of the rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, may increase;
- payment of compensation is made regardless of the circumstances under which the salary was delayed;
- the delay must be calculated for weekends, including holidays;
- if the salary payment date falls on a weekend, it must be paid in advance, otherwise compensation will begin to accrue;
- the period for calculating the fine begins counting from the day that follows the settlement day until the time of payment of wages;
- compensation is calculated with interest based on actual, full or partial non-payment.
Some sites offer specialized calculators that allow you to calculate the amount of compensation payments by entering initial information. But even without using it, you can calculate compensation without difficulty. It is only necessary to multiply the entire salary, or part of it that was withheld, by the base rate of the Central Bank and the result multiplied by the period of delay in days.
If compensation is not forthcoming, even without a reminder from the employee, then the latter has the right to seek help from regulatory authorities. And in addition to salary compensation, the enterprise will also pay a fine, which is clearly established: for the enterprise - up to 50 thousand rubles, and for its manager the sanction will be up to 20 thousand rubles. If an individual entrepreneur delays his salary, he will pay a fine of up to 5 thousand rubles.
Delayed wages are not only negatively assessed by tax and labor inspectors, but can also serve as a reason for imposing sanctions on a negligent employer. At the same time, it is necessary to correctly fill out the 6-NDFL declaration when wages are delayed, taking into account all the nuances, according to the explanations of the tax authorities.
Read here when you are required by law to submit a zero 6NDFL.
You can see an example of filling out 6-NDFL for 9 months of 2021 below.
Legal basis
Remuneration of employees of an organization is an obligation, not a right of the employer, which is regulated by labor legislation. Transfer deadlines are approved by internal local documents:
- collective agreement;
- internal labor rules;
- labor contracts and agreements.
The head of the company does not have the right to make decisions on changing them. If the payment of wages is untimely for more than 14 days, most individuals have the right to resign after a written warning from management in accordance with Article 142 of the Labor Code. In addition, if labor inspectors and tax officials establish the fact of a delay, penalties may be applied to the employer for unpaid wages in accordance with the administrative code.
For repeated cases - up to criminal punishment. This does not depend on what remuneration system is used in the organization. Sanctions can be applied even for delaying advance payments to employees.
It is important! In case of delay, the employer is obliged to pay the company employees monetary compensation, which is tied not to the salary, but to the key rate of the Central Bank.
Letter No. BS-4 11/9194 contains an explanation of how to correctly reflect the indicators in 6-NDFL in case of delay in payment of wages.
General principle of filling out calculation 6 personal income tax
To avoid further questions, it is necessary to consider the reflection of indicators in the report in cases of salary delays.
If the salary for the first three months was transferred with a delay only in April, tax can be withheld only on the day of direct transfer of income. In our situation, the actual payment is in April. For 1-3 months, an example of filling out report 6 of the first section will look like this:
When filling out the form for the first six months, on page 070 we include the tax paid in April. In addition, page 070 indicates the entire amount of tax calculated for the first half of the year. Line 080 reflects all personal income tax not withheld at the reporting date.
Accrued wages for the first three months are reflected on page 020 and page 040 in both the report for the first three months and for six months. Since wages were not paid in the first three months, the second section for the first quarter is not completed. Let's look at how to fill out the 2nd section for the first half of the year using an example:
- in 100 – date, the last day of the month for which the salary was accrued;
- 110 indicates the date of the tax withheld on the day the income was transferred to employees;
- in 120 the day following the day of payment of income is indicated.
- 100 – 31.07;
- 110 – 24.08;
- 120 – 25.08;
- 130 – 60 thousand rubles;
- 140 – 7.8 thousand rubles.
As an example of filling out salary payments, the completed form 6 of form will be as follows:
Salaries for September were paid in October
For the 1st-3rd quarter, the form must be submitted to the tax office no later than 31.10. We will fill out the form if there is a delay in the transfer of earned funds. In the first section, all indicators are reflected as a cumulative total from the beginning of the year. Data on accrued amounts is indicated here, regardless of the date of payment.
In the second section, you should indicate data only for the third quarter: income that was paid to individuals and taxes transferred to the treasury. If the delayed salary was paid in October, this should be indicated in the lines:
For example, consider the option when wages for the 09th month in the organization were accrued in the amount of 270 thousand rubles, deductions from wages in the amount of 13% amounted to 35.1 thousand rubles. According to the collective agreement, the salary date is the 7th of the next month. Wages for August were paid with a delay only on September 27. Fill out the form line by line:
- 100 – September 30;
- 110 – September 27;
- 120 – September 28;
- 130 – 270 thousand rubles;
- 140 – 35.1 thousand rubles.
If wages are paid late in installments, income tax amounts should be withheld from each transfer to employee cards. This is explained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/ 43 479 dated July 25, 2021. In reporting 6 personal income tax, filling out lines 100-140 should be completed in several blocks for each delay repayment date separately.
If employees' salaries were paid earlier than the end of the month: 6 personal income tax details of filling out
Tax payment deadline
The employer's obligation to transfer personal income tax to the budget arises for the taxpayer only on the day of payment of the second part of the income. The tax is not considered paid if it reaches the treasury before the day of the month for which the salary was accrued.
Compensation due to delayed payment of wages should not be reflected in Form 6-NDFL. Firstly, this is not recognized as income according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 217, paragraph 3. Secondly, it is not considered a deduction for tax purposes.
Calculators for calculating compensation for non-payment of earned funds are publicly available on some specialized websites. To do this, you need to enter the initial data. It's easy to do the calculation yourself. It is necessary to multiply the amount of unpaid wages by the number of days overdue and the base rate of the Central Bank.
Correctly filling out form 6-NDFL in the case of accrued but unpaid wages will protect you from the application of sanctions by tax authorities, which could aggravate the difficult financial situation of the organization.
Late income fee
Separately, it is worth mentioning the transfer of compensation for delayed income. What then should be indicated in 6 personal income tax when payment is delayed ? Nothing! And there are two reasons for this:
- this payment is not subject to tax on the basis of clause 3 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- it is not included in the amounts of deductions for the purposes of 6-NDFL.
Also see “Tax deductions in 6-NDFL: reflecting amounts correctly.”
Read also
05.09.2016
Legislative acts
Filling out the report is regulated in Tax Code Art. 230 clause 2. All business entities that acted as tax agents in a calendar year are required to submit 6 personal income taxes if earnings and taxes were accrued in at least one period. The reporting quarters are considered to be 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th quarters. At the same time, the deadlines for submitting declarations are clearly defined.
Section 1 must be completed on an accrual basis. In the second, information is entered in the reporting period when the payments were made.
If wages are calculated in one quarter and transferred in another, the information in the declaration should be reflected after completion. This applies to situations where there is a delay in wages.
For example, wages were accrued on March 5, tax was withheld on March 6. This should be reflected in the 1st quarter report in the first section.
Tax agents miss the point of filling out the second section. In this case, the transfer of salaries to individuals was made in the 2nd quarter. In the form, in the 2nd part, you need to reflect the transfer of previously accrued income for the 1st quarter.
The Tax Code clearly states that the day of receipt of wages is recognized as the last date of the month in which income was accrued. In this case, the transfer may not be made.
According to the Tax Code, agents are required to withhold personal income tax from accrued wages at the time of transfer. The tax must be transferred no later than the next business day. This applies not only to salaries, but also to sick leave and vacation leaves.
Reporting for this situation needs to be generated, and you only need to fill in the data in section 1 regarding accrued wages. Lines to reflect taxes must be entered with zeros.
Let's sum it up
- The employer can withhold personal income tax only from the salary actually paid, and must transfer the tax to the budget no later than the next working day after payment. Therefore, in situations where the payment date differs from that established by local regulations, it is the salary day that changes, but not the procedure for withholding and paying personal income tax to the budget.
- This situation should be reflected in 6-NDFL by analogy with a salary paid on time.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
What will an employer face if income is not paid on time?
The right to timely pay income to employees is enshrined in the following acts:
- In the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- in a collective agreement;
- in internal documents of the organization;
- in employment contracts with employees.
If there have been no income payments, questions may arise not only from the tax service in the absence of payments, but also from labor inspectors.
Employees have the right to refuse work after prior notice to the employer due to delayed wages within 2 weeks of the due date for payment. This right is enshrined in the Labor Code, Art. 142. If employees exercise this option, the employer will be obliged to reimburse them the average wage for each day in parts or in full until the debt is repaid.
In addition, employees will need to be paid compensation for delayed wages, which is calculated at the Bank of the Russian Federation rate.
The employer will be subject to penalties for violating Art. 5.27 AK. If measures are not taken to repay the debt, criminal punishment is possible in accordance with the Criminal Code, paragraph 1 of Art. 145.
Reflection of the advance in the report
Advance is the part of the salary that the employer is required to pay in accordance with the law. The Labor Code states that an employee must receive payment for work twice a month. Preliminary payments are associated with this, which are usually paid in the middle of the month. The exact date is specified in internal documents and the agreement with the employee.
There is no special line in the 6 personal income tax report for salary advances. But in this case it is necessary to reflect the income received. Conditions of the Tax Code:
- Personal income tax must be calculated on the date of actual receipt of money.
- The tax must be issued at the time of salary payment, so that according to all documents it is calculated from the employees’ income, and not from the company’s accounts.
- The date of receipt of income is usually considered to be the last day of the month, including weekends.
Advice! This means that at the time the advance is issued, it is not yet considered income, which means there is no need to reflect it in the report. This can be done on the day you receive your basic salary. Tax is calculated on both incomes at the same time.
Example of registration of 6 personal income tax in case of non-payment of wages
The organization is going through difficult financial times. Salaries this year are accrued on time during January - May, but payments are delayed. In June, the employer began to repay debts to staff. The final payment was made on June 25, and the tax was transferred at the same time. In subsequent periods, calculations and transfers of taxes and wages were made on time. The salary was accrued on the last day of the month, the transfer was made on the first working day of the next month.
In this case, is it necessary to submit the calculation of 6 personal income taxes for the 1st quarter? And how to fill out a declaration for six months?
The monthly wage fund is 100.00 thousand rubles. Accordingly, for 6 months the income is 600.00 thousand rubles. There are no deductions, personal income tax is calculated only at 13%.
Filling out 6 personal income taxes in case of delay in payment of wages for the 1st quarter is as follows:
- 010 – tax rate 13%;
- 020 – wage fund for three months 300,000;
- 030 – no deductions were applied 0;
- 040 – amount of calculated personal income tax 39,000;
- 070 – 140 – 0.
An example of filling out a report for the 1st half of the year:
- 010 – tax rate 13%;
- 020 – wage fund for six months 600,000;
- 030 – no deductions were applied 0;
- 040 – amount of calculated tax for 6 months 78,000;
- 070 – amount of tax withheld for 5 months 65,000;
- 100 –
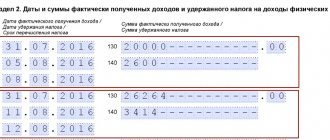
| 31.01.2017 | 28.02.2017 | 31.03.2017 | 30.04.2017 | 31.05.2017 |
- 110 –
| 25.06.2017 | 25.06.2017 | 25.06.2017 | 25.06.2017 | 25.06.2017 |
- 120 –
| 26.06.2017 | 26.06.2017 | 26.06.2017 | 26.06.2017 | 26.06.2017 |
- 130 –
| 100000 | 100000 | 100000 | 100000 | 100000 |
- 140 –
| 13000 | 13000 | 13000 | 13000 | 13000 |
Reports for 9 months and a year are generated as usual.
In the case of unpaid income, when filling out the declaration, it is important to fill out lines 070 and 080, where you should enter data on personal income taxes actually withheld or not withheld.
If the January salary was paid in the next month and then all payments were made on time, the form is filled out as usual.
Late payment of wages due to the fault of the employer can cause not only fines and sanctions from tax authorities and labor inspectorates, but also certain difficulties for accountants in how to reflect accrued wages in 6 personal income taxes. When preparing the calculation, it is important to timely reflect information, if necessary, on line 080 and fill out section 2, taking into account debt repayment.
How to fill out a report when personal income tax is not transferred to the budget
Sometimes situations arise when employees’ wages were paid, taxes were withheld, but they were not transferred to the budget on time. Such nuances may appear in the following cases:
- The company has an unstable financial position;
- accountant's mistake;
- technical failures and other reasons.
How to fill out 6 personal income taxes if tax is withheld but not paid? The report shows the amount of accrued income for all individuals and the calculation of tax amounts. It does not record the fact of personal income tax payment. Even line 120 does not imply the actual date of transfer of funds, but the deadline when this needs to be done. Consequently, 6 personal income tax is filled out in the usual manner, as if the tax was transferred on time.
Important! The tax inspectorate may consider displaying the actual date of personal income tax payment in the report as providing false information and fine the tax agent. The fine is 500 rubles.
Despite the fact that the report will be completed in the same form, this does not relieve the employer of responsibility for violating tax laws. For each day of delay, a penalty will be imposed on the tax agent (Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Penalties will apply from the next day after the date indicated in line 120.
In addition, inspectors will check the deadline specified in line 120 and the actual date of transfer and impose a fine on the taxpayer for violation of the law in the amount of 20% of the amount of unpaid tax.
Non-payment of wages: legislation and business practice
The legislation provides for a whole arsenal of levers to protect an employee in cases of delay in his salary payments:
- employer's financial liability (monetary compensation for delayed payments) - Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- administrative responsibility (part 1 of article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) for officials, individual entrepreneurs and organizations;
- criminal liability (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation), including a fine;
- employee self-defense function: suspension of work by an employee until salary payments are made (Part 2 of Article 142, 379 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
However, in the context of a deepening economic crisis, an increasing number of companies are experiencing an acute shortage of available cash. The objective financial difficulties that arise in this case carry high risks of the formation and rapid growth of wage arrears.
In this case, how should an accountant enter information into Form 6-NDFL? What if non-payments are protracted: a month, a quarter or more?
Let's look at the problem using the example of filling out a calculation taking into account clarifications issued by fiscal authorities.
Deadlines for issuing wages
Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the obligation to pay wages to employees within the specified time frame. The dates for issuing wages are determined individually at each enterprise. They are prescribed in the organization’s local documentation and in the employment contracts of hired employees. The prescribed dates must be strictly observed, and if the payment day falls on a weekend or a public holiday, then transfers are made in advance, but in no case later.
The legislation of the Russian Federation obliges employers to split wages into two payments. At the beginning of the month, the salary is usually paid, and in the second half of the month an advance payment is made. More frequent wage payments are not prohibited, but breaks between them cannot exceed 15 calendar days.
Delay in salary, advance payment, vacation compensation or payment of settlement amounts can result in serious consequences for the employer. The minimum of these is the mandatory accrual of compensation for overdue days. This rule is stipulated in Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, the presence of a delay of 15 days allows employees to temporarily withdraw from their duties until the debt is fully repaid.
Such an offense will also not go unpunished by government agencies. Employers who delay payments for a long time or do so systematically face administrative or criminal penalties.
General principle of filling out the 6-NDFL calculation
At the end of May 2021, the tax service issued a letter regarding the reflection of information in 6-NDFL, for a situation where salaries were not paid throughout the entire quarter (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated May 24, 2016 No. BS-4-11/9194).
Since the issues of reflecting information on “carrying forward” salaries were considered by the tax department in earlier letters (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated February 25, 2016 No. BS-4-11 / [email protected] ), where special attention was paid to filling out section 2 of the calculation, in explanation No. BS-4-11/9194, the fiscal authorities focused in more detail on filling out section 1 for the situation of “protracted debt” for salary payments.
So, we can highlight the following features of entering information into the calculation in case of “overdue” salary payment:
- In line 070, which provides for the reflection of the amount of tax withheld in the reporting period, information is entered regarding the total amount of tax for individuals withheld by the tax agent - in the reporting period - in accordance with clause 4 of Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Additional information on this section can be found in the article “Procedure for filling out line 070 of form 6-NDFL.”
- In line 080, which provides for the reflection of the amount of tax not withheld in the reporting period, information is entered regarding the total amount of tax for individuals not withheld by the tax agent in the reporting period in accordance with paragraph 5 of Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
You can also clarify the principle of filling out individual positions on the website: “Procedure for filling out line 080 of form 6-NDFL.”
- Since tax withholding from individuals is made directly upon the actual payment of income, therefore, if the salary is actually paid outside the reporting period, then 0 is entered in lines 070 and 080.
General provisions
At the end of May, tax authorities published a letter that reveals the course of action if wages have not been paid for the entire quarter. Since information about the so-called “carrying forward” wages was considered by the Federal Tax Service in letters earlier, in the key to filling out the second section, the fiscal officials explained in more detail how to fill out section 1. They explained how it is necessary to express the “lingering debt” for wages.
The clarifications affected both the first and second sections, as well as how the tax should be displayed. Since the accrued salary was not paid, and deductions to the budget are made only directly from the funds paid.
6-NDFL: wages accrued but not paid (example)
Now let's move on to reflecting in the 1st and 2nd sections of form 6-NDFL the situation in which wages are accrued but not paid in the reporting period, and such a delay is of a long protracted nature, for example, several months.
The variety of situations that arise when making salary payments can be found on our website, in particular in the article “6-NDFL - if the salary was paid for several days.”
Let's look at an example.
Example
Due to the insolvency of the main buyer, in the first five months of 2021, the company was unable to repay wage arrears to staff. The situation began to improve only in June: the repayment of the debt for the previous months was made in full on June 26, and on the same day the personal income tax was transferred to the budget. Subsequently, the salary payment schedule was not violated: payments were made on the first working day following the reporting month.
Assumptions adopted in the calculation: monthly payroll is 100,000 rubles, deductions are not provided to employees, personal income tax is paid at a rate of 13%.
Filling out form 6-NDFL for the 1st quarter of 2021 and the first half of 2019 will be as follows:
| Form string | Indicator (date or amount of payment/tax) | ||||
| 1st quarter 2021 | |||||
| 300 000 | |||||
| 300 000 × 13% = 39 000 | |||||
| For the first half of 2021 | |||||
| 600 000 | |||||
| 600 000 × 13% = 78 000 | |||||
| 500 000 × 13% = 65 000 | |||||
| 100 000 | 100 000 | 100 000 | 100 000 | 100 000 | |
| 13 000 | 13 000 | 13 000 | 13 000 | 13 000 | |
You can see a sample of filling out the second section of the report below.
6-NDFL for the 1st quarter of 2021:
6-NDFL for the first half of 2021:
Thus, a feature of filling out the calculation for long-term non-payment of wages compared to other situations is the entry of information in lines 070 and 080, which is carried out on the principle of actual withholding/non-withholding of tax on personal income by tax agents.
Section 2 calculations
Section 2 of the calculation in Form 6-NDFL for the corresponding reporting period reflects those transactions that were carried out over the last three months of this reporting period. If an operation was started in one reporting period and completed in another reporting period, then it is reflected in the completion period. Since in the described case the salary was not paid until April, in relation to this income, section 2 of the 6-NDFL calculation is filled out, starting with the calculation of 6-NDFL for the six months of 2021.
In this case, line 100 of Section 2 “Date of actual receipt of income” is filled in taking into account the provisions of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, line 110 of Section 2 “Date of tax withholding” - taking into account the provisions of paragraph 4 of Article 226 and paragraph 7 of Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, line 120 of Section 2 “Tax payment deadline” - taking into account the provisions of paragraph 6 of Article 226 and paragraph 9 of Article 226.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.