The specifics of maintaining work books and personnel documents are regulated by labor law. When hiring an employee for a full-time position, he must sign an employment contract. To legally formalize the labor relationship, the employer issues an order to appoint a person to a vacant position, and after the actual start of work, they make entries in the work book. But if the employer did not make an entry in the work book about hiring, transfer or dismissal, this is considered a gross mistake for which one must be held accountable.
Work records and employer obligations
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are required by labor law to fill out work books for all hired employees. This form is a document that systematizes data on a person’s labor activity for all years.
Legislative regulation of the nuances of registration of work books is expressed through:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Rules issued by the Government of the Russian Federation as part of Resolution No. 225 dated April 16, 2003;
- Instructional collections prepared by the Ministry of Labor and systematized in Decree No. 69 dated October 10, 2003.
In the work book, the employer must reflect the following set of information about the work activities of the owner of the form:
- information identifying the employee;
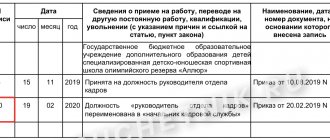
- information about the assigned work (the name of the position for which the person was hired, indicating the period of stay in it);
- facts of internal and external transfers;
- reasons for dismissals;
- non-material types of incentives.
Also see “Rules for filling out work books in 2021.”
The employer is not authorized to decide in whose books information about employment is entered and whose forms are ignored.
If an error was made while filling out the form, the entry must be invalidated, after which the correct data is entered. Responsibility for failure to make an entry in the work book is provided for by the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in Art. 5.27 (fine - up to 50,000 rubles).
Labor control and supervision bodies receive information from complaints and statements from employers affected by negligence about the infringement of their rights regarding the reflection of their accumulated experience in work books.
The norms of Regulation No. 875 dated September 1, 2012 provide for the initiation of an unscheduled inspection of the employer upon receipt of a signal of an offense. If suspicions are confirmed that an enterprise or individual entrepreneur has failed to fulfill the full range of obligations as an employer, administrative measures are applied to them.
Also see “Gratitude in the work book: sample and what it gives.”
If information is not entered
We make an entry if it was missed - this is the only correct decision. The most common situations are as follows.
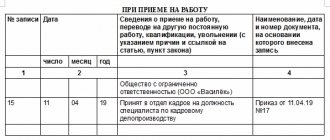
- There is a line about reception, but there is no line about payment. Upon dismissal, each person must control the entry of data: if they managed to miss it, you need to immediately contact the HR department.
- There is no information regarding transfer to another position. Since the book is not issued during the transfer process, this can only be found out upon dismissal, and if the corresponding point was missed, then it must be entered.
Important! Filling in the missing information is the task of the employer, regardless of whether he is former or new. The personnel department of the enterprise where the employee is employed can also enter data based on the order of dismissal from the previous place. This situation is possible only if it is impossible to do this in the previous place.
How to recover missed entries in your work record
Omission of an entry in the work book about a change in the nature of a citizen’s work activity or his work status is recognized as an employer’s mistake. The employer due to whose fault the form reflected incomplete information about a person’s employment is obligated to correct the deficiency.
If the employer has not made an entry in the work book, the basis for making changes to it cannot be oral testimony of officials.
In addition, for each case of correction of errors, it is necessary to issue an internal order from the head of the company.
When, at the time of discovery of a gap in the records, a person is employed by another employer, the current employer must reflect the missing data. To do this, he needs documentary support for the information entered from the previous employer who made the mistake.
The missing entry is reflected in the following sequence:
- data is entered in the empty lines after the last entry;
- enter the next sequential record number;
- the date should reflect the actual period of relevance of the missing entry.
As a result, the omission is eliminated, but with the simultaneous appearance of an inaccuracy in the form of a violation of the chronological order of making entries.
Also see “Employment agreement without a work book.”
Read also
31.08.2018
Answers to common questions
Question: An employee needs to make an entry in the work record about missed work, but there is no more space in the record book, what should be done in this case?
Answer: In this case, an insert is added to the labor document and the necessary information is entered into it. After this, the insert is filed to the work book. This insert is a continuation of the workbook, so for convenience it is recommended to attach it at the end of the book. This way, the chronological order of the entries in both the book and the insert will be maintained. The most reliable way is to sew the form into a book.
What will happen to the organization for violating labor laws?
The amount of the fine does not depend on the severity of the violations or their number.
True, judicial practice has taken the path of assigning one fine for several offenses, and not for each one separately. 2.1 Information bulletin of judicial practice on administrative cases of the Arkhangelsk Regional Court for the first quarter of 2008. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
Disqualification of the head of an organization and administrative suspension of its activities are prescribed by a judge in Articles 3.12, 23.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The last punishment is applied in the event of a threat to the life and health of people - we do not consider such violations in the article.
Why do labor inspectorates like to fine you?
Let's look at what common mistakes you can be fined for.
| Composition of the violation | Examples of violations |
| Mandatory personnel documents have not been completed | The employer does not have: |
| HR documentation is not maintained correctly |
|
| The procedure, timing of payments and their execution were violated |
|
| Other violations |
|
So, how to properly organize your daily work with personnel documents so that the labor inspector does not take your organization by surprise, even with an unexpected inspection?
The court's decision
The courts of two instances assessed the evidence presented in the case materials in accordance with Article 71 of the Arbitration Procedural Code of the Russian Federation and came to the conclusion that the manager’s application for reimbursement of expenses incurred in the bankruptcy case is justified in relation to postal expenses and expenses for publishing information in the media and transportation costs. However, the arbitration manager was denied the application to recover the costs of inserts for the work book due to the lack of evidence confirming these costs.
The Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District agreed with the conclusions of its colleagues in the resolution of January 19, 2021 in case No. A32-11222/2014. The arbitrators noted that according to the provisions of Article 20.6 of the Federal Law of October 26, 2002 N 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy),” the arbitration manager has the right to remuneration in a bankruptcy case. Remuneration in a bankruptcy case is paid from the debtor’s funds in a fixed amount. However, Article 20.7 of the Bankruptcy Law also provides that, at the expense of the debtor in the amount of actual costs, expenses incurred by the insolvency administrator are paid. But only on condition that they are justified and documented.
Checking our documentation
Review personnel papers. Your organization must have the following documents and forms available.
It includes: provisions on the protection of personal data of employees, internal labor regulations, instructions on labor protection. In any form, you can prepare, for example, a statement for each act, in which employees will sign that they are familiar with the contents of the document. 22, part 3 art. 68, articles 87, 135, 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Pay slip
You must develop and approve its form yourself. He notifies about the components of wages and deductions from wages. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If wages are transferred to bank cards, the procedure for issuing pay slips to employees is determined in the local act of Rostrud Letter No. 739-6-1 dated March 18, 2010. Let us remind you that the payslip must be issued with one of the payroll parts. 136 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The book of accounting for the movement of work books and inserts in them is kept by personnel officers, if there is such a department, and the receipt and expenditure book - as a rule, by the accounting department. Both books must be laced, numbered, certified by the signature of the head of the organization and sealed with a wax seal or sealed. For this, purchase a separate metal seal and sealing wax or sealing wax. 41 Rules
We suggest you read: How to check out of an apartment while in another city
They have a unified form No. T-2. You will have to give a personal card to the employee for signature not only upon hiring, but also with each new entry in his work book (for example, in connection with a change of position or advanced training). Therefore, keep in mind that personal cards are kept on paper. 12 Rules.
ADVICE
Prepare a template of the employment contract in advance, including in it all the requirements established by Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, mandatory information. And do not forget to include a line in it for the employee’s signature indicating that he has received his copy of the document. 67 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The time worked by employees must be taken into account according to unified forms No. T-12 or T-13st. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is these completed forms that the accountant receives as primary accounting documents for accounting and tax accounting purposes, on the basis of which he will calculate wages, reflect them in expenses, and fill out payslips for employees.
Vacation schedule
It is approved 2 weeks before the start of the year for which the vacations are planned, according to the unified form No. T-7st. 123 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
ADVICE
In the local regulations, state that vacation dates can be postponed by agreement of the parties. Without such a clause, the inspector may consider even your written agreements with the employee to change the periods of his vacations to be a violation of Art. 124 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Remember that without the employee's written consent, you cannot change the start date of his leave (for example, ask him to go on leave later), nor the end date. If you need the employee to take leave early, ask them for a written statement agreeing to the withdrawal and determining when they are ready to use their remaining vacation days.